Mybatis中的设计模式
Mybatis中的设计模式
Mybatis中使用了大量的设计模式。
以下列举一些看源码时,觉得还不错的用法:
创建型模式
工厂方法模式
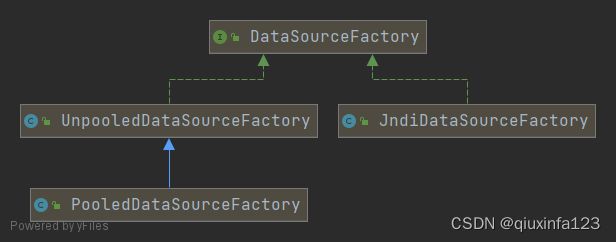
DataSourceFactory
通过不同的子类工厂,实例化不同的DataSource
TransactionFactory
通过不同的工厂,生产不同的Transaction
单例模式
ErrorContext是单例模式,但只是线程级别的:
private static final ThreadLocal<ErrorContext> LOCAL = new ThreadLocal<>();
private ErrorContext() {
}
public static ErrorContext instance() {
ErrorContext context = LOCAL.get();
if (context == null) {
context = new ErrorContext();
LOCAL.set(context);
}
return context;
}
Configuration 类虽然正常情况下只有一个实例,但是它的设计并不符合单例模式
public Configuration(Environment environment) {
this();
this.environment = environment;
}
可以看到,它的构造器并没有私有化,我们可以new多个实例
LogFactory也不是单例模式,每次都会通过构造器实例化对象
private LogFactory() {
// disable construction
}
public static Log getLog(Class<?> aClass) {
return getLog(aClass.getName());
}
public static Log getLog(String logger) {
try {
return logConstructor.newInstance(logger);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new LogException("Error creating logger for logger " + logger + ". Cause: " + t, t);
}
}
结构型模式
代理模式
在初始化配置时,会调用MapperRegistry的addMapper方法将Mapper接口存储在knownMappers中,key为Mapper接口,value为MapperProxyFactory实例
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
if (type.isInterface()) {
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<>(type));
// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run
// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the
// mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try.
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
当我们通过UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);获取Mapper接口时,则会调用MapperRegistry#getMapper,返回Mapper接口的代理类
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
代理类的生成
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
可以看到,使用的是JDK动态代理,MapperProxy实现了InvocationHandler接口,我们关注MapperProxy#invoke即可:
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else if (method.isDefault()) {
return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
调用mapper接口,最终执行的就是我们编写的SQL
行为型模式
模板方法模式
BaseExecutor
BaseExecutor实现了Executor接口,定义了模板方法,并将钩子方法留给子类实现:
| 模板方法 | 钩子方法 |
|---|---|
| query | doQuery |
| update | doUpdate |
| flushStatements | doFlushStatements |
| queryCursor | doQueryCursor |
BaseTypeHandler
BaseTypeHandler实现了TypeHandler接口,定义模板方法,将钩子方法留给子类实现:
-
setNonNullParameter
-
getNullableResult
| 模板方法 | 钩子方法 |
|---|---|
| setParameter | setNonNullParameter |
| getResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName) | getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName) |
| getResult(ResultSet rs, int columnIndex) | getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, int columnIndex) |
| getResult(CallableStatement cs, int columnIndex) | getNullableResult(CallableStatement cs, int columnIndex) |
策略模式
在DefaultParameterHandler#setParameters中,
@Override
public void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("setting parameters").object(mappedStatement.getParameterMap().getId());
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if (parameterMappings != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < parameterMappings.size(); i++) {
ParameterMapping parameterMapping = parameterMappings.get(i);
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) {
Object value;
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) { // issue #448 ask first for additional params
value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
} else if (parameterObject == null) {
value = null;
} else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {
value = parameterObject;
} else {
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
}
TypeHandler typeHandler = parameterMapping.getTypeHandler();
JdbcType jdbcType = parameterMapping.getJdbcType();
if (value == null && jdbcType == null) {
jdbcType = configuration.getJdbcTypeForNull();
}
try {
typeHandler.setParameter(ps, i + 1, value, jdbcType);
} catch (TypeException | SQLException e) {
throw new TypeException("Could not set parameters for mapping: " + parameterMapping + ". Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
}
}
重点关注:
TypeHandler typeHandler = parameterMapping.getTypeHandler();
JdbcType jdbcType = parameterMapping.getJdbcType();
if (value == null && jdbcType == null) {
jdbcType = configuration.getJdbcTypeForNull();
}
try {
typeHandler.setParameter(ps, i + 1, value, jdbcType);
} catch (TypeException | SQLException e) {
throw new TypeException("Could not set parameters for mapping: " + parameterMapping + ". Cause: " + e, e);
}
根据参数映射,拿到类型处理器,就是策略模式的应用,不同的类型处理器setParameter方法实现并不一样,这就是不同的参数类型,使用不同的类型处理器处理。
在解析结果集时,也是一样的,不同的类型需要使用不同的类型处理器获取结果:
DefaultResultSetHandler#getPropertyMappingValue通过ResultMap的属性映射:
private Object getPropertyMappingValue(ResultSet rs, MetaObject metaResultObject, ResultMapping propertyMapping, ResultLoaderMap lazyLoader, String columnPrefix)
throws SQLException {
if (propertyMapping.getNestedQueryId() != null) {
return getNestedQueryMappingValue(rs, metaResultObject, propertyMapping, lazyLoader, columnPrefix);
} else if (propertyMapping.getResultSet() != null) {
addPendingChildRelation(rs, metaResultObject, propertyMapping); // TODO is that OK?
return DEFERRED;
} else {
final TypeHandler<?> typeHandler = propertyMapping.getTypeHandler();
final String column = prependPrefix(propertyMapping.getColumn(), columnPrefix);
return typeHandler.getResult(rs, column);
}
}
DefaultResultSetHandler#applyAutomaticMappings自动映射也是一样的:
private boolean applyAutomaticMappings(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, MetaObject metaObject, String columnPrefix) throws SQLException {
List<UnMappedColumnAutoMapping> autoMapping = createAutomaticMappings(rsw, resultMap, metaObject, columnPrefix);
boolean foundValues = false;
if (!autoMapping.isEmpty()) {
for (UnMappedColumnAutoMapping mapping : autoMapping) {
final Object value = mapping.typeHandler.getResult(rsw.getResultSet(), mapping.column);
if (value != null) {
foundValues = true;
}
if (value != null || (configuration.isCallSettersOnNulls() && !mapping.primitive)) {
// gcode issue #377, call setter on nulls (value is not 'found')
metaObject.setValue(mapping.property, value);
}
}
}
return foundValues;
}