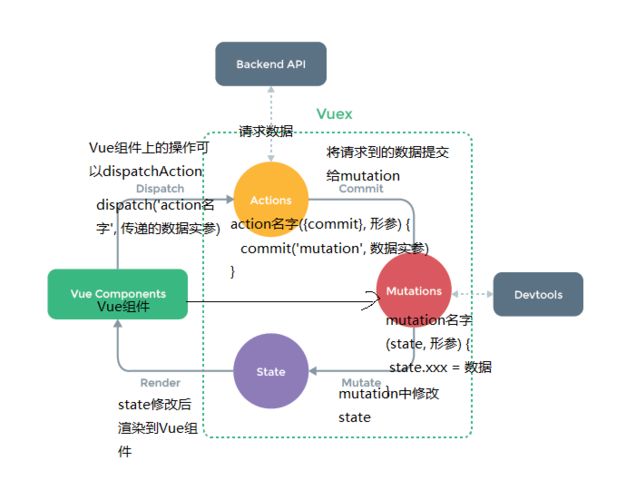
详细说说vuex
- Vuex 是什么
- Vuex有几个属性及作用
- 注意事项
- vuex 使用举例
- Vuex3和Vuex4有哪些区别
- 创建 Store 的方式
- 在组件中使用 Store
- 辅助函数的用法
- 响应式的改进
- Vuex4 支持多例模式
Vuex 是什么
Vuex是一个专门为Vue.js应用设计的状态管理构架,它统一管理和维护各个Vue组件的可变化状态。
Vuex采用 集中式存储管理应用 的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化。
Vuex也集成到Vue的官方调试工具devtools extension,提供了诸如零配置的time-travel调试、状态快照导入导出等高级调试功能。
Vuex可以管理复杂应用的数据状态,比如兄弟组件的通信、多层嵌套的组件的传值等。
当多个组件依赖于同一个状态时,由于多层嵌套使得传参的方法变得复杂,另外如果使用父子组件直接引用或者通过事件来变更和同步状态的多份拷贝,会使得该模式变得脆弱,从而无法维护代码。
这时就需要使用Vuex来解决这个问题。
更多详细内容,请微信搜索“前端爱好者“, 戳我 查看 。
Vuex有几个属性及作用
Vuex有五个主要属性,包括:
- state、
- getters、
- mutations、
- actions、
- modules**
下面分别阐述它们的作用:
- state:vuex的基本数据,用来存储变量。
- getters:从基本数据(state)派生的数据,相当于state的计算属性。
- mutations:提交更新数据的方法,必须是同步的(如果需要异步使用action)。每个 mutation 都有一个字符串的 事件类型 (type) 和一个回调函数 (handler)。回调函数是进行实际状态更改的地方,并且它会接受 state 作为第一个参数,提交载荷作为第二个参数。
- actions:和mutation的功能大致相同,不同之处在于actions提交的是 mutation,而不是直接变更状态。并且,action可以包含任意异步操作。简单的说就是异步操作数据,view 层通过 store.dispath 来分发action。
- modules:模块化vuex,可以让每一个模块拥有自己的state、mutation、action、getters,使得结构非常清晰,方便管理。
注意事项
- 只用来读取的状态集中放在 store 中; 改变状态的⽅式是提交 mutations , 这是个同步的事物; 异步逻辑应该封装在 action 中。
- 在 main.js 引⼊ store , 注⼊ 。新建了⼀个目录 store , … export
- 场景有:单页应用中, 组件之间的状态 、音乐播放 、登录状态 、加⼊购物车
vuex 使用举例
Vuex 是一个用于 Vue.js 的状态管理工具,它使得我们可以将应用中多个组件共享的状态抽取出来,统一管理。
下面是一个简单的 Vuex 使用示例:
- 安装 Vuex:
npm install vuex --save
- 在项目中引入 Vuex 并创建一个 Vuex Store:
import Vue from 'vue';
import Vuex from 'vuex';
Vue.use(Vuex);
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0,
},
mutations: {
increment(state) {
state.count++;
},
decrement(state) {
state.count--;
},
},
});
在上面的代码中,我们创建了一个 Vuex Store,定义了一个 count 状态,以及两个修改该状态的 mutation 方法 increment 和 decrement。
- 在 Vue 组件中使用 Vuex Store:
import Vue from 'vue';
import store from './store';
new Vue({
el: '#app',
store,
computed: {
count() {
return this.$store.state.count;
},
},
methods: {
increment() {
this.$store.commit('increment');
},
decrement() {
this.$store.commit('decrement');
},
},
});
在上面的代码中,我们在 Vue 组件中通过 this.$store 访问 Vuex Store,通过 this.$store.state.count 访问 count 状态,通过 this.$store.commit('increment') 和 this.$store.commit('decrement') 调用 mutation 方法修改状态。
以上就是一个简单的 Vuex 使用示例,通过 Vuex 我们可以方便地管理应用中多个组件共享的状态。
Vuex3和Vuex4有哪些区别
Vuex 3 是用于 Vue 2 的版本,而 Vuex 4 是用于 Vue 3 的版本。
下面是 Vuex 3 和 Vuex 4 在一些重要方面的异同点:
创建 Store 的方式
Vuex 3:使用 new Vuex.Store() 创建 store 实例
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const store = new Vuex.Store({
// 配置项
})
export default store
Vuex 4:使用 createStore 函数创建 store 实例
import { createStore } from 'vuex'
const store = createStore({
// 配置项
})
export default store
Vuex 4 中使用 createStore 函数来创建 store 实例,而不是直接在 Vue 实例上挂载。
在组件中使用 Store
Vuex 3:
- 使用 this.$store 访问 store 实例,
- 通过 this.$store.state 访问状态,
- 通过 this.$store.commit() 进行提交 mutation,
- 通过 this.$store.dispatch() 进行分发 action。
export default {
computed: {
count() {
return this.$store.state.count
}
},
methods: {
increment() {
this.$store.commit('increment')
},
incrementAsync() {
this.$store.dispatch('incrementAsync')
}
}
}
Vuex 4:
- 使用 useStore 函数来获取 store 实例,
- 通过 store.state 访问状态,
- 通过 store.commit() 进行提交 mutation,
- 通过 store.dispatch() 进行分发 action。
import { useStore } from 'vuex'
export default {
setup() {
const store = useStore()
const count = computed(() => store.state.count)
const increment = () => {
store.commit('increment')
}
const incrementAsync = () => {
store.dispatch('incrementAsync')
}
return {
count,
increment,
incrementAsync
}
}
}
虽然 Vuex4 推荐使用更符合 Composition API 风格的 useStore() 来获取 store 实例。
但是并没有移除 this.$store,但是在 和 Vue2 选项式写法中还是支持使用 $store 的。
辅助函数的用法
Vuex 3:
使用 mapState、mapGetters、mapMutations 和 mapActions 辅助函数来进行映射,简化在组件中对 store 的访问。
import { mapState, mapGetters, mapMutations, mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
computed: {
...mapState(['count']),
...mapGetters(['doubleCount']),
},
methods: {
...mapMutations(['increment']),
...mapActions(['incrementAsync']),
}
}
Vuex 4:使用 Composition API 中的 computed 函数和普通的 JavaScript 函数来实现类似的功能。
import { computed, useStore } from 'vuex'
export default {
setup() {
const store = useStore()
const count = computed(() => store.state.count)
const doubleCount = computed(() => store.getters.doubleCount)
const increment = () => {
store.commit('increment')
}
const incrementAsync = () => {
store.dispatch('incrementAsync')
}
return {
count,
doubleCount,
increment,
incrementAsync
}
}
}
Vuex4 支持选项式写法的辅助函数,在使用时和 Vuex3 一模一样的。
但是需要注意辅助函数不能在组合式写法 setup 中使用。
响应式的改进
- Vuex 3:使用 Vue 2 的响应式系统 ( Object.defineProperty ) 进行状态的监听和更新。
- Vuex 4:使用 Vue 3 的响应式系统 ( proxy ) 进行状态的监听和更新,可以利用 Composition API 中的reactive 和 computed 函数进行更加灵活和高效的状态管理。
实质上这是 Vue2 和 Vue3 的区别,只是由于 Vue 2 匹配的 Vuex 3,Vue 3 匹配的 Vuex 4 的原因,严格来说不能算作 Vuex3 与 Vuex4 的不同。
Vuex4 支持多例模式
Vuex 3 是单例模式的,即整个应用只能有一个全局的 Vuex Store 实例。
而在 Vuex 4 中,你可以通过 useStore 函数在不同组件中创建多个独立的 Vuex Store 实例,从而支持多例模式。
以下是一个示例展示了如何在 Vuex 4 中使用 useStore 辅助函数创建多个独立的 Vuex Store 实例:
<template>
<div>
<p>Counter 1: {{ counter1 }}</p>
<p>Counter 2: {{ counter2 }}</p>
<button @click="incrementCounter1">Increment Counter 1</button>
<button @click="incrementCounter2">Increment Counter 2</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { useStore } from 'vuex'
export default {
setup() {
// 使用 useStore 辅助函数创建 Vuex Store 实例
const store1 = useStore('store1')
const store2 = useStore('store2')
// 通过 store1.state.count 获取第一个 Store 的状态
const count1 = store1.state.count
// 通过 store2.state.count 获取第二个 Store 的状态
const count2 = store2.state.count
// 通过 store1.commit() 提交 mutations 到第一个 Store
const incrementCounter1 = () => {
store1.commit('increment')
}
// 通过 store2.commit() 提交 mutations 到第二个 Store
const incrementCounter2 = () => {
store2.commit('increment')
}
return {
count1,
count2,
incrementCounter1,
incrementCounter2
}
}
}
</script>
上述示例展示了如何在 Vue 组件中使用 useStore 辅助函数创建多个独立的 Vuex Store 实例,并通过这些实例分别访问和修改各自的状态和 mutations。
这是 Vuex 4 相对于 Vuex 3 的一个重要的改进,使得 Vuex 在支持多例模式的场景下更加灵活和可扩展。
参考文档
- https://www.jb51.net/article/281760.htm
- Vuex 4 官方文档:vuex.vuejs.org/zh/
- Vuex 3 官方文档:v3.vuex.vuejs.org/zh/