【python基础】可变不可变数据类型
Python 可变数据类型和不可变类型总结
可变数据类型
可变数据类型 :当该数据类型的对应变量的值发生了改变,那么它对应的内存地址不发生改变,对于这种数据类型,就称可变数据类型
不可变数据类型
不可变数据类型: 当该数据类型的对应变量的值发生了改变,那么它对应的内存地址也会发生改变,对于这种数据类型,就称不可变数据类型
不可变类型的方法及原理实现:
使用索引访问:通过索引获取不可变对象的特定元素。不可变对象通常使用数组或指针实现,通过索引直接访问内存中的特定位置。
使用切片操作:对不可变对象进行切片操作时,会创建一个新的对象,包含切片范围内的元素。
使用内置函数:例如 len()、str()、int() 等函数,这些函数返回的是一个新的对象,不会对原对象进行修改。
可变类型的方法及原理实现:
添加元素:可变对象提供了 append()、insert()、extend() 等方法来向对象中添加新元素。这些方法会直接在原对象的内存地址上进行修改,而不是创建新的对象。
删除元素:可变对象提供了 remove()、pop()、del 等方法来删除元素。这些方法会直接在原对象的内存地址上进行修改,而不是创建新的对象。
修改元素:可以通过索引或切片操作来修改可变对象中的元素。这种修改是直接在原对象的内存地址上进行的,而不是创建新的对象。
需要注意的是,对可变类型进行操作时,多个变量可能会共享同一个对象,因此需要谨慎处理,以避免意外的结果
python中可变数据类型有:字典dict, 列表list, 集合set;不可变数据类型有:整型int,浮点型float,字符串string和元组tuple。
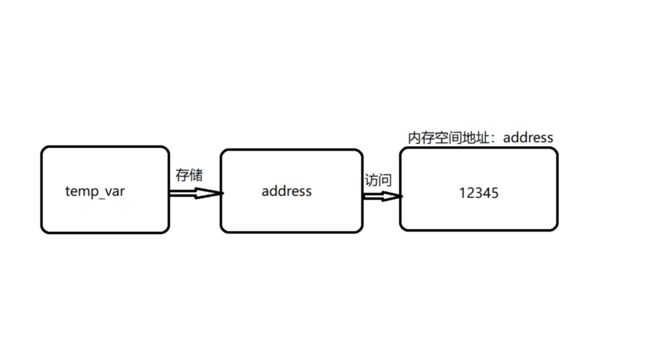
在python当中,一切皆对象。所以python变量也是对象。变量:对象的引用。变量存储的是对象的地址,变量的变指的是对象地址的变化,而不是地址指向内存空间的值。举例:如上图,定义变量temp_var = 12345,程序会在内存当中开辟一块空间存储整型数据12345,然后把该空间的地址存储到temp_var中,所以实际上temp_var是12345的引用。
可变与不可变最本质的区别在于内存中存储的地址所指向的值是否可以被修改。可变数据类型:变量存储的内存地址所指向的值发生了改变,内存地址不发生变化;不可变数据类型:变量存储的内存地址所指向的值发生了改变,内存地址发生变化。
字典,列表和集合数据类型验证,定义并初始化temp_var_one变量,并利用temp_var_one定义和初始化temp_var_two,两者引用相同,指向的是同一个内存空间。内存空间存储的是字典/列表/集合,字典/列表/集合值的变化不会引起变量存储的内存空间地址变化。所以字典/列表/集合就是可变数据类型。
# 字典数据类型验证
temp_var_one = {"a": 1, "b": 2, "c": 3}
temp_var_two = temp_var_one
print(id(temp_var_one)) # id为1202100539648
print(id(temp_var_two)) # id为1202100539648
temp_var_two.update({"d": 4})
print(id(temp_var_one)) # id为1202100539648
print(id(temp_var_two)) # id为1202100539648# 集合数据类型验证
temp_var_one = {1, 2, 3}
temp_var_two = temp_var_one
print(id(temp_var_one)) # id为1724139533248
print(id(temp_var_two)) # id为1724139533248
temp_var_two.add(4)
print(id(temp_var_one)) # id为1724139533248
print(id(temp_var_two)) # id为1724139533248# 列表数据类型验证
temp_var_one = [1, 2, 3]
temp_var_two = temp_var_one
print(id(temp_var_one)) # id为2323147827968
print(id(temp_var_two)) # id为2323147827968
temp_var_two.append(4)
print(id(temp_var_one)) # id为2323147827968
print(id(temp_var_two)) # id为2323147827968整型,浮点型,字符串,元组数据类型验证,定义并初始化temp_var_one变量,并利用temp_var_one定义和初始化temp_var_two,两者引用相同,指向的是同一个内存空间。内存空间存储的是整型/浮点型/字符串/元组,整型/浮点型/字符串/元组的变化会引起变量存储的内存空间地址变化。所以整型/浮点型/字符串/元组就是可变数据类型。
# 整型数据类型验证
temp_var_one = 3
temp_var_two = temp_var_one
print(id(temp_var_one)) # id为2623080130928
print(id(temp_var_two)) # id为2623080130928
temp_var_two = 2
print(id(temp_var_one)) # id为2623080130928
print(id(temp_var_two)) # id为2623080130896# 浮点型数据类型验证
temp_var_one = 3.14
temp_var_two = temp_var_one
print(id(temp_var_one)) # id为2016210395920
print(id(temp_var_two)) # id为2016210395920
temp_var_two = 3.14159
print(id(temp_var_one)) # id为2016210395920
print(id(temp_var_two)) # id为2016209169264# 浮点型数据类型验证
temp_var_one = "olivier"
temp_var_two = temp_var_one
print(id(temp_var_one)) # id为1912564360624
print(id(temp_var_two)) # id为1912564360624
temp_var_two = "olivier_"
print(id(temp_var_one)) # id为1912564360624
print(id(temp_var_two)) # id为1912564662128# 元组数据类型验证
temp_var_one = (1, 2, 3)
temp_var_two = temp_var_one
print(id(temp_var_one)) # id为2376541232448
print(id(temp_var_two)) # id为2376541232448
temp_var_two += (4,)
print(id(temp_var_one)) # id为2376541232448
print(id(temp_var_two)) # id为2376541265808