MIT6.830-2022-lab5实验思路详细讲解
系列目录
lab1 地址 : lab1
lab2 地址 :lab2
lab3 地址 :lab3
lab4 地址 :lab4
lab5 地址 :lab5
lab6 地址 :lab6
文章目录
- 系列目录
- 前言
- 一、实验背景
- 二、实验正文
-
- Exercise 1 :Search
- Exercise 2 :Insert - Splitting Pages
- Exercise 3 :Delete - Redistributing pages
- Exercise 4:Delete - Redistributing pages
- 总结
前言
Datebase中很重要的一部分就是index而index的数据结构的实现大部分则是b+。笔者希望通过此次的lab整体的复习一下关于数据库中关于b+树的部分。
一、实验背景
| 术语 | 概述 |
|---|---|
| B树 / B-树 | 多路搜索树,非叶子结点存储指向关键字范围的字节点;所有关键字在整棵树中出现,且只出现一次,非叶子结点可以命中 |
| B+树 | 在B树的基础上,为叶子结点增加链表指针,所有关键字都在叶子结点中出现,非叶子结点作为叶子结点的索引;B+树总是到叶子结点才命中。 |
| B*树 | 在B+树的基础上,为非叶子结点也增加链表指针,将结点的最低利用率从1/2 提升到 2/3 |
选用B+的原因:
- B+树的磁盘读写代价更低
B+树的内部结点并没有指向关键字具体信息的指针。因此其内部结点相对叶节点更小。如果把所有同一内部结点的关键字存放在同一盘块中,那么盘块所能容纳的关键字数量也越多。一次性读入内存中的需要查找的关键字也就越多。相对来说IO读写次数也就降低了;
- B+树查询效率更加稳定
由于非终结点并不是最终指向文件内容的结点,而只是叶子结点中关键字的索引。所以任何关键字的查找必须走一条从根结点到叶子结点的路。所有关键字查询的路径长度相同,导致每一个数据的查询效率相当;
- B+树便于范围查询(范围查找是数据库的常态)
B树在提高了IO性能的同时并没有解决元素遍历的我效率低下的问题,正是为了解决这个问题,B+树应用而生。 B+树只需要去遍历叶子节点就可以实现整棵树的遍历(链表) 。 而且在数据库中基于范围的查询是非常频繁的,而B树不支持这样的操作或者说效率太低;
二、实验正文
在实验开头介绍一个USF的数据结构可视化的网址,挺多高阶数据结构的。
USF数据结构可视化网址
Exercise 1 :Search
在exercise1中需要完成的是关于B+树的查找。
- B+树的单列查找:
寻找value为8的节点:与根结点判断,比7大,则进入右子节点。然后从右子节点的第一个开始遍历。找到了第一个索引值8,则继续下沉到叶子结点返回。
B+树的查找
- B+树的范围查找:
如果是查询到8~11则搜索8后沿着叶子结点的列表遍历即可。
回到 Exercise 1则是实现findLeafPage() 函数,递归返回所需的叶子结点。且操作符的类型为> 、>= 、 < 、 <= 、 != 、=。所以只需要实现单列查找即可。
对于lab中的节点来说主要有4类:
-
BTreeRootPtrPage(根结点页面):B+树的根节点。
header: 储存slot使用情况。root: 根节点的value。rootCategory:根节点类型dirty: 是否是脏页。oldData: 用于回滚。
-
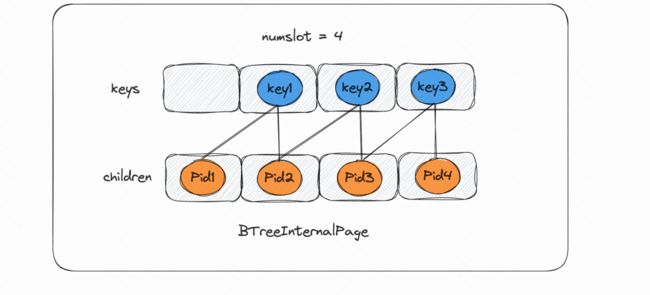
BTreeInternalPage (内部节点页面): B+树的内部节点
int numSlot: 内部节点中最多能存储指针的数量。byte[] header: 储存slot使用情况。Field[] keys: 存储key的数组。int [] children: 存储page的序号,用于每个key指向左右children的point。也因此如果keys是m,children则是m+1。int childCategorychild:节点的类型(either leaf or internal)
-
BTreeLeafPage(叶子节点页面): B+树的叶子节点
int numSlot: 叶节点中最多能存储指针的数量。byte[] header: 储存slot使用情况。int leftSibling: 左叶子节点,为0则为空。int rightSibling: 右叶子节点,为0则为空。Tuple[] tuples: 存放的具体元组数据。
-
BTreeHeaderPage(Header节点页面):用于记录整个B+树中的一个页面的使用情况
BTreePageId pid: 记录目标页面的夜pageId。int numSlot: 叶节点中最多能存储指针的数量。byte[] header: 储存slot使用情况。int nextPage: 指向下一个 headerPage,为0则为空。int prevPage: 指向上一个 headerPage,为0则为空。
除4种页面之外还有一些辅助类:
-
BTreePageId:以上四个页的唯一标识符。
tableid:该page所在table的id。
pgNo:所在page的no(所在的table中的第几个页)。
pgcateg:用于标识BTreePage的类型。 -
BTreeEntry: BTreeInternalPage所更新的单位,虽然BTreeInternalPage页面中存储的是keys与children,但是实际更新(查找、插入、删除等)的单位则是BTreeEntry对象。
Field key: entry的key。BTreePageId leftChild:左孩子的page id。BTreePageId rightChild:右孩子的page id。RecordId rid: 记录entry位于哪个page。
对于BTreeInternalPage来说keys,childern在lab中初始的大小都相同,只是开始赋值的索引不相同:
keys = new Field[numSlots];
try {
// allocate and read the keys of this page
// start from 1 because the first key slot is not used
// since a node with m keys has m+1 pointers
keys[0] = null;
for (int i = 1; i < keys.length; i++)
keys[i] = readNextKey(dis, i);
} catch (NoSuchElementException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
children = new int[numSlots];
try {
// allocate and read the child pointers of this page
for (int i = 0; i < children.length; i++)
children[i] = readNextChild(dis, i);
} catch (NoSuchElementException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
接着就是根据outline的提示补充函数:
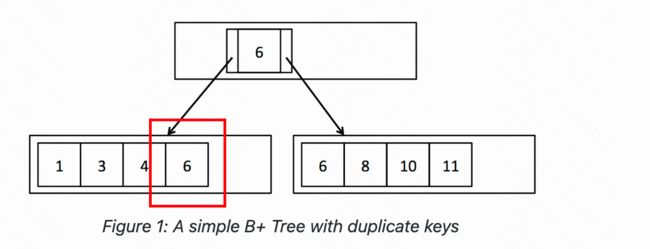
- 给定值1,此函数应返回第一个叶页。同样,给定值8,该函数应返回第二页。而在某种case下,如果给我们一个键值6。可能有重复的键,所以两个叶页上可能都有6个。在这种情况下,函数应该返回第一个(左)叶页。
- 递归的搜索页面,直到搜索到所需的叶子节点页面。如果pgcateg() = BTreePageId.LEAF 则表明这是叶子页面退出递归,否则则是内部页面,需要利用BTreeInternalPage.iterator() 遍历页面中的entrys,并与每个key值做比较,递归进入到下一层的节点。
- 建议不要直接调用BufferPool.getPage() 来获取每个内部页面和叶页,而是调用我们提供的包装器函数BTreeFile.getPage() 。它的工作方式与BufferPool.get page() 完全相同,但需要一个额外的参数来跟踪脏页列表。在接下来的两个练习中,该函数将非常重要,在这两个练习中将实际更新数据,因此需要跟踪脏页。
findLeafPage() 实现访问的每个内部(非叶)页面都应该使用READ_ONLY权限获取,但返回的叶页面除外,该页应该使用作为函数参数提供的权限获取。
- findLeafPage():
/**
* 递归获取叶子节点
* Recursive function which finds and locks the leaf page in the B+ tree corresponding to
* the left-most page possibly containing the key field f. It locks all internal
* nodes along the path to the leaf node with READ_ONLY permission, and locks the
* leaf node with permission perm.
*
* If f is null, it finds the left-most leaf page -- used for the iterator
*
* @param tid - the transaction id
* @param dirtypages - the list of dirty pages which
* should be updated with all new dirty pages
* @param pid - the current page being searched
* @param perm - the permissions with which to lock the leaf page
* @param f - the field to search for
* @return the left-most leaf page possibly containing the key field f
*/
private BTreeLeafPage findLeafPage(TransactionId tid, Map<PageId, Page> dirtypages, BTreePageId pid, Permissions perm,
Field f)
throws DbException, TransactionAbortedException {
// some code goes here
// 四种节点情况:ROOT_PTR 、INTERNAL 、LEAF、HEADER;
int type = pid.pgcateg();
if(type == BTreePageId.LEAF){
return (BTreeLeafPage) getPage(tid,dirtypages,pid,perm);
}
// 非叶子节点直接使用READ权限遍历entries
BTreeInternalPage internalPage = (BTreeInternalPage) getPage(tid,dirtypages,pid,Permissions.READ_ONLY);
Iterator<BTreeEntry> it = internalPage.iterator();
BTreeEntry entry = null;
while (it.hasNext()){
entry = it.next();
// 为空则获取leftChild
if(f == null){
return findLeafPage(tid,dirtypages,entry.getLeftChild(),perm,f);
}
if(entry.getKey().compare(Op.GREATER_THAN_OR_EQ,f)){
return findLeafPage(tid,dirtypages, entry.getLeftChild(), perm,f);
}
}
// 最后一层节点为叶子节点,且内部节点的entry不应该为空
assert entry != null;
return findLeafPage(tid,dirtypages, entry.getRightChild(), perm,f);
}
Exercise 2 :Insert - Splitting Pages
对于第2个练习,首先需要了解B+树的插入是怎么完成的。根据outline中的提示可以简单画一个图:
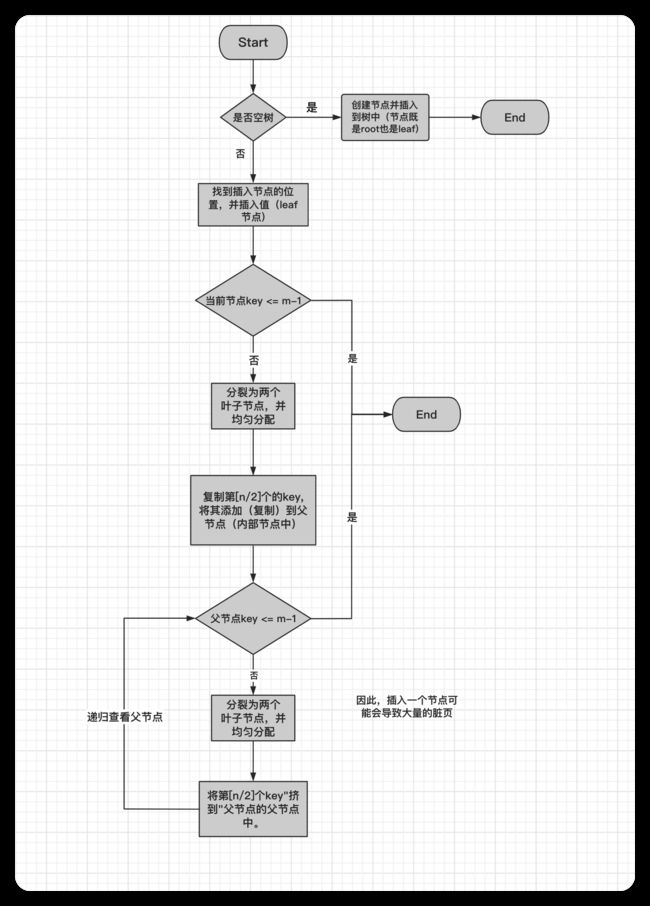
而其中需要区分的则是分裂节点(叶节点与内部节点):

可以看出有两个注意点:
- 叶节点的分裂需要复制一份数据的备份到父节点。而内部节点不需要刻意维护数据在底层,所以其分裂的key是被挤到 父节点的。
- 叶子节点的分裂还需要维护两个节点之间的指向。
再回到outline中给出的hint:
- 每当你想要创建一个新的页,或者因为分裂节点需要创建新页。你可以调用
getEmptyPage()去获得新页,这个函数可以复用因为合并而被删除的页。- 提供
BTreeLeafPage.iterator()与BTreeInternalPage.iterator()去迭代每个页中的tuples / entries。同时可以利用BTreeLeafPage.reverseIterator()与TreeLeafPage.reverseIterator()进行分裂的两个页面之间的重新分配。- 对于Entry :
- 更新Entry对象将不会更新实际的页,需要更新实际的页可以调用
BTreeInternalPage.updateEntry(),- 删除一个Entry实际上是删除一个key与一个child pointer,需要删除操作可以调用:
BTreeInternalPage.deleteKeyAndLeftChild()与BTreeInternalPage.deleteKeyAndRightChild()。- 对于插入同样是插入一个key与一个single child pointer。可以使用
BTreeInternalPage.insertEntry()去插入一个Entry,并保持key在entries中的顺序。- 调用
splitLeafPage()与splitInternalPage()产生新的页面或者修改页面数据时需要更新dirtypages。每次获取页面调用BTreeFile.getPage()他会先获取本地的`dirtypages``,如果没有则再去调用BufferPool。
- splitLeafPage func:
/**
* Split a leaf page to make room for new tuples and recursively split the parent node
* as needed to accommodate a new entry. The new entry should have a key matching the key field
* of the first tuple in the right-hand page (the key is "copied up"), and child pointers
* pointing to the two leaf pages resulting from the split. Update sibling pointers and parent
* pointers as needed.
*
* Return the leaf page into which a new tuple with key field "field" should be inserted.
*
* @param tid - the transaction id
* @param dirtypages - the list of dirty pages which should be updated with all new dirty pages
* @param page - the leaf page to split
* @param field - the key field of the tuple to be inserted after the split is complete. Necessary to know
* which of the two pages to return.
* @return the leaf page into which the new tuple should be inserted
* @throws DbException
* @throws IOException
* @throws TransactionAbortedException
* @see #getParentWithEmptySlots(TransactionId, Map, BTreePageId, Field)
*/
public BTreeLeafPage splitLeafPage(TransactionId tid, Map<PageId, Page> dirtypages, BTreeLeafPage page, Field field)
throws DbException, IOException, TransactionAbortedException {
// some code goes here
//
// Split the leaf page by adding a new page on the right of the existing
// page and moving half of the tuples to the new page. Copy the middle key up
// into the parent page, and recursively split the parent as needed to accommodate
// the new entry. getParentWithEmtpySlots() will be useful here. Don't forget to update
// the sibling pointers of all the affected leaf pages. Return the page into which a
// tuple with the given key field should be inserted.
// 先处理子节点:
// 创建一个右叶节点,并进行均匀分配
BTreeLeafPage newRigPage = (BTreeLeafPage) getEmptyPage(tid,dirtypages,BTreePageId.LEAF);
int tuplesNum = page.getNumTuples();
Iterator<Tuple> reverseIt = page.reverseIterator();
for(int i = 0 ; i < tuplesNum / 2 ; i++){
Tuple tuple = reverseIt.next();
page.deleteTuple(tuple);
newRigPage .insertTuple(tuple);
}
// leftNode <=> page <=> rightNode 需要变成 leftNode <=> leftNode <=> page <=> newRigPage <=> rightNode
BTreePageId rightSiblingId = page.getRightSiblingId();
BTreeLeafPage rightNode = rightSiblingId == null ? null : (BTreeLeafPage) getPage(tid,dirtypages,rightSiblingId,Permissions.READ_ONLY);
if(rightNode != null){
rightNode.setLeftSiblingId(newRigPage.getId());
newRigPage.setRightSiblingId(rightNode.getId());
dirtypages.put(rightNode.getId(),rightNode);
}
page.setRightSiblingId(newRigPage.getId());
newRigPage.setLeftSiblingId(page.getId());
dirtypages.put(newRigPage.getId(),newRigPage);
dirtypages.put(page.getId(),page);
// 开始处理父节点:
// "复制"中间节点并插入父节点中,并设置指针
Field midKey = newRigPage.iterator().next().getField(keyField);
BTreeEntry insertEntry = new BTreeEntry(midKey,page.getId(),newRigPage.getId());
BTreeInternalPage parentPage = getParentWithEmptySlots(tid,dirtypages,page.getParentId(),field);
parentPage.insertEntry(insertEntry);
dirtypages.put(parentPage.getId(),parentPage);
updateParentPointers(tid,dirtypages,parentPage);
// return the leaf page into which the new tuple should be inserted
if(field.compare(Op.GREATER_THAN_OR_EQ,midKey)){
return newRigPage;
}
return page;
}
其中值得注意的是以下这个方法:
getParentWithEmptySlots:获取具有读写权限的父页面,如果父节点中key的数量到达了n-1,则会调用splitInternalPage()方法继续递归,最终返回一个可以插入新key的内部节点。
-
- splitInternalPage func:
/**
* Split an internal page to make room for new entries and recursively split its parent page
* as needed to accommodate a new entry. The new entry for the parent should have a key matching
* the middle key in the original internal page being split (this key is "pushed up" to the parent).
* The child pointers of the new parent entry should point to the two internal pages resulting
* from the split. Update parent pointers as needed.
*
* Return the internal page into which an entry with key field "field" should be inserted
*
* @param tid - the transaction id
* @param dirtypages - the list of dirty pages which should be updated with all new dirty pages
* @param page - the internal page to split
* @param field - the key field of the entry to be inserted after the split is complete. Necessary to know
* which of the two pages to return.
* @return the internal page into which the new entry should be inserted
* @throws DbException
* @throws IOException
* @throws TransactionAbortedException
* @see #getParentWithEmptySlots(TransactionId, Map, BTreePageId, Field)
* @see #updateParentPointers(TransactionId, Map, BTreeInternalPage)
*/
public BTreeInternalPage splitInternalPage(TransactionId tid, Map<PageId, Page> dirtypages,
BTreeInternalPage page, Field field)
throws DbException, IOException, TransactionAbortedException {
// some code goes here
//
// Split the internal page by adding a new page on the right of the existing
// page and moving half of the entries to the new page. Push the middle key up
// into the parent page, and recursively split the parent as needed to accommodate
// the new entry. getParentWithEmtpySlots() will be useful here. Don't forget to update
// the parent pointers of all the children moving to the new page. updateParentPointers()
// will be useful here. Return the page into which an entry with the given key field
// should be inserted.
BTreeInternalPage newRigPage = (BTreeInternalPage) getEmptyPage(tid,dirtypages,BTreePageId.INTERNAL);
int entriesNum = page.getNumEntries();
Iterator<BTreeEntry> reverseIt = page.reverseIterator();
for(int i = 0 ; i < entriesNum / 2; i++){
// !!! 与分裂叶节点不同的是内部节点的单位是Entries,用于唯一标示的则是entry中的RecordId的,而插入操作则会改变RecordId
// 因此需要先删除后插入
BTreeEntry entry = reverseIt.next();
// 删除哪个child
page.deleteKeyAndRightChild(entry);
newRigPage.insertEntry(entry);
}
// 将子节点挤到父节点中,并设置指针指向
BTreeEntry midEntry = reverseIt.next();
page.deleteKeyAndRightChild(midEntry);
midEntry.setLeftChild(page.getId());
midEntry.setRightChild(newRigPage.getId());
BTreeInternalPage parent = getParentWithEmptySlots(tid,dirtypages,page.getParentId(), midEntry.getKey());
parent.insertEntry(midEntry);
updateParentPointers(tid,dirtypages,page);
updateParentPointers(tid,dirtypages,newRigPage);
updateParentPointers(tid,dirtypages,parent);
// 更新脏页并返回
dirtypages.put(page.getId(),page);
dirtypages.put(parent.getId(),parent);
dirtypages.put(newRigPage.getId(),newRigPage);
if(field.compare(Op.GREATER_THAN_OR_EQ,midEntry.getKey())){
return newRigPage;
}
return page;
}
Exercise 3 :Delete - Redistributing pages
对于outline给出的删除逻辑,可以简单总结一个图:

从lab给出的图可以知道重新分配下leaf与internal节点的区别:

- 叶节点之间需要维护新的指针指向,而内部节点不需要。
- 叶节点与父亲节点之间的关系是复制关系,而内部节点则必须唯一,也就是需要挤上去。
- 还有一个比较难看出的是 :内部节点被挤下来的父节点的孩子节点应该指谁,叶子节点本来就是最后一层则不用考虑这个问题。代码中注解提到的则是:
Keys can be thought of as rotating through the parent entry, so the original key in the parent is “pulled down” to the left-hand page, and the last key in the right-hand page is “pushed up” to the parent. Update parent pointers as needed.
更偏向于被旋转下来。笔者简单画一个图:
理解了上面,则代码相关就相对比较简单:
/**
* Steal tuples from a sibling and copy them to the given page so that both pages are at least
* half full. Update the parent's entry so that the key matches the key field of the first
* tuple in the right-hand page.
*
* @param page - the leaf page which is less than half full
* @param sibling - the sibling which has tuples to spare
* @param parent - the parent of the two leaf pages
* @param entry - the entry in the parent pointing to the two leaf pages
* @param isRightSibling - whether the sibling is a right-sibling
* @throws DbException
*/
public void stealFromLeafPage(BTreeLeafPage page, BTreeLeafPage sibling,
BTreeInternalPage parent, BTreeEntry entry, boolean isRightSibling) throws DbException {
// some code goes here
//
// Move some of the tuples from the sibling to the page so
// that the tuples are evenly distributed. Be sure to update
// the corresponding parent entry.
Iterator<Tuple> siblingIt = isRightSibling ? sibling.iterator() : sibling.reverseIterator();
int sourceTuplesNum = page.getNumTuples();
int siblingTuplesNum = sibling.getNumTuples();
int midTuplesNum = ( sourceTuplesNum + siblingTuplesNum ) / 2;
while ( sourceTuplesNum < midTuplesNum){
Tuple siblingTuple = siblingIt.next();
sibling.deleteTuple(siblingTuple);
page.insertTuple(siblingTuple);
sourceTuplesNum++;
}
Tuple headSibling = siblingIt.next();
entry.setKey(headSibling.getField(keyField));
parent.updateEntry(entry);
}
/**
* Steal entries from the left sibling and copy them to the given page so that both pages are at least
* half full. Keys can be thought of as rotating through the parent entry, so the original key in the
* parent is "pulled down" to the right-hand page, and the last key in the left-hand page is "pushed up"
* to the parent. Update parent pointers as needed.
*
* @param tid - the transaction id
* @param dirtypages - the list of dirty pages which should be updated with all new dirty pages
* @param page - the internal page which is less than half full
* @param leftSibling - the left sibling which has entries to spare
* @param parent - the parent of the two internal pages
* @param parentEntry - the entry in the parent pointing to the two internal pages
* @throws DbException
* @throws TransactionAbortedException
* @see #updateParentPointers(TransactionId, Map, BTreeInternalPage)
*/
public void stealFromLeftInternalPage(TransactionId tid, Map<PageId, Page> dirtypages,
BTreeInternalPage page, BTreeInternalPage leftSibling, BTreeInternalPage parent,
BTreeEntry parentEntry) throws DbException, TransactionAbortedException {
// some code goes here
// Move some of the entries from the left sibling to the page so
// that the entries are evenly distributed. Be sure to update
// the corresponding parent entry. Be sure to update the parent
// pointers of all children in the entries that were moved.
// case: left-【 1、2、3、4、5、7 】 right-[ 9、10 】 parent:8,分配后的则为:【1、2、3、4】、5、【 7、 8、 9、 10 】
// 且交换后的节点需要填补的空缺为 7 ~ 8 与 8 ~ 9 ,所以是 7 的 rightChild 与 8 的 leftChild
// 也可理解为b+每个父子节点其实都是一个范围,而这个范围是要被弥补的,如果被替代的话,例如8为父节点那么被替换下来的话7~8,8~9就需要被替代
// 而再广的范围则是7、9两边扩展开
// 因此可以理解为父节点旋转下来,然后需要重新插入排序
Iterator<BTreeEntry> leftIt = leftSibling.reverseIterator();
BTreeEntry itEntry = leftIt.next();
BTreeEntry oldParent = new BTreeEntry(parentEntry.getKey(),itEntry.getRightChild(),page.iterator().next().getLeftChild());
page.insertEntry(oldParent);
int sourceEntriesNum = page.getNumEntries();
int siblingEntriesNum = leftSibling.getNumEntries();
int halfEntriesNum = ( sourceEntriesNum + siblingEntriesNum) / 2;
while ( sourceEntriesNum < halfEntriesNum ){
leftSibling.deleteKeyAndRightChild(itEntry);
page.insertEntry(itEntry);
sourceEntriesNum++;
itEntry = leftIt.next();
}
// 新的父节点被旋转上去的则无需担心子节点指向
BTreeEntry newParent = itEntry;
leftSibling.deleteKeyAndRightChild(newParent);
parentEntry.setKey(newParent.getKey());
parent.updateEntry(parentEntry);
// 设置脏页
dirtypages.put(page.getId(),page);
dirtypages.put(leftSibling.getId(),leftSibling);
dirtypages.put(parent.getId(),parent);
updateParentPointers(tid,dirtypages,page);
}
/**
* Steal entries from the right sibling and copy them to the given page so that both pages are at least
* half full. Keys can be thought of as rotating through the parent entry, so the original key in the
* parent is "pulled down" to the left-hand page, and the last key in the right-hand page is "pushed up"
* to the parent. Update parent pointers as needed.
*
* @param tid - the transaction id
* @param dirtypages - the list of dirty pages which should be updated with all new dirty pages
* @param page - the internal page which is less than half full
* @param rightSibling - the right sibling which has entries to spare
* @param parent - the parent of the two internal pages
* @param parentEntry - the entry in the parent pointing to the two internal pages
* @throws DbException
* @throws TransactionAbortedException
* @see #updateParentPointers(TransactionId, Map, BTreeInternalPage)
*/
public void stealFromRightInternalPage(TransactionId tid, Map<PageId, Page> dirtypages,
BTreeInternalPage page, BTreeInternalPage rightSibling, BTreeInternalPage parent,
BTreeEntry parentEntry) throws DbException, TransactionAbortedException {
// some code goes here
// Move some of the entries from the right sibling to the page so
// that the entries are evenly distributed. Be sure to update
// the corresponding parent entry. Be sure to update the parent
// pointers of all children in the entries that were moved.
// case: left-【 1、2 】 right-[4、5、7、9、10 】 parent:3,分配后的则为:【1、2、3、4】、5、【 7、 8、 9、 10 】
Iterator<BTreeEntry> rightIt = rightSibling.iterator();
BTreeEntry itEntry = rightIt.next();
BTreeEntry oldParent = new BTreeEntry(parentEntry.getKey(),page.reverseIterator().next().getRightChild(),
itEntry.getLeftChild());
page.insertEntry(oldParent);
int sourceEntriesNum = page.getNumEntries();
int siblingEntriesNum = rightSibling.getNumEntries();
int halfEntriesNum = ( sourceEntriesNum + siblingEntriesNum) / 2;
while ( sourceEntriesNum < halfEntriesNum ){
rightSibling.deleteKeyAndLeftChild(itEntry);
page.insertEntry(itEntry);
sourceEntriesNum++;
itEntry = rightIt.next();
}
// 新的父节点被旋转上去的则无需担心子节点指向
BTreeEntry newParent = itEntry;
rightSibling.deleteKeyAndLeftChild(newParent);
parentEntry.setKey(newParent.getKey());
parent.updateEntry(parentEntry);
// 设置脏页
dirtypages.put(page.getId(),page);
dirtypages.put(rightSibling.getId(),rightSibling);
dirtypages.put(parent.getId(),parent);
updateParentPointers(tid,dirtypages,page);
}
Exercise 4:Delete - Redistributing pages
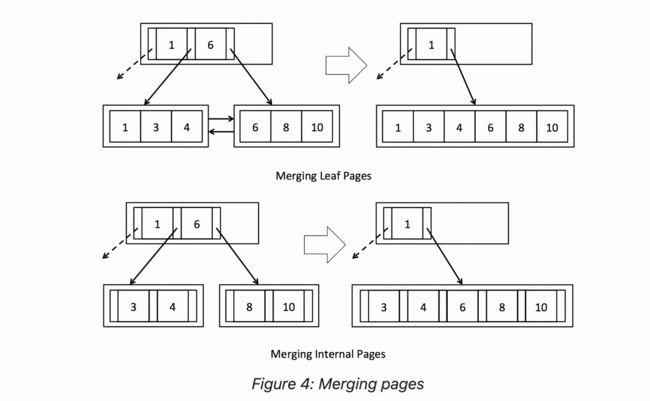
对于Merge部分相对于会简单一些,需要注意的则是内部节点的父节点不是删除而是拉下来。
/**
* Merge two leaf pages by moving all tuples from the right page to the left page.
* Delete the corresponding key and right child pointer from the parent, and recursively
* handle the case when the parent gets below minimum occupancy.
* Update sibling pointers as needed, and make the right page available for reuse.
*
* @param tid - the transaction id
* @param dirtypages - the list of dirty pages which should be updated with all new dirty pages
* @param leftPage - the left leaf page
* @param rightPage - the right leaf page
* @param parent - the parent of wo pages
* @param parentEntry - the entry in the parent corresponding to the leftPage and rightPage
* @throws DbException
* @throws IOException
* @throws TransactionAbortedException
* @see #deleteParentEntry(TransactionId, Map, BTreePage, BTreeInternalPage, BTreeEntry)
*/
public void mergeLeafPages(TransactionId tid, Map<PageId, Page> dirtypages,
BTreeLeafPage leftPage, BTreeLeafPage rightPage, BTreeInternalPage parent, BTreeEntry parentEntry)
throws DbException, IOException, TransactionAbortedException {
// some code goes here
//
// Move all the tuples from the right page to the left page, update
// the sibling pointers, and make the right page available for reuse.
// Delete the entry in the parent corresponding to the two pages that are merging -
// deleteParentEntry() will be useful here
Iterator<Tuple> rightIt = rightPage.iterator();
while (rightIt.hasNext()){
Tuple next = rightIt.next();
rightPage.deleteTuple(next);
leftPage.insertTuple(next);
}
// 设置指针
BTreePageId newRightNode = rightPage.getRightSiblingId();
if(newRightNode == null){
leftPage.setRightSiblingId(null);
}else {
leftPage.setRightSiblingId(newRightNode);
BTreeLeafPage newRightPage = (BTreeLeafPage) getPage(tid, dirtypages, newRightNode, Permissions.READ_WRITE);
newRightPage.setLeftSiblingId(leftPage.getId());
}
setEmptyPage(tid,dirtypages,rightPage.pid.getPageNumber());
deleteParentEntry(tid,dirtypages,leftPage,parent,parentEntry);
dirtypages.put(leftPage.getId(),leftPage);
dirtypages.put(parent.getId(),parent);
}
/**
* Merge two internal pages by moving all entries from the right page to the left page
* and "pulling down" the corresponding key from the parent entry.
* Delete the corresponding key and right child pointer from the parent, and recursively
* handle the case when the parent gets below minimum occupancy.
* Update parent pointers as needed, and make the right page available for reuse.
*
* @param tid - the transaction id
* @param dirtypages - the list of dirty pages which should be updated with all new dirty pages
* @param leftPage - the left internal page
* @param rightPage - the right internal page
* @param parent - the parent of the two pages
* @param parentEntry - the entry in the parent corresponding to the leftPage and rightPage
* @throws DbException
* @throws IOException
* @throws TransactionAbortedException
* @see #deleteParentEntry(TransactionId, Map, BTreePage, BTreeInternalPage, BTreeEntry)
* @see #updateParentPointers(TransactionId, Map, BTreeInternalPage)
*/
public void mergeInternalPages(TransactionId tid, Map<PageId, Page> dirtypages,
BTreeInternalPage leftPage, BTreeInternalPage rightPage, BTreeInternalPage parent, BTreeEntry parentEntry)
throws DbException, IOException, TransactionAbortedException {
// some code goes here
//
// Move all the entries from the right page to the left page, update
// the parent pointers of the children in the entries that were moved,
// and make the right page available for reuse
// Delete the entry in the parent corresponding to the two pages that are merging -
// deleteParentEntry() will be useful here
Iterator<BTreeEntry> rightIt = rightPage.iterator();
// 与叶节点的区别-需要将父节点拉下来
BTreeEntry pullNode = new BTreeEntry(parentEntry.getKey(),leftPage.reverseIterator().next().getRightChild(),
rightPage.iterator().next().getLeftChild());
leftPage.insertEntry(pullNode);
while (rightIt.hasNext()){
BTreeEntry next = rightIt.next();
rightPage.deleteKeyAndLeftChild(next);
leftPage.insertEntry(next);
}
updateParentPointers(tid,dirtypages,leftPage);
setEmptyPage(tid,dirtypages,rightPage.pid.getPageNumber());
deleteParentEntry(tid,dirtypages,leftPage,parent,parentEntry);
dirtypages.put(leftPage.getId(),leftPage);
dirtypages.put(parent.getId(),parent);
}
总结
如果只是对于b+的插入、删除,而完成分裂,合并,窃取等操作,而完成实验则会相对容易。但是如果算上附加练习BTreeTest则就是前5个lab中最难的,因为看了下大概的测试,是要先启动200个插入线程(每个休眠100s,给前期页分裂留下时间)然后再启动800个线程,总共1000个线程进行插入。然后再删除,再插入。最后查询,并进行排序判断。这个过程肯定会导致大量的脏页,但是依照严格两阶段锁定,即使全是脏页,也不能提交,得等事务提交再提交,因此不能重试太多次。而lab中虽然有个二级缓存,但是二级缓存其实只是个中间变量,存取写入的页。而大量的read权限的页则需要重新获取,所以可以弄个三级缓存。读 -> 写 - > BufferPool。
Page getPage(TransactionId tid, Map<PageId, Page> dirtypages, BTreePageId pid, Permissions perm)
throws DbException, TransactionAbortedException {
if (dirtypages.containsKey(pid)) {
return dirtypages.get(pid);
} else if(localReadPage.containsKey(pid) && perm != Permissions.READ_WRITE){
return localReadPage.get(pid);
} else {
Page p = Database.getBufferPool().getPage(tid, pid, perm);
if (perm == Permissions.READ_WRITE) {
dirtypages.put(pid, p);
}
localReadPage.put(pid,p);
return p;
}
}
这样会因为获取不到读权限而回滚的次数少很多。且就算回滚了,以往是测试代码层会过一遍,但是如果想过附加实验,需要自己进行redo,这段代码也需要自己加上去。且因为是1000个线程,而b+树涉及大量的指针指向,所以需要在操作指针时,需要保证同步代码块。以及前面的代码应该及时释放掉不需要的权限,否则以b+树的数据结构很容易死锁。 打算有时间再回来过附加练习了,如有不足欢迎指正、讨论~。
gitee地址