深入理解Dubbo-7.服务消费调用源码分析
- 作者简介:大家好,我是爱吃芝士的土豆倪,24届校招生Java选手,很高兴认识大家
- 系列专栏:Spring源码、JUC源码、Kafka原理、分布式技术原理
- 如果感觉博主的文章还不错的话,请三连支持一下博主哦
- 博主正在努力完成2023计划中:源码溯源,一探究竟
- 联系方式:nhs19990716,加我进群,大家一起学习,一起进步,一起对抗互联网寒冬
文章目录
- 客户端发起调用
-
- JavassistProxyFactory.getProxy
- InvokerInvocationHandler.invoke
-
- MockClusterInvoker
- AbstractCluster$InterceptorInvokerNode.invoker
- ClusterInterceptor.intercept
- AbstractClusterInvoker.invoke
- ZoneAwareClusterInvoker.doInvoke
- AbstractCluster$InterceptorInvokerNode.invoker
- AbstractClusterInvoker.invoke
- FailoverClusterInvoker.doInvoke
- 负载均衡算法
-
- 负载均衡初始
- select
- AbstractClusterInvoker.doSelect
- RandomLoadBalance.doSelect
- 抽奖
- 总结
- Invoker.invoke
-
- RegistryDirectory.toInvokers
- RegistryDirectory.InvokerDelegate
- ProtocolFilterWrapper
-
- AbstractProtocol.refer
- AsyncToSyncInvoker.invoke
- DubboInvoker.invoke
- DubboInvoker.doInvoke
- ReferenceCountExchangeClient.request
- HeaderExchangeClient.request
- HeaderExchangeChannel.request
- 服务端接收数据的处理流程
-
- 服务端接收到消息
- handler.channelRead()
-
- DubboProtocol.createServer:
- Exchanger.bind
- 通过扩展点选择到HeaderExchanger
- HeaderExchangeHandler.received
- handleRequest
- DubboProtocol$requestHandler
-
- getInvoker
- invoker.invoke()
- DelegateProviderMetaDataInvoker
- AbstractProxyInvoker
- JavassistProxyFactory.doInvoke
- 服务实例是什么时候生成的
- 总结
- 服务实例是什么时候生成的
- 总结
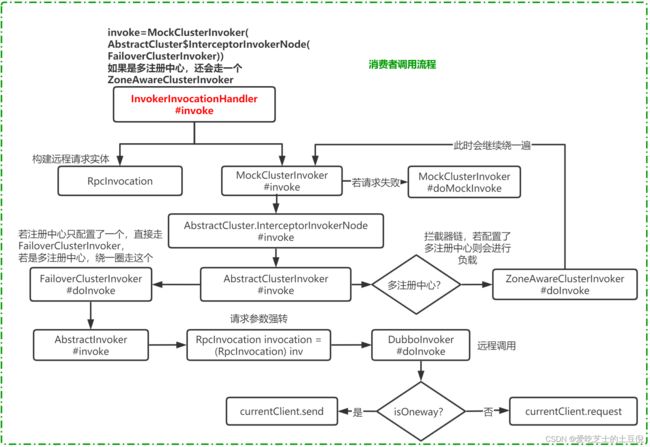
客户端发起调用
在上一节课中,我们已经服务消费者在启动时被注入一个动态代理类的实现过程,大家再来回顾一下服务消费者启动过程中做了什么事情呢?
服务启动过程中,主要会构建一个动态代理类,并且在构建动态代理之前,会从注册中心上获取服务提供者的地址,并且会订阅服务提供者的状态。
然后,采用DubboProtocol协议,和服务端建立一个远程通信,并保存到Invoker中进行返回。那接下来,我们再去看服务调用的时候,请求的执行过程。
JavassistProxyFactory.getProxy
在创建代理对象时,会执行下面这段代码,一旦代码被调用,就会触发InvokerInvocationHandler。
public <T> T getProxy(Invoker<T> invoker, Class<?>[] interfaces) {
return (T) Proxy.getProxy(interfaces).newInstance(new
InvokerInvocationHandler(invoker));
}
当调用sayHello方法时,会触发handler.invoker
public java.lang.String sayHello(java.lang.String arg0){
Object[] args = new Object[1];
args[0] = ($w)$1;
Object ret = handler.invoke(this, methods[0], args);
return (java.lang.String)ret;
}
InvokerInvocationHandler.invoke
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) {
return method.invoke(this.invoker, args);
} else {
String methodName = method.getName();
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
// 如果判断是属于Object的方法,就不用反射调用了
if (parameterTypes.length == 0) {
if ("toString".equals(methodName)) {
return this.invoker.toString();
}
if ("$destroy".equals(methodName)) {
this.invoker.destroy();
return null;
}
if ("hashCode".equals(methodName)) {
return this.invoker.hashCode();
}
} else if (parameterTypes.length == 1 && "equals".equals(methodName)) {
return this.invoker.equals(args[0]);
}
//数据传输对象
RpcInvocation rpcInvocation = new RpcInvocation(method, this.invoker.getInterface().getName(), args);
String serviceKey = this.invoker.getUrl().getServiceKey();
rpcInvocation.setTargetServiceUniqueName(serviceKey);
if (this.consumerModel != null) {
rpcInvocation.put("consumerModel", this.consumerModel);
rpcInvocation.put("methodModel", this.consumerModel.getMethodModel(method));
}
// 此时的invoker取决于我们传递过来的invoker是什么
return this.invoker.invoke(rpcInvocation).recreate();
}
}
进入到InvokerInvocationHandler.invoke方法。
其中invoker这个对象, 是在启动注入动态代理类时,初始化的一个调用器对象,我们得先要知道它是谁,才能知道它下一步调用的是哪个对象的方法.
它应该是: MockClusterInvoker,因为它是通过MockClusterWrapper来进行包装的。这个可以看前面的cluster.join()部分,就能够发现。
MockClusterWrapper
public <T> Invoker<T> join(Directory<T> directory) throws RpcException {
return new MockClusterInvoker(directory, this.cluster.join(directory));
}
MockClusterInvoker
public Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
Result result = null;
// mock配置参数
String value = this.getUrl().getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), "mock", Boolean.FALSE.toString()).trim();
if (value.length() != 0 && !"false".equalsIgnoreCase(value)) {
// 如果 mock 参数以 "force" 开头,则强制进行 mock 操作
if (value.startsWith("force")) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("force-mock: " + invocation.getMethodName() + " force-mock enabled , url : " + this.getUrl());
}
// 执行 mock 操作
result = this.doMockInvoke(invocation, (RpcException)null);
} else {
try {
// 执行服务方法
result = this.invoker.invoke(invocation);
// 如果结果出现异常,则进行 mock 操作
if (result.getException() != null && result.getException() instanceof RpcException) {
RpcException rpcException = (RpcException)result.getException();
if (rpcException.isBiz()) {
throw rpcException;
}
result = this.doMockInvoke(invocation, rpcException);
}
} catch (RpcException var5) {
// 如果出现异常,则进行 mock 操作
if (var5.isBiz()) {
throw var5;
}
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("fail-mock: " + invocation.getMethodName() + " fail-mock enabled , url : " + this.getUrl(), var5);
}
// 执行 mock 操作
result = this.doMockInvoke(invocation, var5);
}
}
} else {
// 直接执行服务方法
// 无mock
result = this.invoker.invoke(invocation);
}
return result;
}
AbstractCluster$InterceptorInvokerNode.invoker
拦截器链的组成是:ConsumerContextClusterInterceptor -> ZoneAwareClusterInvoker。
在调用服务接口之前,ConsumerContextClusterInterceptor会负责设置上下文信息,以确保上下文在整个调用链中可用。
然后,调用interceptor.intercept方法来进行拦截处理。这个方法会依次调用拦截器链中的每个拦截器的intercept方法。
通过拦截器链的处理,可以在调用服务接口前后进行一些额外的操作,如参数校验、日志记录等。它提供了对服务调用过程的灵活控制和扩展能力。
public Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
Result asyncResult;
try {
this.interceptor.before(this.next, invocation);
asyncResult = this.interceptor.intercept(this.next, invocation);
}
......
其中before方法是设置上下文信息,接着调用interceptor.interceppt方法进行拦截处理
ClusterInterceptor.intercept
调用ClusterInterceptor的默认方法。
default Result intercept(AbstractClusterInvoker<?> clusterInvoker, Invocation
invocation) throws RpcException {
return clusterInvoker.invoke(invocation);
}
此时传递过来的clusterInvoker对象,是拦截器链中的第二个节点 ZoneAwareClusterInvoker
AbstractClusterInvoker.invoke
因为ZoneAwareClusterInvoker 中没有invoke方法,所以实际上是调用其父类的AbstractClusterInvoker.invoke
public Result invoke(final Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
this.checkWhetherDestroyed();
// 绑定attachment到invocation中
Map<String, Object> contextAttachments = RpcContext.getContext().getObjectAttachments();
if (contextAttachments != null && contextAttachments.size() != 0) {
((RpcInvocation)invocation).addObjectAttachments(contextAttachments);
}
//获取invoker列表,这里的列表应该是直接从directory中获取
List<Invoker<T>> invokers = this.list(invocation);
//初始化负载均衡算法
LoadBalance loadbalance = this.initLoadBalance(invokers, invocation);
//调用子类的doInvoke方法
RpcUtils.attachInvocationIdIfAsync(this.getUrl(), invocation);
return this.doInvoke(invocation, invokers, loadbalance);
}
ZoneAwareClusterInvoker.doInvoke
ZonAwareCluster,就是之前我们说过的,如果一个服务注册在多个注册中心,那么消费者去消费时,会根据区域进行路由,选择一个注册中心进行服务消费。
public Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, final List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException {
//遍历注册中心
Iterator var4 = invokers.iterator();
Invoker balancedInvoker;
while(var4.hasNext()) {
balancedInvoker = (Invoker)var4.next();
// 判断是否需要通过mockInvoker来触发调用
MockClusterInvoker<T> mockClusterInvoker = (MockClusterInvoker)balancedInvoker;
if (mockClusterInvoker.isAvailable() && mockClusterInvoker.getRegistryUrl().getParameter("registry.preferred", false)) {
return mockClusterInvoker.invoke(invocation);
}
}
// 是否制定了zone进行调用
String zone = invocation.getAttachment("registry_zone");
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(zone)) {
Iterator var10 = invokers.iterator();
while(var10.hasNext()) {
Invoker<T> invoker = (Invoker)var10.next();
MockClusterInvoker<T> mockClusterInvoker = (MockClusterInvoker)invoker;
if (mockClusterInvoker.isAvailable() && zone.equals(mockClusterInvoker.getRegistryUrl().getParameter("registry.zone"))) {
return mockClusterInvoker.invoke(invocation);
}
}
String force = invocation.getAttachment("registry_zone_force");
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(force) && "true".equalsIgnoreCase(force)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No registry instance in zone or no available providers in the registry, zone: " + zone + ", registries: " + (String)invokers.stream().map((invokerx) -> {
return ((MockClusterInvoker)invokerx).getRegistryUrl().toString();
}).collect(Collectors.joining(",")));
}
}
// 通过负载均衡算法,从多个注册中心中随机选择一个节点
balancedInvoker = this.select(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, (List)null);
if (balancedInvoker.isAvailable()) {//进入到指定注册中心的服务列表进行调用
return balancedInvoker.invoke(invocation);
} else {
Iterator var13 = invokers.iterator();
MockClusterInvoker mockClusterInvoker;
//如果没有一个invoker通过负载均衡算法被指定,则选择第一个有效的invoker进行调用。
do {
if (!var13.hasNext()) {
throw new RpcException("No provider available in " + invokers);
}
Invoker<T> invoker = (Invoker)var13.next();
mockClusterInvoker = (MockClusterInvoker)invoker;
//选择指定的一个区域的invoker进行调用
} while(!mockClusterInvoker.isAvailable());
return mockClusterInvoker.invoke(invocation);
}
}
调用链路又会经过一遍 MockClusterInvoker - > AbstractCluster$InterceptorInvokerNode
AbstractCluster$InterceptorInvokerNode.invoker
再次进入到这个方法中,不过此时的调用链路发生了变化。
这个拦截器是的组成是: ConsumerContextClusterInterceptor -> FailoverClusterInvoker
继续进入到AbstractClusterInvoker中的invoke,但是此时AbstractClusterInvoker是通过
FailoverClusterInvoker来实现的,所以再次调用doInvoke时,会调用FailoverClusterInvoker中的doInvoke方法
AbstractClusterInvoker.invoke
因为FailoverClusterInvoker中没有invoke方法,所以实际上是调用其父类的AbstractClusterInvoker.invoke
public Result invoke(final Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
this.checkWhetherDestroyed();
// 绑定attachment到invocation中
Map<String, Object> contextAttachments = RpcContext.getContext().getObjectAttachments();
if (contextAttachments != null && contextAttachments.size() != 0) {
((RpcInvocation)invocation).addObjectAttachments(contextAttachments);
}
//获取invoker列表,这里的列表应该是直接从directory中获取
List<Invoker<T>> invokers = this.list(invocation);
//初始化负载均衡算法
LoadBalance loadbalance = this.initLoadBalance(invokers, invocation);
//调用子类的doInvoke方法
RpcUtils.attachInvocationIdIfAsync(this.getUrl(), invocation);
return this.doInvoke(invocation, invokers, loadbalance);
}
FailoverClusterInvoker.doInvoke
FailoverClusterInvoker,顾名思义,就是集群容错的处理,默认的集群容错策略是重试,所以也不难猜出这里面的实现方式。
这段代码逻辑也很好理解,因为我们之前在讲Dubbo的时候说过容错机制,而failover是失败重试,所以这里面应该会实现容错的逻辑
- 获得重试的次数,并且进行循环
- 获得目标服务,并且记录当前已经调用过的目标服务防止下次继续将请求发送过去
- 如果执行成功,则返回结果
- 如果出现异常,判断是否为业务异常,如果是则抛出,否则,进行下一次重试
- 这里的 Invoker 是 Provider 的一个可调用 Service 的抽象, Invoker 封装了 Provider 地址及 Service 接口信息
- Directory 代表多个 Invoker ,可以把它看成 List ,但与 List 不同的是,它的值可能是动态变化的,比如注册中心推送变更
- Cluster 将 Directory 中的多个 Invoker 伪装成一个 Invoker ,对上层透明,伪装过程包含了容错逻辑,调用失败后,重试另一个
- Router 负责从多个 Invoker 中按路由规则选出子集,比如读写分离,应用隔离等LoadBalance 负责从多个 Invoker 中选出具体的一个用于本次调用,选的过程包含了负载均衡
- 算法,调用失败后,需要重选
public Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, final List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException {
//获取服务提供者的协议invoker
List<Invoker<T>> copyInvokers = invokers;
// 校验invoker
this.checkInvokers(invokers, invocation);
//获取调用的目标方法名
String methodName = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation);
//获得重试次数
int len = this.getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, "retries", 2) + 1;
if (len <= 0) {
len = 1;
}
RpcException le = null;
List<Invoker<T>> invoked = new ArrayList(invokers.size());
Set<String> providers = new HashSet(len);
//for循环进行重试
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
if (i > 0) {
this.checkWhetherDestroyed();
copyInvokers = this.list(invocation);
this.checkInvokers(copyInvokers, invocation);
}
//从多个invoker中通过负载均衡算法,选择一个inovke进行调用。
Invoker<T> invoker = this.select(loadbalance, invocation, copyInvokers, invoked);
invoked.add(invoker);//记录已经调用过的目标服务,如果重试时,已经调用过的目标服务不再发起调用。
RpcContext.getContext().setInvokers(invoked);
try {
//发起远程调用
Result result = invoker.invoke(invocation);
if (le != null && logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Although retry the method " + methodName + " in the service " + this.getInterface().getName() + " was successful by the provider " + invoker.getUrl().getAddress() + ", but there have been failed providers " + providers + " (" + providers.size() + "/" + copyInvokers.size() + ") from the registry " + this.directory.getUrl().getAddress() + " on the consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " using the dubbo version " + Version.getVersion() + ". Last error is: " + le.getMessage(), le);
}
Result var13 = result;
return var13;
} catch (RpcException var18) {
if (var18.isBiz()) {
throw var18;
}
le = var18;
} catch (Throwable var19) {
le = new RpcException(var19.getMessage(), var19);
} finally {
providers.add(invoker.getUrl().getAddress());
}
}
throw new RpcException(le.getCode(), "Failed to invoke the method " + methodName + " in the service " + this.getInterface().getName() + ". Tried " + len + " times of the providers " + providers + " (" + providers.size() + "/" + copyInvokers.size() + ") from the registry " + this.directory.getUrl().getAddress() + " on the consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " using the dubbo version " + Version.getVersion() + ". Last error is: " + le.getMessage(), (Throwable)(le.getCause() != null ? le.getCause() : le));
}
负载均衡算法
负载均衡初始
//初始化负载均衡算法
LoadBalance loadbalance = this.initLoadBalance(invokers, invocation);
// 扩展点
protected LoadBalance initLoadBalance(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, Invocation invocation) {
return CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(invokers) ? (LoadBalance)ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(LoadBalance.class).getExtension(((Invoker)invokers.get(0)).getUrl().getMethodParameter(RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation), "loadbalance", "random")) : (LoadBalance)ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(LoadBalance.class).getExtension("random");
}
select
Invoker<T> invoker = this.select(loadbalance, invocation, copyInvokers, invoked);
- loadbalance 表示具体的负载均衡算法实例
- invocation 表示请求的参数
- invokers,表示服务提供者的实例列表,如果有多个,这里就是一个集合
protected Invoker<T> select(LoadBalance loadbalance, Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, List<Invoker<T>> selected) throws RpcException {
// 如果服务提供者列表为空,返回null
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(invokers)) {
return null;
} else {
// 获取调用的方法名
String methodName = invocation == null ? "" : invocation.getMethodName();
// 获取sticky参数的值,默认为false
boolean sticky = ((Invoker)invokers.get(0)).getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, "sticky", false);
// 如果stickyInvoker不为空,并且它不在服务提供者列表中,则将stickyInvoker置为null。stickyInvoker是之前选中的服务提供者。
if (this.stickyInvoker != null && !invokers.contains(this.stickyInvoker)) {
this.stickyInvoker = null;
}
// 如果sticky为true,并且stickyInvoker不为空,并且selected为空或者不包含stickyInvoker,并且进行可用性检查并且stickyInvoker是可用的,则返回stickyInvoker
if (sticky && this.stickyInvoker != null && (selected == null || !selected.contains(this.stickyInvoker)) && this.availablecheck && this.stickyInvoker.isAvailable()) {
return this.stickyInvoker;
} else {
// 如果不满足上述条件,则调用doSelect方法选择一个合适的服务提供者
Invoker<T> invoker = this.doSelect(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, selected);
// 如果sticky为true,则将选中的服务提供者赋值给stickyInvoker
if (sticky) {
this.stickyInvoker = invoker;
}
// 返回选中的服务提供者
return invoker;
}
}
}
AbstractClusterInvoker.doSelect
- 如果invokers只有一个,则直接返回
- 否则,调用负载均衡算法获得一个目标invoker
private Invoker<T> doSelect(LoadBalance loadbalance, Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, List<Invoker<T>> selected) throws RpcException {
// 如果服务提供者列表为空,返回null
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(invokers)) {
return null;
// 如果只有一个服务提供者,直接返回该服务提供者
} else if (invokers.size() == 1) {
return (Invoker)invokers.get(0);
} else {
// 使用负载均衡算法选择一个服务提供者
Invoker<T> invoker = loadbalance.select(invokers, this.getUrl(), invocation);
//如果selected集合中包含这次选择出来的invoker, 或这invoker是一个失效的服务,则重新选择一个新的invoker返回。
if (selected != null && selected.contains(invoker) || !invoker.isAvailable() && this.getUrl() != null && this.availablecheck) {
try {
// 重新选择一个合适的服务提供者
Invoker<T> rInvoker = this.reselect(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, selected, this.availablecheck);
if (rInvoker != null) {
invoker = rInvoker;
} else {
int index = invokers.indexOf(invoker);
try {
// 如果无法重新选择,则选择下一个服务提供者
invoker = (Invoker)invokers.get((index + 1) % invokers.size());
} catch (Exception var9) {
logger.warn(var9.getMessage() + " may because invokers list dynamic change, ignore.", var9);
}
}
} catch (Throwable var10) {
logger.error("cluster reselect fail reason is :" + var10.getMessage() + " if can not solve, you can set cluster.availablecheck=false in url", var10);
}
}
return invoker;
}
}
Invoker invoker = loadbalance.select(invokers, this.getUrl(), invocation);
因为前面介绍过,在负载均衡初始的时候,使用了扩展点,所以loadbalance 其实是 RandomLoadBalance
RandomLoadBalance.doSelect
执行随机负载均衡算法。
protected <T> Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
int length = invokers.size();
boolean sameWeight = true;
int[] weights = new int[length];
// 下面这个循环有两个作用,第一是计算总权重 totalWeight,
// 第二是检测每个服务提供者的权重是否相同
int firstWeight = this.getWeight((Invoker)invokers.get(0), invocation);
weights[0] = firstWeight;
int totalWeight = firstWeight;
int offset;
int i;
for(offset = 1; offset < length; ++offset) {
i = this.getWeight((Invoker)invokers.get(offset), invocation);
weights[offset] = i;
// 累加权重
totalWeight += i;
// 检测当前服务提供者的权重与上一个服务提供者的权重是否相同,
// 不相同的话,则将 sameWeight 置为 false。
if (sameWeight && i != firstWeight) {
sameWeight = false;
}
}
// 下面的 if 分支主要用于获取随机数,并计算随机数落在哪个区间上
if (totalWeight > 0 && !sameWeight) {
// 随机获取一个 [0, totalWeight) 区间内的数字
offset = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(totalWeight);
// 循环让 offset 数减去服务提供者权重值,当 offset 小于0时,返回相应的 Invoker。
// 举例说明一下,我们有 servers = [A, B, C],weights = [5, 3, 2],offset =7。
// 第一次循环,offset - 5 = 2 > 0,即 offset > 5,
// 表明其不会落在服务器 A 对应的区间上。
// 第二次循环,offset - 3 = -1 < 0,即 5 < offset < 8,
// 表明其会落在服务器 B 对应的区间上
for(i = 0; i < length; ++i) {
// 让随机值 offset 减去权重值
offset -= weights[i];
if (offset < 0) {
// 返回相应的 Invoker
return (Invoker)invokers.get(i);
}
}
}
// 如果所有服务提供者权重值相同,此时直接随机返回一个即可
return (Invoker)invokers.get(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(length));
}
以上代码也就是抽奖的核心思路。
抽奖
总结
两台服务器的通信,用最基本的常识去思考,如果要保证一定成功,对客户端来说就是不断重试,对服务端来说要避免多次重试所带来的数据变更的问题,要考虑幂等的问题。
Invoker.invoke
继续回到FailoverClusterInvoker这个类中的代码来,这里会通过负载返回的invoker对象,来调用invoke方法进行远程通信。
//发起远程调用
Result result = invoker.invoke(invocation);
这个Invoker其实在 RegistryDirectory 的 toInvokers 方法中,对Invoker进行初始化时就定义好了。
RegistryDirectory.toInvokers
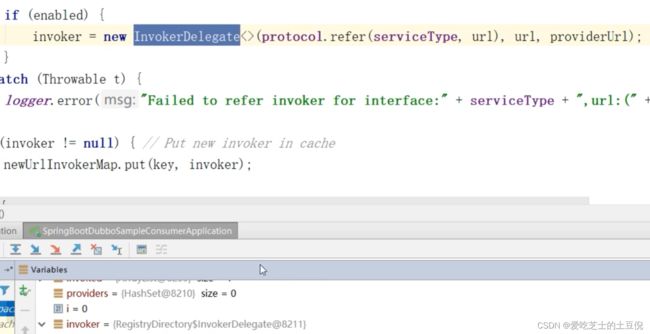
invoker = new RegistryDirectory.InvokerDelegate(this.protocol.refer(this.serviceType, url), url, providerUrl);
所以最终我们的Invoker对象实际上是 RegistryDirectory$InvokerDelegate() ,在debug过程中也能够发现这一点。
RegistryDirectory.InvokerDelegate
private static class InvokerDelegate<T> extends InvokerWrapper<T> {
private URL providerUrl;
public InvokerDelegate(Invoker<T> invoker, URL url, URL providerUrl) {
super(invoker, url);
this.providerUrl = providerUrl;
}
public URL getProviderUrl() {
return this.providerUrl;
}
}
但是其没有invoke方法,所以去其父类。
public class InvokerWrapper<T> implements Invoker<T> {
...
public Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
return this.invoker.invoke(invocation);
}
...
}
再回到这个
invoker = new RegistryDirectory.InvokerDelegate(this.protocol.refer(this.serviceType, url), url, providerUrl);
因为protocol 是自适应扩展点,所以会根据配置对其进行包装,具体可以扩展点SPI知识。
所以最终debug中,可以看到最终的invoker是
ProtocolFilterWrapper
在ProtocolFilterWrapper的调用中,实际会调用一个匿名内部类的invoke方法,这里构建了一个filter进行逐项的过滤
private static <T> Invoker<T> buildInvokerChain(final Invoker<T> invoker, String key, String group) {
final Invoker<T> last = invoker;
List<Filter> filters = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Filter.class).getActivateExtension(invoker.getUrl(), key, group); // 激活扩展点
if (!filters.isEmpty()) {
for(int i = filters.size() - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
final Filter filter = (Filter)filters.get(i);
last = new Invoker<T>() {
public Class<T> getInterface() {
return invoker.getInterface();
}
public URL getUrl() {
return invoker.getUrl();
}
public boolean isAvailable() {
return invoker.isAvailable();
}
public Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
Result asyncResult;
try {
asyncResult = filter.invoke(last, invocation);
} catch (Exception var15) {
Exception e = var15;
if (filter instanceof ListenableFilter) {
ListenableFilter listenableFilter = (ListenableFilter)filter;
try {
Listener listenerx = listenableFilter.listener(invocation);
if (listenerx != null) {
listenerx.onError(e, invoker, invocation);
}
} finally {
listenableFilter.removeListener(invocation);
}
} else if (filter instanceof Listener) {
Listener listener = (Listener)filter;
listener.onError(var15, invoker, invocation);
}
throw var15;
} finally {
;
}
return asyncResult.whenCompleteWithContext((r, t) -> {
if (filter instanceof ListenableFilter) {
ListenableFilter listenableFilter = (ListenableFilter)filter;
Listener listener = listenableFilter.listener(invocation);
try {
if (listener != null) {
if (t == null) {
listener.onResponse(r, invoker, invocation);
} else {
listener.onError(t, invoker, invocation);
}
}
} finally {
listenableFilter.removeListener(invocation);
}
} else if (filter instanceof Listener) {
Listener listenerx = (Listener)filter;
if (t == null) {
listenerx.onResponse(r, invoker, invocation);
} else {
listenerx.onError(t, invoker, invocation);
}
}
});
}
public void destroy() {
invoker.destroy();
}
public String toString() {
return invoker.toString();
}
};
}
}
return last;
}
而实际的Invoker其实通过debug是
在toInvokers这个方法中,invoker是通过 protocol.refer来构建的。那么我们再来分析一下refer里面做了什么?
protocol.refer(serviceType, url), url, providerUrl)
我们去看一下它的实现,首先protocol,是被依赖注入进来的自适应扩展点Protocol$Adaptive. ,此时传进去的数,此时url对应的地址应该是dubbo://开头的协议地址,所以最终获得的是通过包装之后的DubboProtocol象。
QosProtocolWrapper(ProtocolFilterWrapper(ProtocolListenerWrapper(DubboProtocol)))
AbstractProtocol.refer
DubboProtocol中没有refer方法,而是调用父类的refer。
@Override
public <T> Invoker<T> refer(Class<T> type, URL url) throws RpcException {
return new AsyncToSyncInvoker<>(protocolBindingRefer(type, url));
}
AsyncToSyncInvoker.invoke
经过装饰器、过滤器对invoker进行增强和过滤之后,来到了AsyncToSyncInvoker.invoke方法,这里采用的是异步的方式来进行通信
public Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
Result asyncResult = this.invoker.invoke(invocation);
try {
//如果配置的是同步通信,则通过get阻塞式获取返回结果
if (InvokeMode.SYNC == ((RpcInvocation)invocation).getInvokeMode()) {
asyncResult.get(2147483647L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
return asyncResult;
}
......
}
DubboInvoker.invoke
DubboInvoker继承了AbstractInvoker这个抽象类,而DubboInvoker中没有invoke这个方法,所以这里调用的是AbstractInvoker.invoke方法。
进入到DubboInvoker这个方法中,那么意味着正式进入到服务通信层面了。前面的很多细节分析,无非就是做了三件事
- 多注册中心的拦截以及分发
- 负载均衡以及集群容错
- 请求过滤和包装
public Result invoke(Invocation inv) throws RpcException {
// 检查当前 Invoker 是否已经被销毁
if (this.destroyed.get()) {
this.logger.warn("Invoker for service " + this + " on consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " is destroyed, , dubbo version is " + Version.getVersion() + ", this invoker should not be used any longer");
}
// 将 Invocation 类型转换为 RpcInvocation 类型
RpcInvocation invocation = (RpcInvocation)inv;
// 设置当前 Invoker 对象到 RpcInvocation 中
invocation.setInvoker(this);
// 如果附加属性不为空,则添加到 RpcInvocation 对象中
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmptyMap(this.attachment)) {
invocation.addObjectAttachmentsIfAbsent(this.attachment);
}
// 将 RpcContext 中的上下文附加属性添加到 RpcInvocation 对象中
Map<String, Object> contextAttachments = RpcContext.getContext().getObjectAttachments();
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmptyMap(contextAttachments)) {
invocation.addObjectAttachments(contextAttachments);
}
// 设置调用模式到 RpcInvocation 中
invocation.setInvokeMode(RpcUtils.getInvokeMode(this.url, invocation));
// 如果是异步调用,则在 RpcInvocation 中附加调用 ID
RpcUtils.attachInvocationIdIfAsync(this.getUrl(), invocation);
AsyncRpcResult asyncResult;
try {
// 调用 doInvoke 方法进行远程调用
asyncResult = (AsyncRpcResult)this.doInvoke(invocation);
} catch (InvocationTargetException var7) {
Throwable te = var7.getTargetException();
if (te == null) {
asyncResult = AsyncRpcResult.newDefaultAsyncResult((Object)null, var7, invocation);
} else {
if (te instanceof RpcException) {
((RpcException)te).setCode(3);
}
asyncResult = AsyncRpcResult.newDefaultAsyncResult((Object)null, te, invocation);
}
} catch (RpcException var8) {
if (!var8.isBiz()) {
throw var8;
}
asyncResult = AsyncRpcResult.newDefaultAsyncResult((Object)null, var8, invocation);
} catch (Throwable var9) {
asyncResult = AsyncRpcResult.newDefaultAsyncResult((Object)null, var9, invocation);
}
RpcContext.getContext().setFuture(new FutureAdapter(asyncResult.getResponseFuture()));
return asyncResult;
}
DubboInvoker.doInvoke
调用doInvoke方法发起远程请求。
protected Result doInvoke(final Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// 将 Invocation 类型转换为 RpcInvocation 类型
RpcInvocation inv = (RpcInvocation)invocation;
// 获取调用方法名,并将 path 和 version 附加到 RpcInvocation 中
String methodName = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation);
inv.setAttachment("path", this.getUrl().getPath());
inv.setAttachment("version", this.version);
ExchangeClient currentClient;
// 从 clients 中选择一个 ExchangeClient 进行远程调用
if (this.clients.length == 1) {
currentClient = this.clients[0];
} else {
// 轮询
currentClient = this.clients[this.index.getAndIncrement() % this.clients.length];
}
try {
// 判断是否是单向调用
boolean isOneway = RpcUtils.isOneway(this.getUrl(), invocation);
// 计算超时时间
int timeout = this.calculateTimeout(invocation, methodName);
if (isOneway) {
// 如果是单向调用,则将 RpcInvocation 对象发送到服务端
boolean isSent = this.getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, "sent", false);
currentClient.send(inv, isSent);
// 返回 AsyncRpcResult,表示调用结果还未返回
return AsyncRpcResult.newDefaultAsyncResult(invocation);
} else {
// 否则,创建一个线程池 executor,并将执行结果封装到 CompletableFuture 对象中
ExecutorService executor = this.getCallbackExecutor(this.getUrl(), inv);
CompletableFuture<AppResponse> appResponseFuture = currentClient.request(inv, timeout, executor).thenApply((obj) -> {
return (AppResponse)obj;
});
// 将 FutureContext 中的 Future 对象设置为 appResponseFuture
FutureContext.getContext().setCompatibleFuture(appResponseFuture);
// 返回 AsyncRpcResult,表示调用结果还未返回
AsyncRpcResult result = new AsyncRpcResult(appResponseFuture, inv);
result.setExecutor(executor);
return result;
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
......
}
}
currentClient还记得是一个什么对象吗?
在DubboProtocol里的initClient()中
private ExchangeClient initClient(URL url) {
.....
Object client;
if (url.getParameter("lazy", false)) {
client = new LazyConnectExchangeClient(url, this.requestHandler);
} else {
client = Exchangers.connect(url, this.requestHandler);
}
......
}
}
public static ExchangeClient connect(URL url, ExchangeHandler handler) throws RemotingException {
.....
url = url.addParameterIfAbsent("codec", "exchange");
return getExchanger(url).connect(url, handler);
}
}
public static Exchanger getExchanger(URL url) {
String type = url.getParameter("exchanger", "header");
return getExchanger(type);
}
public static Exchanger getExchanger(String type) {
return (Exchanger)ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Exchanger.class).getExtension(type);
}
由于是扩展点,所以相当于它实际是一个ReferenceCountExchangeClient(HeaderExchangeClient())
所以它的调用链路是
ReferenceCountExchangeClient->HeaderExchangeClient->HeaderExchangeChannel->(request方法)
ReferenceCountExchangeClient.request
最终,把构建好的RpcInvocation,组装到一个Request对象中进行传递
public CompletableFuture<Object> request(Object request, int timeout, ExecutorService executor) throws RemotingException {
return this.client.request(request, timeout, executor);
}
- ReferenceCountExchangeClient 用来记录调用次数
- HeaderExchangeClient 用来开启心跳机制、以及启动失败重连任务
HeaderExchangeClient.request
public HeaderExchangeClient(Client client, boolean startTimer) {
Assert.notNull(client, "Client can't be null");
this.client = client;
this.channel = new HeaderExchangeChannel(client);
if (startTimer) {
URL url = client.getUrl();
this.startReconnectTask(url);
this.startHeartBeatTask(url);
}
}
public CompletableFuture<Object> request(Object request, int timeout, ExecutorService executor) throws RemotingException {
return this.channel.request(request, timeout, executor);
}
HeaderExchangeChannel.request
进入到HeaderExchangeChannel.request 来发起请求,这个类的主要职责就是和服务端进行数据交互
public CompletableFuture<Object> request(Object request, int timeout, ExecutorService executor) throws RemotingException {
if (this.closed) {
throw new RemotingException(this.getLocalAddress(), (InetSocketAddress)null, "Failed to send request " + request + ", cause: The channel " + this + " is closed!");
} else {
// 创建请求对象
Request req = new Request();
req.setVersion(Version.getProtocolVersion());
req.setTwoWay(true);
req.setData(request);
DefaultFuture future = DefaultFuture.newFuture(this.channel, req, timeout, executor);
try {
//发送请求
this.channel.send(req);
return future;
} catch (RemotingException var7) {
future.cancel();
throw var7;
}
}
}
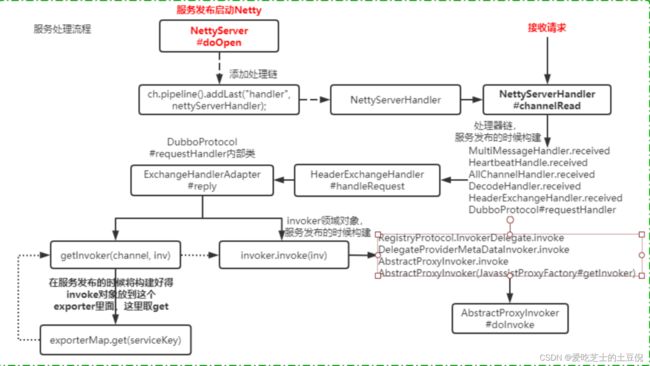
服务端接收数据的处理流程
客户端请求发出去之后,服务端会收到这个请求的消息,然后触发调用。
服务端接收到消息
服务端这边接收消息的处理链路,也比较复杂,我们回到NettServer中创建io的过程。
bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NettyEventLoopFactory.serverSocketChannelClass())
.option(ChannelOption.SO_REUSEADDR, Boolean.TRUE)
.childOption(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, Boolean.TRUE)
.childOption(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
// FIXME: should we use getTimeout()?
int idleTimeout = UrlUtils.getIdleTimeout(getUrl());
NettyCodecAdapter adapter = new NettyCodecAdapter(getCodec(),getUrl(), NettyServer.this);
if (getUrl().getParameter(SSL_ENABLED_KEY, false)) {
ch.pipeline().addLast("negotiation",
SslHandlerInitializer.sslServerHandler(getUrl(), nettyServerHandler));
}
ch.pipeline()
.addLast("decoder", adapter.getDecoder())
.addLast("encoder", adapter.getEncoder())
.addLast("server-idle-handler", new IdleStateHandler(0, 0,
idleTimeout, MILLISECONDS))
.addLast("handler", nettyServerHandler);
}
});
服务端启动的时候,配置的消息处理是handler配置的是nettyServerHandler
final NettyServerHandler nettyServerHandler = new NettyServerHandler(getUrl(),this);
所以,服务端收到消息之后,会调用NettyServerHandler中的channelRead方法
handler.channelRead()
服务端收到读的请求是,会进入这个方法。
接着通过handler.received来处理msg,这个handle的链路很长,比较复杂,我们需要逐步剖析
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
NettyChannel channel = NettyChannel.getOrAddChannel(ctx.channel(), this.url, this.handler);
this.handler.received(channel, msg);
}
服务端收到读的请求是,会进入这个方法。接着通过handler.received来处理msg ,而这个handler 是在服务发布的时候构建得。
DubboProtocol.createServer:
server = Exchangers.bind(url, this.requestHandler);
Exchanger.bind
public static ExchangeServer bind(URL url, ExchangeHandler handler) throws RemotingException {
if (url == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("url == null");
} else if (handler == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("handler == null");
} else {
url = url.addParameterIfAbsent("codec", "exchange");
return getExchanger(url).bind(url, handler);
}
}
通过扩展点选择到HeaderExchanger
public ExchangeServer bind(URL url, ExchangeHandler handler) throws RemotingException {
return new HeaderExchangeServer(Transporters.bind(url, new ChannelHandler[]{new DecodeHandler(new HeaderExchangeHandler(handler))}));
}
起链路如下:
MultiMessageHandler(复合消息处理) —> HeartbeatHandle(心跳消息处理,接收心跳并发送心跳响应) —> AllChannelHandler (业务线程转化处理器,把接收到的消息封装成ChannelEventRunnable可执行任
务给线程池处理)—> DecodeHandler (业务解码处理器)—> HeaderExchangeHandler —> DubboProtocol#requestHandler(new ExchangeHandlerAdapter())
而在构建 NettyServerHandler 得时候将 this 传了进去。this 即 NettyServer 。NettyServer是 AbstractPeer 得子类。所以 handler.received 此时会调用AbsstractPeer.received方法,这个方法用来判断服务端是否关闭了,如果关闭就直接返回,否则,通过handler处理链进行层层调用。
public void received(Channel ch, Object msg) throws RemotingException {
if (closed) {
return;
}
handler.received(ch, msg);
}
HeaderExchangeHandler.received
交互层请求响应处理,有三种处理方式
- handlerRequest,双向请求
- handler.received 单向请求
- handleResponse 响应消息
public void received(Channel channel, Object message) throws RemotingException {
ExchangeChannel exchangeChannel = HeaderExchangeChannel.getOrAddChannel(channel);
// 如果接收到的消息是请求类型
if (message instanceof Request) {
Request request = (Request)message;
// 如果请求是事件类型
if (request.isEvent()) {
this.handlerEvent(channel, request);
// 如果请求是双向类型
} else if (request.isTwoWay()) {
this.handleRequest(exchangeChannel, request);
// 如果请求不是事件类型也不是双向类型
} else {
this.handler.received(exchangeChannel, request.getData());
}
// 如果接收到的消息是响应类型
} else if (message instanceof Response) {
handleResponse(channel, (Response)message);
// 如果接收到的消息是字符串类型
} else if (message instanceof String) {
// 如果是客户端发送的字符串消息,则报错
if (isClientSide(channel)) {
Exception e = new Exception("Dubbo client can not supported string message: " + message + " in channel: " + channel + ", url: " + channel.getUrl());
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
// 如果是服务器端接收到的字符串消息,则进行处理
} else {
String echo = this.handler.telnet(channel, (String)message);
if (echo != null && echo.length() > 0) {
channel.send(echo);
}
}
// 如果接收到的消息不是请求、响应或字符串类型
} else {
this.handler.received(exchangeChannel, message);//单向请求
}
}
handleRequest
接着调用handleRequest方法。这个方法中,构建返回的对象Response,并且最终会通过异步的方式来把msg传递到invoker中进行调用 handler.reply
void handleRequest(final ExchangeChannel channel, Request req) throws RemotingException {
Response res = new Response(req.getId(), req.getVersion());
Object data;
if (req.isBroken()) {
data = req.getData();
String msg;
if (data == null) {
msg = null;
} else if (data instanceof Throwable) {
msg = StringUtils.toString((Throwable)data);
} else {
msg = data.toString();
}
res.setErrorMessage("Fail to decode request due to: " + msg);
res.setStatus((byte)40);
channel.send(res);
} else {
data = req.getData();
try {
CompletionStage<Object> future = this.handler.reply(channel, data);// 可以返回一个结果
future.whenComplete((appResult, t) -> {
try {
if (t == null) {
res.setStatus((byte)20);
res.setResult(appResult);
} else {
res.setStatus((byte)70);
res.setErrorMessage(StringUtils.toString(t));
}
channel.send(res);
} catch (RemotingException var5) {
logger.warn("Send result to consumer failed, channel is " + channel + ", msg is " + var5);
}
});
} catch (Throwable var6) {
res.setStatus((byte)70);
res.setErrorMessage(StringUtils.toString(var6));
channel.send(res);
}
}
}
此时的handler.reply,应该是DubboProtocol中构建的匿名内部类
所以调用handler.reply方法,自然就进入到了该匿名内部类中的reply方法中来。
DubboProtocol$requestHandler
private ExchangeHandler requestHandler = new ExchangeHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public CompletableFuture<Object> reply(ExchangeChannel channel, Object message) throws RemotingException {
//如果消息类型不是invocation,则抛出异常表示无法识别
if (!(message instanceof Invocation)) {
throw new RemotingException(channel, "Unsupported request: "
+ (message == null ? null : (message.getClass().getName() + ": " + message))
+ ", channel: consumer: " + channel.getRemoteAddress() + " --> provider: " + channel.getLocalAddress());
}
//获得请求参数
Invocation inv = (Invocation) message;
// 获取 invoker 领域对象,这个对象是在发布服务的时候构建,然后封装成 exporter 存在map里面的。
//根据key从发布的服务列表中查找到指定的服务端invoke,这个就是之前在讲服务发布时,涉及到的invoke对象。
Invoker<?> invoker = getInvoker(channel, inv);
// need to consider backward-compatibility if it's a callback
if (Boolean.TRUE.toString().equals(inv.getObjectAttachments().get(IS_CALLBACK_SERVICE_INVOKE))) {
String methodsStr = invoker.getUrl().getParameters().get("methods");
boolean hasMethod = false;
if (methodsStr == null || !methodsStr.contains(",")) {
hasMethod = inv.getMethodName().equals(methodsStr);
} else {
String[] methods = methodsStr.split(",");
for (String method : methods) {
if (inv.getMethodName().equals(method)) {
hasMethod = true;
break;
}
}
}
if (!hasMethod) {
logger.warn(new IllegalStateException("The methodName " + inv.getMethodName()
+ " not found in callback service interface ,invoke will be ignored."
+ " please update the api interface. url is:"
+ invoker.getUrl()) + " ,invocation is :" + inv);
return null;
}
}
RpcContext.getContext().setRemoteAddress(channel.getRemoteAddress());
//发起请求调用,此时得到的invoker对象
Result result = invoker.invoke(inv); // 发起对应调用
return result.thenApply(Function.identity());
}
//......省略代码
};
getInvoker
Invoker<?> invoker = getInvoker(channel, inv);
相当于根据key来获取一个value值
回顾下之前,在发布的时候,调用了一个DubboProtocol.export
public <T> Exporter<T> export(Invoker<T> invoker) throws RpcException {
URL url = invoker.getUrl();
String key = serviceKey(url);
DubboExporter<T> exporter = new DubboExporter(invoker, key, this.exporterMap);
// 构建好了之后,把key 和 value存进去
this.exporterMap.put(key, exporter);
}
// 而getInvoker也会从map中拿到这个值
Invoker<?> getInvoker(Channel channel, Invocation inv) throws RemotingException {
......
DubboExporter<?> exporter = (DubboExporter)this.exporterMap.get(serviceKey);
if (exporter == null) {
throw new RemotingException(channel, "Not found exported service: " + serviceKey + " in " + this.exporterMap.keySet() + ", may be version or group mismatch , channel: consumer: " + channel.getRemoteAddress() + " --> provider: " + channel.getLocalAddress() + ", message:" + this.getInvocationWithoutData(inv));
} else {
return exporter.getInvoker();
}
}
invoker.invoke()
invoker.invoke,发起本地服务调用,但是此时调用之前,invoke并不是一个直接调用的对象,而是包装过的。
在 ServiceConfig#doExportUrlsFor1Protocol 构建包装。最后的调用链路如下:
RegistryProtocol.InvokerDelegate.invoke —> DelegateProviderMetaDataInvoker.invoke —> AbstractProxyInvoker.invoke —> AbstractProxyInvoker(JavassistProxyFactory#getInvoker)
InvokerDelegate 未实现父类 InvokerWrapper invoke方法。进入到InvokerWrapper.invoke方法,这个是一个Invoker包装类,包装了URL地址信息和真正的Invoker代理对象。
public Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
}
DelegateProviderMetaDataInvoker
这里是一个委派类,它提供了服务提供者的元数序信息。
public Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
}
AbstractProxyInvoker
接着进入到AbstractProxyInvoker的invoke方法,在这个方法中,我们可以看到它会调用子类的doInvoke方法,获得返回结果。
其中proxy,表示服务端的对象实例,这个实例很显然是在构建动态代理Invoker对象时保存进来的。
public Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
try {
Object value = this.doInvoke(this.proxy, invocation.getMethodName(), invocation.getParameterTypes(), invocation.getArguments());
CompletableFuture<Object> future = this.wrapWithFuture(value);
CompletableFuture<AppResponse> appResponseFuture = future.handle((obj, t) -> {
AppResponse result = new AppResponse();
if (t != null) {
if (t instanceof CompletionException) {
result.setException(t.getCause());
} else {
result.setException(t);
}
} else {
result.setValue(obj);
}
return result;
});
return new AsyncRpcResult(appResponseFuture, invocation);
} catch (InvocationTargetException var5) {
if (RpcContext.getContext().isAsyncStarted() && !RpcContext.getContext().stopAsync()) {
this.logger.error("Provider async started, but got an exception from the original method, cannot write the exception back to consumer because an async result may have returned the new thread.", var5);
}
return AsyncRpcResult.newDefaultAsyncResult((Object)null, var5.getTargetException(), invocation);
} catch (Throwable var6) {
throw new RpcException("Failed to invoke remote proxy method " + invocation.getMethodName() + " to " + this.getUrl() + ", cause: " + var6.getMessage(), var6);
}
}
JavassistProxyFactory.doInvoke
最后进入到具体的子类,也就是在服务的发布的时候通过 构建的
@Override
public <T> Invoker<T> getInvoker(T proxy, Class<T> type, URL url) {
// TODO Wrapper cannot handle this scenario correctly: the classname contains '$'
final Wrapper wrapper = Wrapper.getWrapper(proxy.getClass().getName().indexOf('$') < 0 ? proxy.getClass() : type);
return new AbstractProxyInvoker<T>(proxy, type, url) {
@Override
protected Object doInvoke(T proxy, String methodName,
Class<?>[] parameterTypes,
Object[] arguments) throws Throwable {
return wrapper.invokeMethod(proxy, methodName, parameterTypes, arguments);
}
};
}
服务实例是什么时候生成的
从上面的代码中可以看到,getInvoker中传递的proxy,实际就是对象实例,而这个参数是在serviceConfig中,
Invoker<?> invoker = PROXY_FACTORY.getInvoker(ref, (Class) interfaceClass, url);
而 ref这个成员变量,是在spring启动时创建bean对象时,会注入这个对象的实例保存到ref中。
总结
至此,服务消费的处理流程就分析完了。
ow new RpcException("Failed to invoke remote proxy method " + invocation.getMethodName() + " to " + this.getUrl() + ", cause: " + var6.getMessage(), var6);
}
}
#### JavassistProxyFactory.doInvoke
最后进入到具体的子类,也就是在服务的发布的时候通过 构建的
```java
@Override
public Invoker getInvoker(T proxy, Class type, URL url) {
// TODO Wrapper cannot handle this scenario correctly: the classname contains '$'
final Wrapper wrapper = Wrapper.getWrapper(proxy.getClass().getName().indexOf('$') < 0 ? proxy.getClass() : type);
return new AbstractProxyInvoker(proxy, type, url) {
@Override
protected Object doInvoke(T proxy, String methodName,
Class[] parameterTypes,
Object[] arguments) throws Throwable {
return wrapper.invokeMethod(proxy, methodName, parameterTypes, arguments);
}
};
}
服务实例是什么时候生成的
从上面的代码中可以看到,getInvoker中传递的proxy,实际就是对象实例,而这个参数是在serviceConfig中,
Invoker<?> invoker = PROXY_FACTORY.getInvoker(ref, (Class) interfaceClass, url);
而 ref这个成员变量,是在spring启动时创建bean对象时,会注入这个对象的实例保存到ref中。
总结
至此,服务消费的处理流程就分析完了。
[外链图片转存中…(img-UMv5Gkfe-1702461052791)]