Android ClassLoader类加载机制
Android ClassLoader类加载机制
概述
我们知道Java中的 ClassLoader可以加载 jar 文件和Class文件。在Android中,它们加载的是dex文件。
Android中的ClassLoader类型分别是系统类加载器和自定义加载器。其中系统类加载器主要包括3种,分别是 BootClassLoader 、PathClassLoader 和 DexClassLoader 。
- BootClassLoader
Android 系统启动时会使用BootClassLoader来预加载常用类。 - DexClassLoader
DexClassLoader可以加载dex文件以及包含dex的压缩文件(apk和jar文件) - PathClassLoader
Android 系统使用PathClassLoader来加载系统类和应用程序的类
platform/libcore/dalvik/src/main/java/dalvik/system
- PathClassLoader.java
- DexClassLoader.java
- BaseDexClassLoader.java
- DexPathList.java
- DexFile.java
platform/art/runtime/native
- dalvik_system_DexFile.cc
platform/ojluni/src/main/java/java/lang/
- ClassLoader.java
五种类加载构造函数
1. PathClassLoader
它提供了一个简单的ClassLoader实现,它对列表进行操作的文件和目录,但没有尝试从网络加载类.
public class PathClassLoader extends BaseDexClassLoader {
public PathClassLoader(String dexPath, ClassLoader parent) {
super(dexPath, null, null, parent);
}
public PathClassLoader(String dexPath, String librarySearchPath, ClassLoader parent{
super(dexPath, null, librarySearchPath, parent);
}
@libcore.api.CorePlatformApi
public PathClassLoader(
String dexPath, String librarySearchPath, ClassLoader parent,
ClassLoader[] sharedLibraryLoaders) {
super(dexPath, librarySearchPath, parent, sharedLibraryLoaders);
}
}
2. PathClassLoader
一个类装入器,从包含classes.dex条目的.jar和code .apk文件中装入类。这可用于执行未作为应用程序的一部分安装的代码.
public class DexClassLoader extends BaseDexClassLoader {
public DexClassLoader(String dexPath, String optimizedDirectory,
String librarySearchPath, ClassLoader parent) {
super(dexPath, null, librarySearchPath, parent);
}
}
3. BaseDexClassLoader
用于定制如何报告dex文件加载的钩子。同时负责初始化DexPathList
public class BaseDexClassLoader extends ClassLoader {
@UnsupportedAppUsage
private final DexPathList pathList;
public BaseDexClassLoader(String dexPath,
String librarySearchPath, ClassLoader parent, ClassLoader[] sharedLibraryLoaders,
boolean isTrusted) {
super(parent);
//在创建路径列表之前设置共享库。ART依赖于类加载器层次结构在加载dex文件之前完成。
this.sharedLibraryLoaders = sharedLibraryLoaders == null
? null
: Arrays.copyOf(sharedLibraryLoaders, sharedLibraryLoaders.length);
this.pathList = new DexPathList(this, dexPath, librarySearchPath, null, isTrusted);
if (reporter != null) {
reportClassLoaderChain();
}
}
//设置dex加载通知的报告器。一旦设置完毕,BaseDexClassLoader的所有新实例都将在构建已加载的dex文件时报告。
@libcore.api.CorePlatformApi
public static void setReporter(Reporter newReporter) {
reporter = newReporter;
}
}
4. ClassLoader
类加载器是负责装入类的对象
public abstract class ClassLoader {
private ClassLoader parent; //记录父类加载器
protected ClassLoader() {
this(getSystemClassLoader(), false);
}
protected ClassLoader(ClassLoader parentLoader) {
this(parentLoader, false);
}
ClassLoader(ClassLoader parentLoader, boolean nullAllowed) {
if (parentLoader == null && !nullAllowed) {
//父类的类加载器为空,则抛出异常
throw new NullPointerException("parentLoader == null && !nullAllowed");
}
parent = parentLoader;
}
}
//----------------------------------------
static private class SystemClassLoader {
public static ClassLoader loader = ClassLoader.createSystemClassLoader();
}
private static ClassLoader createSystemClassLoader() {
String classPath = System.getProperty("java.class.path", ".");
String librarySearchPath = System.getProperty("java.library.path", "");
return new PathClassLoader(classPath, librarySearchPath, BootClassLoader.getInstance());
}
PathClassLoader加载类的过程
在\libcore\dalvik\src\main\java\dalvik\system\DexClassLoader.java文件下:
public class PathDexClassLoader extends BaseDexClassLoader {
public PathDexClassLoader (String dexPath, String optimizedDirectory,String libraryPath, ClassLoader parent) {
super(dexPath, new File(optimizedDirectory), libraryPath, parent);
}
}
在此处调用了父类BaseDexClassLoader的构造函数,在同一目录下的BaseDexClassLoader.java中:
public BaseDexClassLoader(String dexPath, File optimizedDirectory,
String libraryPath, ClassLoader parent) {
super(parent);
this.pathList = new DexPathList(this, dexPath, libraryPath, optimizedDirectory);
}
此处调用了父类ClassLoader的构造函数,然后生成一个DexPathList对象,在同一目录下的DexPathList.java文件中:
public DexPathList(ClassLoader definingContext, String dexPath,
String libraryPath, File optimizedDirectory) {
//省略参数校验以及异常处理的代码
this.definingContext = definingContext;
……
this.dexElements = makeDexElements(splitDexPath(dexPath), optimizedDirectory,
suppressedExceptions);
……
this.nativeLibraryDirectories = splitLibraryPath(libraryPath);
}
在DexPathList.java文件中有一段关键的代码makeDexElements :
private static Element[] makeDexElements(ArrayList<File> files, File optimizedDirectory,
ArrayList<IOException> suppressedExceptions) {
// ……
for (File file : files) {
File zip = null;
DexFile dex = null;
String name = file.getName();
if (name.endsWith(DEX_SUFFIX)) {//.dex文件
// Raw dex file (not inside a zip/jar).
try {
dex = loadDexFile(file, optimizedDirectory);
} catch (IOException ex) {
System.logE("Unable to load dex file: " + file, ex);
}
} else if (name.endsWith(APK_SUFFIX) || name.endsWith(JAR_SUFFIX)
|| name.endsWith(ZIP_SUFFIX)) {
//.apk .jar .zip文件
zip = file;
try {
dex = loadDexFile(file, optimizedDirectory);
} catch (IOException suppressed) {
suppressedExceptions.add(suppressed);
}
} else if (file.isDirectory()) {
// We support directories for looking up resources.
// This is only useful for running libcore tests.
elements.add(new Element(file, true, null, null));
} else {
System.logW("Unknown file type for: " + file);
}
}
//……
return elements.toArray(new Element[elements.size()]);
}
我们再点进
loadDexFile(file, optimizedDirectory)方法看一下:
private static DexFile loadDexFile(File file, File optimizedDirectory)
throws IOException {
if (optimizedDirectory == null) {
return new DexFile(file);
} else {
String optimizedPath = optimizedPathFor(file, optimizedDirectory);
return DexFile.loadDex(file.getPath(), optimizedPath, 0);
}
}
//生成odex的目录
private static String optimizedPathFor(File path,
File optimizedDirectory) {
String fileName = path.getName();
if (!fileName.endsWith(DEX_SUFFIX)) {
int lastDot = fileName.lastIndexOf(".");
if (lastDot < 0) {
fileName += DEX_SUFFIX;
} else {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(lastDot + 4);
sb.append(fileName, 0, lastDot);
sb.append(DEX_SUFFIX);
fileName = sb.toString();
}
}
File result = new File(optimizedDirectory, fileName);
return result.getPath();
}
optimizedPathFor主要是对文件的后缀进行修正,如果没有后缀名,就在末尾加上.dex,如果文件结尾不是.dex,就将后缀替换为.dex,然后创建我们的.dex文件,然后返回我们创建的.dex文件的路径,继续执行DexFile.loadDex() 函数:
static public DexFile loadDex(String sourcePathName, String outputPathName,
int flags) throws IOException {
return new DexFile(sourcePathName, outputPathName, flags);
}
这里直接返回了一个DexFile对象,下面来看看这个类的构造函数:
//sourceName 我们要加载的自己的.jar文件路径
// outputName 在optimizedPathFor()中修正的dex的路径
private DexFile(String sourceName, String outputName, int flags) throws IOException {
if (outputName != null) {
try {
String parent = new File(outputName).getParent();
if (Libcore.os.getuid() != Libcore.os.stat(parent).st_uid) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Optimized data directory " + parent
+ " is not owned by the current user. Shared storage cannot protect"
+ " your application from code injection attacks.");
}
} catch (ErrnoException ignored) {
// assume we'll fail with a more contextual error later
}
}
//我们的重点就是在openDexFile()函数上
mCookie = openDexFile(sourceName, outputName, flags);
mFileName = sourceName;
guard.open("close");
//System.out.println("DEX FILE cookie is " + mCookie);
}
openDexFile函数的返回值是一个整型,保存在mCookie中,文件名保存在mFileName中:
private static int openDexFile(String sourceName, String outputName,
int flags) throws IOException {
return openDexFileNative(new File(sourceName).getCanonicalPath(),
(outputName == null) ? null : new File(outputName).getCanonicalPath(),
flags);
}
在openDexFile()中只是调用了openDexFileNative () ,继续跟入在\dalvik\vm\native\dalvik _system_DexFile.cpp文件中的openDexFileNative() 函数,接下重点就在这个函数:
static void Dalvik_dalvik_system_DexFile_openDexFileNative(const u4* args,
JValue* pResult)
{
//args[0]: sourceName java层传入的
//args[1]: outputName
StringObject* sourceNameObj = (StringObject*) args[0];
StringObject* outputNameObj = (StringObject*) args[1];
DexOrJar* pDexOrJar = NULL;
JarFile* pJarFile;
RawDexFile* pRawDexFile;
//DexOrJar* JarFile* RawDexFile* 目录
char* sourceName;
char* outputName;
//……
sourceName = dvmCreateCstrFromString(sourceNameObj);
if (outputNameObj != NULL)
outputName = dvmCreateCstrFromString(outputNameObj);
else
outputName = NULL;
/*判断要加载的dex是否为系统中的dex文件
* gDvm ???
*/
if (dvmClassPathContains(gDvm.bootClassPath, sourceName)) {
ALOGW("Refusing to reopen boot DEX '%s'", sourceName);
dvmThrowIOException(
"Re-opening BOOTCLASSPATH DEX files is not allowed");
free(sourceName);
free(outputName);
RETURN_VOID();
}
/*
* Try to open it directly as a DEX if the name ends with ".dex".
* If that fails (or isn't tried in the first place), try it as a
* Zip with a "classes.dex" inside.
*/
//判断sourcename扩展名是否是.dex
if (hasDexExtension(sourceName)
&& dvmRawDexFileOpen(sourceName, outputName, &pRawDexFile, false) == 0) {
ALOGV("Opening DEX file '%s' (DEX)", sourceName);
pDexOrJar = (DexOrJar*) malloc(sizeof(DexOrJar));
pDexOrJar->isDex = true;
pDexOrJar->pRawDexFile = pRawDexFile;
pDexOrJar->pDexMemory = NULL;
//.jar文件
} else if (dvmJarFileOpen(sourceName, outputName, &pJarFile, false) == 0) {
ALOGV("Opening DEX file '%s' (Jar)", sourceName);
pDexOrJar = (DexOrJar*) malloc(sizeof(DexOrJar));
pDexOrJar->isDex = false;
pDexOrJar->pJarFile = pJarFile;
pDexOrJar->pDexMemory = NULL;
} else {
//都不满足,抛出异常
ALOGV("Unable to open DEX file '%s'", sourceName);
dvmThrowIOException("unable to open DEX file");
}
if (pDexOrJar != NULL) {
pDexOrJar->fileName = sourceName;
//把pDexOr这个结构体中的内容加到gDvm中的userDexFile结构的hash表中,便于Dalvik以后的查找
addToDexFileTable(pDexOrJar);
} else {
free(sourceName);
}
free(outputName);
RETURN_PTR(pDexOrJar);
}
接下来再看对.dex文件的处理函数dvmRawDexFileOpen
int dvmRawDexFileOpen(const char* fileName, const char* odexOutputName,
RawDexFile** ppRawDexFile, bool isBootstrap)
{
DvmDex* pDvmDex = NULL;
char* cachedName = NULL;
int result = -1;
int dexFd = -1;
int optFd = -1;
u4 modTime = 0;
u4 adler32 = 0;
size_t fileSize = 0;
bool newFile = false;
bool locked = false;
dexFd = open(fileName, O_RDONLY); //打开dex文件
if (dexFd < 0) goto bail;
/* If we fork/exec into dexopt, don't let it inherit the open fd. */
dvmSetCloseOnExec(dexFd);//dexfd不继承
//校验dex文件的标志,将第8字节开始的4个字节赋值给adler32。
if (verifyMagicAndGetAdler32(dexFd, &adler32) < 0) {
ALOGE("Error with header for %s", fileName);
goto bail;
}
//得到dex文件的大小和修改时间,保存在modTime和filesize中
if (getModTimeAndSize(dexFd, &modTime, &fileSize) < 0) {
ALOGE("Error with stat for %s", fileName);
goto bail;
}
//odexOutputName就是odex文件名,如果odexOutputName为空,则自动生成一个。
if (odexOutputName == NULL) {
cachedName = dexOptGenerateCacheFileName(fileName, NULL);
if (cachedName == NULL)
goto bail;
} else {
cachedName = strdup(odexOutputName);
}
//主要是验证缓存文件名的正确性,之后将dexOptHeader结构写入fd中
optFd = dvmOpenCachedDexFile(fileName, cachedName, modTime,
adler32, isBootstrap, &newFile, /*createIfMissing=*/true);
locked = true;
if (newFile) {
u8 startWhen, copyWhen, endWhen;
bool result;
off_t dexOffset;
dexOffset = lseek(optFd, 0, SEEK_CUR); //文件指针的位置
result = (dexOffset > 0);
if (result) {
startWhen = dvmGetRelativeTimeUsec();
//将dex文件中的内容拷贝到当前odex文件,也就是dexOffset开始
result = copyFileToFile(optFd, dexFd, fileSize) == 0;
copyWhen = dvmGetRelativeTimeUsec();
}
if (result) {
//优化odex文件
result = dvmOptimizeDexFile(optFd, dexOffset, fileSize,
fileName, modTime, adler32, isBootstrap);
}
}
/*
* Map the cached version. This immediately rewinds the fd, so it
* doesn't have to be seeked anywhere in particular.
*/
//将odex文件映射到内存空间(mmap),并用mprotect将属性置为只读属性,并将映射的dex结构放在pDvmDex数据结构中,具体代码在下面。
if (dvmDexFileOpenFromFd(optFd, &pDvmDex) != 0) {
ALOGI("Unable to map cached %s", fileName);
goto bail;
}
……
}
int dvmDexFileOpenFromFd(int fd, DvmDex** ppDvmDex)
{
DvmDex* pDvmDex;
DexFile* pDexFile;
MemMapping memMap;
int parseFlags = kDexParseDefault;
int result = -1;
if (gDvm.verifyDexChecksum)
parseFlags |= kDexParseVerifyChecksum;
if (lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_SET) < 0) {
ALOGE("lseek rewind failed");
goto bail;
}
//mmap映射fd文件,就是我们之前的odex文件
if (sysMapFileInShmemWritableReadOnly(fd, &memMap) != 0) {
ALOGE("Unable to map file");
goto bail;
}
pDexFile = dexFileParse((u1*)memMap.addr, memMap.length, parseFlags);
if (pDexFile == NULL) {
ALOGE("DEX parse failed");
sysReleaseShmem(&memMap);
goto bail;
}
pDvmDex = allocateAuxStructures(pDexFile);
if (pDvmDex == NULL) {
dexFileFree(pDexFile);
sysReleaseShmem(&memMap);
goto bail;
}
/* tuck this into the DexFile so it gets released later */
//将映射odex文件的内存拷贝到DvmDex的结构中
sysCopyMap(&pDvmDex->memMap, &memMap);
pDvmDex->isMappedReadOnly = true;
*ppDvmDex = pDvmDex;
result = 0;
bail:
return result;
}
/*dalvik\libdex\SysUtil.cpp
*/
int sysMapFileInShmemWritableReadOnly(int fd, MemMapping* pMap)
{
off_t start;
size_t length;
void* memPtr;
assert(pMap != NULL);
//获得文件长度和文件开始地址
if (getFileStartAndLength(fd, &start, &length) < 0)
return -1;
//映射文件
memPtr = mmap(NULL, length, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_FILE | MAP_PRIVATE,
fd, start);
//……
//将保护属性置为只读属性
if (mprotect(memPtr, length, PROT_READ) < 0) {
//…….
}
pMap->baseAddr = pMap->addr = memPtr;
pMap->baseLength = pMap->length = length;
return 0;
//……
}
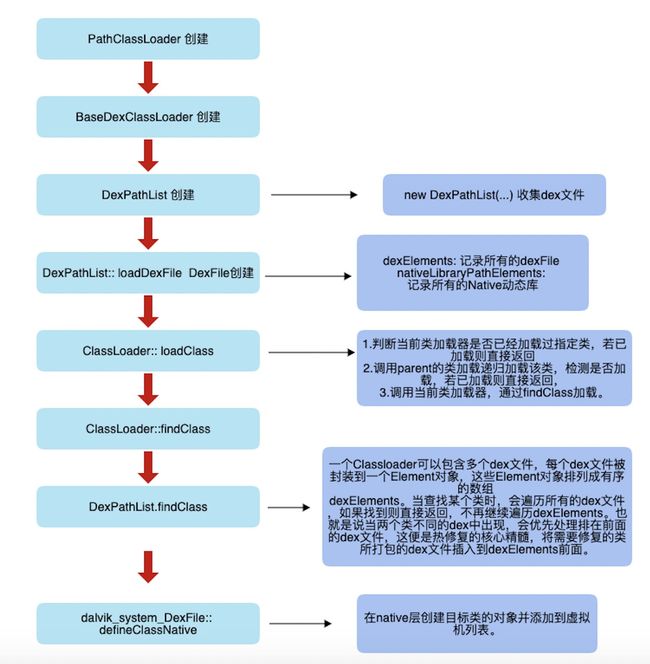
简单梳理一下整个的加载流程:
首先是对文件名的修正,后缀名置为”.dex”作为输出文件,然后生个一个DexPathList对象函数直接返回一个DexPathList对象;
在DexPathList的构造函数中调用makeDexElements()函数,在makeDexElement()函数中调用loadDexFile()开始对.dex或者是.jar .zip .apk文件进行处理;
跟入loadDexFile()函数中,调用optimizedPathFor()函数对optimizedDiretcory路径进行修正;
之后才真正通过DexFile.loadDex()开始加载文件中的数据,其中的加载也只是返回一个DexFile对象;
在DexFile类的构造函数中,重点便放在了其调用的openDexFile()函数,在openDexFile()中调用了openDexFileNative()真正进入native层;
DexClassLoader创建完成后,就已经拥有了目标程序的文件路径,native lib路径,以及parent类加载器对象。接下来开始执行loadClass()来加载相应的类。
ClassLoader::loadClass
public Class<?> loadClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
return loadClass(name, false);
}
protected Class<?> loadClass(String name, boolean resolve)
throws ClassNotFoundException
{
// First, check if the class has already been loaded
Class<?> c = findLoadedClass(name);
if (c == null) {
try {
if (parent != null) {
c = parent.loadClass(name, false);
} else {
c = findBootstrapClassOrNull(name);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// ClassNotFoundException thrown if class not found
// from the non-null parent class loader
}
if (c == null) {
// If still not found, then invoke findClass in order
// to find the class.
c = findClass(name);
}
}
return c;
}
该方法的加载流程如下:
- 判断当前类加载器是否已经加载过指定类,若已加载则直接返回,否则继续执行
- 调用parent的类加载递归加载该类,检测是否加载,若已加载则直接返回,否则继续执行;
- 调用当前类加载器,通过findClass加载
ClassLoader::findLoadedClass
protected final Class<?> findLoadedClass(String name) {
ClassLoader loader;
if (this == BootClassLoader.getInstance())
loader = null;
else
loader = this;
return VMClassLoader.findLoadedClass(loader, name);
}
BaseDexClassLoader:: findClass
@Override
protected Class<?> findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
...
List<Throwable> suppressedExceptions = new ArrayList<Throwable>();
Class c = pathList.findClass(name, suppressedExceptions);
...
return c;
}
DexPathList.findClass
在此实例指向的dex文件中查找已命名类。这将在最早列出的path元素中找到一个。如果找到了类,但还没有定义,则此方法将在构造此实例时使用的定义上下文中定义它。
public Class<?> findClass(String name, List<Throwable> suppressed) {
for (Element element : dexElements) {
Class<?> clazz = element.findClass(name, definingContext, suppressed);
if (clazz != null) {
return clazz;
}
}
if (dexElementsSuppressedExceptions != null) {
suppressed.addAll(Arrays.asList(dexElementsSuppressedExceptions));
}
return null;
}
这里是核心逻辑,一个ClassLoader可以包含多个dex文件,每个dex文件被封装到一个Element对象,这些Element对象排列成有序的数组 dexElements 。当查找某个类时,会遍历所有的dex文件,如果找到则直接返回,不再继续遍历dexElements。也就是说当两个类不同的dex中出现,会优先处理排在前面的dex文件,这便是热修复的核心,将需要修复的类所打包的dex文件插入到dexElements前面。
DexFile::loadClassBinaryName
element.findClass` 最后走到 `dexFile.loadClassBinaryName
@UnsupportedAppUsage
public Class loadClassBinaryName(String name, ClassLoader loader, List<Throwable> suppressed) {
return defineClass(name, loader, mCookie, this, suppressed);
}
private static Class defineClass(String name, ClassLoader loader, Object cookie,
DexFile dexFile, List<Throwable> suppressed) {
Class result = null;
try {
result = defineClassNative(name, loader, cookie, dexFile);
} catch (NoClassDefFoundError e) {
if (suppressed != null) {
suppressed.add(e);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
if (suppressed != null) {
suppressed.add(e);
}
}
return result;
}
dalvik_system_DexFile.cc:: defineClassNative
static jclass DexFile_defineClassNative(JNIEnv* env,
jclass,
jstring javaName,
jobject javaLoader,
jobject cookie,
jobject dexFile) {
std::vector<const DexFile*> dex_files;
const OatFile* oat_file;
if (!ConvertJavaArrayToDexFiles(env, cookie, /*out*/ dex_files, /*out*/ oat_file)) {
VLOG(class_linker) << "Failed to find dex_file";
DCHECK(env->ExceptionCheck());
return nullptr; //dex文件为空, 则直接返回
}
ScopedUtfChars class_name(env, javaName);
if (class_name.c_str() == nullptr) {
VLOG(class_linker) << "Failed to find class_name";
return nullptr; //类名为空, 则直接返回
}
const std::string descriptor(DotToDescriptor(class_name.c_str()));
const size_t hash(ComputeModifiedUtf8Hash(descriptor.c_str()));
for (auto& dex_file : dex_files) {
const dex::ClassDef* dex_class_def =
OatDexFile::FindClassDef(*dex_file, descriptor.c_str(), hash); //将类名转换为hash码
if (dex_class_def != nullptr) {
ScopedObjectAccess soa(env);
ClassLinker* class_linker = Runtime::Current()->GetClassLinker();
StackHandleScope<1> hs(soa.Self());
Handle<mirror::ClassLoader> class_loader(
hs.NewHandle(soa.Decode<mirror::ClassLoader>(javaLoader)));
ObjPtr<mirror::DexCache> dex_cache =
class_linker->RegisterDexFile(*dex_file, class_loader.Get());
if (dex_cache == nullptr) {
// OOME or InternalError (dexFile already registered with a different class loader).
soa.Self()->AssertPendingException();
return nullptr;
}
ObjPtr<mirror::Class> result = class_linker->DefineClass(soa.Self(),
descriptor.c_str(),
hash,
class_loader,
*dex_file,
*dex_class_def);
//添加使用过的dex文件。这只对DexFile是必需的。因为通常的类加载器已经保持它们的dex文件的活动。>InsertDexFileInToClassLoader(soa.Decode(dexFile),
class_loader.Get());
if (result != nullptr) {
// 找到目标对象
return soa.AddLocalReference<jclass>(result);
}
}
}
return nullptr;
}