Pytorch学习(1)
引用文章pytorch入门(超详细)
什么是pytorch?
pytorch是一个基于Python的科学计算包,它主要有两个用途:
类似于Numpy但是能利用GPU加速
一个非常灵活和快速用于深度学习的研究平台。
import torch
#构建一个5x3的未初始化的矩阵
x = torch.empty(5,3)
print(x)
#tensor([[9.9184e-39, 8.7245e-39, 9.2755e-39],
[8.9082e-39, 9.9184e-39, 8.4490e-39],
[9.6429e-39, 1.0653e-38, 1.0469e-38],
[4.2246e-39, 1.0378e-38, 9.6429e-39],
[9.2755e-39, 9.7346e-39, 1.0745e-38]])
pytorch基础用法
tensor与numpy的转化
torch tensor和numpy公用一段空间,因此改变其中一个的值,会影响另外一个值。
a = torch.ones(5)
print(a)
#tensor([ 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.])
b = a.numpy()
print(b)
#[1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
可以用tensor.to()将创建的张量转移至gpu或cpu
import torch
x = torch.empty(5, 3)
print(x)
if torch.cuda.is_available():
device = torch.device("cuda") # 一个CUDA device对象。
y = torch.ones_like(x, device=device) # 直接在GPU上创建tensor
print(x)
x = x.to(device) # 也可以使用``.to("cuda")``把一个tensor从CPU移到GPU上
z = x + y
print(z)
print(z.to("cpu", torch.double)) # ``.to``也可以在移动的过程中修改dtype
#输出:
tensor([[-4.2086e+02, 6.1517e-43, -4.2086e+02],
[ 6.1517e-43, -4.2098e+02, 6.1517e-43],
[-4.2098e+02, 6.1517e-43, -4.2096e+02],
[ 6.1517e-43, -4.2096e+02, 6.1517e-43],
[-4.2097e+02, 6.1517e-43, -4.2097e+02]])
tensor([[-4.2086e+02, 6.1517e-43, -4.2086e+02],
[ 6.1517e-43, -4.2098e+02, 6.1517e-43],
[-4.2098e+02, 6.1517e-43, -4.2096e+02],
[ 6.1517e-43, -4.2096e+02, 6.1517e-43],
[-4.2097e+02, 6.1517e-43, -4.2097e+02]])
tensor([[-419.8618, 1.0000, -419.8618],
[ 1.0000, -419.9810, 1.0000],
[-419.9810, 1.0000, -419.9595],
[ 1.0000, -419.9595, 1.0000],
[-419.9731, 1.0000, -419.9731]], device='cuda:0')
tensor([[-419.8618, 1.0000, -419.8618],
[ 1.0000, -419.9810, 1.0000],
[-419.9810, 1.0000, -419.9595],
[ 1.0000, -419.9595, 1.0000],
[-419.9731, 1.0000, -419.9731]], dtype=torch.float64)
如果两个张量不在同一个device,则编译出错。
Autograd:自动求导
PyTorch的核心是autograd包。如果它的属性requires_grad是True,那么PyTorch就会追踪所有与之相关的operation。当完成(正向)计算之后, 我们可以调用backward(),PyTorch会自动的把所有的梯度都计算好。其中grade属性包含tensor相关的梯度。
可以调用detach(),组织pytorch记录梯度计算的信息,节约内存。例如在模型的预测时,我们不需要计算梯度,可以使用 with torch.no_grad()。
Autograd实现与Fuction类相关,他们完整记录了计算的流程,因此每个tensor(初始建立的tensor除外)有一个grad_fn属性
x = torch.ones(2, 2, requires_grad=True)
print(x)
y = x + 2
z = y * y * 3
out = z.mean()
out.backward()
print(x.grad)
#
tensor([[1., 1.],
[1., 1.]], requires_grad=True)
tensor([[4.5000, 4.5000],
[4.5000, 4.5000]])在定义x时,一定要设置梯度,否则运行错误。
用Pytorch训练网络
阅读上一篇文章,总体将pytorch的训练步骤划分为以下几个步骤:
- 定义一个网络模型,通常有一系列可以训练的参数
- 迭代一个数据集(dataset)
- 处理网络的输入
- 计算损失函数loss(调用forward正向传播)
- 计算loss对与各个参数的梯度(用backward反向传播)
- 更新参数
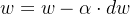
pytorch.nn.conv2d(inputs_channel, outputs_channel, kernel_size)
pytorch.nn.function.max_pool2d(kernel_size, stride,padding) stride默认为kernel_size
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class Net(nn.Model):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.conv2d(1, 6, 5)
self.conv2 = nn.conv2d(6, 16, 5)
self.fc1 = nn.linear(16*5*5, 120)
self.fc2 = nn.linear(120, 84)
self.fc3 = nn.linear(84, 10)
def forward(self, x):
#32*32 -> 28*28 -> 14*14
x = self.conv1(x)
x = F.relu(x)
x = F.max_pool2d(x, (2, 2))
#14*14 -> 10*10 -> 5*5
x = self.conv2(x)
x = F.relu(x)
x = F.max_pool2d(x, (2, 2))
x = x.view(-1, self.num_flat_features(x))
x = self.fc1(x)
x = F.relu(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = F.relu(x)
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
def num_flat_features(self, x):
size = x.size[1:] #除了batch以外的其他维度
num_features = 1
for s in size:
num_features *= s
return num_features
#建立一个Net类实例
net = Net()测试网络
随机尝试用一个32*32的输入来检验网络,而MNIST是28*28。
input = torch.randn(1, 1, 32, 32)
out = net(input)
print(out)
#输出:
tensor([[-0.1178, 0.1123, 0.0038, -0.1217, -0.0899, 0.0041, -0.0068, 0.0319,
0.0486, 0.0315]], grad_fn=)