本文主要讲一样组件化之间是如何通讯的
组件化通讯方案
目前主流的主要有以下三种方式:
1、
URL路由2、
target-action3、
protocol匹配
URL路由
目前iOS上大部分路由工具都是基于URL匹配的,或者是根据命名约定,用runtime方法进行动态调用
这些动态化的方案的优点是实现简单,缺点是需要维护字符串表,或者依赖于命名约定,无法在编译时暴露出所有问题,需要在运行时才能发现错误。
URL路由方式主要是以蘑菇街为代表的的MGJRouter
其实现思路是:
App启动时实例化各组件模块,然后这些组件向
ModuleManager注册Url,有些时候不需要实例化,使用class注册当组件A需要调用组件B时,向
ModuleManager传递URL,参数跟随URL以GET方式传递,类似openURL。然后由ModuleManager负责调度组件B,最后完成任务。
// 1、注册某个URL
MGJRouter.registerURLPattern("app://home") { (info) in
print("info: \(info)")
}
//2、调用路由
MGJRouter.openURL("app://home")
URL 路由的优点
极高的动态性,适合经常开展运营活动的app,例如电商
方便地统一管理多平台的路由规则
易于适配URL Scheme
URl 路由的缺点
传参方式有限,并且无法利用编译器进行参数类型检查,因此所有的参数都是通过字符串转换而来
只适用于界面模块,不适用于通用模块
参数的格式不明确,是个灵活的 dictionary,也需要有个地方可以查参数格式。
不支持storyboard
依赖于字符串硬编码,难以管理,蘑菇街做了个后台专门管理。
无法保证所使用的的模块一定存在
解耦能力有限,url 的”注册”、”实现”、”使用”必须用相同的字符规则,一旦任何一方做出修改都会导致其他方的代码失效,并且重构难度大
除了CTMediator,还有以下这些三方框架
- routable-ios
- JLRoutes
- HHRouter
target-action
这个方案是基于OC的runtime、category特性动态获取模块,例如通过NSClassFromString获取类并创建实例,通过performSelector + NSInvocation动态调用方法
其主要的代表框架是casatwy的CTMediator
其实现思路是:
1、利用分类为路由添加新接口,在接口中通过字符串获取对应的类
2、通过runtime创建实例,动态调用实例的方法
//******* 1、分类定义新接口
extension CTMediator{
@objc func A_showHome()->UIViewController?{
let params = [
kCTMediatorParamsKeySwiftTargetModuleName: "CJLBase_Example"
]
if let vc = self.performTarget("A", action: "Extension_HomeViewController", params: params, shouldCacheTarget: false) as? UIViewController{
return vc
}
return nil
}
}
//******* 2、模块提供者提供target-action的调用方式(对外需要加上public关键字)
class Target_A: NSObject {
@objc func Action_Extension_HomeViewController(_ params: [String: Any])->UIViewController{
let home = HomeViewController()
return home
}
}
//******* 3、使用
if let vc = CTMediator.sharedInstance().A_showHome() {
self.navigationController?.pushViewController(vc, animated: true)
}
其模块间的引用关系如下图所示
优点
利用
分类可以明确声明接口,进行编译检查实现方式
轻量
缺点
需要在
mediator和target中重新添加每一个接口,模块化时代码较为繁琐在
category中仍然引入了字符串硬编码,内部使用字典传参,一定程度上也存在和 URL 路由相同的问题无法保证使用的模块一定存在,target在修改后,使用者只能在运行时才能发现错误
可能会创建过多的 target 类
CTMediator源码分析
- 通过分类中调用的
performTarget来到CTMediator中的具体实现,即performTarget:action:params:shouldCacheTarget:,主要是通过传入的name,找到对应的target和action
- (id)performTarget:(NSString *)targetName action:(NSString *)actionName params:(NSDictionary *)params shouldCacheTarget:(BOOL)shouldCacheTarget
{
if (targetName == nil || actionName == nil) {
return nil;
}
//在swift中使用时,需要传入对应项目的target名称,否则会找不到视图控制器
NSString *swiftModuleName = params[kCTMediatorParamsKeySwiftTargetModuleName];
// generate target 生成target
NSString *targetClassString = nil;
if (swiftModuleName.length > 0) {
//swift中target文件名拼接
targetClassString = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@.Target_%@", swiftModuleName, targetName];
} else {
//OC中target文件名拼接
targetClassString = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"Target_%@", targetName];
}
//缓存中查找target
NSObject *target = [self safeFetchCachedTarget:targetClassString];
//缓存中没有target
if (target == nil) {
//通过字符串获取对应的类
Class targetClass = NSClassFromString(targetClassString);
//创建实例
target = [[targetClass alloc] init];
}
// generate action 生成action方法名称
NSString *actionString = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"Action_%@:", actionName];
//通过方法名字符串获取对应的sel
SEL action = NSSelectorFromString(actionString);
if (target == nil) {
// 这里是处理无响应请求的地方之一,这个demo做得比较简单,如果没有可以响应的target,就直接return了。实际开发过程中是可以事先给一个固定的target专门用于在这个时候顶上,然后处理这种请求的
[self NoTargetActionResponseWithTargetString:targetClassString selectorString:actionString originParams:params];
return nil;
}
//是否需要缓存
if (shouldCacheTarget) {
[self safeSetCachedTarget:target key:targetClassString];
}
//是否响应sel
if ([target respondsToSelector:action]) {
//动态调用方法
return [self safePerformAction:action target:target params:params];
} else {
// 这里是处理无响应请求的地方,如果无响应,则尝试调用对应target的notFound方法统一处理
SEL action = NSSelectorFromString(@"notFound:");
if ([target respondsToSelector:action]) {
return [self safePerformAction:action target:target params:params];
} else {
// 这里也是处理无响应请求的地方,在notFound都没有的时候,这个demo是直接return了。实际开发过程中,可以用前面提到的固定的target顶上的。
[self NoTargetActionResponseWithTargetString:targetClassString selectorString:actionString originParams:params];
@synchronized (self) {
[self.cachedTarget removeObjectForKey:targetClassString];
}
return nil;
}
}
}
- 进入
safePerformAction:target:params:实现,主要是通过invocation进行参数传递+消息转发
- (id)safePerformAction:(SEL)action target:(NSObject *)target params:(NSDictionary *)params
{
//获取方法签名
NSMethodSignature* methodSig = [target methodSignatureForSelector:action];
if(methodSig == nil) {
return nil;
}
//获取方法签名中的返回类型,然后根据返回值完成参数传递
const char* retType = [methodSig methodReturnType];
//void类型
if (strcmp(retType, @encode(void)) == 0) {
...
}
//...省略其他类型的判断
}
protocol class
protocol匹配的实现思路是:
1、将
protocol和对应的类进行字典匹配2、通过用
protocol获取class,在动态创建实例
protocol比较典型的三方框架就是阿里的BeeHive。BeeHive借鉴了Spring Service、Apache DSO的架构理念,采用AOP+扩展App生命周期API形式,将业务功能、基础功能模块以模块方式以解决大型应用中的复杂问题,并让模块之间以Service形式调用,将复杂问题切分,以AOP方式模块化服务。
BeeHive 核心思想
1、各个模块间调用从直接调用对应模块,变成调用
Service的形式,避免了直接依赖。2、App生命周期的分发,将耦合在
AppDelegate中逻辑拆分,每个模块以微应用的形式独立存在。
示例如下(本想用swift写的,但是有点问题,暂时用OC写):
//******** 1、注册
[[BeeHive shareInstance] registerService:@protocol(HomeServiceProtocol) service:[BHViewController class]];
//******** 2、使用
#import "BHService.h"
id< HomeServiceProtocol > homeVc = [[BeeHive shareInstance] createService:@protocol(HomeServiceProtocol)];
优点
1、利用接口调用,实现了参数传递时的类型安全
2、直接使用模块的protocol接口,无需再重复封装
缺点
1、用框架来创建所有对象,创建方式不同,即不支持外部传入参数
2、用
OC runtime创建对象,不支持swift3、只做了
protocol和class的匹配,不支持更复杂的创建方式 和依赖注入4、无法保证所使用的protocol 一定存在对应的模块,也无法直接判断某个protocol是否能用于获取模块
除了BeeHive,还有Swinject
BeeHive 模块注册
在BeeHive主要是通过BHModuleManager来管理各个模块的。BHModuleManager中只会管理已经被注册过的模块。
BeeHive提供了三种不同的调用形式,静态plist,动态注册,annotation。Module、Service之间没有关联,每个业务模块可以单独实现Module或者Service的功能。
1、 Annotation方式注册
这种方式主要是通过BeeHiveMod宏进行Annotation标记
//***** 使用
BeeHiveMod(ShopModule)
//***** BeeHiveMod的宏定义
#define BeeHiveMod(name) \
class BeeHive; char * k##name##_mod BeeHiveDATA(BeehiveMods) = ""#name"";
//***** BeeHiveDATA的宏定义
#define BeeHiveDATA(sectname) __attribute((used, section("__DATA,"#sectname" ")))
//***** 全部转换出来后为下面的格式
char * kShopModule_mod __attribute((used, section("__DATA,""BeehiveMods"" "))) = """ShopModule""";
这里针对__attribute需要说明以下几点
第一个参数
used:用来修饰函数,被used修饰以后,意味着即使函数没有被引用,在Release下也不会被优化。如果不加这个修饰,那么Release环境链接器下会去掉没有被引用的段。通过使用
__attribute__((section("name")))来指明哪个段。数据则用__attribute__((used))来标记,防止链接器会优化删除未被使用的段,然后将模块注入到__DATA中
此时Module已经被存储到Mach-O文件的特殊段中,那么如何取呢?
- 进入
BHReadConfiguration方法,主要是通过Mach-O找到存储的数据段,取出放入数组中
NSArray* BHReadConfiguration(char *sectionName,const struct mach_header *mhp)
{
NSMutableArray *configs = [NSMutableArray array];
unsigned long size = 0;
#ifndef __LP64__
// 找到之前存储的数据段(Module找BeehiveMods段 和 Service找BeehiveServices段)的一片内存
uintptr_t *memory = (uintptr_t*)getsectiondata(mhp, SEG_DATA, sectionName, &size);
#else
const struct mach_header_64 *mhp64 = (const struct mach_header_64 *)mhp;
uintptr_t *memory = (uintptr_t*)getsectiondata(mhp64, SEG_DATA, sectionName, &size);
#endif
unsigned long counter = size/sizeof(void*);
// 把特殊段里面的数据都转换成字符串存入数组中
for(int idx = 0; idx < counter; ++idx){
char *string = (char*)memory[idx];
NSString *str = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:string];
if(!str)continue;
BHLog(@"config = %@", str);
if(str) [configs addObject:str];
}
return configs;
}
2、读取本地Pilst文件
- 首先,需要设置好路径
[BHContext shareInstance].moduleConfigName = @"BeeHive.bundle/BeeHive";//可选,默认为BeeHive.bundle/BeeHive.plist
-
创建plist文件,
Plist文件的格式也是数组中包含多个字典。字典里面有两个Key,一个是@"moduleLevel",另一个是@"moduleClass"。注意根的数组的名字叫@“moduleClasses”。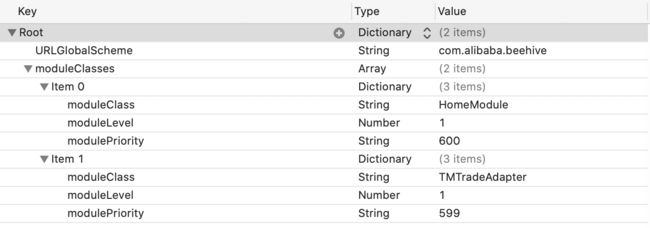 image
image 进入
loadLocalModules方法,主要是从Plist里面取出数组,然后把数组加入到BHModuleInfos数组里面。
//初始化context时,加载Modules和Services
-(void)setContext:(BHContext *)context
{
_context = context;
static dispatch_once_t onceToken;
dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{
[self loadStaticServices];
[self loadStaticModules];
});
}
//加载modules
- (void)loadStaticModules
{
// 读取本地plist文件里面的Module,并注册到BHModuleManager的BHModuleInfos数组中
[[BHModuleManager sharedManager] loadLocalModules];
//注册所有modules,在内部根据优先级进行排序
[[BHModuleManager sharedManager] registedAllModules];
}
- (void)loadLocalModules
{
//plist文件路径
NSString *plistPath = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:[BHContext shareInstance].moduleConfigName ofType:@"plist"];
//判断文件是否存在
if (![[NSFileManager defaultManager] fileExistsAtPath:plistPath]) {
return;
}
//读取整个文件[@"moduleClasses" : 数组]
NSDictionary *moduleList = [[NSDictionary alloc] initWithContentsOfFile:plistPath];
//通过moduleClasses key读取 数组 [[@"moduleClass":"aaa", @"moduleLevel": @"bbb"], [...]]
NSArray *modulesArray = [moduleList objectForKey:kModuleArrayKey];
NSMutableDictionary *moduleInfoByClass = @{}.mutableCopy;
//遍历数组
[self.BHModuleInfos enumerateObjectsUsingBlock:^(NSDictionary * _Nonnull obj, NSUInteger idx, BOOL * _Nonnull stop) {
[moduleInfoByClass setObject:@1 forKey:[obj objectForKey:kModuleInfoNameKey]];
}];
[modulesArray enumerateObjectsUsingBlock:^(NSDictionary * _Nonnull obj, NSUInteger idx, BOOL * _Nonnull stop) {
if (!moduleInfoByClass[[obj objectForKey:kModuleInfoNameKey]]) {
//存储到 BHModuleInfos 中
[self.BHModuleInfos addObject:obj];
}
}];
}
3、load方法注册
该方法注册Module就是在Load方法里面注册Module的类
+ (void)load
{
[BeeHive registerDynamicModule:[self class]];
}
- 进入
registerDynamicModule实现
+ (void)registerDynamicModule:(Class)moduleClass
{
[[BHModuleManager sharedManager] registerDynamicModule:moduleClass];
}
- (void)registerDynamicModule:(Class)moduleClass
{
[self registerDynamicModule:moduleClass shouldTriggerInitEvent:NO];
}
- (void)registerDynamicModule:(Class)moduleClass
shouldTriggerInitEvent:(BOOL)shouldTriggerInitEvent
{
[self addModuleFromObject:moduleClass shouldTriggerInitEvent:shouldTriggerInitEvent];
}
其底层还是同第一种方式一样,最终会走到addModuleFromObject:shouldTriggerInitEvent:方法中
- load方法,还可以使用
BH_EXPORT_MODULE宏代替
#define BH_EXPORT_MODULE(isAsync) \
+ (void)load { [BeeHive registerDynamicModule:[self class]]; } \
-(BOOL)async { return [[NSString stringWithUTF8String:#isAsync] boolValue];}
BH_EXPORT_MODULE宏里面可以传入一个参数,代表是否异步加载Module模块,如果是YES就是异步加载,如果是NO就是同步加载。
2、BeeHive 模块事件
BeeHive会给每个模块提供生命周期事件,用于与BeeHive宿主环境进行必要信息交互,感知模块生命周期的变化。
BeeHive各个模块会收到一些事件。在BHModuleManager中,所有的事件被定义成了BHModuleEventType枚举。如下所示,其中有2个事件很特殊,一个是BHMInitEvent,一个是BHMTearDownEvent
typedef NS_ENUM(NSInteger, BHModuleEventType)
{
//设置Module模块
BHMSetupEvent = 0,
//用于初始化Module模块,例如环境判断,根据不同环境进行不同初始化
BHMInitEvent,
//用于拆除Module模块
BHMTearDownEvent,
BHMSplashEvent,
BHMQuickActionEvent,
BHMWillResignActiveEvent,
BHMDidEnterBackgroundEvent,
BHMWillEnterForegroundEvent,
BHMDidBecomeActiveEvent,
BHMWillTerminateEvent,
BHMUnmountEvent,
BHMOpenURLEvent,
BHMDidReceiveMemoryWarningEvent,
BHMDidFailToRegisterForRemoteNotificationsEvent,
BHMDidRegisterForRemoteNotificationsEvent,
BHMDidReceiveRemoteNotificationEvent,
BHMDidReceiveLocalNotificationEvent,
BHMWillPresentNotificationEvent,
BHMDidReceiveNotificationResponseEvent,
BHMWillContinueUserActivityEvent,
BHMContinueUserActivityEvent,
BHMDidFailToContinueUserActivityEvent,
BHMDidUpdateUserActivityEvent,
BHMHandleWatchKitExtensionRequestEvent,
BHMDidCustomEvent = 1000
};
主要分为三种
-
1、
系统事件:主要是指Application生命周期事件!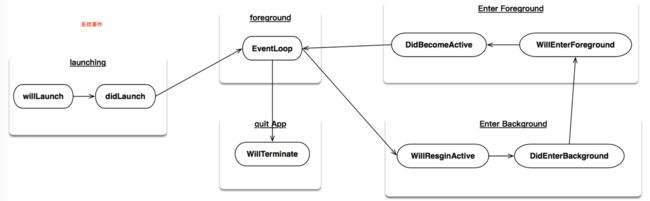 image
image
一般的做法是AppDelegate改为继承自BHAppDelegate
@interface TestAppDelegate : BHAppDelegate
-
2、
应用事件:官方给出的流程图,其中modSetup、modInit等,可以用于编码实现各插件模块的设置与初始化。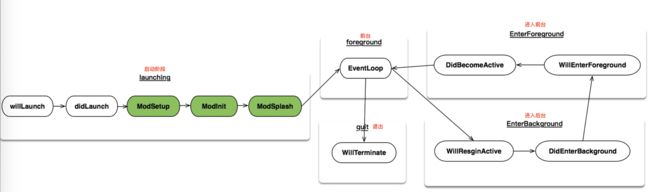 image
image 3、
自定义事件
以上所有的事件都可以通过调用BHModuleManager的triggerEvent:来处理。
- (void)triggerEvent:(NSInteger)eventType
{
[self triggerEvent:eventType withCustomParam:nil];
}
- (void)triggerEvent:(NSInteger)eventType
withCustomParam:(NSDictionary *)customParam {
[self handleModuleEvent:eventType forTarget:nil withCustomParam:customParam];
}
#pragma mark - module protocol
- (void)handleModuleEvent:(NSInteger)eventType
forTarget:(id)target
withCustomParam:(NSDictionary *)customParam
{
switch (eventType) {
//初始化事件
case BHMInitEvent:
//special
[self handleModulesInitEventForTarget:nil withCustomParam :customParam];
break;
//析构事件
case BHMTearDownEvent:
//special
[self handleModulesTearDownEventForTarget:nil withCustomParam:customParam];
break;
//其他3类事件
default: {
NSString *selectorStr = [self.BHSelectorByEvent objectForKey:@(eventType)];
[self handleModuleEvent:eventType forTarget:nil withSeletorStr:selectorStr andCustomParam:customParam];
}
break;
}
}
从上面的代码中可以发现,除去BHMInitEvent初始化事件和BHMTearDownEvent拆除Module事件这两个特殊事件以外,所有的事件都是调用的handleModuleEvent:forTarget:withSeletorStr:andCustomParam:方法,其内部实现主要是遍历 moduleInstances 实例数组,调用performSelector:withObject:方法实现对应方法调用
- (void)handleModuleEvent:(NSInteger)eventType
forTarget:(id)target
withSeletorStr:(NSString *)selectorStr
andCustomParam:(NSDictionary *)customParam
{
BHContext *context = [BHContext shareInstance].copy;
context.customParam = customParam;
context.customEvent = eventType;
if (!selectorStr.length) {
selectorStr = [self.BHSelectorByEvent objectForKey:@(eventType)];
}
SEL seletor = NSSelectorFromString(selectorStr);
if (!seletor) {
selectorStr = [self.BHSelectorByEvent objectForKey:@(eventType)];
seletor = NSSelectorFromString(selectorStr);
}
NSArray> *moduleInstances;
if (target) {
moduleInstances = @[target];
} else {
moduleInstances = [self.BHModulesByEvent objectForKey:@(eventType)];
}
//遍历 moduleInstances 实例数组,调用performSelector:withObject:方法实现对应方法调用
[moduleInstances enumerateObjectsUsingBlock:^(id moduleInstance, NSUInteger idx, BOOL * _Nonnull stop) {
if ([moduleInstance respondsToSelector:seletor]) {
#pragma clang diagnostic push
#pragma clang diagnostic ignored "-Warc-performSelector-leaks"
//进行方法调用
[moduleInstance performSelector:seletor withObject:context];
#pragma clang diagnostic pop
[[BHTimeProfiler sharedTimeProfiler] recordEventTime:[NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@ --- %@", [moduleInstance class], NSStringFromSelector(seletor)]];
}
}];
}
注意:这里所有的
Module必须是遵循BHModuleProtocol的,否则无法接收到这些事件的消息。
3、BeeHive模块调用
在BeeHive中是通过BHServiceManager来管理各个Protocol的。BHServiceManager中只会管理已经被注册过的Protocol。
注册Protocol的方式总共有三种,和注册Module是一样一一对应的
1、Annotation方式注册
//****** 1、通过BeeHiveService宏进行Annotation标记
BeeHiveService(HomeServiceProtocol,BHViewController)
//****** 2、宏定义
#define BeeHiveService(servicename,impl) \
class BeeHive; char * k##servicename##_service BeeHiveDATA(BeehiveServices) = "{ \""#servicename"\" : \""#impl"\"}";
//****** 3、转换后的格式,也是将其存储到特殊的段
char * kHomeServiceProtocol_service __attribute((used, section("__DATA,""BeehiveServices"" "))) = "{ \"""HomeServiceProtocol""\" : \"""BHViewController""\"}";
2、读取本地plist文件
- 首先同Module一样,需要先设置好路径
[BHContext shareInstance].serviceConfigName = @"BeeHive.bundle/BHService";
-
设置plist文件
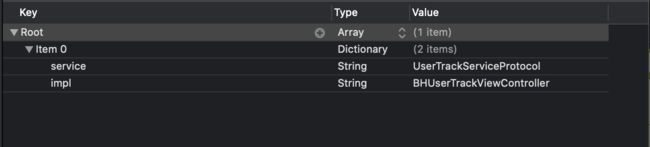 image
image 同样也是在
setContext时注册services
//加载services
-(void)loadStaticServices
{
[BHServiceManager sharedManager].enableException = self.enableException;
[[BHServiceManager sharedManager] registerLocalServices];
}
- (void)registerLocalServices
{
NSString *serviceConfigName = [BHContext shareInstance].serviceConfigName;
//获取plist文件路径
NSString *plistPath = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:serviceConfigName ofType:@"plist"];
if (!plistPath) {
return;
}
NSArray *serviceList = [[NSArray alloc] initWithContentsOfFile:plistPath];
[self.lock lock];
//遍历并存储到allServicesDict中
for (NSDictionary *dict in serviceList) {
NSString *protocolKey = [dict objectForKey:@"service"];
NSString *protocolImplClass = [dict objectForKey:@"impl"];
if (protocolKey.length > 0 && protocolImplClass.length > 0) {
[self.allServicesDict addEntriesFromDictionary:@{protocolKey:protocolImplClass}];
}
}
[self.lock unlock];
}
3、load方法注册
在Load方法里面注册Protocol协议,主要是调用BeeHive里面的registerService:service:完成protocol的注册
+ (void)load
{
[[BeeHive shareInstance] registerService:@protocol(UserTrackServiceProtocol) service:[BHUserTrackViewController class]];
}
- (void)registerService:(Protocol *)proto service:(Class) serviceClass
{
[[BHServiceManager sharedManager] registerService:proto implClass:serviceClass];
}
到此,三种方式就创建完成了
Protocol的获取
Protocol与Module的区别在于,Protocol比Module多了一个方法,可以返回Protocol实例对象
- (id)createService:(Protocol *)proto;
{
return [[BHServiceManager sharedManager] createService:proto];
}
- (id)createService:(Protocol *)service
{
return [self createService:service withServiceName:nil];
}
- (id)createService:(Protocol *)service withServiceName:(NSString *)serviceName {
return [self createService:service withServiceName:serviceName shouldCache:YES];
}
- (id)createService:(Protocol *)service withServiceName:(NSString *)serviceName shouldCache:(BOOL)shouldCache {
if (!serviceName.length) {
serviceName = NSStringFromProtocol(service);
}
id implInstance = nil;
//判断protocol是否已经注册过
if (![self checkValidService:service]) {
if (self.enableException) {
@throw [NSException exceptionWithName:NSInternalInconsistencyException reason:[NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@ protocol does not been registed", NSStringFromProtocol(service)] userInfo:nil];
}
}
NSString *serviceStr = serviceName;
//如果有缓存,则直接从缓存中获取
if (shouldCache) {
id protocolImpl = [[BHContext shareInstance] getServiceInstanceFromServiceName:serviceStr];
if (protocolImpl) {
return protocolImpl;
}
}
//获取类后,然后响应下层的方法
Class implClass = [self serviceImplClass:service];
if ([[implClass class] respondsToSelector:@selector(singleton)]) {
if ([[implClass class] singleton]) {
if ([[implClass class] respondsToSelector:@selector(shareInstance)])
//创建单例对象
implInstance = [[implClass class] shareInstance];
else
//创建实例对象
implInstance = [[implClass alloc] init];
if (shouldCache) {
//缓存
[[BHContext shareInstance] addServiceWithImplInstance:implInstance serviceName:serviceStr];
return implInstance;
} else {
return implInstance;
}
}
}
return [[implClass alloc] init];
}
createService会先检查Protocol协议是否是注册过的。然后接着取出字典里面对应的Class,如果实现了shareInstance方法,那么就创建一个单例对象,如果没有,那么就创建一个实例对象。如果还实现了singleton,就能进一步的把implInstance和serviceStr对应的加到BHContext的servicesByName字典里面缓存起来。这样就可以随着上下文传递了
- 进入
serviceImplClass实现,从这里可以看出 protocol和类是通过字典绑定的,protocol作为key,serviceImp(类的名字)作为value
- (Class)serviceImplClass:(Protocol *)service
{
//通过字典将 协议 和 类 绑定,其中协议作为key,serviceImp(类的名字)作为value
NSString *serviceImpl = [[self servicesDict] objectForKey:NSStringFromProtocol(service)];
if (serviceImpl.length > 0) {
return NSClassFromString(serviceImpl);
}
return nil;
}
Module & Protocol
这里简单总结下:
对于
Module:数组存储对于
Protocol:通过字典将protocol与类进行绑定,key为protocol,value为serviceImp即类名
辅助类
BHConfig类:是一个单例,其内部有一个NSMutableDictionary类型的config属性,该属性维护了一些动态的环境变量,作为BHContext的补充存在BHContext类:是一个单例,其内部有两个NSMutableDictionary的属性,分别是modulesByName和servicesByName。这个类主要用来保存上下文信息的。例如在application:didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:的时候,就可以初始化大量的上下文信息
//保存信息
[BHContext shareInstance].application = application;
[BHContext shareInstance].launchOptions = launchOptions;
[BHContext shareInstance].moduleConfigName = @"BeeHive.bundle/BeeHive";//可选,默认为BeeHive.bundle/BeeHive.plist
[BHContext shareInstance].serviceConfigName = @"BeeHive.bundle/BHService";
BHTimeProfiler类:用来进行计算时间性能方面的ProfilerBHWatchDog类:用来开一个线程,监听主线程是否堵塞
参考链接
- BeeHive —— 一个优雅但还在完善中的解耦框架
- BeeHive,一次iOS模块化解耦实践