SpringBoot:异步任务基础与源码剖析
官网文档:How To Do @Async in Spring | Baeldung。
@Async注解
Spring框架基于@Async注解提供了对异步执行流程的支持。
最简单的例子是:使用@Async注解修饰一个方法,那么这个方法将在一个单独的线程中被执行,即:从同步执行流程转换为异步执行流程。
此外,Spring框架中,事件Event也是支持异步处理操作的。
@EnableAsync注解|核心接口
通过在配置类上添加@EnableAsync注解,可以为Spring应用程序启用异步执行流程的支持
@Configuration
@EnableAsync
public class SpringAsyncConfig { ... }该注解提供了一些可配置属性,
annotation:默认情况下,@EnableAsync会告诉Spring程序去探查所有被@Async注解修饰的、以及@javax.ejb.Asynchronous.注解;
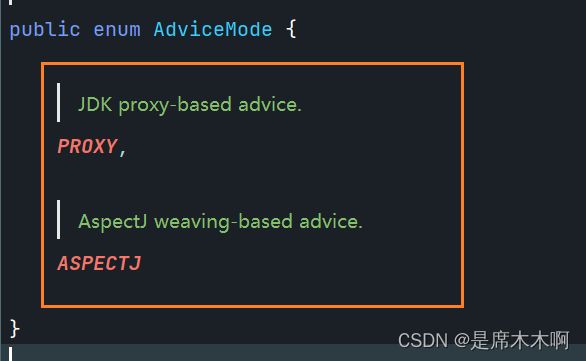
mode:指定异步流程生效的方式:JDK Proxy还是AspectJ;
proxtTargetClass:只有在mode为AdviceMode.PROXY(JDK动态代理)时才会生效,用于指定要使用的动态代理类型:CGLIB或者JDK;
order:设置AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor执行异步调用的顺序。
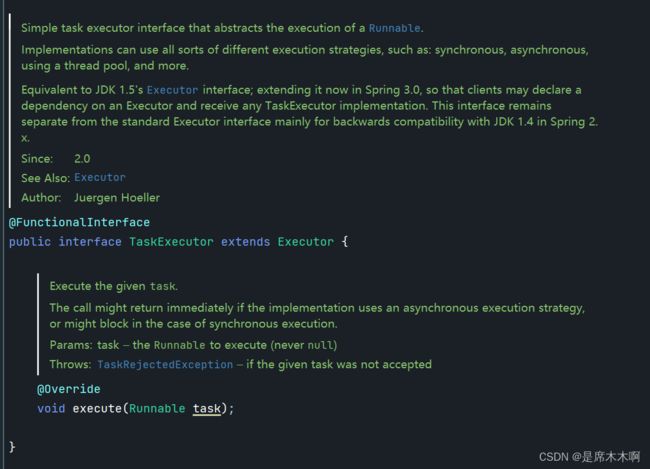
而在AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类的内部,则是通过TaskExecutor提供了一个线程池,来更加具体的负责执行某一个异步流程的。
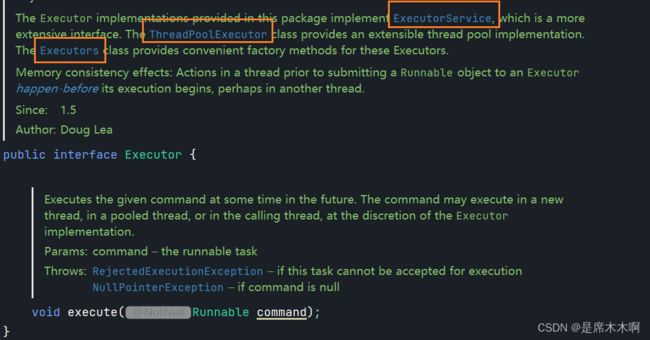
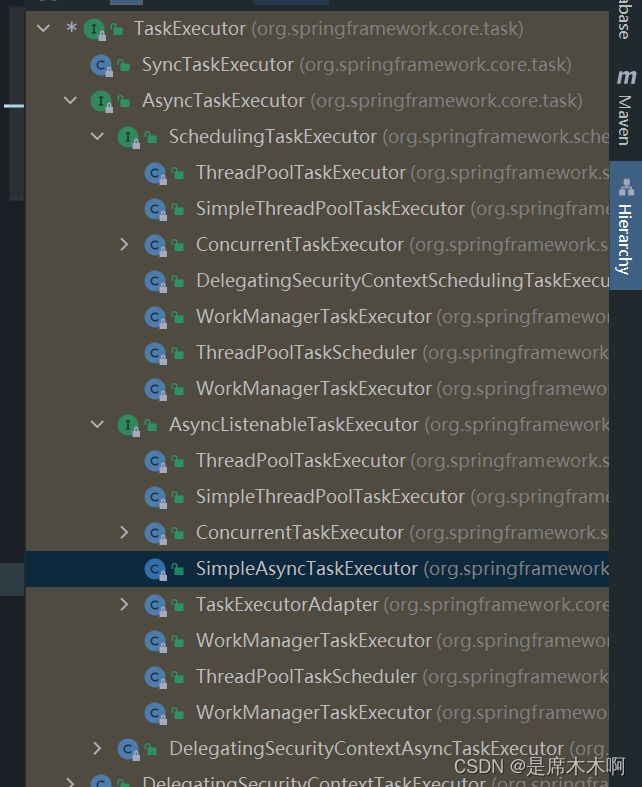
再往深入查看,就会发现,该接口的父接口Executor,与之相关的就是我们经常谈论的和并发编程相关的Executor框架了。
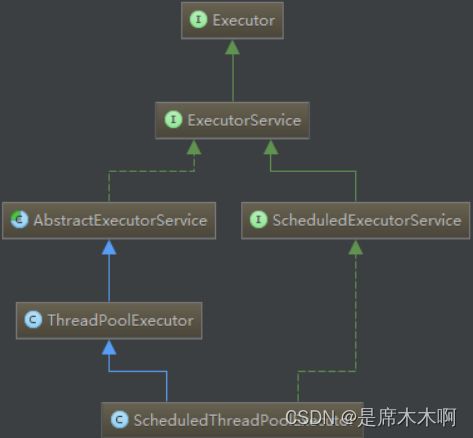
再看Spring框架内部提供的TaskExecutor接口的继承结构,如下图所示,
因此,要使用@EnableAsync注解开启异步流程执行的支持,可能就需要去对TaskExecutor接口实例的线程池参数进行配置。
SpringBoot默认线程池配置
根据以上解读,不难发现:其实SpringBoot内部是通过维护线程池的方式去执行异步任务的,那么,这个默认的线程池对应于Exector框架的哪一个实现子类?相关的配置参数又是什么呢?
要解决上述疑惑,需要先去找到TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration类,该类定义了默认注入的线程池实例及其配置参数。
默认线程池类型:ThreadPoolTaskExecutor
默认线程池配置参数:TaskExecutionProperties.Pool
详细参数信息,对应于一个静态内部类Pool,源码如下,
public static class Pool {
/**
* Queue capacity. An unbounded capacity does not increase the pool and therefore
* ignores the "max-size" property.
*/
private int queueCapacity = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
/**
* Core number of threads.
*/
private int coreSize = 8;
/**
* Maximum allowed number of threads. If tasks are filling up the queue, the pool
* can expand up to that size to accommodate the load. Ignored if the queue is
* unbounded.
*/
private int maxSize = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
/**
* Whether core threads are allowed to time out. This enables dynamic growing and
* shrinking of the pool.
*/
private boolean allowCoreThreadTimeout = true;
/**
* Time limit for which threads may remain idle before being terminated.
*/
private Duration keepAlive = Duration.ofSeconds(60);
public int getQueueCapacity() {
return this.queueCapacity;
}
public void setQueueCapacity(int queueCapacity) {
this.queueCapacity = queueCapacity;
}
public int getCoreSize() {
return this.coreSize;
}
public void setCoreSize(int coreSize) {
this.coreSize = coreSize;
}
public int getMaxSize() {
return this.maxSize;
}
public void setMaxSize(int maxSize) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
}
public boolean isAllowCoreThreadTimeout() {
return this.allowCoreThreadTimeout;
}
public void setAllowCoreThreadTimeout(boolean allowCoreThreadTimeout) {
this.allowCoreThreadTimeout = allowCoreThreadTimeout;
}
public Duration getKeepAlive() {
return this.keepAlive;
}
public void setKeepAlive(Duration keepAlive) {
this.keepAlive = keepAlive;
}
}从中可以找到默认的配置参数,
@Async注解使用
使用时的两个限制
1.它只能应用于公共方法
2.从同一个类中调用异步方法将不起作用(会绕过代理,而直接去调用底层方法本身)
注解修饰对象
查看@Async注解的源码,可看到:它用于修饰class、interface、method,并且提供了一个value属性,用于在@Autowired和@@Qualifier注解组合自动装配时,指定要使用哪一个线程池。因为原则上来讲,我们是可以通过@Bean注解,在一个Spring容器中注入多个线程池实例的。
package org.springframework.scheduling.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* Annotation that marks a method as a candidate for asynchronous execution.
*
* Can also be used at the type level, in which case all the type's methods are
* considered as asynchronous. Note, however, that {@code @Async} is not supported
* on methods declared within a
* {@link org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration @Configuration} class.
*
*
In terms of target method signatures, any parameter types are supported.
* However, the return type is constrained to either {@code void} or
* {@link java.util.concurrent.Future}. In the latter case, you may declare the
* more specific {@link org.springframework.util.concurrent.ListenableFuture} or
* {@link java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture} types which allow for richer
* interaction with the asynchronous task and for immediate composition with
* further processing steps.
*
*
A {@code Future} handle returned from the proxy will be an actual asynchronous
* {@code Future} that can be used to track the result of the asynchronous method
* execution. However, since the target method needs to implement the same signature,
* it will have to return a temporary {@code Future} handle that just passes a value
* through: e.g. Spring's {@link AsyncResult}, EJB 3.1's {@link javax.ejb.AsyncResult},
* or {@link java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture#completedFuture(Object)}.
*/
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Async {
/**
* A qualifier value for the specified asynchronous operation(s).
*
May be used to determine the target executor to be used when executing
* the asynchronous operation(s), matching the qualifier value (or the bean
* name) of a specific {@link java.util.concurrent.Executor Executor} or
* {@link org.springframework.core.task.TaskExecutor TaskExecutor}
* bean definition.
*
When specified on a class-level {@code @Async} annotation, indicates that the
* given executor should be used for all methods within the class. Method-level use
* of {@code Async#value} always overrides any value set at the class level.
* @since 3.1.2
*/
String value() default "";
}
使用方式1:修饰方法method
根据上面的使用限制,被@Async注解修饰的方法,和主调方法不能位于同一个类中,并且也必须是public类型的公共方法。
package com.example.soiladmin;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
//@Async注解测试类
@Component
public class AsyncTestMethod {
@Async
public void asyncTest(){
try {
System.out.println(String.format("start:%s",Thread.currentThread().getName()));
Thread.sleep(1500);
System.out.println(String.format("end:%s",Thread.currentThread().getName()));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
调用方法,
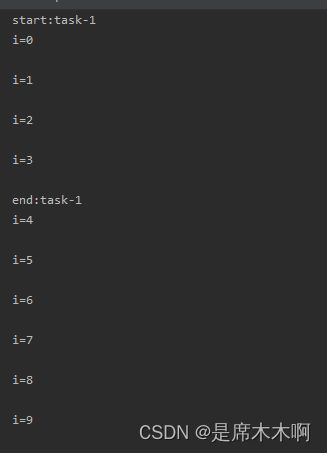
注意到:被@Async修饰的方法线程睡眠了1.5s,如果它是异步执行的,那么就不会阻塞后面for循环的执行。
@Autowired
private AsyncTestMethod asyncTestMethod;
@Test
public void asyncTestMethod_1(){
asyncTestClass.asyncTest();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(300);
System.out.println(String.format("i=%d\n",i));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}打印结果,
使用方式2:修饰类class
为了方便,我们直接将使用方式1中的类拷贝一份,然后使用@Async注解修饰class类,而非Method方法。
package com.example.soiladmin;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Async
public class AsyncTestClass {
public void asyncTest(){
try {
System.out.println(String.format("start:%s",Thread.currentThread().getName()));
Thread.sleep(1500);
System.out.println(String.format("end:%s",Thread.currentThread().getName()));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
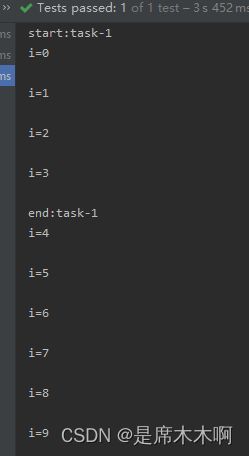
主调方法,
@Autowired
private AsyncTestClass asyncTestClass;
@Test
public void asyncTestClass_2(){
asyncTestClass.asyncTest();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(300);
System.out.println(String.format("i=%d\n",i));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}打印结果,
使用方式3:带返回值的方法
以上测试案例都是不带返回值的,但是一般情况下,我们可能还希望获取异步执行的结果,然后对结果进行合并、分析等,那么就可以为@Async注解修饰的方法声明一java.util.concurrent接口类型的返回类型。
但是这里有一个注意点:就是要Future是一个接口,我们没办法直接去new一个接口,所以还要找到Future接口的实现子类。
比较常用的是Spring框架提供的实现子类AsyncResult,
我们继续简单看一下AsyncResult实现子类的基本结构,
基本上提供了获取异步执行结果的get方法、对成功/失败情况进行处理的回调函数addCallBack、将返回结果继续进行封装为AsyncResult类型值的forValue,简单来讲,就是对jdk原生的concurrent包下的Future接口进行了功能拓展和增强。
异步方法如下,
/**
* 数列求和: An = 2 ^ n(n>=0),求累加和S(n)---这里为了测试效果(出于增加耗时考虑),不直接使用求和公式
* @param n
* @return
*/
@Async
public ListenableFuture asyncSequenceSum(int n){
Double sum = 0.0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
sum += Math.pow(2,i);
}
return new AsyncResult<>(sum);
} 测试方法如下,
以下两种方式都可以拿到执行结果,调用回调函数。
官网给的是第二种写法,
@Test
public void asyncTestMethodWithReturns_nor(){
System.out.println("开始执行...");
ListenableFuture asyncResult = asyncTestMethod.asyncSequenceSum(10);
//添加回调函数
asyncResult.addCallback(
new SuccessCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(Double result) {
System.out.println("执行成功:" + result.doubleValue());
}
},
new FailureCallback() {
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable ex) {
System.out.println("执行失败:"+ex.getMessage());
}
}
);
//直接尝试获取结果-[只能拿到结果,如果执行出错,就会抛出异常]
try {
Double aDouble = asyncResult.get();
System.out.println("计算结果:"+aDouble.doubleValue());
} catch (ExecutionException | InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Test
public void asyncTestMethodWithReturns_normal(){
System.out.println("开始执行...");
ListenableFuture asyncResult = asyncTestMethod.asyncSequenceSum(10);
//等待执行结果
while (true){
if (asyncResult.isDone()){
//直接尝试获取结果-[只能拿到结果,如果执行出错,就会抛出异常]
try {
Double aDouble = asyncResult.get();
System.out.println("计算结果:"+aDouble.doubleValue());
//添加回调函数
asyncResult.addCallback(
new SuccessCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(Double result) {
System.out.println("执行成功:" + result.doubleValue());
}
},
new FailureCallback() {
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable ex) {
System.out.println("执行失败:"+ex.getMessage());
}
}
);
} catch (ExecutionException | InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//终止循环
break;
}
System.out.println("Continue doing something else. ");
}
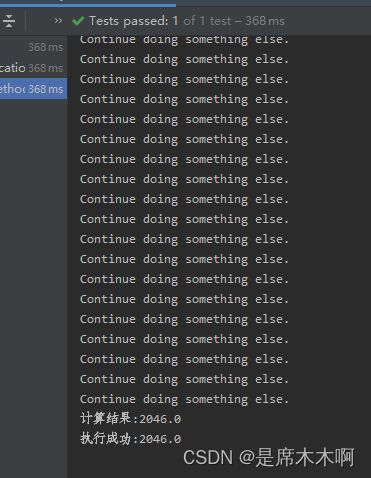
} 执行结果,
自定义线程池配置参数
上面提到,SpringBoot内置了1个ThreadPoolTaskExecutor线程池实例,在实际开发中,根据需要,我们也可以结合@Configuration注解自定义新的线程池,也可以通过通过实现AsyncConfigurer接口直接替换掉原有的线程池。
定义新的线程池
这种情况下,Spring容器就会出现多个线程池实例,所以在使用@Async注解时,要通过value属性指定具体要使用哪一个线程池实例。
@Configuration
@EnableAsync
public class SpringAsyncConfig {
@Bean(name = "threadPoolTaskExecutor")
public Executor threadPoolTaskExecutor() {
return new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
}
}使用示例,
@Async("threadPoolTaskExecutor")
public void asyncMethodWithConfiguredExecutor() {
System.out.println("Execute method with configured executor - "
+ Thread.currentThread().getName());
}替换默认线程池
替换默认线程池需要实现AsyncConfigurer接口,通过重写getAsyncExecutor() ,从而让自定义的线程池变为Spring框架默认使用的线程池。
示例代码如下,
@Configuration
@EnableAsync
public class SpringAsyncConfig implements AsyncConfigurer {
@Override
public Executor getAsyncExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor threadPoolTaskExecutor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
threadPoolTaskExecutor.initialize();
return threadPoolTaskExecutor;
}
}配置线程池参数
除了上述自定义新的线程池的方法,也可以通过SpringBoot配置文件,重新对默认线程池的参数进行修改。
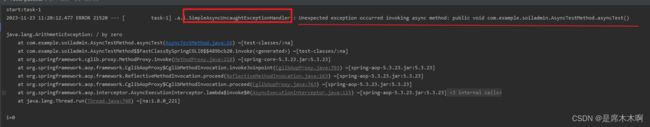
异步处理流程的异常处理
内置异常处理类:SimpleAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler
SpringBoot框架内置的异常处理类为SimpleAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler,仅仅是对异
常信息进行了打印处理。
package org.springframework.aop.interceptor;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
/**
* A default {@link AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler} that simply logs the exception.
*
* @author Stephane Nicoll
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 4.1
*/
public class SimpleAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler implements AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler {
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(SimpleAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler.class);
@Override
public void handleUncaughtException(Throwable ex, Method method, Object... params) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Unexpected exception occurred invoking async method: " + method, ex);
}
}
}
当我们不做任何处理时,默认就是上述异常处理类在起作用。
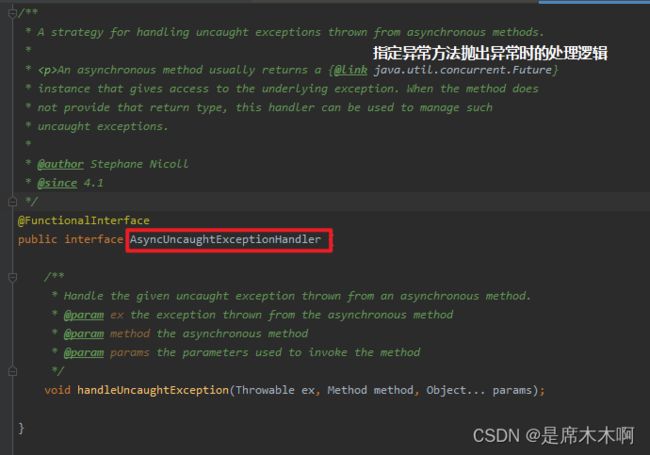
继续向上扒拉源码,会发现它的父接口AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler,其作用就是:指定异步方法执行过程中,抛出异常时的因对策略。
自定义异常处理类|配置
我们也可以通过实现接口AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler,来自定义异常处理逻辑。
如下所示,为自定义的异常处理类:CustomAsyncExceptionHandler。
package com.example.soilcommon.core.async;
import org.springframework.aop.interceptor.AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* 异步处理流程异常处理类:
* [1]对于返回值为Future类型的异步执行方法,异常会被抛出给主调方法
* [2]对于返回值为void类型的异步执行方法,异常不会被抛出,即:在主调方法中没办法通过try...catch捕获到异常信息
* 当前配置类针对情况[2]进行统一的异常处理
*/
@Component("customAsyncExceptionHandler")
public class CustomAsyncExceptionHandler implements AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler {
/**
* Handle the given uncaught exception thrown from an asynchronous method.
* @param throwable the exception thrown from the asynchronous method
* @param method the asynchronous method
* @param params the parameters used to invoke the method
*/
@Override
public void handleUncaughtException(Throwable throwable, Method method, Object... params) {
System.out.println("Exception message - " + throwable.getMessage());
System.out.println("Method name - " + method.getName());
for (Object param : params) {
System.out.println("Parameter value - " + param);
}
}
}
接下来我们对其进行配置,使其生效,需要重写AsyncConfigurer接口getAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler方法,
package com.example.soilcommon.core.async;
import org.springframework.aop.interceptor.AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.aop.interceptor.SimpleAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.AsyncConfigurer;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync;
@Configuration
@EnableAsync
public class AsyncConfig implements AsyncConfigurer {
/**
* 指定要使用哪一个具体的异常处理类
* 原因:SpringBoot框架默认使用内置的SimpleAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler进行异常处理
*/
@Autowired
@Qualifier("customAsyncExceptionHandler")
private AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler asyncUncaughtExceptionHandler;
/**
* The {@link AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler} instance to be used
* when an exception is thrown during an asynchronous method execution
* with {@code void} return type.
*/
@Override
public AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler getAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler() {
return this.asyncUncaughtExceptionHandler;
}
}
最终异步方法执行抛出异常时,打印的信息就是我们自定义的了,
参考文章:How To Do @Async in Spring | Baeldung