深入理解Zookeeper系列-2.Zookeeper基本使用和分布式锁原理
- 作者简介:大家好,我是爱吃芝士的土豆倪,24届校招生Java选手,很高兴认识大家
- 系列专栏:Spring源码、JUC源码、Kafka原理、分布式技术原理
- 如果感觉博主的文章还不错的话,请三连支持一下博主哦
- 博主正在努力完成2023计划中:源码溯源,一探究竟
- 联系方式:nhs19990716,加我进群,大家一起学习,一起进步,一起对抗互联网寒冬
文章目录
- 集群环境安装
- Zookeeper java客户端的使用
-
- Curator
- 代码
- 权限操作
-
- 权限模式
- 节点监听
- 分布锁的实现
-
- InterProcessMutex
集群环境安装
在zookeeper集群中,各个节点总共有三种角色,分别是:leader,follower,observer
集群模式我们采用模拟3台机器来搭建zookeeper集群。分别复制安装包到三台机器上并解压,同时copy一份zoo.cfg。
- 修改配置文件
- 修改端口
- server.1=IP1:2888:3888 【2888:访问zookeeper的端口;3888:重新选举leader的端口】
- server.2=IP2.2888:3888
- server.3=IP3.2888:2888
- server.A=B:C:D:其 中
- A 是一个数字,表示这个是第几号服务器;
- B 是这个服务器的 ip地址;
- C 表示的是这个服务器与集群中的 Leader 服务器交换信息的端口;
- D 表示的是万一集群中的 Leader 服务器挂了,需要一个端口来重新进行选举,选出一个新
的 Leader,而这个端口就是用来执行选举时服务器相互通信的端口。如果是伪集群的配置方
式,由于 B 都是一样,所以不同的 Zookeeper 实例通信端口号不能一样,所以要给它们分配
不同的端口号。 - 在集群模式下,集群中每台机器都需要感知到整个集群是由哪几台机器组成的,在配置文件
中,按照格式server.id=host:port:port,每一行代表一个机器配置。id: 指的是server ID,用
来标识该机器在集群中的机器序号
- 新建datadir目录,设置myid
在每台zookeeper机器上,我们都需要在数据目录(dataDir)下创建一个myid文件,该文件只有一行内容,对应每台机器的Server ID数字;比如server.1的myid文件内容就是1。【必须确保每个服务器的myid文件中的数字不同,并且和自己所在机器的zoo.cfg中server.id的id值一致,id的范围是1~255】
- 启动zookeeper
需要注意的是,如果使用云服务器搭建的话,需要开放端口。
Zookeeper java客户端的使用
针对zookeeper,比较常用的Java客户端有zkclient、curator。由于Curator对于zookeeper的抽象层次
比较高,简化了zookeeper客户端的开发量。使得curator逐步被广泛应用。
- 封装zookeeper client与zookeeper server之间的连接处理
- 提供了一套fluent风格的操作api
- 提供zookeeper各种应用场景(共享锁、leader选举)的抽象封装
Curator
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.curatorgroupId>
<artifactId>curator-frameworkartifactId>
<version>4.2.0version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.curatorgroupId>
<artifactId>curator-recipesartifactId>
<version>4.2.0version>
dependency>
代码
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
CuratorFramework curatorFramework=
CuratorFrameworkFactory.builder().
connectString("192.168.216.128:2181,192.168.216.129:2181,192.168.216.130:2181").
sessionTimeoutMs(5000). // 会话超时,定时心跳机制
retryPolicy(new ExponentialBackoffRetry
(1000,3)).//重试
connectionTimeoutMs(4000).build();
curatorFramework.start(); //表示启动.
//创建
// create(curatorFramework);
//修改
// update(curatorFramework);
//查看
// get(curatorFramework);
operatorWithAsync(curatorFramework);
create(curatorFramework);
}
private static String get(CuratorFramework curatorFramework) throws Exception {
String rs=new String(curatorFramework.getData().forPath("/first_auth"));
System.out.println(rs);
return rs;
}
private static String create(CuratorFramework curatorFramework) throws Exception {
String path=curatorFramework.create().
creatingParentsIfNeeded().
withMode(CreateMode.PERSISTENT).forPath("/first","Hello Gupaao".getBytes());
System.out.println("创建成功的节点: "+path);
return path;
}
private static String update(CuratorFramework curatorFramework) throws Exception {
curatorFramework.setData().forPath("/first","Hello GuPaoEdu.cn".getBytes());
return null;
}
//异步访问 | 同步(future.get())
//redisson
private static String operatorWithAsync(CuratorFramework curatorFramework) throws Exception {
// 之前说过,数据同步的时候需要投票,如果我们可以使用异步的请求
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
curatorFramework.create().creatingParentsIfNeeded().
withMode(CreateMode.PERSISTENT).inBackground(new BackgroundCallback() {
@Override
public void processResult(CuratorFramework client, CuratorEvent event) throws Exception {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+event.getResultCode());
countDownLatch.countDown();
}
}).forPath("/second","second".getBytes());
//TODO ...
System.out.println("before");
countDownLatch.await(); //阻塞
System.out.println("after");
return "";
}
测试 进入zookeeper
ls /
get first 就可以看到这个数据了
权限操作
我们可以设置当前节点增删改查的权限。
read
write(修改)
delete
create(创建)
admin
简写: rwdca
private static String authOperation(CuratorFramework curatorFramework) throws Exception {
List<ACL> acls=new ArrayList<>();
ACL acl=new ACL(ZooDefs.Perms.CREATE| ZooDefs.Perms.DELETE,new Id("digest", DigestAuthenticationProvider.generateDigest("u1:u1")));
ACL acl1=new ACL(ZooDefs.Perms.ALL,new Id("digest", DigestAuthenticationProvider.generateDigest("u2:u2")));
acls.add(acl);
acls.add(acl1);
curatorFramework.create().creatingParentsIfNeeded().withMode(CreateMode.PERSISTENT).
withACL(acls).forPath("/first_auth","123".getBytes());
return null;
}
List<AuthInfo> list=new ArrayList<>();
AuthInfo authInfo=new AuthInfo("digest","u2:u2".getBytes());
list.add(authInfo);
CuratorFramework curatorFramework=
CuratorFrameworkFactory.builder().
connectString("192.168.216.128:2181,192.168.216.129:2181,192.168.216.130:2181").
sessionTimeoutMs(5000).
retryPolicy(new ExponentialBackoffRetry
(1000,3)).
connectionTimeoutMs(4000).authorization(list).build();
curatorFramework.start(); //表示启动.
权限模式
- Ip 通过ip地址粒度来进行权限控制,例如配置 [ip:192.168.0.1], 或者按照网段 ip:192.168.0.1/24 ;
- Digest:最常用的控制模式,类似于 username:password ;设置的时候需要
- DigestAuthenticationProvider.generateDigest() SHA-加密和base64编码
- World: 最开放的控制模式,这种权限控制几乎没有任何作用,数据的访问权限对所有用户开放。 world:anyone
- Super: 超级用户,可以对节点做任何操作
- auth 不需要id。不过这里应该用 expression 来表示。即(scheme:expression:perm)
节点监听
- 当前节点的创建(NodeCreated)
- 子节点的变更事件(NodeChildrenChanged) ->Dubbo
- 当前被监听的节点的数据变更事件:NodeDataChanged
- 当前节点被删除的时候会触发 NodeDeleted
ZooKeeper zooKeeper;
public void originApiTest() throws IOException, KeeperException, InterruptedException {
ZooKeeper zooKeeper=new ZooKeeper("192.168.216.128:2181", 5000, new Watcher() {
@Override
public void process(WatchedEvent watchedEvent) {
//表示连接成功之后,会产生的回调时间
}
});
Stat stat=new Stat();
zooKeeper.getData("/first", new DataWatchListener(),stat); //针对当前节点
/* zooKeeper.exists(); //针对当前节点
zooKeeper.getChildren(); //针对子节点的监听*/
}
class DataWatchListener implements Watcher{
@Override
public void process(WatchedEvent watchedEvent) {
// 事件回调
String path=watchedEvent.getPath();
// 再次注册监听
try {
zooKeeper.getData(path,this,new Stat());
} catch (KeeperException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private static void addNodeCacheListener(CuratorFramework curatorFramework,String path) throws Exception {
NodeCache nodeCache=new NodeCache(curatorFramework,path,false);
NodeCacheListener nodeCacheListener=new NodeCacheListener() {
@Override
public void nodeChanged() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Receive Node Changed");
System.out.println(""+nodeCache.getCurrentData().getPath()+"->"+new String(nodeCache.getCurrentData().getData()));
}
};
nodeCache.getListenable().addListener(nodeCacheListener);
nodeCache.start();
}
private static void addPathChildCacheListener(CuratorFramework curatorFramework,String path) throws Exception {
PathChildrenCache childrenCache=new PathChildrenCache(curatorFramework,path,true);
PathChildrenCacheListener childrenCacheListener=new PathChildrenCacheListener() {
@Override
public void childEvent(CuratorFramework curatorFramework, PathChildrenCacheEvent pathChildrenCacheEvent) throws Exception {
System.out.println("子节点事件变更的回调");
ChildData childData=pathChildrenCacheEvent.getData();
System.out.println(childData.getPath()+"-"+new String(childData.getData()));
}
};
childrenCache.getListenable().addListener(childrenCacheListener);
childrenCache.start(PathChildrenCache.StartMode.NORMAL);
}
addNodeCacheListener(curatorFramework,"/first");
addPathChildCacheListener(curatorFramework,"/first");
需要在main方法中 不让其结束
System.in.read();
分布锁的实现
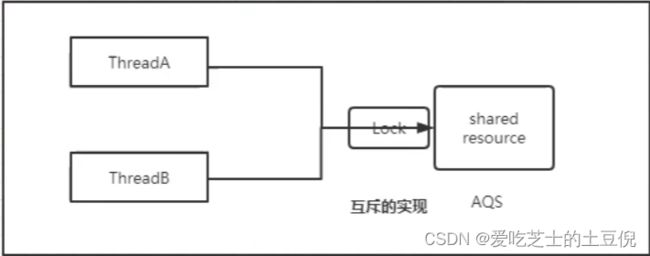
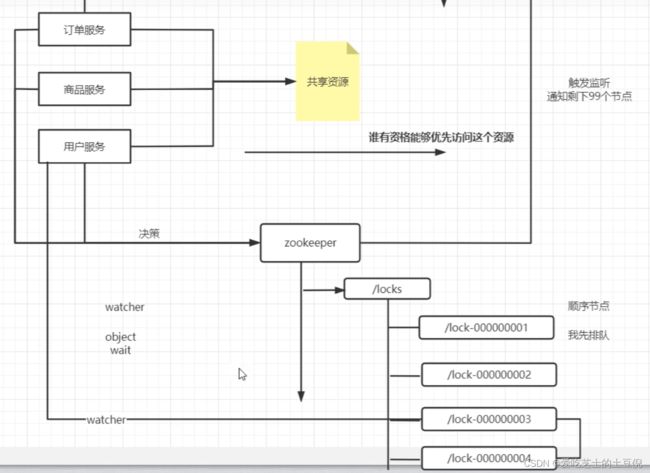
两个线程访问一个共享资源,就会造成数据的不确定性。所以需要加锁。
但是在分布式的场景下,线程变成进程
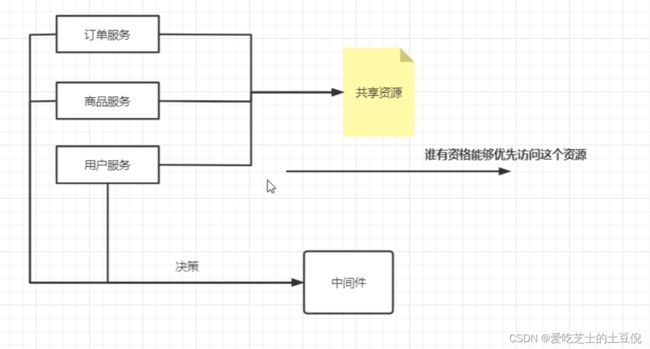
那么应该怎么做呢?如果使用Zookeeper来实现呢?
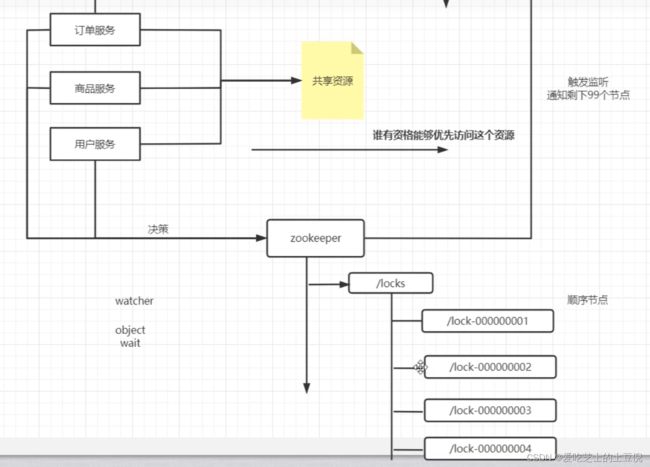
按照zookeeper的特性,只会有一个节点成功,其他的都是失败特性。如果处理完了,其他节点监听这个,当成功的那个节点删除了之后,回调通知再次获得锁即可。
但是会存在一个问题,比如说有100个节点,那么他就会触发99次来通知剩下的节点,为了解决这样的一个问题,一次性唤醒所有的话,我们可以使用顺序节点
先写入后,先排队
这样的话,我们每个节点只需要监听上一个顺序的变化即可,如果我们发现了一个节点删除了,然后去判断自己是不是序号最好的就ok,如果是最小的,那就发起获取锁的动作,如果不是就等着。
CuratorFramework curatorFramework=
CuratorFrameworkFactory.builder().
connectString("192.168.216.128:2181,192.168.216.129:2181,192.168.216.130:2181").
sessionTimeoutMs(5000).
retryPolicy(new ExponentialBackoffRetry
(1000,3)).
connectionTimeoutMs(4000).build();
curatorFramework.start(); //表示启动.
/**
* locks 表示命名空间
* 锁的获取逻辑是放在zookeeper
* 当前锁是跨进程可见
*/
InterProcessMutex lock=new InterProcessMutex(curatorFramework,"/locks");
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
new Thread(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"->尝试抢占锁");
try {
lock.acquire();//抢占锁,没有抢到,则阻塞
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"->获取锁成功");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
Thread.sleep(4000);
lock.release(); //释放锁
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"->释放锁成功");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"t-"+i).start();
}
}
InterProcessMutex
private final ConcurrentMap<Thread, InterProcessMutex.LockData> threadData;
// 首先看 acquire 方法
public void acquire() throws Exception {
if (!this.internalLock(-1L, (TimeUnit)null)) {
throw new IOException("Lost connection while trying to acquire lock: " + this.basePath);
}
}
private boolean internalLock(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws Exception {
// 获得当前线程
Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread();
InterProcessMutex.LockData lockData = (InterProcessMutex.LockData)this.threadData.get(currentThread);
if (lockData != null) {
// 首先判断在同一个线程是否有重入的情况
// 如果有重入,则 +1
lockData.lockCount.incrementAndGet();
return true;
} else {
// 如果没有重入
String lockPath = this.internals.attemptLock(time, unit, this.getLockNodeBytes());
if (lockPath != null) {
// 说明注册成功
InterProcessMutex.LockData newLockData = new InterProcessMutex.LockData(currentThread, lockPath);
// 存进map中
this.threadData.put(currentThread, newLockData);
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
进入 attemptLock
String attemptLock(long time, TimeUnit unit, byte[] lockNodeBytes) throws Exception {
long startMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
Long millisToWait = unit != null ? unit.toMillis(time) : null;
byte[] localLockNodeBytes = this.revocable.get() != null ? new byte[0] : lockNodeBytes;
int retryCount = 0;
String ourPath = null;
boolean hasTheLock = false;
boolean isDone = false;
// 这里面是一个死循环
while(!isDone) {
isDone = true;
try {
// try里面的逻辑,会在循环中会去创建一个锁
ourPath = this.driver.createsTheLock(this.client, this.path, localLockNodeBytes);
hasTheLock = this.internalLockLoop(startMillis, millisToWait, ourPath);
} catch (NoNodeException var14) {
// catch里面的逻辑实际上是重试逻辑
if (!this.client.getZookeeperClient().getRetryPolicy().allowRetry(retryCount++, System.currentTimeMillis() - startMillis, RetryLoop.getDefaultRetrySleeper())) {
throw var14;
}
isDone = false;
}
}
return hasTheLock ? ourPath : null;
}
进入createsTheLock
public String createsTheLock(CuratorFramework client, String path, byte[] lockNodeBytes) throws Exception {
// 本质上就是创建一个临时有序节点
String ourPath;
if (lockNodeBytes != null) {
ourPath = (String)((ACLBackgroundPathAndBytesable)client.create().creatingParentContainersIfNeeded().withProtection().withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL)).forPath(path, lockNodeBytes);
} else {
ourPath = (String)((ACLBackgroundPathAndBytesable)client.create().creatingParentContainersIfNeeded().withProtection().withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL)).forPath(path);
}
return ourPath;
}
// try里面的逻辑,会在循环中会去创建一个锁
ourPath = this.driver.createsTheLock(this.client, this.path, localLockNodeBytes);
// 此时去判断拿没拿到锁,拿到了以后去判断是不是最小的
hasTheLock = this.internalLockLoop(startMillis, millisToWait, ourPath);
internalLockLoop
private boolean internalLockLoop(long startMillis, Long millisToWait, String ourPath) throws Exception {
boolean haveTheLock = false;
boolean doDelete = false;
try {
if (this.revocable.get() != null) {
((BackgroundPathable)this.client.getData().usingWatcher(this.revocableWatcher)).forPath(ourPath);
}
while(this.client.getState() == CuratorFrameworkState.STARTED && !haveTheLock) { // while循环判断客户端的连接没有断开,并且没有获得锁的情况下
// 拿到排序之后的节点
List<String> children = this.getSortedChildren();
String sequenceNodeName = ourPath.substring(this.basePath.length() + 1);
// 去执行一个判断锁的逻辑
PredicateResults predicateResults = this.driver.getsTheLock(this.client, children, sequenceNodeName, this.maxLeases);
// 是否获得锁
if (predicateResults.getsTheLock()) {
haveTheLock = true;
} else {
// 否则进入监听的逻辑
String previousSequencePath = this.basePath + "/" + predicateResults.getPathToWatch();
synchronized(this) {
try {
((BackgroundPathable)this.client.getData().usingWatcher(this.watcher)).forPath(previousSequencePath);
if (millisToWait == null) {
// 在监听中告诉其等待
this.wait();
} else {
millisToWait = millisToWait - (System.currentTimeMillis() - startMillis);
startMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (millisToWait > 0L) {
this.wait(millisToWait);
} else {
doDelete = true;
break;
}
}
} catch (NoNodeException var19) {
}
}
}
}
} catch (Exception var21) {
ThreadUtils.checkInterrupted(var21);
doDelete = true;
throw var21;
} finally {
if (doDelete) {
this.deleteOurPath(ourPath);
}
}
return haveTheLock;
}
进入getsTheLock
public PredicateResults getsTheLock(CuratorFramework client, List<String> children, String sequenceNodeName, int maxLeases) throws Exception {
// 得到索引,验证合法性
int ourIndex = children.indexOf(sequenceNodeName);
validateOurIndex(sequenceNodeName, ourIndex);
// 判断是不是最小的,如果不是就取 -1之后的数
boolean getsTheLock = ourIndex < maxLeases;
String pathToWatch = getsTheLock ? null : (String)children.get(ourIndex - maxLeases);
return new PredicateResults(pathToWatch, getsTheLock);
// 首先,通过children.indexOf(sequenceNodeName)方法获取当前客户端创建的节点在子节点列表中的索引位置,并验证其合法性。然后,判断当前节点是否是最小的(即序号最小)。如果是最小的,则直接获取锁;否则,通过计算得到当前节点前面的一个节点名称,并将其设置为需要监听的节点路径,等待该节点释放锁后再尝试获取锁。
}
-----------------------------------------------释放
// 当收到这个节点发生变化以后
private final Watcher watcher = new Watcher() {
public void process(WatchedEvent event) {
LockInternals.this.client.postSafeNotify(LockInternals.this);
}
};
// 去唤醒当前的进程下处于阻塞的线程
default CompletableFuture<Void> postSafeNotify(Object monitorHolder) {
return this.runSafe(() -> {
synchronized(monitorHolder) {
monitorHolder.notifyAll();
}
});
}
比如说用户服务有个线程去监控,不可能是不断的轮询,没什么意义,那么发现没办法抢占就先阻塞,也就是抢占失败,当前一个节点被删除了之后,会有一个watcher通知,那么就会去唤醒,那么会再次调用这个逻辑,判断是不是最小的,如果是就抢占到了。