【Hive】——DQL
1 SELECT
1.1 语法
从哪里查询取决于FROM关键字后面的table_reference。可以是普通物理表、视图、join结果或子查询结果。
[WITH CommonTableExpression (, CommonTableExpression)*]
SELECT [ALL | DISTINCT] select_expr, select_expr, ...
FROM table_reference
[WHERE where_condition]
[GROUP BY col_list]
[ORDER BY col_list]
[CLUSTER BY col_list
| [DISTRIBUTE BY col_list] [SORT BY col_list]
]
[LIMIT [offset,] rows];
1.2 执行顺序
- from > where > group(含聚合)> having >order > select;
- 聚合语句(sum,min,max,avg,count)要比having子句优先执行
- where子句在查询过程中执行优先级别优先于聚合语句(sum,min,max,avg,count)
2 ALL、DISTINCT
用于指定查询返回结果中重复的行如何处理。
- 如果没有给出这些选项,则默认值为ALL(返回所有匹配的行)。
--返回所有匹配的行
select state from t_usa_covid19_p;
--相当于
select all state from t_usa_covid19_p;
- DISTINCT指定从结果集中删除重复的行。
- 多个字段distinct 整体去重。
--返回所有匹配的行 去除重复的结果
select distinct state from t_usa_covid19_p;
--多个字段distinct 整体去重
select county,state from t_usa_covid19_p;
select distinct county,state from t_usa_covid19_p;
select distinct sex from student;
3 WHERE
- 在WHERE表达式中,可以使用Hive支持的任何函数和运算符,但聚合函数除外。那么为什么不能在where子句中使用聚合函数呢?
- 因为聚合函数要使用它的前提是结果集已经确定。而where子句还处于“确定”结果集的过程中,因而不能使用聚合函数。
- 从Hive 0.13开始,WHERE子句支持某些类型的子查询。
案例
select * from t_usa_covid19_p where 1 > 2; -- 1 > 2 返回false
select * from t_usa_covid19_p where 1 = 1; -- 1 = 1 返回true
--where条件中使用函数 找出州名字母长度超过10位的有哪些
select * from t_usa_covid19_p where length(state) >10 ;
--where子句支持子查询
SELECT *
FROM A
WHERE A.a IN (SELECT foo FROM B);
反例:
--注意:where条件中不能使用聚合函数
--报错 SemanticException:Not yet supported place for UDAF 'count'
--聚合函数要使用它的前提是结果集已经确定。
--而where子句还处于“确定”结果集的过程中,因而不能使用聚合函数。
select state,count(deaths)
from t_usa_covid19_p where count(deaths) >100 group by state;
4 分区查询、分区裁剪
- 针对Hive分区表,在查询时可以指定分区查询,减少全表扫描,也叫做分区裁剪。
- 所谓分区裁剪指:对分区表进行查询时,会检查WHERE子句或JOIN中的ON子句中是否存在对分区字段的过滤,如果存在,则仅访问查询符合条件的分区,即裁剪掉没必要访问的分区。
--找出来自加州,累计死亡人数大于1000的县 state字段就是分区字段 进行分区裁剪 避免全表扫描
select * from t_usa_covid19_p where state ="California" and deaths > 1000;
--多分区裁剪
select * from t_usa_covid19_p where count_date = "2021-01-28" and state ="California" and deaths > 1000;
4 GROUP BY
- GROUP BY语句用于结合聚合函数,根据一个或多个列对结果集进行分组。
- 出现在GROUP BY中select_expr的字段:要么是GROUP BY分组的字段;要么是被聚合函数应用的字段。
- 原因:避免出现一个字段多个值的歧义。
分组字段出现select_expr中,一定没有歧义,因为就是基于该字段分组的,同一组中必相同;
被聚合函数应用的字段,也没歧义,因为聚合函数的本质就是多进一出,最终返回一个结果。
--根据state州进行分组
--SemanticException:Expression not in GROUP BY key 'deaths'
--deaths不是分组字段 报错
--state是分组字段 可以直接出现在select_expr中
select state,deaths
from t_usa_covid19_p where count_date = "2021-01-28" group by state;
–被聚合函数应用
select state,sum(deaths)
from t_usa_covid19_p where count_date = “2021-01-28” group by state;
5 HAVING
- 在SQL中增加HAVING子句原因是,WHERE关键字无法与聚合函数一起使用。
- HAVING子句可以让我们筛选分组后的各组数据,并且可以在Having中使用聚合函数,因为此时where,group by已经执行结束,结果集已经确定。
--统计死亡病例数大于10000的州
--where语句中不能使用聚合函数 语法报错
select state,sum(deaths)
from t_usa_covid19_p where count_date = "2021-01-28" and sum(deaths) >10000 group by state;
--先where分组前过滤(此处是分区裁剪),再进行group by分组, 分组后每个分组结果集确定 再使用having过滤
select state,sum(deaths)
from t_usa_covid19_p
where count_date = "2021-01-28"
group by state
having sum(deaths) > 10000;
--这样写更好 即在group by的时候聚合函数已经作用得出结果 having直接引用结果过滤 不需要再单独计算一次了
select state,sum(deaths) as cnts
from t_usa_covid19_p
where count_date = "2021-01-28"
group by state
having cnts> 10000;
- having 和 where 的区别:
having是在分组后对数据进行过滤
where是在分组前对数据进行过滤
having后面可以使用聚合函数
where后面不可以使用聚合函数
6 LIMIT
- LIMIT用于限制SELECT语句返回的行数。
- LIMIT接受一个或两个数字参数,这两个参数都必须是非负整数常量。
第一个参数指定要返回的第一行的偏移量(从 Hive 2.0.0开始),第二个参数指定要返回的最大行数。当给出单个参数时,它代表最大行数,并且偏移量默认为0。
--没有限制返回2021.1.28 加州的所有记录
select * from t_usa_covid19_p
where count_date = "2021-01-28"
and state ="California";
--返回结果集的前5条
select * from t_usa_covid19_p
where count_date = "2021-01-28"
and state ="California"
limit 5;
--返回结果集从第1行开始 共3行
select * from t_usa_covid19_p
where count_date = "2021-01-28"
and state ="California"
limit 2,3; --注意 第一个参数偏移量是从0开始的
7 ORDER BY
- Hive SQL中的ORDER BY语法类似于标准SQL语言中的ORDER BY语法,会对输出的结果进行全局排序。
因此当底层使用MapReduce引擎执行的时候,只会有一个reducetask执行。如果输出的行数太大,会导致需要很长的时间才能完成全局排序。 - 默认排序为升序(ASC),也可以指定为DESC降序。
在Hive 2.1.0和更高版本中,支持在ORDER BY子句中为每个列指定null类型结果排序顺序。
ASC顺序的默认空排序顺序为NULLS FIRST,而DESC顺序的默认空排序顺序为NULLS LAST。
8 CLUSTER BY
8.1 概述
- 根据指定字段将数据分组,每组内再根据该字段正序排序(只能正序)。
概况起来就是:根据同一个字段,分且排序。 - 分组规则hash散列(分桶表规则一样):Hash_Func(col_name) % reducetask个数
- 分为几组取决于reducetask的个数
8.2 案例
select * from student;
--不指定reduce task个数
--日志显示:Number of reduce tasks not specified. Estimated from input data size: 1
select * from student cluster by num;
--手动设置reduce task个数
set mapreduce.job.reduces =2;
select * from student cluster by num;
8.3 限制性
CLUSTER BY无法单独完成,因为分和排序的字段只能是同一个;
ORDER BY更不能在这里使用,因为是全局排序,只有一个输出,无法满足分的需求。
9 DISTRIBUTE BY+SORT BY
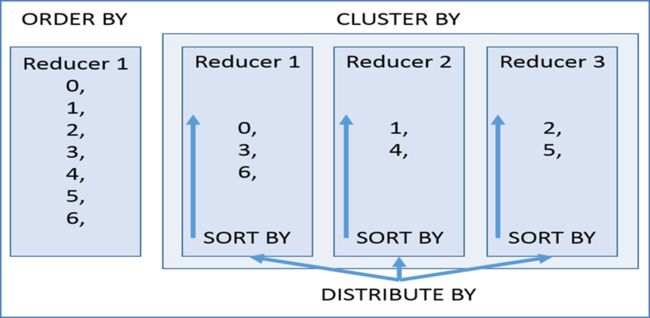
- DISTRIBUTE BY +SORT BY就相当于把CLUSTER BY的功能一分为二:
- DISTRIBUTE BY负责根据指定字段分组;
- SORT BY负责分组内排序规则。
- 分组和排序的字段可以不同。
--案例:把学生表数据根据性别分为两个部分,每个分组内根据年龄的倒序排序。
select * from student distribute by sex sort by age desc;

5. 如果DISTRIBUTE BY +SORT BY的字段一样,则:CLUSTER BY=DISTRIBUTE BY +SORT BY
--下面两个语句执行结果一样
select * from student distribute by num sort by num;
select * from student cluster by num;
10 ORDER BY, CLUSTER BY,DISTRIBUTE BY对比
- order by全局排序,因此只有一个reducer,结果输出在一个文件中,当输入规模大时,需要较长的计算时间。
- distribute by根据指定字段将数据分组,算法是hash散列。sort by是在分组之后,每个组内局部排序。
- cluster by既有分组,又有排序,但是两个字段只能是同一个字段。
- 如果distribute和sort的字段是同一个时,此时,cluster by = distribute by + sort by
11 UNION
11.1 概述
- UNION用于将来自于多个SELECT语句的结果合并为一个结果集。
- 使用DISTINCT关键字与只使用UNION默认值效果一样,都会删除重复行。1.2.0之前的Hive版本仅支持UNION ALL,在这种情况下不会消除重复的行。
- 使用ALL关键字,不会删除重复行,结果集包括所有SELECT语句的匹配行(包括重复行)。
- 每个select_statement返回的列的数量和名称必须相同。
- 如果要将ORDER BY,SORT BY,CLUSTER BY,DISTRIBUTE BY或LIMIT应用于单个SELECT,则将子句放在括住SELECT的括号内。
- 如果要将ORDER BY,SORT BY,CLUSTER BY,DISTRIBUTE BY或LIMIT子句应用于整个UNION结果,则将将ORDER BY,SORT BY,CLUSTER BY,DISTRIBUTE BY或LIMIT放在最后一个之后。
11.2 语法
select_statement
UNION [ALL | DISTINCT]
select_statement
UNION [ALL | DISTINCT]
select_statement ...;
--使用DISTINCT关键字与使用UNION默认值效果一样,都会删除重复行。
select num,name from student_local
UNION
select num,name from student_hdfs;
--和上面一样
select num,name from student_local
UNION DISTINCT
select num,name from student_hdfs;
--使用ALL关键字会保留重复行。
select num,name from student_local
UNION ALL
select num,name from student_hdfs;
--如果要将ORDER BY,SORT BY,CLUSTER BY,DISTRIBUTE BY或LIMIT应用于单个SELECT
--请将子句放在括住SELECT的括号内
SELECT num,name FROM (select num,name from student_local LIMIT 2) subq1
UNION
SELECT num,name FROM (select num,name from student_hdfs LIMIT 3) subq2
--如果要将ORDER BY,SORT BY,CLUSTER BY,DISTRIBUTE BY或LIMIT子句应用于整个UNION结果
--请将ORDER BY,SORT BY,CLUSTER BY,DISTRIBUTE BY或LIMIT放在最后一个之后。
select num,name from student_local
UNION
select num,name from student_hdfs
order by num desc;
12 Subqueries(子查询)
12.1 from 子句中的子查询
- 在Hive0.12版本,仅在FROM子句中支持子查询。
必须要给子查询一个名称,因为FROM子句中的每个表都必须有一个名称。子查询返回结果中的列必须具有唯一的名称。子查询返回结果中的列在外部查询中可用,就像真实表的列一样。子查询也可以是带有UNION的查询表达式。 - Hive支持任意级别的子查询,也就是所谓的嵌套子查询。
- Hive 0.13.0和更高版本中的子查询名称之前可以包含可选关键字AS。
--from子句中子查询(Subqueries)
--子查询
SELECT num
FROM (
select num,name from student_local
) tmp;
--包含UNION ALL的子查询的示例
SELECT t3.name
FROM (
select num,name from student_local
UNION distinct
select num,name from student_hdfs
) t3;
12.2 where 子句中的子查询
- 不相关子查询:该子查询不引用父查询中的列,可以将查询结果视为IN和NOT IN语句的常量;
- 相关子查询:子查询引用父查询中的列;
--where子句中子查询(Subqueries)
--不相关子查询,相当于IN、NOT IN,子查询只能选择一个列。
--(1)执行子查询,其结果不被显示,而是传递给外部查询,作为外部查询的条件使用。
--(2)执行外部查询,并显示整个结果。
SELECT *
FROM student_hdfs
WHERE student_hdfs.num IN (select num from student_local limit 2);
--相关子查询,指EXISTS和NOT EXISTS子查询
--子查询的WHERE子句中支持对父查询的引用
SELECT A
FROM T1
WHERE EXISTS (SELECT B FROM T2 WHERE T1.X = T2.Y);
13 CTE(Common table Expressions)
13.1 概述
- 公用表表达式(CTE)是一个临时结果集:该结果集是从WITH子句中指定的简单查询派生而来的,紧接在SELECT或INSERT关键字之前。
- CTE仅在单个语句的执行范围内定义。
- CTE可以在 SELECT,INSERT, CREATE TABLE AS SELECT或CREATE VIEW AS SELECT语句中使用。

13.2 案例
--select语句中的CTE
with q1 as (select num,name,age from student where num = 95002)
select *
from q1;
-- from风格
with q1 as (select num,name,age from student where num = 95002)
from q1
select *;
-- chaining CTEs 链式
with q1 as ( select * from student where num = 95002),
q2 as ( select num,name,age from q1)
select * from (select num from q2) a;
-- union
with q1 as (select * from student where num = 95002),
q2 as (select * from student where num = 95004)
select * from q1 union all select * from q2;
--视图,CTAS和插入语句中的CTE
-- insert
create table s1 like student;
with q1 as ( select * from student where num = 95002)
from q1
insert overwrite table s1
select *;
select * from s1;
-- ctas
create table s2 as
with q1 as ( select * from student where num = 95002)
select * from q1;
-- view
create view v1 as
with q1 as ( select * from student where num = 95002)
select * from q1;
select * from v1;
14 JOIN
14.1 概述
- 在Hive中,当下版本3.1.2总共支持6种join语法。分别是:
inner join(内连接)、left join(左连接)、right join(右连接)、full outer join(全外连接)、left semi join(左半开连接)、cross join(交叉连接,也叫做笛卡尔乘积)。 - 从Hive 0.13.0开始,支持隐式联接表示法(请参阅HIVE-5558)。允许FROM子句连接以逗号分隔的表列表,而省略JOIN关键字。
- 从Hive 2.2.0开始,支持ON子句中的复杂表达式,支持不相等连接(请参阅HIVE-15211和HIVE-15251)。在此之前,Hive不支持不是相等条件的联接条件。
14.2 语法规则
table_reference:是join查询中使用的表名,也可以是子查询别名(查询结果当成表参与join)。
table_factor:与table_reference相同,是联接查询中使用的表名,也可以是子查询别名。
join_condition:join查询关联的条件,如果在两个以上的表上需要连接,则使用AND关键字。
join_table:
table_reference [INNER] JOIN table_factor [join_condition]
| table_reference {LEFT|RIGHT|FULL} [OUTER] JOIN table_reference join_condition
| table_reference LEFT SEMI JOIN table_reference join_condition
| table_reference CROSS JOIN table_reference [join_condition] (as of Hive 0.10)
join_condition:
ON expression
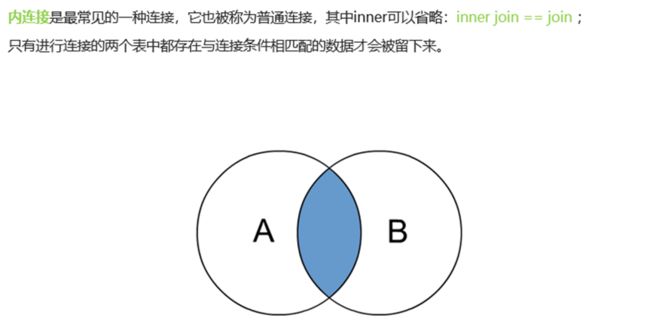
14.3 inner join 内连接
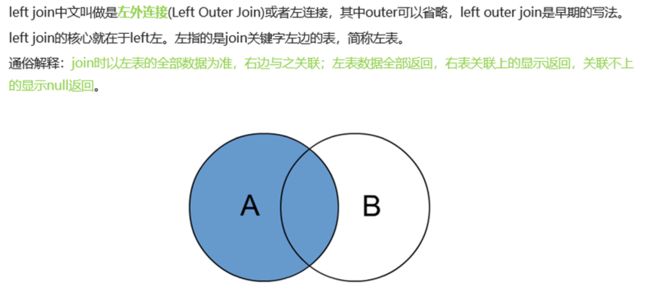
14.4 left join 左连接
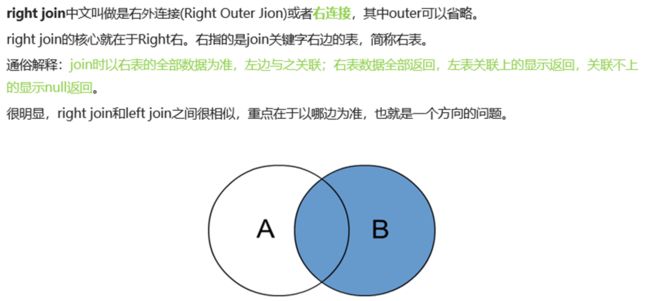
14.5 right join 右连接
14.6 full outer join 全外连接
14.7 left semi join 左半开连接
左半开连接(LEFT SEMI JOIN)会返回左边表的记录,前提是其记录对于右边的表满足ON语句中的判定条件。
从效果上来看有点像inner join之后只返回左表的结果。
select *
from employee e left semi join employee_address e_addr
on e.id =e_addr.id;
--相当于 inner join 只不过效率高一些
select e.*
from employee e inner join employee_address e_addr
on e.id =e_addr.id;
14.8 cross join 交叉连接
14.9 join注意事项
- 允许使用复杂的联接表达式,支持非等值连接
SELECT a.* FROM a JOIN b ON (a.id = b.id)
SELECT a.* FROM a JOIN b ON (a.id = b.id AND a.department = b.department)
SELECT a.* FROM a LEFT OUTER JOIN b ON (a.id <> b.id)
- 同一查询中可以连接2个以上的表
SELECT a.val, b.val, c.val FROM a JOIN b ON (a.key = b.key1) JOIN c ON (c.key = b.key2)
- 如果每个表在联接子句中使用相同的列,则Hive将多个表上的联接转换为单个MR作业
SELECT a.val, b.val, c.val FROM a JOIN b ON (a.key = b.key1) JOIN c ON (c.key = b.key1)
--由于联接中仅涉及b的key1列,因此被转换为1个MR作业来执行
SELECT a.val, b.val, c.val FROM a JOIN b ON (a.key = b.key1) JOIN c ON (c.key = b.key2)
--会转换为两个MR作业,因为在第一个连接条件中使用了b中的key1列,而在第二个连接条件中使用了b中的key2列。
-- 第一个map / reduce作业将a与b联接在一起,然后将结果与c联接到第二个map / reduce作业中。
- join时的最后一个表会通过reducer流式传输,并在其中缓冲之前的其他表,因此,将大表放置在最后有助于减少reducer阶段缓存数据所需要的内存
SELECT a.val, b.val, c.val FROM a JOIN b ON (a.key = b.key1) JOIN c ON (c.key = b.key1)
--由于联接中仅涉及b的key1列,因此被转换为1个MR作业来执行,并且表a和b的键的特定值的值被缓冲在reducer的内存中。然后,对于从c中检索的每一行,将使用缓冲的行来计算联接。
SELECT a.val, b.val, c.val FROM a JOIN b ON (a.key = b.key1) JOIN c ON (c.key = b.key2)
--计算涉及两个MR作业。其中的第一个将a与b连接起来,并缓冲a的值,同时在reducer中流式传输b的值。
-- 在第二个MR作业中,将缓冲第一个连接的结果,同时将c的值通过reducer流式传输。
5. 在join的时候,可以通过语法STREAMTABLE提示指定要流式传输的表。如果省略STREAMTABLE提示,则Hive将流式传输最右边的表。
SELECT /*+ STREAMTABLE(a) */ a.val, b.val, c.val FROM a JOIN b ON (a.key = b.key1) JOIN c ON (c.key = b.key1)
--a,b,c三个表都在一个MR作业中联接,并且表b和c的键的特定值的值被缓冲在reducer的内存中。
-- 然后,对于从a中检索到的每一行,将使用缓冲的行来计算联接。如果省略STREAMTABLE提示,则Hive将流式传输最右边的表。
6. join在WHERE条件之前进行
7. 如果除一个要连接的表之外的所有表都很小,则可以将其作为仅map作业执行(mapjoin)。
SELECT /*+ MAPJOIN(b) */ a.key, a.value FROM a JOIN b ON a.key = b.key
--不需要reducer。对于A的每个Mapper,B都会被完全读取。限制是不能执行FULL / RIGHT OUTER JOIN b。