MyBatis使用注解操作及XML操作
文章目录
- 1. 注解操作
-
- 1.1 打印日志
- 1.2 参数传递
- 1.3 增(Insert)
-
- 注意1:重命名
- 注意2:返回主键
- 1.4 删(Delete)
- 1.5 改(Update)
- 1.6 查(Select)
-
- 1. 配置,开启驼峰命名
- 2. 起别名
- 3. 使用注解
- 2. XML操作
-
- 2.1 配置数据库连接字符串和Mybatis
- 2.2 写持久层代码
-
- 1. 添加mapper接口
- 2. 添加 UserInfoXMLMapper.xml
- 3. 简单实现查
- 2.3 单元测试
- 2.4 增删改查操作
-
- 1. 增(Insert)
-
- 注意1:重命名
- 注意2:返回主键
- 2. 删(Delete)
- 3. 改(Update)
- 4. 查(Select)
- 3. 多表查询
-
- 3.1 准备工作
- 3.2 查询工作
1. 注解操作
MyBatis的操作分为注解和XML操作两种, 上篇博客介绍了MyBatis配置和简单操作,最后也进行了查询,而那种查询操作就是使用注解的方式。
这篇博客和上一篇具有一定关联性,
可以点击上一篇跳转。
下面介绍更多的操作。
1.1 打印日志
在Mybatis当中我们可以借助⽇志, 查看到sql语句的执⾏、执⾏传递的参数以及执⾏结果。
配置代码如下:
mybatis:
configuration:
# 打印日志
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
1.2 参数传递
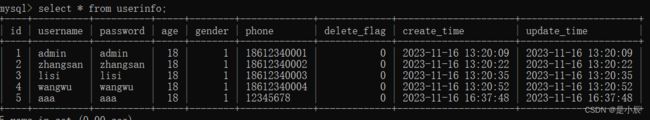
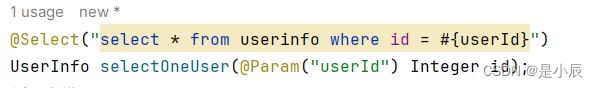
如果我们查询一个id为4的用户,可以直接查询。

运行测试方法:


会得到了想要的结果。
但是,可以发现一种弊端,这种方法是写死的,难道又想获得id为其他的用户,还写许多的方法吗?
答案是不用,可以通过#{…}使用参数传递的方式进行解决。

这样,当不管查询任意id的用户,只需要传递不同参数即可,不需要修改方法中的代码。
注意:
- 如果参数只有一个,那么#{}中的名字可以随便写,idea会自己识别。一般还是相同最好。
- 如果参数为多个,#{}中的名字要和方法参数名字一一对应。
也可以通过 @Param , 设置参数的别名, 如果使⽤ Param 设置别名, #{…}⾥⾯的属性名必须和@Param 设置的⼀样。
1.3 增(Insert)
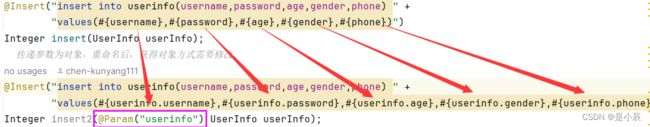
增加使用Insert注解,使用规则和Select相同。但是查询必须要接受返回值,而插入可以没有返回值,也可以有。这里模仿MySql中返回整型,表示影响的行数。
代码:
@Insert("insert into userinfo(username,password,age,gender,phone) " +
"values(#{username},#{password},#{age},#{gender},#{phone})")
Integer insert(UserInfo userInfo);
测试代码:
@Test
void insert() {
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setUsername("aaa");
userInfo.setPassword("aaa");
userInfo.setAge(18);
userInfo.setGender(1);
userInfo.setPhone("12345678");
Integer result = userInfoMapper.insert(userInfo);
log.info("insert 方法, 执行结果: {}",result);
}
注意1:重命名
这里需要注意,如果使用重命名,传递参数为对象,重命名后,获得对象方式需要修改,使用参数.属性 来获取。
注意2:返回主键
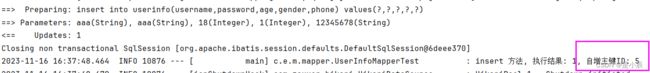
Insert 语句默认返回的是 受影响的⾏数,但有些情况下, 数据插⼊之后, 还需要有后续的关联操作, 需要获取到新插⼊数据的id。
如果想要拿到⾃增id, 需要在Mapper接⼝的⽅法上添加⼀个Options的注解。
@Options(useGeneratedKeys = true, keyProperty = "id")
@Insert("insert into userinfo(username,password,age,gender,phone) " +
"values(#{username},#{password},#{age},#{gender},#{phone})")
Integer insert(UserInfo userInfo);
useGeneratedKeys:这会令 MyBatis 使⽤ JDBC 的 getGeneratedKeys ⽅法来取出由数据库内部⽣成的主键(⽐如:像 MySQL 和 SQL Server 这样的关系型数据库管理系统的⾃动递增字段),默认值:false。
keyProperty:指定能够唯⼀识别对象的属性,MyBatis 会使⽤ getGeneratedKeys 的返回值或insert 语句的 selectKey ⼦元素设置它的值,默认值:未设置(unset)。
测试代码:
@Test
void insert() {
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setUsername("aaa");
userInfo.setPassword("aaa");
userInfo.setAge(18);
userInfo.setGender(1);
userInfo.setPhone("12345678");
Integer result = userInfoMapper.insert(userInfo);
log.info("insert 方法, 执行结果: {}, 自增主键ID: {}",result,userInfo.getId());
}
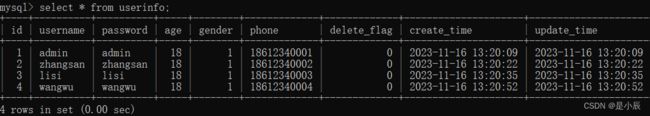
1.4 删(Delete)
删使用Delete注解。
代码:
@Delete("delete from userinfo where id = #{id}")
Integer delete(Integer id);
测试代码:
@Test
void delete() {
Integer id = 5;
Integer result = userInfoMapper.delete(id);
log.info("delete方法, 执行结果: {}",result);
}
1.5 改(Update)
改使用Update注解。
@Update("update userinfo set age = #{age} where id = #{id}")
Integer update(UserInfo userInfo);
测试代码:
@Test
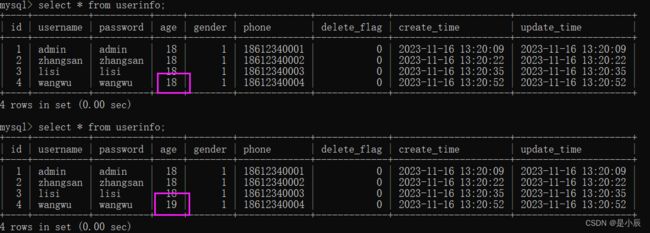
void update() {
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setId(4);
userInfo.setAge(19);
Integer result = userInfoMapper.update(userInfo);
if(result > 0){
log.info("方法执行成功");
}
}
1.6 查(Select)
正常查时,只有Java对象属性和数据库字段⼀模⼀样时, 才会进
⾏赋值。

而前面查时,后面三个并不相同,但是还是成功赋值了,这是为什么呢?
1. 配置,开启驼峰命名
其实是因为通常数据库列使⽤蛇形命名法进⾏命名(下划线分割各个单词), ⽽ Java 属性⼀般遵循驼峰命名法约定。我们可以进行配置使这两种命名⽅式之间启⽤⾃动映射。
mybatis:
configuration:
# 自动转驼峰
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true
2. 起别名
@Select("select id, username, password, age, gender, phone," +
" delete_flag as deleteFlag, create_time as createTime, update_time as updateTime" +
" from userinfo")
List<UserInfo> queryAllUser();
这样也可以解决问题,但是没有直接配置简单,推荐还是配置。
3. 使用注解
除了上面两种,还可以使用Results注解。
使用规则:
@Results(id = "BaseMap",value = {
@Result(column = "delete_flag", property = "deleteFlag"),
@Result(column = "create_time", property = "createTime"),
@Result(column = "update_time", property = "updateTime")
})
@Select("select id, username, password, age, gender, phone," +
" delete_flag, create_time, update_time" +
" from userinfo")
List<UserInfo> queryAllUser();
column是数据库字段,property是Java对象属性。
起个id方便其他方法使用,如图:

后面在使用,通过ResultMap注解加id即可。
如果使用这种方法,既然转换了,记得全部字段属性转换。
2. XML操作
MyBatis的开发有两种方式,上面的注解是其中一种,它主要适合简单的增删查改功能。它要实现一些复杂的SQL的功能,就会非常的麻烦,所有还有另一种开发方式,XML。
Mybatis XML操作方式需要下面两步:
- 配置数据库连接字符串和Mybatis。
- 写持久层代码。
2.1 配置数据库连接字符串和Mybatis
此步骤需要进⾏两项设置,数据库连接字符串设置和 MyBatis 的 XML ⽂件配置。
如果是application.yml⽂件, 配置内容如下:
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mybatis_test?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false
username: root
password: 131452
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
mybatis:
# XML开发
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*Mapper.xml
2.2 写持久层代码
持久层代码分两部分
- ⽅法定义 Interface
- ⽅法实现: XXX.xml
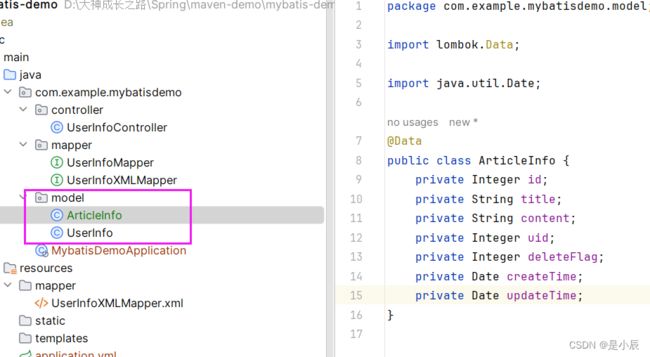
1. 添加mapper接口
package com.example.mybatisdemo.mapper;
import com.example.mybatisdemo.model.UserInfo;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import java.util.List;
@Mapper
public interface UserInfoXMLMapper {
List<UserInfo> selectAllUser();
}
2. 添加 UserInfoXMLMapper.xml
创建UserInfoXMLMapper.xml文件,mapper包,**Mapper.xml。
添加固定的配置代码:
DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.example.mybatisdemo.mapper.UserInfoXMLMapper">
mapper>
3. 简单实现查
代码如下:
DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.example.mybatisdemo.mapper.UserInfoXMLMapper">
<select id="selectAllUser" resultType="com.example.mybatisdemo.model.UserInfo">
select username, password, age, gender, phone from userinfo
select>
mapper>
对应关系如下:

< mapper> 标签:需要指定 namespace 属性,表⽰命名空间,值为 mapper 接⼝的全限定名,包括全包名.类名。
< select >标签 :是⽤来执⾏数据库的查询操作的:
id :是和 Interface (接⼝)中定义的⽅法名称⼀样的,表⽰对接⼝的具体实现⽅法。
resultType :是返回的数据类型,也就是开头我们定义的实体类。
2.3 单元测试
Alt+Insert自动生成测试类:
填写代码:
package com.example.mybatisdemo.mapper;
import com.example.mybatisdemo.model.UserInfo;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.List;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
@Slf4j
@SpringBootTest
class UserInfoXMLMapperTest {
@Autowired
private UserInfoXMLMapper userInfoXMLMapper;
@Test
void selectAllUser() {
List<UserInfo> list = userInfoXMLMapper.selectAllUser();
log.info(list.toString());
}
}
2.4 增删改查操作
1. 增(Insert)
接口:
Integer insertUser(UserInfo userInfo);
xml:
<insert id="insertUser">
insert into userinfo (username, password, age, gender, phone)
value(#{username}, #{password}, #{age},#{gender},#{phone})
insert>
测试:
@Test
void insertUser() {
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setUsername("bbb");
userInfo.setPassword("bbb");
userInfo.setAge(20);
userInfo.setGender(2);
userInfo.setPhone("12312321");
Integer result = userInfoXMLMapper.insertUser(userInfo);
log.info("执行影响行数: {}",result);
}
注意1:重命名
使用@Param,规则和注解一样。
Integer insertUser(@Param("insertinfo") UserInfo userInfo);
<insert id="insertUser">
insert into userinfo (username, password, age, gender, phone)
value(#{insertinfo.username}, #{insertinfo.password}, #{insertinfo.age},#{insertinfo.gender},#{insertinfo.phone})
insert>
注意2:返回主键
接⼝定义不变, Mapper.xml 实现 设置useGeneratedKeys 为true和keyProperty属性,属性为获取主键。
<insert id="insertUser"> useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
insert into userinfo (username, password, age, gender, phone)
value(#{username}, #{password}, #{age},#{gender},#{phone})
insert>
2. 删(Delete)
Integer deleteUser(Integer id);
<delete id="deleteUser">
delete from userinfo where id = #{id}
delete>
3. 改(Update)
Integer updateUser(UserInfo userInfo);
<update id="updateUser">
update userinfo set username=#{username} where id=#{id}
update>
4. 查(Select)
查时,如果表的字段和Java对象属性名不同,也不会赋值,结果方案有三种:
- 起别名
- 结果映射
- 开启驼峰命名
其中1,3的解决办法和注解⼀样,不再多说, 接下来看下xml如果来写结果映射。
<resultMap id="BaseMap" type="com.example.mybatisdemo.model.UserInfo">
<id column="id" property="id">id>
<result column="delete_flag" property="deleteFlag">result>
<result column="create_time" property="createTime">result>
<result column="update_time" property="updateTime">result>
resultMap>
<select id="selectAllUser" resultMap="BaseMap" resultType="com.example.mybatisdemo.model.UserInfo">
select username, password, age, gender, phone from userinfo
select>
3. 多表查询
多表查询和单表差不多,就是SQL语句写起来麻烦点。
下面稍微演示一下。
3.1 准备工作
前面操作都是在操作一张用户表,现在在添加一张文章表,进行多表查询。
数据准备:

插入些数据:

3.2 查询工作
查询id为1的作者的文章和作者信息。
SQL查询:
mysql> select tu.username,tu.age,tu.gender,
-> ta.title,ta.content
-> from userinfo tu left join articleinfo ta on tu.id = ta.uid
-> where tu.id = 1;
+----------+-----+--------+----------+--------------+
| username | age | gender | title | content |
+----------+-----+--------+----------+--------------+
| admin | 18 | 1 | Java | Java正文 |
| admin | 18 | 1 | 数据结构 | 数据结构正文 |
+----------+-----+--------+----------+--------------+
2 rows in set (0.01 sec)
但是要使用MyBatis查询,Java文章实体类中并没有用户的属性,所有必须要补充完整,补充完整如下:
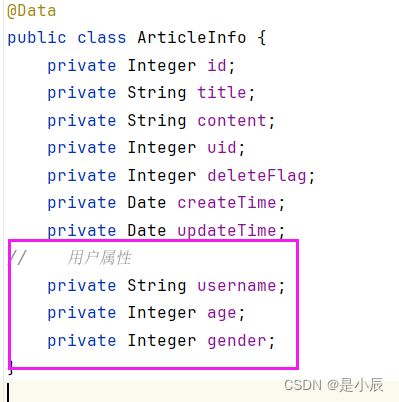
定义接口:
@Mapper
public interface ArticleInfoMapper {
@Select("select tu.username,tu.age,tu.gender," +
"ta.title,ta.content " +
"from userinfo tu right join articleinfo ta on tu.id = ta.uid " +
"where ta.uid = #{id};")
List<ArticleInfo> queryUserByUid(Integer id);
}
基本和单表相同,就是SQL语句不同,别名也可以正常使用。