Python之Appium 2自动化测试(Android篇)
一、环境搭建及准备工作
1、Appium 2 环境搭建
- 请参考另一篇文章: Windows系统搭建Appium 2 和 Appium Inspector 环境
2、安装 Appium-Python-Client,版本要求3.0及以上
pip install Appium-Python-Client
Version: 3.1.0
3、手机连接电脑,并在dos窗口启动 Appium Server

4、演示环境APP软件:ES文件浏览器
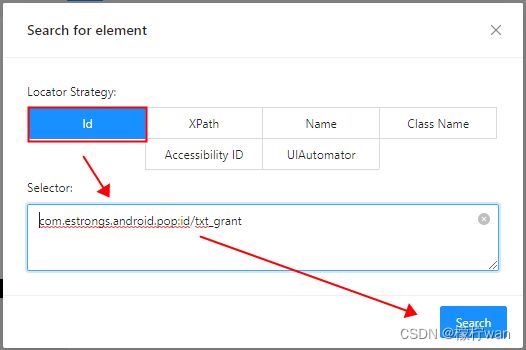
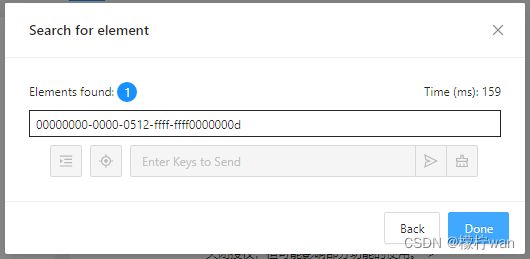
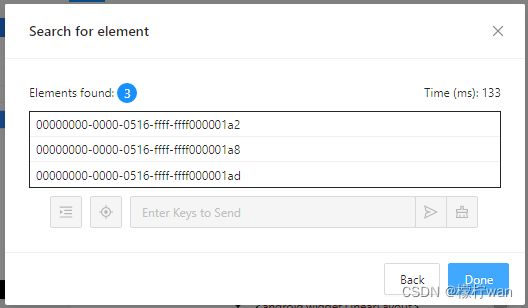
5、查看元素唯一方法
- 唯一
- 不唯一
二、编写自动化脚本
from appium import webdriver
from appium.options.common.base import AppiumOptions
from appium.webdriver.common.appiumby import AppiumBy
def create_driver():
"""
AppiumOptions():
用于配置 Appium 测试的通用选项,可用于 Android 和 iOS 平台
可以设置通用的测试选项,如平台名称、版本、自动化引擎等
"""
# 创建 AppiumOptions 对象
options = AppiumOptions()
# 加载测试的配置选项和参数(Capabilities配置)
options.load_capabilities({
# 自动化测试的引擎
"automationName": "uiautomator2",
# 平台名称
"platformName": "Android",
# 系统版本
"platformVersion": "11",
# 设备的名称
"deviceName": "RK3399",
# 待测试应用的包名
"appPackage": "com.estrongs.android.pop",
# 待测试应用的活动(Activity)名称
"appActivity": ".app.openscreenad.NewSplashActivity",
# 设置使用 Unicode 编码方式发送字符串到设备的键盘
"unicodeKeyboard": "true",
# 设置重置设备的软键盘状态并隐藏键盘
"restKeyboard": "true"
})
# Appium服务器地址端口,本地用http://127.0.0.1:4723
appium_host = 'http://192.168.100.15:4723'
return webdriver.Remote(appium_host, options=options)
def close_driver(driver):
"""关闭驱动"""
if driver:
driver.quit()
if __name__ == "__main__":
driver = create_driver()
# 设置隐式等待时间为10秒
driver.implicitly_wait(10)
# 元素定位代码...
# 关闭驱动
close_driver(driver)
三、元素定位方式
1、根据id定位
# ID 定位方法
el = driver.find_element(AppiumBy.ID, "com.estrongs.android.pop:id/txt_grant")
el.click()
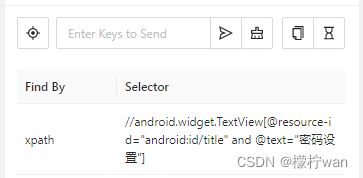
2、根据xpath定位
# xpath 方法
el1 = driver.find_element(AppiumBy.XPATH, '//android.widget.TextView[@resource-id="android:id/title" and @text="密码设置"]')
el1.click()
# xpath 简写方法
el2 = driver.find_element(AppiumBy.XPATH, '//*[@text="密码设置"]')
el2.click()
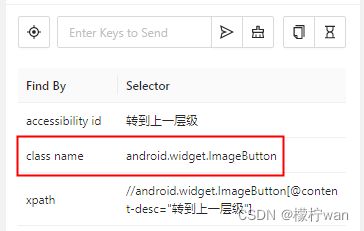
3、根据class定位 (建议少用,重复名称较多)
# 使用class name定位
el3 = driver.find_element(AppiumBy.CLASS_NAME, "android.widget.ImageButton")
el3.click()
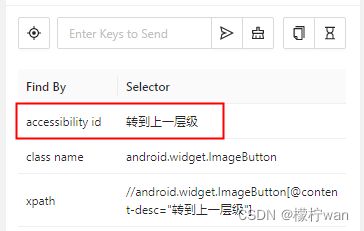
4、根据Accessibility ID定位
# 使用Accessibility ID定位
el4 = driver.find_element(AppiumBy.ACCESSIBILITY_ID, '转到上一层级')
el4.click()
5、根据UIAutomator定位
- UIAutomator元素定位是 Android 系统原生支持的定位方式,虽然与 xpath 类似,但比它更加好用,且支持元素全部属性定位.定位原理是通过android 自带的android uiautomator的类库去查找元素。 Appium元素定位方法其实也是基于Uiautomator来进行封装的。
# 使用UIAutomator定位元素 (id定位)
el5 = driver.find_element(AppiumBy.ANDROID_UIAUTOMATOR, 'new UiSelector().resourceId("com.estrongs.android.pop:id/txt_grant")')
el5.click()
# 使用UIAutomator定位元素 (test定位)
el6 = driver.find_element(AppiumBy.ANDROID_UIAUTOMATOR, 'new UiSelector().text("搜索")')
el6.click()
# 使用UIAutomator定位元素 (class name定位)
el7 = driver.find_element(AppiumBy.ANDROID_UIAUTOMATOR, 'new UiSelector().className("android.widget.ImageButton")')
el7.click()
6、相同元素定位

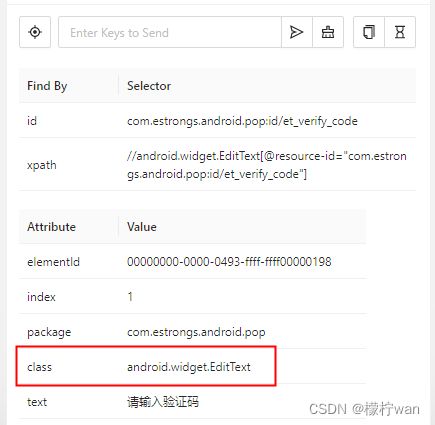
如上图,三个输入框的class属性都是一样的,如果要根据class属性分别来获取这三个值,就使用driver.find_elements方式。代码实现如下(注意 driver.find_elements 多个 s):
# 使用class name和索引定位,查找的元素列表中的特定元素
el8 = driver.find_elements(AppiumBy.CLASS_NAME, "android.widget.EditText")
# 输入邮箱
el8[0].send_keys("[email protected]")
# 输入验证码
el8[1].send_keys("654321")
# 输入密码
el8[2].send_keys("123456")
四、点击 - 输入 - 清空操作
# 运行ES文件浏览器软件,并点击同意
el = driver.find_element(AppiumBy.ID, "com.estrongs.android.pop:id/txt_grant")
el.click()
# 单机操作(相当于鼠标点击):click()
el1 = driver.find_element(AppiumBy.XPATH, '//*[@text="搜索"]')
el1.click()
# 输入:send_keys()
el2 = driver.find_element(AppiumBy.CLASS_NAME, "android.widget.EditText")
el2.send_keys("Android自动化")
# 清空: clear()
el3 = driver.find_element(AppiumBy.CLASS_NAME, "android.widget.EditText")
el3.clear()
五、swipe()方法模拟滑动操作
- 滑动操作是模拟用户在应用程序界面上进行手势滑动的操作。在Appium中,可以使用swipe()方法来执行滑动操作。它需要指定起始点和终止点的坐标,并且可以设置滑动的持续时间。滑动操作通常用于测试应用程序界面的可滚动性、页面切换和内容展示等功能。
# 获取屏幕尺寸
screen_size = driver.get_window_size()
# 从下向上滑动
def swipeUp():
# 定义起始点和终止点的坐标
start_x = screen_size['width'] * 0.5
start_y = screen_size['height'] * 0.9
end_x = screen_size['width'] * 0.5
end_y = screen_size['height'] * 0.1
# swipe()方法执行滑动操作,duration参数来指定滑动的持续时间,单位为毫秒(ms)
driver.swipe(start_x, start_y, end_x, end_y, duration=2000)
swipeUp()
# 从上向下滑动
def swipDown():
start_x = screen_size['width'] * 0.5
start_y = screen_size['height'] * 0.1
end_x = screen_size['width'] * 0.5
end_y = screen_size['height'] * 0.9
driver.swipe(start_x, start_y, end_x, end_y, duration=2000)
swipDown()
# 从右向左滑动
def swipe_left_to():
start_x = screen_size['width'] * 0.9
start_y = screen_size['height'] * 0.5
end_x = screen_size['width'] * 0.1
end_y = screen_size['height'] * 0.5
driver.swipe(start_x, start_y, end_x, end_y, duration=2000)
swipe_left_to()
# 从左向右滑动
def swipe_right_to():
start_x = screen_size['width'] * 0.1
start_y = screen_size['height'] * 0.5
end_x = screen_size['width'] * 0.9
end_y = screen_size['height'] * 0.5
driver.swipe(start_x, start_y, end_x, end_y, duration=2000)
swipe_right_to()
文章持续更新中…