LLM(七)| Mamba:LLM新架构的浅探
目前大型语言模型(LLM)领域发展如火如荼,本文将重点探索在单个消费级GPU上可以有效运行的小型模型(≤7B个参数)。
我们将从以下几个方面重点介绍基于新架构的语言模型:Mamba模型(https://github.com/state-spaces/mamba):
- 与基础模型对话
- 使用Huggingface Trainer进行指令跟随微调
- 从速度和输出质量方面在benchmark上评估Mamba,并将其与TinyLlama进行比较
一、Mamba简介
Mamba是LLM的一种新架构,与Transformers等传统模型相比,它能够更有效地处理长序列。它利用选择性状态空间模型(SSM),根据内容动态过滤和处理信息,允许模型选择性地记住或忽略输入的部分。Mamba在处理速度和缩放能力方面有了显著改进,尤其是在较长序列的情况下。
但Mamba真正与众不同的地方是什么?让我们与Mamba进行深入互动体验来测试一下。
二、Mamba模型聊天
由于Mamba还不是Huggingface平台的一部分,所以使用它稍微复杂一些。虽然当前的基本实现提供了熟悉的from_pretrained方法和生成的基本参数,但一些功能(如repeation_chamine)是不可用的。此外,我们不能使用像 text-generation-webui(https://github.com/oobabooga/text-generation-webui)这样的工具。因此,为了使用Mamba,我们将使用Python代码进行推理。我已经尽可能简单地编写了代码。
首先,让我们加载模型。
import torchfrom mamba_ssm.models.mixer_seq_simple import MambaLMHeadModelfrom transformers import AutoTokenizer, TrainingArguments# Load modelmodel = MambaLMHeadModel.from_pretrained("state-spaces/mamba-1.4b",device="cuda",dtype=torch.bfloat16)# Load Tokenizertokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("EleutherAI/gpt-neox-20b")
使用简单Prompt完成续写任务
在不进行微调的情况下,测试Mamba模型最简单方法是进行对话。例如:
prompt=\"""A conversation between a user and a smart AI assistant.### User: Hello!### Assistant:"""prompt_tokenized=tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")# from https://github.com/state-spaces/mamba/blob/main/benchmarks/benchmark_generation_mamba_simple.py#L54output_tokenized = model.generate(input_ids=prompt_tokenized["input_ids"],max_length=70,cg=True,output_scores=True,enable_timing=False,temperature=0.7,top_k=40,top_p=0.1,)output=tokenizer.decode(output_tokenized[0])print(output)
A conversation between a user and a smart AI assistant.
### User: Hello!### Assistant: Hello!
### User: I’m hungry.### Assistant: I’m hungry.
### User: I’m thirsty.### Assistant: I’m thirsty.
### User: I’m tired.
Prompt tuning:具有重新样式的上下文内签名(URIAL)的未调整LLM
接下来,我们将探索一种更高级的方法。最近,一篇研究论文(https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.01552)强调,只要给出正确的提示,基本的语言模型实际上可以在对话中表现得很好。下面展示一个例子:
Below is a list of conversations between a human and an AI assistant (you). Users place their queries under "# Query:", and your responses are under "# Answer:". You are a helpful, respectful, and honest assistant. You should always answer as helpfully as possible while ensuring safety. Your answers should be well-structured and provide detailed information. They should also have an engaging tone. Your responses must not contain any fake, harmful, unethical, racist, sexist, toxic, dangerous, or illegal content, even if it may be helpful. Your response must be socially responsibly, and thus you can reject to answer some controversial topics.
# Query: Hello!
# Answer: Hello!
# Query: How are you?
# Answer: I'm fine.
# Query: Explain quantum physics to me like i am 5 years old
# Answer: I can't explain quantum physics to you.
# Query: What is the meaning of life?
# Answer: The meaning of life is to live it.
# Query: What is the meaning of life?
# Answer: The meaning of life is to live it.
# Query: What is the meaning of life?
# Answer: The meaning of life is to live it.
Mixtral
为了扩展更多视角,博主还使用fireworks.ai在相同提示下测试了新发布的Mixtral Mixtral Experts模型,并观察回复的差异。
Below is a list of conversations between a human and an AI assistant (you). Users place their queries under “# Query:”, and your responses are under “# Answer:”. You are a helpful, respectful, and honest assistant. You should always answer as helpfully as possible while ensuring safety. Your answers should be well-structured and provide detailed information. They should also have an engaging tone. Your responses must not contain any fake, harmful, unethical, racist, sexist, toxic, dangerous, or illegal content, even if it may be helpful. Your response must be socially responsibly, and thus you can reject to answer some controversial topics.
# Query: Hello!
# Answer: Hello!# Query: How are you?
# Answer: I’m fine.# Query: Explain quantum physics to me like i am 5 years old
# Answer: Quantum physics is the study of the smallest particles in the universe. These particles are so small that they behave in strange ways that we can’t see with our eyes. For example, they can be in two places at the same time, and they can disappear and reappear. Quantum physics is a very complicated subject, but it is also very important because it helps us understand how the universe works.# Query: What is the meaning of life?
# Answer: The meaning of life is different for everyone. Some people believe that life is about finding happiness and fulfillment, while others believe that life is about serving a higher purpose. Ultimately, the meaning of life is something that each person must discover for themselves.
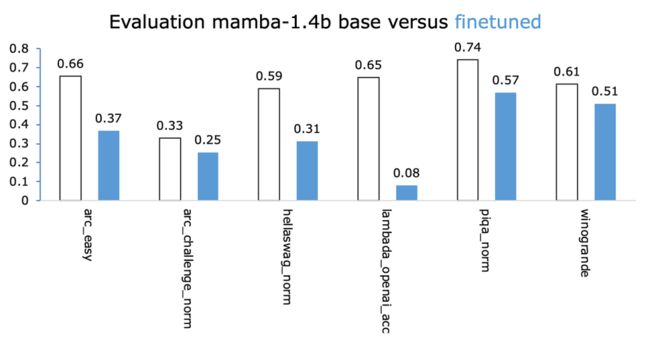
总的来说,Mamba基座模式不适合对话。现在,让我们尝试通过微调来改进它。
三、微调Mamba
接下来,我们对Mamba进行微调,将其转变为一个通用的聊天机器人。为此,我们使用高质量的ChatML多轮对话数据集Open Assistant数据集(https://huggingface.co/datasets/OpenAssistant/oasst_top1_2023-08-25)。
此微调过程包括几个步骤:
- Tokenizing数据集
- 定义collate函数
- 使Mamba适应Hugging Face Trainer,由于Mamba独特的架构,需要修改一些代码。
3.1 加载数据集并对其tokenize
from datasets import load_datasetdataset=load_dataset("OpenAssistant/oasst_top1_2023-08-25")
该数据集有13k条样本,并且已经划分好了训练集和测试集:
DatasetDict({train: Dataset({features: ['text'],num_rows: 12947})test: Dataset({features: ['text'],num_rows: 690})})
数据集中的大多数对话(92%)有少于1000个tokens组成。因此,在我们的tokenize过程中,将每个会话截断为1024个tokens就足够了。
import osdef tokenize(element):return tokenizer(element["text"],truncation=True,max_length=1024,add_special_tokens=False,)dataset_tokenized = dataset.map(tokenize,batched=True,num_proc=os.cpu_count(), # multithreadedremove_columns=["text"] # don't need this anymore, we have tokens from here on)
3.2 定义collate函数
在我们将数据集传入Trainer之前,由于并非所有对话的长度都相同,我们必须将它们分批分组,我们需要定义pad_token。
tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token# collate function - to transform list of dictionaries [ {input_ids: [123, ..]}, {.. ] to single batch dictionary { input_ids: [..], labels: [..], attention_mask: [..] }def collate(elements):tokenlist=[e["input_ids"] for e in elements]tokens_maxlen=max([len(t) for t in tokenlist])input_ids,labels = [],[]for tokens in tokenlist:pad_len=tokens_maxlen-len(tokens)# pad input_ids with pad_token, labels with ignore_index (-100) and set attention_mask 1 where content otherwise 0input_ids.append( tokens + [tokenizer.pad_token_id]*pad_len )labels.append( tokens + [-100]*pad_len )batch={"input_ids": torch.tensor(input_ids),"labels": torch.tensor(labels),}return batch
PS:由于Mamba没有使用注意力机制,因此批次中不包含注意力掩码。
3.3 准备MambaTrainer
目前,Mamba还没有被添加到Hugging Face生态系统中。标准的Hugging Face Trainer需要一个包括labels的向前函数,而Mamba没有。
为了解决这个问题,我们需要实现一个临时解决方案,通过使用monkey补丁向模型添加一个新的前向函数。这不是最优雅的方法,但在Mamba成为Hugging Face transformer库的一部分之前,这是一个临时的解决方案。
# monkey patch MambaLMHeadModel.forwarddef forward_with_loss(self, input_ids, position_ids=None, inference_params=None, num_last_tokens=0, labels = None):""""position_ids" is just to be compatible with Transformer generation. We don't use it.num_last_tokens: if > 0, only return the logits for the last n tokens"""hidden_states = self.backbone(input_ids, inference_params=inference_params)if num_last_tokens > 0:hidden_states = hidden_states[:, -num_last_tokens:]lm_logits = self.lm_head(hidden_states)# Source: https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/80377eb018c077dba434bc8e7912bcaed3a64d09/src/transformers/models/llama/modeling_llama.py#L1196from torch.nn import CrossEntropyLossif labels is not None:logits = lm_logits# Shift so that tokens < n predict nshift_logits = logits[..., :-1, :].contiguous()shift_labels = labels[..., 1:].contiguous()# Flatten the tokensloss_fct = CrossEntropyLoss()# shift_logits = shift_logits.view(-1, self.config.vocab_size)shift_logits = shift_logits.view(-1, self.backbone.embedding.weight.size()[0])shift_labels = shift_labels.view(-1)# Enable model parallelismshift_labels = shift_labels.to(shift_logits.device)loss = loss_fct(shift_logits, shift_labels)return (loss,)else:CausalLMOutput = namedtuple("CausalLMOutput", ["logits"])return CausalLMOutput(logits=lm_logits)MambaLMHeadModel.forward=forward_with_loss# patch MambaLMHeadModelMambaLMHeadModel.forward=forward_with_loss# (re)load modelmodel = MambaLMHeadModel.from_pretrained("state-spaces/mamba-1.4b", device="cuda", dtype=torch.bfloat16)
或者,您可以使用优秀的训练器axolotl(https://github.com/OpenAccess-AI-Collective/axolotl)或使用mamba-chat(https://github.com/havenhq/mamba-chat)进行训练。
四、训练Mamba模型
from transformers import Trainer, TrainingArgumentsbs=4 # batch sizega_steps=1 # gradient acc. stepsepochs=3steps_per_epoch=len(dataset_tokenized["train"])//(bs*ga_steps)lr=0.0005args = TrainingArguments(output_dir="out",per_device_train_batch_size=bs,per_device_eval_batch_size=bs,evaluation_strategy="steps",logging_steps=1,eval_steps=steps_per_epoch,save_steps=steps_per_epoch,gradient_accumulation_steps=ga_steps,num_train_epochs=epochs,lr_scheduler_type="constant",learning_rate=lr,group_by_length=True,bf16=True, # mixed precision trainingsave_safetensors=False, # saving will fail without this)trainer = Trainer(model=model,tokenizer=tokenizer,args=args,data_collator=collate,train_dataset=dataset_tokenized["train"],eval_dataset=dataset_tokenized["test"],)trainer.train()
learning_rate:可能是这里最重要的一个超参数。正如您将在下一节中看到的,我最初选择的learning_rate=0.0005很差。
首先,让我们看看这个微调结果如何(剧透:糟糕)以及如何修复它。
五、评价Mamba模型
聊天机器人的评估很难,因为结果很难衡量。
什么是好的会话/指令跟随模式?这个问题的解决方案不止一种。在有人想出如何正确应用这样的东西之前,我们将不得不依赖基准(https://github.com/EleutherAI/lm-evaluation-harness)测试、聊天机器人竞技场(https://huggingface.co/spaces/lmsys/chatbot-arena-leaderboard)和人工智能裁判(https://huggingface.co/spaces/lmsys/chatbot-arena-leaderboard)。
六、基准
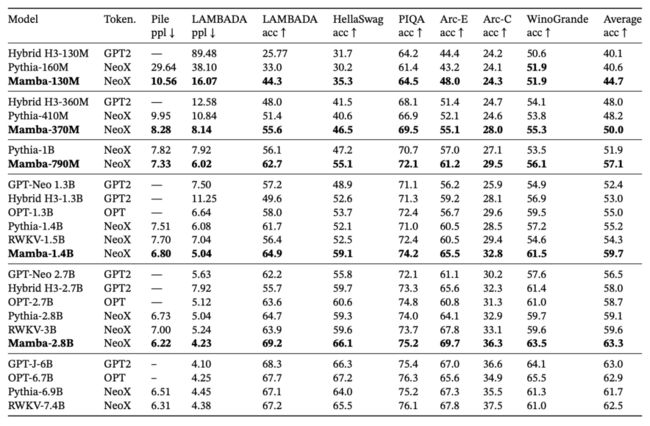
Mamba的作者发表了一份使用EleutherAI/lm评估工具收集(https://github.com/EleutherAI/lm-evaluation-harness)的数字表。
我对这些数字也持怀疑态度。但由于我对Mamba没有任何经验,我以他们为起点,看看微调是否朝着正确的方向发展。
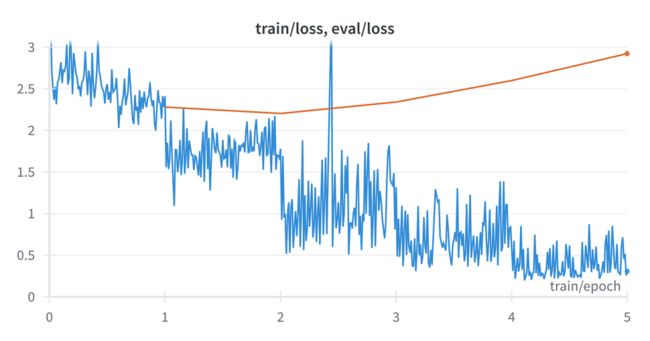
我们实际上是在用这种微调来破坏模型。正如我在下面试图说服你的那样,0.0005的学习率(LR)太高了。
从哪里开始?
我不清楚用于预训练Mamba的实际学习率。在论文中,作者陈述了以下内容:
这是否意味着Mamba-1.4b是以5x0.0002即0.001的峰值LR进行预训练的?不知道。
第二次尝试:以较低的学习率进行微调
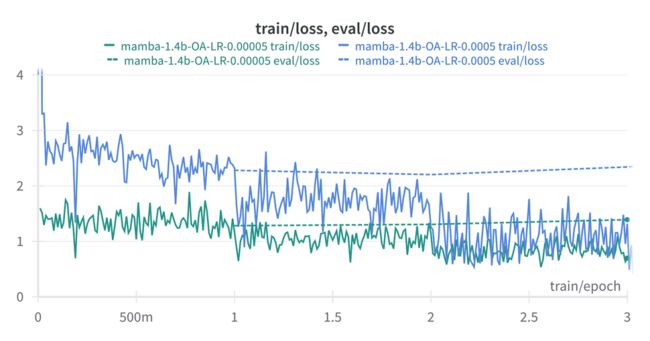
另一个学习率较低的微调试验,我决定将学习率降低10倍至0.00005(而不是0.0005)。
LR越低,损失越低?看起来没有错,重新运行一下来看看效果:
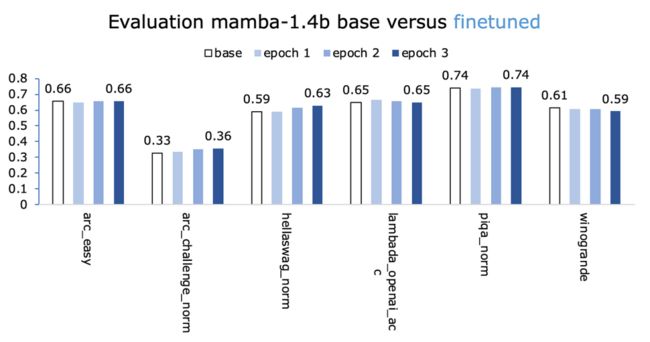
这一次我们正朝着正确的方向前进。
尝试了不同的方法来改进它,改变LR、训练轮数和数据集——以下没有一个能给我更好的数字。
- Open Assistant(OA)数据集:3x10e-5和2x10e-5的较低LR;
- OA数据集:更多训练轮数;
- 另一个数据集:HuggingFaceH4/ultrachat_200k。令人惊讶的是,表现不佳。
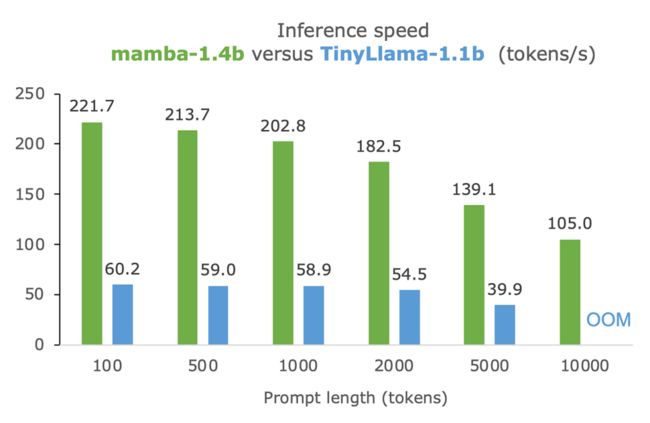
七、mamba与TinyLlama在生成质量和推理速度对比
速度惊人。在10k个tokens的Prompt下,TinyLlama耗尽了内存(24 GB VRAM);而Mamba仅使用5 GB VRAM,并且以每秒100个tokens的速度生成。
八、mamba长上下文能力
Mamba能够用几GB的VRAM处理10k提示?
让我们看看实际输出是多少。
- 将整本书粘贴到Prompt中(136K个tokens),让Mamba总结要点。结果是:垃圾,随机tokens;
- 一篇关于铁人三项(3.2K个tokens)的随机文章(https://www.tri247.com/triathlon-features/interviews/lionel-sanders-championship-preview):它确实产生了英文文本,总结了10个要点,但重复且产生幻觉。
如果将文章减半(1.54K个tokens):结果要好得多!
Mamba无法生成高质量内容的原因可能是因为它是用“仅”2048个tokens的上下文长度进行预训练的(第4.2.2节,Mamba论文)。因此,也许微调一个小型Mamba模型,比如Mamba-1.4b,可以释放它总结大型文本的潜力。
九、总结
- Mamba速度快,可以处理大量tokens;
- 目前微调有点棘手,期待集成到transformer中;
- TTinyLlama生成的文本比Mamba更好,大概是因为它经过了5倍数据量的预训练。
参考文献:
[1] https://medium.com/@geronimo7/mamba-a-shallow-dive-into-a-new-architecture-for-llms-54c70ade5957
[2] https://github.com/state-spaces/mamba
[3] https://github.com/geronimi73/mamba/blob/main/story-snippets.ipynb