LangChain学习二:提示-实战(上半部分)
文章目录
- 上一节内容:LangChain学习一:模型-实战
- 学习目标:提示词及提示词模板的运用
- 学习内容一:什么是提示词?
- 学习内容二:提示词模板
-
- 2.1 入门
- 2.2 模板格式
- 2.3 验证模板
- 2.4 序列化提示模板
- 2.5 将少量示例传递给提示模板(few_shot)
- 2.6 选择提示模板的示例
-
-
- 2.6.1 基于长度的示例选择器
-
- 学习内容三:聊天提示模板
-
- 3.1 聊天提示模板
-
- 3.1 .1 实战:首先需要声明和定义一个模板
- 3.1 .2 实战:把提示词模板放入系统消息提示模板、人类消息提示模板等,并进行组合放入大模型
-
- 3.1.2.1 提示词模板放入SystemMessagePromptTemplate、HumanMessagePromptTemplate、ChatPromptTemplate等
- 3.1.2.2 不同类型的 MessagePromptTemplate
- 3.2 实例选择器
上一节内容:LangChain学习一:模型-实战
LangChain学习一:模型-实战
学习目标:提示词及提示词模板的运用
学习内容一:什么是提示词?
大白话就是我们问大模型的问题
学习内容二:提示词模板
提示模板是生成提示的可重复方法。
就是一个字符串,这个字符串里面包含{变量},我们要用的时候把变量进行赋值,赋值之后我们的模板就实例化成了一句话
提示模板可能包含:
对语言模型的指导,
一组少量示例,以帮助语言模型生成更好的响应,
对语言模型的提问。
2.1 入门
from langchain import PromptTemplate
template = """
给我介绍一下{product}?
"""
prompt = PromptTemplate(
input_variables=["product"],
template=template,
)
out=prompt.format(product="华为")
print(out)

{product}这里声明了一个变量,也可以说是占位符(可以是多个),
然后PromptTemplate进行实例化input_variables代表变量的列表,这里的值一定要和我们声明的相同,template就是我们的定义模板是那句话
prompt.format就是通过变量名='实际值’进行实例化
还有一种方式是,先声明后赋值
from langchain import PromptTemplate
template = """
给我介绍一下{product}?
"""
prompt_template = PromptTemplate.from_template(template)
out=prompt_template.format(product="华为")
print(out)
2.2 模板格式
以上2种情况是默认Python f-string处理的,比如说,下面这个例子,我们就想让字符串里面包含{ok}
from langchain import PromptTemplate
template = """
给我介绍一下{product}{ok}?
"""
prompt = PromptTemplate(
input_variables=["product"],
template=template,
)
out=prompt.format(product="华为")
print(out)
这时候我们就可以通过 template_format 参数指定其他模板格式:
这里我们介绍一下 jinja2

需要加载依赖包
pip install jinja2
from langchain import PromptTemplate
# Make sure jinja2 is installed before running this
template = "请给我介绍一下 {{ project }} {ok}"
prompt_template = PromptTemplate.from_template(template=template, template_format="jinja2")
out=prompt_template.format(project="华为")
print(out)
这时候我们发现{ok}就可以显示了
2.3 验证模板
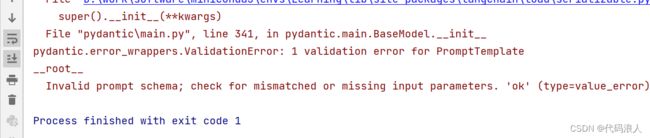
我们在实例化PromptTemplate的时候input_variables可以帮我们校验
template里面是否包含变量,如果不包含就会报错
prompt_template = PromptTemplate(template=template,
input_variables=["project", "foo"])

我们可以通过validate_template=False来禁止此行为
template = "请给我介绍一下 {project}"
prompt_template = PromptTemplate(template=template,
input_variables=["project", "foo"],
validate_template=False)
out=prompt_template.format(project="华为")

注意注意,这里out=prompt_template.format(project="华为")project一定要在template 里面存在,并且不能有其他的变量,不然都会报错
2.4 序列化提示模板
from langchain import PromptTemplate
template = "请给我介绍一下 {project}"
prompt_template = PromptTemplate.from_template(template=template)
# 保存
prompt_template.save("awesome_prompt.json") # Save to JSON file
from langchain.prompts import load_prompt
loaded_prompt = load_prompt("awesome_prompt.json")
out=loaded_prompt.format(project="华为")
print(out)
2.5 将少量示例传递给提示模板(few_shot)
from langchain import PromptTemplate, FewShotPromptTemplate
# 首先,创建少数快照示例的列表。
examples = [
{"word": "开心", "antonym": "悲伤"},
{"word": "高", "antonym": "低"},
]
#接下来,我们指定模板来格式化我们提供的示例。
#为此,我们使用“PromptTemplate”类。
example_formatter_template = """
单词: {word}
反义词: {antonym}\n
"""
example_prompt = PromptTemplate(
input_variables=["word", "antonym"],
template=example_formatter_template,
)
# 最后,我们创建“FewShotPromptTemplate”对象。
few_shot_prompt = FewShotPromptTemplate(
# 以下是我们要插入到提示中的示例。
examples=examples,
# 当我们将示例插入到提示中时,这就是我们想要格式化示例的方式。
example_prompt=example_prompt,
#前缀是位于提示中示例之前的一些文本。
#通常,这包括入侵。
prefix="给出每个输入的反义词",
#后缀是在提示中的示例后面的一些文本。
#通常,这是用户输入的位置
suffix="单词: {input}\n反义词:",
# 输入变量是整个提示所期望的变量.
input_variables=["input"],
#example_separator是用于将前缀、examples和后缀连接在一起的字符串。
example_separator="",
)
#我们现在可以使用“format”方法生成提示。
print(few_shot_prompt.format(input="big"))
结果
给出每个输入的反义词
单词: 开心
反义词: 悲伤
单词: 高
反义词: 低
单词: 大
反义词:
2.6 选择提示模板的示例
通俗点来说就是通过方法找到相似的示例,有以下几种方式
-
LengthBased ExampleSelector(基于长度的示例选择器):这是一种示例选择器,它根据示例的长度来选择要使用的示例。较长的示例可能包含更多的细节和信息,因此可以更全面地回答用户的问题。
-
最大边际相关性 ExampleSelector:这种示例选择器基于与输入之间的边际相关性来选择示例。它计算每个示例与输入之间的相关性,并选择具有最高相关性的示例作为回答。
-
NGram 重叠 ExampleSelector:NGram 重叠示例选择器根据输入和示例之间的共享 N-gram 片段来选择示例。它通过匹配输入和示例之间的共同 N-gram 片段来确定最相关的示例。
-
相似度 ExampleSelector:相似度示例选择器使用文本相似度度量来选择最相关的示例。它计算输入和示例之间的相似度,然后选择与输入最相似的示例作为回答。
这里举个例子介绍下,后面单独出一节来介绍
2.6.1 基于长度的示例选择器
总长度是由max_length控制的,如果我们输入的长一些,就会少从examples 拿一些,输入短,则反之
from langchain import PromptTemplate, FewShotPromptTemplate
# 首先,创建少数快照示例的列表。
from langchain.prompts import LengthBasedExampleSelector
examples = [
{"word": "开心", "antonym": "悲伤"},
{"word": "高", "antonym": "低"},
]
# 接下来,我们指定模板来格式化我们提供的示例。
# 为此,我们使用“PromptTemplate”类。
example_formatter_template = """
单词: {word}
反义词: {antonym}\n
"""
example_prompt = PromptTemplate(
input_variables=["word", "antonym"],
template=example_formatter_template,
)
#我们将使用' LengthBasedExampleSelector '来选择示例。
example_selector = LengthBasedExampleSelector(
# 这些是可供选择的例子。
examples=examples,
#这是用于格式化示例的PromptTemplate。
example_prompt=example_prompt,
# 这是格式化示例的最大长度。
# 长度由下面的get_text_length函数测量。
max_length=25,
)
# 我们现在可以使用' example_selector '来创建' FewShotPromptTemplate '。
dynamic_prompt = FewShotPromptTemplate(
# We provide an ExampleSelector instead of examples.
example_selector=example_selector,
example_prompt=example_prompt,
prefix="给出每个输入的反义词",
suffix="单词: {input}\n反义词:",
input_variables=["input"],
example_separator="",
)
# We can now generate a prompt using the `format` method.
print(dynamic_prompt.format(input="big"))
学习内容三:聊天提示模板
本次介绍一下几个
- 聊天提示模板
- LLM提示模板
- 示例选择器
- 输出解析器
3.1 聊天提示模板
上一节介绍了,模型有聊天模型,也是我们常用的。这一节,我们看一下如何更好地使用聊天模型。聊天模型和LLM模型在上一节也说过了,是有不同的,聊天模型的每条信息
都与一个角色 进行关联
因此,LangChain提供了几个相关的提示模板,以便轻松构建和处理提示。在查询聊天模型时,建议您使用这些与聊天相关的提示模板,而不是PromptTemplate,以充分发挥基础聊天模型的潜力。
"""
@FileName:chat_prompt.py
@Description:
@Author:lucky
@Time:2023/12/9 10:41
"""
from langchain.prompts import (
ChatPromptTemplate,
PromptTemplate,
SystemMessagePromptTemplate,
AIMessagePromptTemplate,
HumanMessagePromptTemplate,
)
from langchain.schema import (
AIMessage,
HumanMessage,
SystemMessage
)
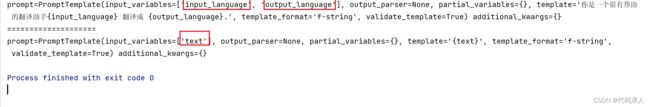
template = "你是一个很有帮助的翻译助手{input_language} 翻译成 {output_language}."
system_message_prompt = SystemMessagePromptTemplate.from_template(template)
print(system_message_prompt)
human_template = "{text}"
print("====================")
human_message_prompt = HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template(human_template)
print(human_message_prompt)
-
ChatPromptTemplate (聊天模板):
这个模板用于生成对话的开头,它通常包含一些问候语或提醒用户如何使用机器人的信息。 -
PromptTemplate (提示模板):
这个模板用于为用户提供特定主题或任务的提示。它可以是一个问题,要求用户提供更多信息,或者是一个指导性的陈述,告诉用户下一步该做什么 -
SystemMessagePromptTemplate(系统消息提示模板):
这个模板用于生成系统消息,向用户提供一些重要的信息,比如机器人无法回答某个问题、请求用户提供更多细节等等。 -
AIMessagePromptTemplate (AI消息提示模板):
这个模板用于生成 AI 机器人的回答。它基于预训练的模型,使用大量的数据和算法来生成针对用户问题的响应。 -
HumanMessagePromptTemplate(人类消息提示模板):
这个模板用于生成人类操作者的回答,当机器人无法回答某个问题时,会将问题转交给人类操作者进行回答。
其中{}里面是变量名称,所以不要用{}在你的提示词中,如果用,那就不要用LangChain提示词模板。
3.1 .1 实战:首先需要声明和定义一个模板
from langchain.callbacks import StreamingStdOutCallbackHandler
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.prompts import (
ChatPromptTemplate,
PromptTemplate,
SystemMessagePromptTemplate,
AIMessagePromptTemplate,
HumanMessagePromptTemplate,
)
from langchain.prompts.chat import ChatPromptValue
from langchain.schema import (
AIMessage,
HumanMessage,
SystemMessage
)
声明一个模板,注意:{变量} 提示词模板的意思就是一个框架里面有一些变量,这些变量也可以理解成为占位符。后面使用提示词模板只要把里面的变量进行具体化就可以了
template = "你是一个很有帮助的翻译助手{input_language} 翻译成 {output_language}."
3.1 .2 实战:把提示词模板放入系统消息提示模板、人类消息提示模板等,并进行组合放入大模型
SystemMessagePromptTemplate、HumanMessagePromptTemplate等都有一个from_template方法,用于把我们提示词模板放入
3.1.2.1 提示词模板放入SystemMessagePromptTemplate、HumanMessagePromptTemplate、ChatPromptTemplate等
from langchain.callbacks import StreamingStdOutCallbackHandler
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.prompts import (
ChatPromptTemplate,
PromptTemplate,
SystemMessagePromptTemplate,
AIMessagePromptTemplate,
HumanMessagePromptTemplate,
)
from langchain.prompts.chat import ChatPromptValue
from langchain.schema import (
AIMessage,
HumanMessage,
SystemMessage
)
template = "你是一个很有帮助的翻译助手{input_language} 翻译成 {output_language}."
system_message_prompt = SystemMessagePromptTemplate.from_template(template)
print(f"========system_message_prompt的格式化结果:{system_message_prompt}============\n\n\n")
human_template = "{text}"
human_message_prompt = HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template(human_template)
print(f"========human_template的格式化结果:{human_template}============\n\n\n")

这时候我们可以构建一个ChatPromptTemplate(聊天模板),把我们的(系统消息提示模板)和(人类消息提示模板)组合起来,放入大模型。
组合方式:ChatPromptTemplate提供了from_messages方法
chat_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([system_message_prompt, human_message_prompt])
print(f"========chat_prompt的格式化结果:{chat_prompt}============3\n\n\n")
组合之后我们可以看一下chat_prompt 这个对象里面有什么,
input_variables:包含了所有的变量
messages:是个列表:包含了所有的模板对象

我们可以format_prompt实例化(就是把模板里面的变量进行赋值),然后通过to_messages打印他的实例结构结果
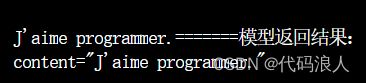
output_to_messages=chat_prompt.format_prompt(input_language="English", output_language="French", text="I love programming.").to_messages()
print(output_to_messages)
![]()
或者你也可以直接使用format,与上面不同的是,format直接返回的是值,或者你也可以用上面的方式使用to_string方法,都是可行的
output = chat_prompt.format(input_language="English", output_language="French", text="I love programming.")
print(f"========format的结果:{output}============4\n\n\n")
# or alternatively
output_2 = chat_prompt.format_prompt(input_language="English", output_language="French",
text="I love programming.").to_string()

总结一下:以上把我们的(系统消息提示模板)和(人类消息提示模板)组合起来,放入ChatPromptTemplate(聊天模板)一共用了三个步骤:
- 分别实例化了 系统消息提示模板 和 人类消息提示模板
- 声明ChatPromptTemplate对象的同时把相关模板实例也放进去
- 对ChatPromptTemplate对象模板进行使用,把变量名换成我们想要的
其上以上三个步骤可以作为一个步骤直接使用,也就是不使用模板的方式,我们观察一下,上面的多有工作都是为了节省一些重复的工作,但是送进大模型的就是具体的话,所以直接用下面的方式
output_3=ChatPromptValue(messages=[
SystemMessage(content='你是把英语翻译成法语的得力助手。', additional_kwargs={}),
HumanMessage(content='I love programming.', additional_kwargs={})])
print(f"========format_prompt的结果:{output_3}===========5\n\n\n")
chat = ChatOpenAI(streaming=True, callbacks=[StreamingStdOutCallbackHandler()],
verbose=True,
# callbacks=[callback],
openai_api_key="none",
openai_api_base="http://127.0.0.1:8000/v1",
model_name="Qwen-7B-Chat"
)
resp = chat(output_3.messages)
print(f"=======模型返回结果:\n{resp}\n\n")
3.1.2.2 不同类型的 MessagePromptTemplate
LangChain 提供了不同类型的 MessagePromptTemplate。其中最常用的是 AIMessagePromptTemplate、SystemMessagePromptTemplate 和 HumanMessagePromptTemplate,分别用于创建 AI 消息、系统消息和人类消息。
同样自定义也有两种方式
- 使用模板
- 直接实例化
使用模板
chat_message_prompt = ChatMessagePromptTemplate.from_template(role="Jedi", template=prompt)
chat_message_out=chat_message_prompt.format(subject="force")
print(f"========chat_message_prompt的格式化结果:{chat_message_out}============7\n\n\n")
直接实例化
out=ChatMessage(content='May the force be with you', additional_kwargs={}, role='Jedi')
print(f"========chat_message_prompt的格式化结果:{out}============8\n\n\n")
至于这个做啥的,这个就是看你自己的场景了。
LangChain 还提供了 MessagesPlaceholder,该占位符可以在格式化期间完全控制要呈现的消息。当您不确定应该使用哪个消息提示模板的角色或者希望在格式化期间插入消息列表时,这可能非常有用。
就是再上一个小节里面,我们把不同的提示模板进行组合,但是前提条件都是我们知道有几个,占位符就是让我们在前提不知道几个的情况下进行的
from langchain.prompts import MessagesPlaceholder
human_prompt = "总结一下我们到目前为止的谈话 {word_count}单词."
human_message_template = HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template(human_prompt)
chat_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="conversation"), human_message_template])
这里就是使用了conversation占位符。下面我们就可再次组合
human_message = HumanMessage(content="What is the best way to learn programming?")
ai_message = AIMessage(content="""\
1. Choose a programming language: Decide on a programming language that you want to learn.
2. Start with the basics: Familiarize yourself with the basic programming concepts such as variables, data types and control structures.
3. Practice, practice, practice: The best way to learn programming is through hands-on experience\
""")
out=chat_prompt.format_prompt(conversation=[human_message, ai_message], word_count="10").to_messages()
print(out)
[HumanMessage(content='What is the best way to learn programming?', additional_kwargs={}),
AIMessage(content='1. Choose a programming language: Decide on a programming language that you want to learn. 2. Start with the basics: Familiarize yourself with the basic programming concepts such as variables, data types and control structures. 3. Practice, practice, practice: The best way to learn programming is through hands-on experience', additional_kwargs={}),
HumanMessage(content='Summarize our conversation so far in 10 words.', additional_kwargs={})]
3.2 实例选择器
说白了就是选择一些例子,给大模型。让大模型参考给出答案
下面介绍一些常用的
-
LengthBased ExampleSelector(基于长度的示例选择器):这是一种示例选择器,它根据示例的长度来选择要使用的示例。较长的示例可能包含更多的细节和信息,因此可以更全面地回答用户的问题。
-
最大边际相关性 ExampleSelector:这种示例选择器基于与输入之间的边际相关性来选择示例。它计算每个示例与输入之间的相关性,并选择具有最高相关性的示例作为回答。
-
NGram 重叠 ExampleSelector:NGram 重叠示例选择器根据输入和示例之间的共享 N-gram 片段来选择示例。它通过匹配输入和示例之间的共同 N-gram 片段来确定最相关的示例。
-
相似度 ExampleSelector:相似度示例选择器使用文本相似度度量来选择最相关的示例。它计算输入和示例之间的相似度,然后选择与输入最相似的示例作为回答。