Java基础(5)——IO流+输入和输出 & Java中的IO流 & 项目应用初步
目录
- 引出
- IO的应用和输入输出定义
-
- 1. IO在项目中应用
- 2. 输入输出的定义
- JAVA中的IO流
-
- 1.文件路径
- 2.主要API
- 3.图形界面JFileChooser
- 4.字节流(byte)In/OutputStream—图片等二进制
-
- 视频文件拷贝解决方案
- 5.字符流Reader/Writer—字符文本数据
- 6.递归在IO中的应用
- IO流在项目中的应用
-
- 1.Properties类-配置文件降低耦合
- 2.对象流-把对象存储为dat文件
- 3.获取配置文件路径方法
- 总结
引出
1.JAVA的IO流用于文件的交互,输入输出的概念;
2.绝对路径,相对路径,主要API;
3.如何找一个文件夹下的所有文件,递归的思想;
4.IO流在项目中的应用
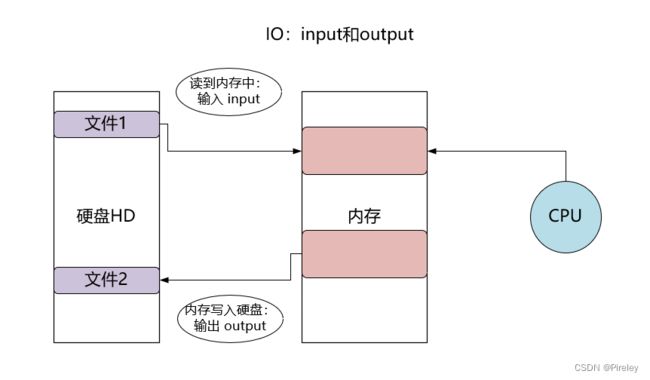
IO的应用和输入输出定义
1. IO在项目中应用
2. 输入输出的定义
JAVA中的IO流
1.文件路径
| 路径 | 定义 | 应用 |
|---|---|---|
| 相对路径 | 以某个位置为基础 | 前端较多 |
| 绝对路径 | 从根目录开始,在Linux中为/ ,在windows中为盘符C: \ |
JAVA中表示方式
"D:\\Myprogram\\idea-workspace\\IOStrem\\IOStrem\\src\\com\\tianju\\resources\\login.Properties"
"D:/Myprogram/idea-workspace/IOStrem/IOStrem/src/com/tianju/resources/login.Properties"
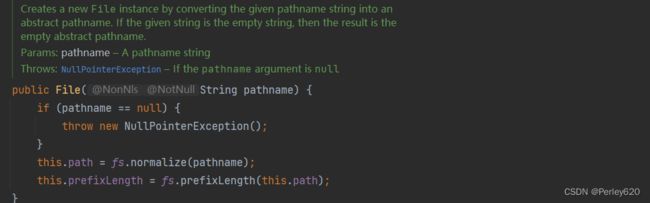
2.主要API
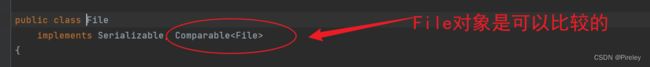
File对象是可比较的
File f = new File("D:\\abc.txt"); //D盘路径
f.createNewFile();
f.mkdir();//文件夹
System.out.println("文件创建成功");
File f = new File("D:\\myfile\\abc.txt"); //D盘路径
f.createNewFile(); //创建
System.out.println("文件创建成功...");
System.out.println("绝对路径:" + f.getAbsolutePath()); //windows加盘符路径
System.out.println("上一级文件夹对象:" + f.getParentFile());
System.out.println("是否可读:" + f.canRead());
System.out.println("是否隐藏:" + f.isHidden());
System.out.println("当前盘可用空间:" + (f.getFreeSpace()/1024/1024/1024)+"G");
System.out.println("是否是文件夹: " + f.isDirectory());
System.out.println("是否是文件: " + f.isFile());
System.out.println(new Date(f.lastModified()));
创建文件,创建文件夹,列出所有文件;
判断文件对象为文件,还是文件夹;
File file = new File("D:\\Program Files (x86)\\FileRecv");
System.out.println(file.isFile()); // 文件对象为文件
System.out.println(file.isDirectory()); // 文件对象为文件夹
File[] files = file.listFiles(); // 列出所有文件
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(files));
// 创建文件,用createNewFile()方法,文件加后缀
File newfile = new File("D:\\Program Files (x86)\\newFile.txt");
try {
newfile.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
// 创建文件夹 mkdir:创建单级目录;mkdirs: 创建多级目录
File fileDir = new File("D:\\Program Files (x86)\\FileRecv");
fileDir.mkdir();
3.图形界面JFileChooser
JFileChooser chooser = new JFileChooser();
// 过滤特定的格式,图片格式
FileNameExtensionFilter filter = new FileNameExtensionFilter(
"JPG & GIF Images", "jpg", "gif");
chooser.setFileFilter(filter);
// parent为null表示出现屏幕中间
int returnVal = chooser.showOpenDialog(null);
if(returnVal == JFileChooser.APPROVE_OPTION) {
// 获取文件名
System.out.println("You chose to open this file: " +
chooser.getSelectedFile().getName());
// 获取绝对路径
System.out.println("路径为"+chooser.getSelectedFile().getAbsolutePath());
4.字节流(byte)In/OutputStream—图片等二进制
字节流以字节为单位进行读写,适用于处理二进制数据,如图片、音频、视频等文件。Java中的字节流主要有InputStream和OutputStream两个抽象类,它们的子类可以实现对文件、网络、内存等不同数据源的读写操作。
输出字节(byte)流
用OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(“D:\IOTest\ioTest1.txt”);
package com.tianju.test;
import java.io.*;
public class OutputStreamDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 输出流,从内存写入文件,用out
// 文件不存在会被创建出来
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("D:\\IOTest\\ioTest1.txt");
out.write(98); // 为小写b
out.write(90); // 为小写z
out.flush();
out.close(); // 记得关闭
// 输入字节流,写入内存,用in
InputStream in = new FileInputStream("D:\\IOTest\\ioTest1.txt");
int n1 = in.read();
int n2 = in.read();
System.out.println("n1为"+n1+",n2为"+n2);
// 转换成char
System.out.println("n1为"+(char)n1+",n2为"+(char)n2);
in.close();
}
}
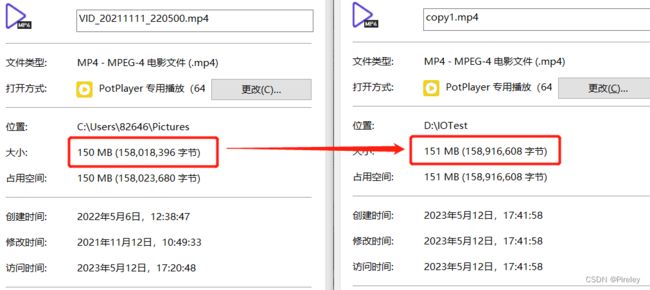
视频文件拷贝解决方案
采用缓存(块)提高效率
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024*1024]; // 1M大小的缓存块
package com.tianju.test;
import java.io.*;
public class CopyVideoDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStream in = new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\82646\\Pictures\\VID_20211111_220500.mp4");
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("D:\\IOTest\\copy1.mp4");
int n = 0;
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024*1024]; // 1M大小的缓存块
double beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
while (true){
n = in.read(buffer);
if (n==-1){
break;
}
out.write(buffer);
}
out.close();
in.close();
double endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("拷贝耗时"+(endTime-beginTime)+"毫秒");
}
}
问题:文件大小变大,原因是最后一次存了缓存块大小的空数据
解决方法:
out.write(buffer,0,n); //从数组中读取0,到长度(实际存入的长度值n)
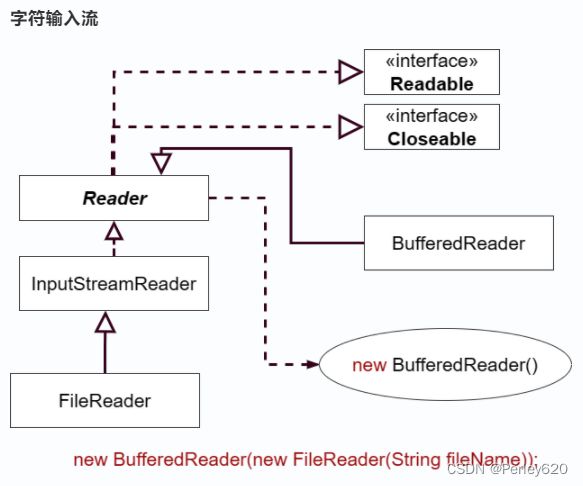
5.字符流Reader/Writer—字符文本数据
字符流= 字节流包装 + 编码 内置缓存—文字
字符流以字符为单位进行读写,适用于处理文本数据,如文本文件、配置文件等。Java中的字符流主要有Reader和Writer两个抽象类,它们的子类可以实现对文本文件、网络、内存等不同数据源的读写操作。
字符流和字节流之间可以通过Java中的InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter类进行转换,例如将字节流转换为字符流可以使用InputStreamReader类,将字符流转换为字节流可以使用OutputStreamWriter类。
BufferedReader的使用;
readLine() 方法
public class BUfferReaderDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String filePath = "D:\\Myprogram\\idea-workspace\\IOStrem\\IOStrem\\src\\com\\tianju\\resources\\login.Properties";
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(
new FileReader(filePath));
String line = null;
while (true){
line = in.readLine();
if (line==null){
break;
}
System.out.println(line);
}
in.close();
}
}
上面简介:
public class BUfferReaderDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String filePath = "D:\\Myprogram\\idea-workspace\\IOStrem\\IOStrem\\src\\com\\tianju\\resources\\login.Properties";
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(
new FileReader(filePath));
String line = null;
while ((line=in.readLine())!=null){
System.out.println(line);
}
in.close();
}
}
6.递归在IO中的应用
递归实压栈和出栈的过程,Stack
写递归的关键是通式和终止条件:
以阶乘为例:
通式:f(n) = n * f(n-1)
终止条件:n=1;f(1) = 1
业务:列举出某个文件夹下所有的文件、文件夹
问题:循环无法解决,难以确定循环次数,文件嵌套文件
解决方案:采用递归的方法
-
临界点:找到文件终止,File f ——> f.isFile()
-
一般规律:File f
如果f为文件夹,File[] fs = f.listFile() ——> 找出所有的文件对象
如果f不为空,则继续对内部每个进行上述过程;
for(File fi : fs){ }
如果是隐藏文件,会出现NullPointerException异常,需要判断
/**
* 递归找到所有的java文件
* @param filePath 文件夹路径
*/
public static void findJavaFile(String filePath) throws IOException {
File file = new File(filePath);
// 判断文件,且后缀为java
if(file.isFile() && file.getName().toLowerCase().endsWith("java")){
System.out.println(file.getAbsoluteFile());
// 统计代码行数
int codeLines = CountCodeLines(file.getAbsoluteFile().toString());
}
File[] files = file.listFiles();
if (files !=null){
for (File f:files){
findJavaFile(f.getAbsolutePath());
}
}
}
需求:统计某个路径下的java代码行数
package com.tianju.test;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class CountCodeLines {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String filePath = "D:\\Myprogram\\idea-workspace";
countJavaCodeLines(filePath);
System.out.println("代码的总行数"+num);
}
/**
* 定义静态的全局变量,用于统计代码总行数
*/
public static int num = 0;
/**
* 计算代码行数的入口程序
* @param filePath 文件夹路径
* @throws IOException 抛出异常
*/
public static void countJavaCodeLines(String filePath) throws IOException{
File file = new File(filePath);
if(file.isFile() && file.getName().toLowerCase().endsWith("java")){
// 统计代码行数
int codeLines = CountCodeLines(file.getAbsoluteFile().toString());
num+=codeLines;
}
File[] files = file.listFiles();
if (files !=null){
for (File f:files){
countJavaCodeLines(f.getAbsolutePath());
}
}
}
/**
* 统计java代码行数
* @param filePath 文件夹的路径
* @throws IOException 抛出异常
* @return 代码行数int
*/
public static int CountCodeLines(String filePath) throws IOException {
File file = new File(filePath);
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
int count = 0;
while (true){
String line = in.readLine(); // 读取行
if (line==null){
break;
}
count++;
}
in.close();
System.out.println(file.getName()+"的行数"+count);
System.out.println("当前总计代码行数"+num);
return count;
}
}
IO流在项目中的应用
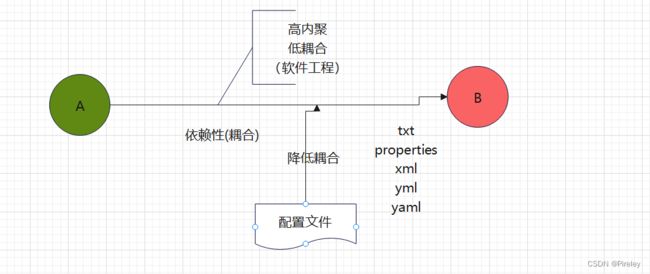
1.Properties类-配置文件降低耦合
使用配置文件降低耦合
将文件和对象关联,key(String) - value(String),常用来解决配置问题,
如果key值不存在,返回为null
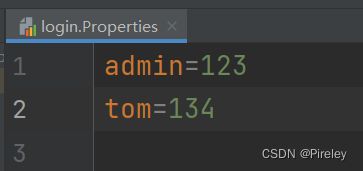
例子:登陆的用户名和密码配置
1.创建文件,后缀需要是.Properties,例如:login.Properties
2.进行配置设置,键值对,用=隔开
3.编写主要逻辑代码
public class LoginServiceImpl implements ILoginService {
private Properties pros; // 在构造器内初始化
public LoginServiceImpl() {
pros = new Properties();
try {
Reader in = new FileReader("D:\\Myprogram\\idea-workspace\\IOStrem\\IOStrem\\src\\com\\woniuxy\\resources\\login.Properties");
pros.load(in);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@Override
public boolean login(String username, String password) {
// 获取用户名对应的密码
if (pros.get(username)==null){ // 用户名不存在,返回null
System.out.println("用户名不存在");
return false;
}
if (pros.get(username).equals(password)){
System.out.println("登陆成功");
return true;
}else {
System.out.println("用户名|密码错误");
return false;
}
}
}
2.对象流-把对象存储为dat文件
要点:
(1)实体类需要实现序列化接口 public class Car implements Serializable;【标记接口】
(2)序列化的版本号最好不要写,交给JVM实现,要保证版本号一致;
功能:
ObjectOutputStream—->对象写入文件
![]()
![]()
![]()
serialVersionUID :在序列化的时候指定的编号, 在反序列化时应该保证版本号一致。
![]()
案例:把car类存储到dat文件中
1)类需要实现序列化的接口
public class Car implements Serializable { // 需要实现序列化的接口
// 序列化的版本号,不要写,交给jvm实现;保证读的和写的对象实体类要一样
// private static final long serialVersionUID = 2L;
private Integer id;
private String name;
public Car() {
}
}
2)从内存写入硬盘文件,为out,用write
ObjectOutputStream out =
new ObjectOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream("D:\\Myprogram\\idea-workspace\\IOStrem\\IOStrem\\src\\com\\woniuxy\\resources\\car.dat")
);
// 存多个的解决方法,存到List中
List<Car> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new Car(1, "BMW"));
list.add(new Car(2, "BYD"));
list.add(new Car(3, "BMW"));
out.writeObject(list); // list也实现了Serializable
out.flush();
out.close();
3)从硬盘读入内存,为in,用read
ObjectInputStream in =
new ObjectInputStream(
new FileInputStream("D:\\Myprogram\\idea-workspace\\IOStrem\\IOStrem\\src\\com\\woniuxy\\resources\\car.dat")
);
// Car car = (Car) in.readObject(); // 读对象,向下转型
// System.out.println(car);
List<Car> list = (List<Car>) in.readObject();
System.out.println(list);
list.forEach(car -> System.out.println(car)); // list的lamda表达式
list.forEach(System.out::println); // 上面的简化写法
in.close(); // 记得关闭
3.获取配置文件路径方法
Thread.currentThread()
.getContextClassLoader()
.getResource(“”)
.getPath()
/**
* 获取配置文件的路径
*/
public class Config {
// 获取当前的路径,拼出dat的路径
private static String path = Thread.currentThread()
.getContextClassLoader()
.getResource("")
.getPath() + "com/tianju/older/resources/";
/**
* 获得dat的路径
* @return 返回dat的路径
*/
public static String getDatPath(){
return path + "older.dat";
}
/**
* 获取login用户名密码文件路径
* @return login的路径
*/
public static String getLoginPath(){return path + "login.properties";}
}
总结
1.JAVA的IO的定义,输入输出相对内存;
2.字节流,字符流,JFileChooser图形界面;
3.递归思想在IO中的应用,找文件夹中文件;
4.对象流的实现,序列化接口,序列号;
5.获取文件路径的解决方法Thread;