String类讲解(1)
本篇文章将讲解String类及其包含的方法
一、介绍String类
String属于引用类型,String类是Java的一个内置类,用于表示字符串,String类中具有许多方法,可以用来操作和处理字符串
二、字符串的构造
下面介绍三种构造字符串的方法:
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.使用常量串直接赋值
String str = "hello";
System.out.println(str); //hello
//2.使用new关键字创建字符串对象
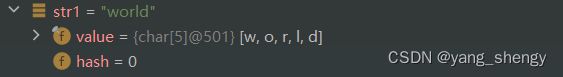
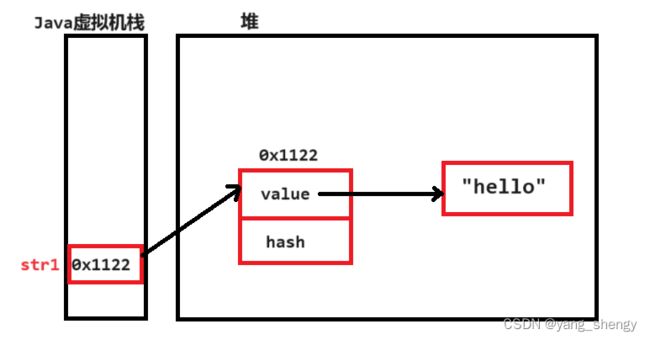
String str1 = new String("world");
System.out.println(str1); //world
//3.通过字符数组构造字符串
char[] arr = {'a', 'b', 'c'};
String str = new String(arr);
System.out.println(str); //abc
}
以上述代码的第二个例子为例画图讲解:
求字符串的长度和判断字符串是否为空:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "hello";
System.out.println(str1.length()); //计算字符串str1的长度
String str4 = "";
System.out.println(str4.isEmpty());
//判断引用所指向的对象的内容是否为空,若为空返回true,否则返回false
String str5 = null;
System.out.println(str5.isEmpty()); //空指针异常
}
三、字符串比较
3.1 ==
String s1 = new String("hello");
String s2 = new String("hello");
System.out.println(s1 == s2);
由于s1和s2都属于引用类型,所以上述代码实际比较的是s1和s2引用的对象的地址,打印结果为false
但是在以下这种情况会返回true,这涉及到了字符串常量池,以后会讲
String s3 = "hello";
String s4 = "hello";
System.out.println(s3 == s4); //字符串常量池
3.2 boolean equals(Object o)方法
equals方法是Object类中的方法,在Object类中equals方法的功能就是比较两个对象的地址,而在String类中重写了equals方法,其功能是比较字符串对象的内容,若相等返回true,否则返回false
String s1 = new String("hello");
String s2 = new String("hello");
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); //true
3.3 int compareTo(String s)方法
该方法和C语言中strcmp函数功能基本一致
String s1 = new String("abc");
String s2 = new String("abcd");
String s3 = new String("azc");
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s2)); //-1(字符数的差)
//1.s1>s2 返回一个大于0的数(s1的ASCII值减去s2的ASCII值)
//2.s13.4 int compareToIgnoreCase(String s)方法
比较两个字符串但忽略大小写
String s1 = new String("hello");
String s2 = new String("HELLO");
System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s2)); //true
四、字符串查找
<方法> char charAt(int index)
<功能>返回字符串下标为index的字符,如果index为负数或导致越界,则抛出异常
String s1 = new String("hello");
System.out.println(s1.charAt(2)); //l
<方法> int indexOf(int ch)
<功能> 返回ch第一次出现的下标,如果字符串中没有ch则返回-1
String s1 = new String("hello");
int index = s1.indexOf('e');
System.out.println(index); //1
<方法> int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex)
<功能> 从下标为fromIndex的位置处开始找ch,返回ch第一次出现的下标,若没有则返回-1
String s1 = new String("hello");
int index = s1.indexOf('l', 3);
System.out.println(index); //3<方法> int indexOf(String str)
<功能> 返回str第一次出现的位置,没有则返回-1,和C语言的strstr用法基本一样
String s = new String("abcdbcd");
int index = s.indexOf("bcd"); //1
<方法> int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex)
<功能> 从fromIndex位置开始找str第一次出现的位置并返回,没有则返回-1
String s = new String("abcdefabc");
int index = s2.indexOf("abc", 3);
System.out.println(index); //6
<方法> int lastIndexOf(int ch)
<功能> 从后往前找,返回ch第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1
String s2 = new String("hello");
int i = s2.lastIndexOf('l'); //3
<方法> int lastIndexOf(int ch, int fromIndex)
<功能> 从fromIndex位置开始从后往前找,返回ch第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1
String s2 = new String("hello");
int i = s2.lastIndexOf('l', 2); //2
<方法> int lastIndexOf(String s)
<功能> 从后往前找,返回字符串第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1
String s2 = new String("abcdefabc");
int i = s2.lastIndexOf("abc");
System.out.println(i); //6
<方法> int lastIndexOf(String s, int fromIndex)
<功能> 从fromIndex位置开始从后往前找从后往前找,返回字符串s第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1
String s2 = new String("abcdefabc");
int i = s2.lastIndexOf("abc", 3);
System.out.println(i); //0
五、字符串转化
5.1 数字与字母之间的转化
//数字转换为字符串
String s1 = String.valueOf(100);
String s2 = String.valueOf(12.4);
String s3 = String.valueOf(true);
System.out.println(s1 +' '+ s2 +' '+ s3); //100 12.4 true 这些都为字符串
//字符串转换为数字
int i = Integer.parseInt("123"); //Integer为包装类型,后面会讲
double d = Double.parseDouble("3.14");
System.out.println(i);
System.out.println(d);
5.2 大小写转换
String s = new String("hello");
String ret = s.toUpperCase();
System.out.println(ret); //HELLO
String s1 = new String("HeLLO");
String ret1 = s1.toLowerCase();
System.out.println(ret1); //hello
//若要转换的字符串不是字母,则原样输出
5.3 字符串与数组之间的转换
//字符串转换为数组
String s = new String("hello");
char[] ch = s.toCharArray();
//遍历并打印数组
for (char c : ch) {
System.out.print(c);
}
//数组转换为字符串
s = new String(ch);
System.out.println(s);
六、字符串替换
String s1 = new String("hehello");
String ret = s1.replaceAll("he", "aa"); //将字符串章所有的he替换为aa
System.out.println(ret); //aaaallo
String ret1 = s1.replaceFirst("he", "aa"); //将字符串中第一个he替换为aa
System.out.println(ret1); //aahello
七、字符串拆分
<方法> String[] split(String regex)
<功能>以regex为分隔符,将整个字符串拆分,若字符串中没有该分隔符则原样输出
String s = new String("undertale&Sans");
String[] ret = s.split("&"); //返回类型为String[]
for (int i = 0; i < ret.length; i++) {
System.out.print(ret[i] +" "); //undertale Sans
}<方法> String[] split(String regex, int limit)
<功能>以regex为分隔符,将整个字符串拆分为limit组,若字符串中没有该分隔符则原样输出
String s1 = new String("hello world hello Sans");
String[] ret1 = s1.split(" ", 3); //分成3部分
for (int i = 0; i < ret1.length; i++) {
System.out.println(ret1[i]);
}
<特殊1>若分隔符为". * +",则要进行转义,在前面加上\\
String s = new String("192.168.1.1");
String[] ret = s1.split("\\.");
for (int i = 0; i < ret.length; i++) {
System.out.print(ret[i] +" "); //192 168 1 1
}
<特殊2>
String s1 = new String("192\\168\\1\\1");
String[] ret = s1.split("\\\\");
for (int i = 0; i < ret.length; i++) {
System.out.print(ret[i] + " "); //192 168 1 1
}
<特殊3>若有多个分隔符,则可以用 "|" 将分隔符隔开
String s2 = new String("name=Sans&age=18");
String[] ret3 = s2.split("=|&");
for (int i = 0; i < ret3.length; i++) {
System.out.print(ret3[i] +" "); //name Sans age 18
}
八、字符串截取
<方法> String subString(int beginIndex)
<功能> 从beginIndex开始截取到字符串结尾
String str = new String("abcdef");
String ret = str.substring(2); // cdef
<方法> String subString(int beginIndex, int endIndex)
<功能> 以区间[beginIndex, endIndex)截取字符串
String str = new String("abcdef");
String ret = str.substring(2, 5); // cde
<其他> String trim()
<功能> 删除字符串开头和结尾的空格
String str = " abc d f ";
System.out.println(str);
String ret = str.trim();
System.out.println("["+ ret +"]");