基于 GPS 定位信息的 Pure-Pursuit 轨迹跟踪实车测试(1)
基于 GPS 定位信息的 Pure-Pursuit 轨迹跟踪实车测试(1)
进行了多组实验,包括顺逆时针转向,直线+圆弧轨迹行驶,以及Pure-Pursuit 轨迹跟踪测试
代码修改
需要修改的代码并不多,主要对 gps_sensor 功能包和 purepursuit 代码的修改
- gps_sensor 发布机器人实际运动轨迹,而不是在 purepursuit 中发布
- gps_sensor 同时实现 mrobot_states_update 功能包的功能,发布机器人状态信息
- purepursuit 将最终的控制指令发送给实际机器人,cmd_to_robot 代替 cmd_to_mrobot
#include #include 数据处理
原始的数据便于查阅,但不便于 MATLAB 进行读取分析,主要包括 ***_pub.txt 和 ***_path.txt 两种待处理数据,分别如下
$GPRMC,085750.20,A,3150.93719306,N,11717.59499143,E,0.071,252.6,161123,5.7,W,D*26
数据长度:83
latitude: 31.848953217667
longitude: 117.293249857167
heading_angle_deg: 252.600000000000
heading_angle_rad: 4.408701690538
heading_angle_rad: -1.874483616642
---------
$GPRMC,085750.30,A,3150.93719219,N,11717.59498178,E,0.297,264.0,161123,5.7,W,D*28
数据长度:83
latitude: 31.848953203167
longitude: 117.293249696333
heading_angle_deg: 264.000000000000
heading_angle_rad: 4.607669225265
heading_angle_rad: -1.675516081915
---------
位姿信息:
0.0169953,0.0210645,-2.24798
速度信息:
1.59198e-11
---------
位姿信息:
0.0183483,0.0200412,2.49058
速度信息:
0.0180464
---------
下面的命令首先使用**grep过滤包含"heading_angle_deg: "的行,然后使用awk**提取每行的第二个字段(即数字部分),最后将结果写入output.txt文件
grep "heading_angle_deg: " input.txt | awk '{print $2}' > output.txt
下面的命令使用**awk匹配包含"位姿信息:"的行,然后使用getline**读取下一行数据并打印出来,最后将结果写入output.txt文件
awk '/位姿信息:/ {getline; print}' input.txt > output.txt
处理前和处理后的文件目录如下
redwall@redwall-G3-3500:~/log/2023--11-16/raw$ tree
.
├── actual_path.txt
├── anticlock_path.txt
├── anticlock_pub.txt
├── clock_path.txt
├── clock_pub.txt
├── gps_path.txt
├── gps_pub.txt
├── lane_path.txt
└── lane_pub.txt
redwall@redwall-G3-3500:~/log/2023--11-16/processed$ tree
.
├── anticlock_path_pose.txt
├── anticlock_path_vel.txt
├── anticlock_pub_sift.txt
├── clock_path_pose.txt
├── clock_path_vel.txt
├── clock_pub_sift.txt
├── gps_path_pose.txt
├── gps_path_vel.txt
├── gps_pub_sift.txt
├── lane_path_pose.txt
├── lane_path_vel.txt
└── lane_pub_sift.txt
数据分析
本次有“卫星”标签的连接车后的蘑菇头,以 10 Hz 的频率获取定位数据
- 分析 lane_pub 和 lane_path(直线+圆弧轨迹运动)
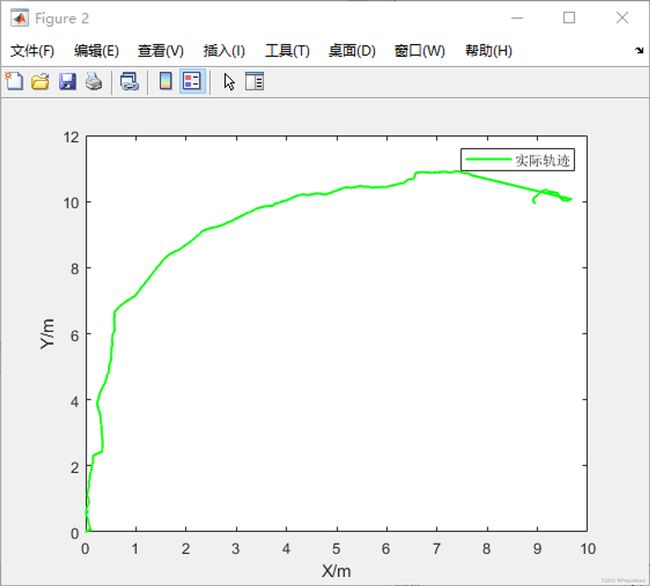
由实际轨迹可知,纬度差应对应 X,经度差应对应 Y,应该修改代码
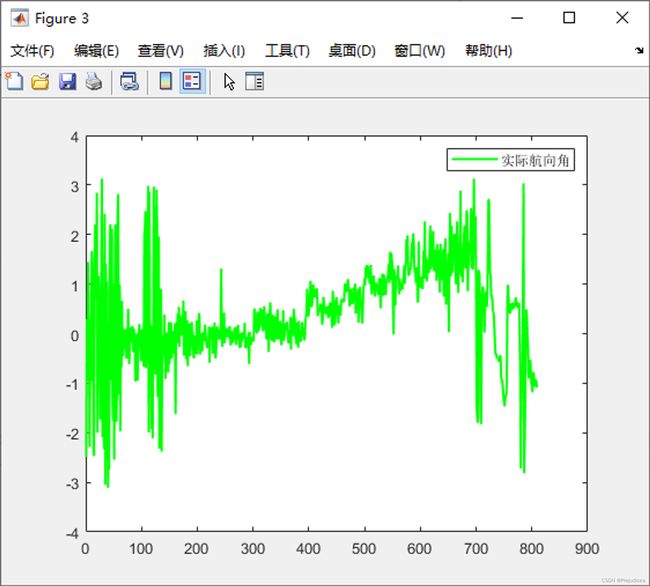
由实际航向角信息,结合实际轨迹,本次天线的基线向量应该是与正北方向重合,顺时针转向时航向角增大,说明天线安装的方式应该是正确的
- 分析 clock_pub 和 clock_path (顺时针原地转向)
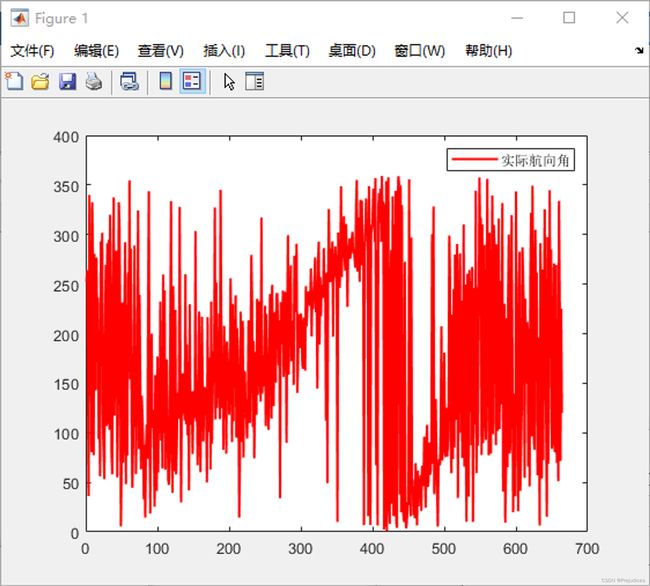
主要是分析航向角信息,由于提高采样频率,因此存在很大的噪声,可以对信号进行去噪处理
本次已经尽量控制两个蘑菇头的安装,安装前用卷尺进行了安装测量,但仍存在误差
结合之前的分析记录,顺时针转向时先增大至 360,再从 0 开始继续增大,下面符合该规律
人为判断的正北朝向并不和实际正北朝向重合,因此起始和终止位置并不为 0 度
- 分析 gps_pub、gps_path 和 actual_path
首先机器人是由北向南开,即初始朝向是向南,由 lane 数据可知,初始朝向是有问题的
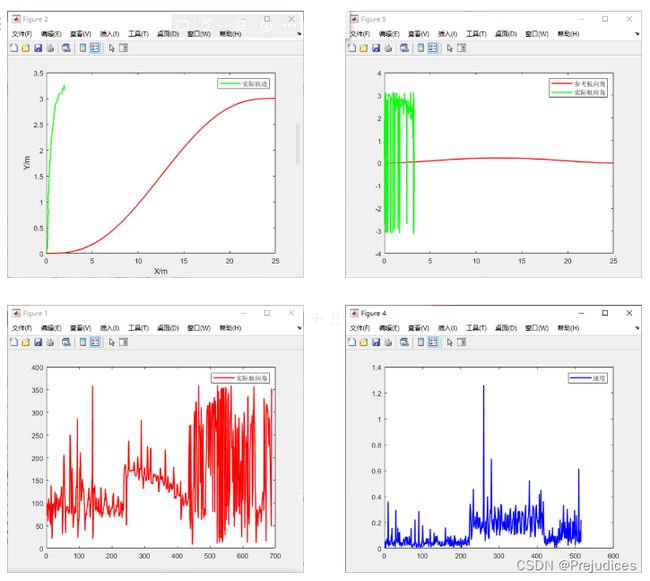
其实 Pure-Pursuit 算法并不需要航向角信息,初始位姿是一个比较大的影响
实际速度会影响预瞄距离,实际速度较小会导致预瞄距离较小,导致控制的不稳定
存在问题
1、和 GPS 串口通信存在问题,读取配置以及信息长度方面存在问题,需要修改
2、GPS 航向角信息的获取仍存在较大问题,准确性比较低
3、GPS 对于高速移动的车辆,厘米级别的定位精度还可以,目前对于低速机器人可能不太适用