手势监听类GestureDetector Listener源码解析
手势监听类GestureDetector
- 前言
- 一、GestureDetector是什么?
- 二、Listener源码解析
-
- 1.OnGestureListener
- 2.OnDoubleTapListener
- 3.OnContextClickListener
- 4.SimpleOnGestureListener
- 总结
前言
在写自定义view的时候,涉及到了手势监听这块的知识,补充下知识营养
一、GestureDetector是什么?
GestureDetector是一个手势监听类,用于监听和处理用户的手势操作。它提供了一些回调方法,可以在用户执行手势时被调用,从而实现手势识别和响应。
GestureDetector类的主要功能包括:
- 检测手势事件:GestureDetector可以监听和处理手势事件,如轻触、滑动、缩放等。当用户执行手势时,GestureDetector会触发相应的回调方法。
- 识别简单手势:GestureDetector可以识别一些简单的手势,如单击、双击、长按等。开发者可以通过GestureDetector的回调方法来处理这些手势事件。
- 自定义手势识别:GestureDetector还提供了自定义手势识别的功能。开发者可以通过实现GestureDetector的回调方法来自定义手势的识别逻辑,从而处理更复杂的手势操作。
使用GestureDetector类,开发者可以方便地实现手势识别和响应,增强应用程序的用户体验。GestureDetector的回调方法通常包括onTouchEvent()、onDown()、onSingleTapUp()、onDoubleTap()等,开发者可以根据需要实现这些方法来处理不同的手势事件。
二、Listener源码解析
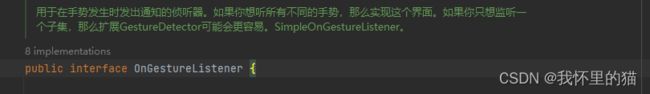
1.OnGestureListener
代码如下:
public interface OnGestureListener {
/**
* Notified when a tap occurs with the down {@link MotionEvent}
* that triggered it. This will be triggered immediately for
* every down event. All other events should be preceded by this.
*
* @param e The down motion event.
*/
boolean onDown(MotionEvent e);
/**
* The user has performed a down {@link MotionEvent} and not performed
* a move or up yet. This event is commonly used to provide visual
* feedback to the user to let them know that their action has been
* recognized i.e. highlight an element.
*
* @param e The down motion event
*/
void onShowPress(MotionEvent e);
/**
* Notified when a tap occurs with the up {@link MotionEvent}
* that triggered it.
*
* @param e The up motion event that completed the first tap
* @return true if the event is consumed, else false
*/
boolean onSingleTapUp(MotionEvent e);
/**
* Notified when a scroll occurs with the initial on down {@link MotionEvent} and the
* current move {@link MotionEvent}. The distance in x and y is also supplied for
* convenience.
*
* @param e1 The first down motion event that started the scrolling.
* @param e2 The move motion event that triggered the current onScroll.
* @param distanceX The distance along the X axis that has been scrolled since the last
* call to onScroll. This is NOT the distance between {@code e1}
* and {@code e2}.
* @param distanceY The distance along the Y axis that has been scrolled since the last
* call to onScroll. This is NOT the distance between {@code e1}
* and {@code e2}.
* @return true if the event is consumed, else false
*/
boolean onScroll(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float distanceX, float distanceY);
/**
* Notified when a long press occurs with the initial on down {@link MotionEvent}
* that trigged it.
*
* @param e The initial on down motion event that started the longpress.
*/
void onLongPress(MotionEvent e);
/**
* Notified of a fling event when it occurs with the initial on down {@link MotionEvent}
* and the matching up {@link MotionEvent}. The calculated velocity is supplied along
* the x and y axis in pixels per second.
*
* @param e1 The first down motion event that started the fling.
* @param e2 The move motion event that triggered the current onFling.
* @param velocityX The velocity of this fling measured in pixels per second
* along the x axis.
* @param velocityY The velocity of this fling measured in pixels per second
* along the y axis.
* @return true if the event is consumed, else false
*/
boolean onFling(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float velocityX, float velocityY);
}
每个方法的解释:
-
boolean onDown(MotionEvent e);- 当一个点击事件发生时,该方法会被立即触发。所有其他的事件都应该以此事件为前提。
- 参数
e是触发该事件的MotionEvent对象。 - 返回一个布尔值,表示事件是否被消费。
-
void onShowPress(MotionEvent e);- 用户执行了一个按下的
MotionEvent,但还没有执行移动或抬起操作。这个事件通常用于向用户提供视觉反馈,让他们知道他们的操作已经被识别,例如高亮显示一个元素。 - 参数
e是触发的MotionEvent对象。
- 用户执行了一个按下的
-
boolean onSingleTapUp(MotionEvent e);- 当一个轻触事件发生时,该方法会被触发。
- 参数
e是触发该事件的MotionEvent对象。 - 返回一个布尔值,表示事件是否被消费。
-
boolean onScroll(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float distanceX, float distanceY);- 当滚动事件发生时,该方法会被触发。滚动事件通常由用户按住并移动屏幕引起。
- 参数
e1是开始滚动的第一个按下的MotionEvent对象。 - 参数
e2是触发当前onScroll的移动MotionEvent对象。 - 参数
distanceX是自上次调用onScroll以来沿X轴滚动的距离。这不是e1和e2之间的距离。 - 参数
distanceY是自上次调用onScroll以来沿Y轴滚动的距离。这也不是e1和e2之间的距离。 - 返回一个布尔值,表示事件是否被消费。
这两个方法也是与手势相关的事件处理方法,我会为你解释它们:
-
void onLongPress(MotionEvent e);- 当用户长时间按住屏幕而不移动或抬起时,该方法会被触发。这通常用于实现长按手势的功能,例如显示上下文菜单。
- 参数
e是触发该事件的MotionEvent对象。
-
boolean onFling(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float velocityX, float velocityY);- 当用户快速滑动屏幕(fling手势)时,该方法会被触发。这通常用于实现快速滚动或滑动操作。
- 参数
e1是开始fling的按下的MotionEvent对象。 - 参数
e2是触发当前onFling的移动MotionEvent对象。 - 参数
velocityX是fling在X轴上的速度,以像素/秒为单位。 - 参数
velocityY是fling在Y轴上的速度,以像素/秒为单位。 - 返回一个布尔值,表示事件是否被消费。
这些方法进一步完善了OnGestureListener接口,使其能够处理更多的手势事件。实现这个接口的类可以提供这些方法的具体实现,以定义如何响应这些手势事件。这样,当用户在应用中执行相应的手势时,应用就能够根据这些方法的实现来做出相应的反应。
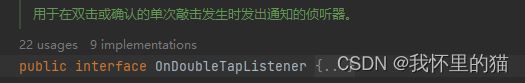
2.OnDoubleTapListener
代码如下:
public interface OnDoubleTapListener {
/**
* Notified when a single-tap occurs.
*
* Unlike {@link OnGestureListener#onSingleTapUp(MotionEvent)}, this
* will only be called after the detector is confident that the user's
* first tap is not followed by a second tap leading to a double-tap
* gesture.
*
* @param e The down motion event of the single-tap.
* @return true if the event is consumed, else false
*/
boolean onSingleTapConfirmed(MotionEvent e);
/**
* Notified when a double-tap occurs. Triggered on the down event of second tap.
*
* @param e The down motion event of the first tap of the double-tap.
* @return true if the event is consumed, else false
*/
boolean onDoubleTap(MotionEvent e);
/**
* Notified when an event within a double-tap gesture occurs, including
* the down, move, and up events.
*
* @param e The motion event that occurred during the double-tap gesture.
* @return true if the event is consumed, else false
*/
boolean onDoubleTapEvent(MotionEvent e);
}
每个方法的解释:
-
boolean onSingleTapConfirmed(MotionEvent e);- 当用户单次点击(single-tap)屏幕时,该方法会被触发。与
OnGestureListener#onSingleTapUp(MotionEvent)不同,此方法只会在检测器确定用户第一次点击没有跟随第二次点击形成双击手势时才会被调用。 - 参数
e是用户单次点击的MotionEvent对象。 - 返回一个布尔值,表示事件是否被消费。
- 当用户单次点击(single-tap)屏幕时,该方法会被触发。与
-
boolean onDoubleTap(MotionEvent e);- 当用户双击屏幕时,该方法会被触发。该方法在第二次点击的
MotionEvent事件的“down”阶段触发。 - 参数
e是用户第一次点击的MotionEvent对象。 - 返回一个布尔值,表示事件是否被消费。
- 当用户双击屏幕时,该方法会被触发。该方法在第二次点击的
-
boolean onDoubleTapEvent(MotionEvent e);- 当在双击手势中发生事件时,该方法会被触发,包括“down”(按下)、“move”(移动)和“up”(抬起)事件。
- 参数
e是在双击手势期间发生的MotionEvent对象。 - 返回一个布尔值,表示事件是否被消费。
这个接口允许实现者(通常是一个类)定义如何处理这些特定的双击事件。当这些事件发生时,相应的方法会被调用,从而实现对手势的监听和处理。这样,当用户在应用中执行双击手势时,应用就能够根据这些方法的实现来做出相应的反应。
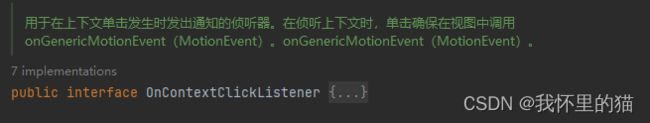
3.OnContextClickListener
public interface OnContextClickListener {
/**
* Notified when a context click occurs.
*
* @param e The motion event that occurred during the context click.
* @return true if the event is consumed, else false
*/
boolean onContextClick(MotionEvent e);
}
onContextClick方法接受一个MotionEvent对象作为参数,该对象包含有关点击事件的信息,例如点击的位置、时间戳等。返回值是一个布尔值,如果该方法处理了点击事件,则返回true,否则返回false。
这个接口可以用于实现自定义的上下文点击行为,例如在用户点击一个控件时显示一个上下文菜单。通过实现这个接口并重写onContextClick方法,你可以定义自己的上下文点击处理逻辑。
4.SimpleOnGestureListener
代码如下:
public static class SimpleOnGestureListener implements OnGestureListener, OnDoubleTapListener,
OnContextClickListener {
public boolean onSingleTapUp(MotionEvent e) {
return false;
}
public void onLongPress(MotionEvent e) {
}
public boolean onScroll(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2,
float distanceX, float distanceY) {
return false;
}
public boolean onFling(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float velocityX,
float velocityY) {
return false;
}
public void onShowPress(MotionEvent e) {
}
public boolean onDown(MotionEvent e) {
return false;
}
public boolean onDoubleTap(MotionEvent e) {
return false;
}
public boolean onDoubleTapEvent(MotionEvent e) {
return false;
}
public boolean onSingleTapConfirmed(MotionEvent e) {
return false;
}
public boolean onContextClick(MotionEvent e) {
return false;
}
}
这段代码是一个简单的Android手势监听器的实现。它定义了一个名为SimpleOnGestureListener的内部类,该类实现了OnGestureListener、OnDoubleTapListener和OnContextClickListener接口。以下是每个方法的功能和解释:
onSingleTapUp(MotionEvent e): 当用户点击屏幕并且手指松开时,该方法会被调用。它返回一个布尔值,如果返回true,则表示事件已经被处理;如果返回false,则表示事件未被处理。在这个方法中,它只是简单地返回了false,所以默认情况下,这个事件未被处理。onLongPress(MotionEvent e): 当用户长按屏幕时,该方法会被调用。在这个方法中,没有实现任何功能,所以默认情况下,长按事件未被处理。onScroll(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float distanceX, float distanceY): 当用户在屏幕上滚动时,该方法会被调用。它返回一个布尔值,如果返回true,则表示事件已经被处理;如果返回false,则表示事件未被处理。在这个方法中,它只是简单地返回了false,所以默认情况下,滚动事件未被处理。onFling(MotionEvent e1, MotionEvent e2, float velocityX, float velocityY): 当用户在屏幕上快速滑动时(例如翻页),该方法会被调用。它返回一个布尔值,如果返回true,则表示事件已经被处理;如果返回false,则表示事件未被处理。在这个方法中,它只是简单地返回了false,所以默认情况下,快速滑动事件未被处理。onShowPress(MotionEvent e): 当用户按下屏幕时,该方法会被调用。在这个方法中,没有实现任何功能,所以默认情况下,按下事件未被处理。onDown(MotionEvent e): 当用户在屏幕上按下并开始触摸事件时,该方法会被调用。它返回一个布尔值,如果返回true,则表示事件已经被处理;如果返回false,则表示事件未被处理。在这个方法中,它只是简单地返回了false,所以默认情况下,按下事件未被处理。onDoubleTap(MotionEvent e): 当用户双击屏幕时,该方法会被调用。它返回一个布尔值,如果返回true,则表示事件已经被处理;如果返回false,则表示事件未被处理。在这个方法中,它只是简单地返回了false,所以默认情况下,双击事件未被处理。onDoubleTapEvent(MotionEvent e): 当在双击手势中发生其他事件时,该方法会被调用。它返回一个布尔值,如果返回true,则表示事件已经被处理;如果返回false,则表示事件未被处理。在这个方法中,它只是简单地返回了false,所以默认情况下,双击事件未被处理。onSingleTapConfirmed(MotionEvent e): 当用户第一次点击屏幕并且该点击不导致双击或长按时,该方法会被调用。它返回一个布尔值,如果返回true,则表示事件已经被处理;如果返回false,则表示事件未被处理。在这个方法中,它只是简单地返回了false,所以默认情况下,这个事件未被处理。onContextClick(MotionEvent e): 当用户在屏幕上点击并且不进行任何其他手势(例如长按或双击)时,该方法会被调用。它返回一个布尔值,如果返回true,则表示事件已经被处理;如果返回false,则表示事件未被处理。在这个方法中,它只是简单地返回了false,所以默认情况下,这个事件未被处理。
以上就是这段代码的解释和每个方法的说明。如果你想根据实际需求修改这些方法的实现,只需要在这些方法内部添加相应的代码即可。
总结
本文介绍了Android手势监听类GestureDetector,包括其基本功能和回调方法OnGestureListener、OnDoubleTapListener、OnContextClickListener及其实现类SimpleOnGestureListener。通过实现这些回调方法,开发者可以监听和处理用户的手势操作,从而实现手势识别和响应。同时,本文也介绍了这些回调方法的具体功能和使用,帮助开发者更好地理解GestureDetector的使用方法。