Redis第2讲——Java三种客户端(Jedis、Lettuce和Redisson)
上篇文章介绍了Redis的9种数据类型和常命令、7种数据结构和9种编码方式。但是如果想要把它应用到项目中,我们还需要一个redis的客户端。redis的Java客户端种类还是很多的,其中使用最广泛的有三种——Jedis、lettuce和redisson,下面我们一起来学习下。
一、Redis客户端简介
介绍之前我们先来了解一下什么是客户端。客户端——即真正的使用者,比如进入redis命令操作有一个redis-cli,这其实就是redis提供的一个基于操作系统(linux、windows)的客户端,此时的使用者是电脑,电脑通过这个客户端可以连接redis并操作redis。同理,在java中如果想要要操作redis同样需要客户端来与redis建立连接。
基于redis开放的通信协议,大神们纷纷开发出了各种语言的redis客户端,包括C、C++、C#、D、java、Python、Ruby等50多种,这些客户端都是基于redis命令做了一层封装,并打包成工具,以便更方便地操作redis。
ps:SpringBoot项目用spring-data-redis的比较多,其实它主要是封装了jedis和lettuce两个客户端,相当于在它们基础上加了一层门面。
在java语言里redis官方最推荐的便是jedis、lettuce和redisson,如下图。
二、Jedis
2.1 简介
Jedis是redis老牌的Java客户端,它把Redis的所有命令封装成了Java可直接调用的方法,但它并没有替我们封装一些基于redis的特殊功能,比如分布式锁等。
官方网址:GitHub - redis/jedis: Redis Java client
2.2 基本使用
2.2.1 导入依赖
redis.clients
jedis
5.0.0
2.2.2 建立连接
Jedis实例连接redis
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1、构建一个Jedis对象,参数为host和prot
Jedis jedis=new Jedis("127.0.0.1",6379);
//2、密码验证(没设置密码的请忽略)
//jedis.auth("password");
//3、返回PONG说明连成功
String ping = jedis.ping();
System.out.println(ping);//PONG
//4、释放资源
jedis.close();
}
}对于Jedis而言,一旦连接上了redis服务器,剩下的操作就非常容易了,因为Jedis提供的API和redis的命令基本相同,比如get命令Jedis里面也是get,set对应set...
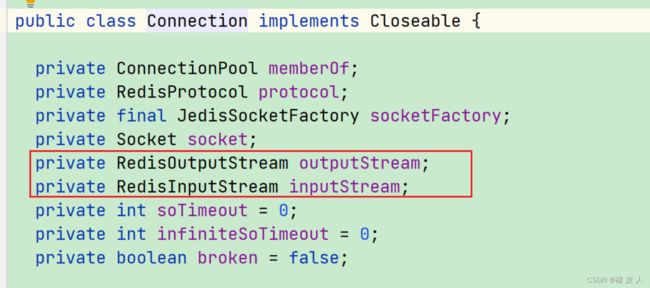
不过我们通常不用这种方式连接redis,而是用连接池,因为在多线程共享一个Jedis实例是线程不安全的。这里并不是说redis处理数据不安全,而是Jedis向reids推数据和获取数据不安全。在单个Jedis实例中有RedisInputStream和RedisOutPutStream两个成员变量,发送命令和获取返回值都是使用这两个变量,显然这很容易发生并发问题。
既然多个线程使用一个实例就会产生问题,那我们就给每个线程分配一个Jedis实例,让他们单独取操作自己的数据,这里就得使用JedisPool线程池来实现了,在使用过程中,我们通常会封装一个工具类:
//引入common-pool线程池依赖包
org.apache.commons
commons-pool2
2.11.1
public class JedisPoolFactory {
private static JedisPool jedisPool = null;
//地址
private static String addr = "127.0.0.1";
//端口
private static int port = 6379;
//密码
private static String auth = "";
static{
try {
JedisPoolConfig config = new JedisPoolConfig();
//连接耗尽时是否阻塞, false报异常,ture阻塞直到超时, 默认true
config.setBlockWhenExhausted(true);
//设置的逐出策略类名, 默认DefaultEvictionPolicy(当连接超过最大空闲时间,或连接数超过最大空闲连接数)
config.setEvictionPolicyClassName("org.apache.commons.pool2.impl.DefaultEvictionPolicy");
//是否启用pool的jmx管理功能, 默认true
config.setJmxEnabled(true);
//MBean ObjectName = new ObjectName("org.apache.commons.pool2:type=GenericObjectPool,name=" + "pool" + i); 默认为"pool", JMX不熟,具体不知道是干啥的...默认就好.
config.setJmxNamePrefix("pool");
//是否启用后进先出, 默认true
config.setLifo(true);
//最大空闲连接数, 默认8个
config.setMaxIdle(8);
//最大连接数, 默认8个
config.setMaxTotal(8);
//获取连接时的最大等待毫秒数(如果设置为阻塞时BlockWhenExhausted),如果超时就抛异常, 小于零:阻塞不确定的时间, 默认-1
config.setMaxWaitMillis(-1);
//逐出连接的最小空闲时间 默认1800000毫秒(30分钟)
config.setMinEvictableIdleTimeMillis(1800000);
//最小空闲连接数, 默认0
config.setMinIdle(0);
//每次逐出检查时 逐出的最大数目 如果为负数就是 : 1/abs(n), 默认3
config.setNumTestsPerEvictionRun(3);
//对象空闲多久后逐出, 当空闲时间>该值 且 空闲连接>最大空闲数 时直接逐出,不再根据MinEvictableIdleTimeMillis判断 (默认逐出策略)
config.setSoftMinEvictableIdleTimeMillis(1800000);
//在获取连接的时候检查有效性, 默认false
config.setTestOnBorrow(false);
//在空闲时检查有效性, 默认false
config.setTestWhileIdle(false);
//逐出扫描的时间间隔(毫秒) 如果为负数,则不运行逐出线程, 默认-1
config.setTimeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis(-1);
jedisPool = new JedisPool(config, addr, port, 3000, auth);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 获取 Jedis 资源
* @return
*/
public static Jedis getJedis() {
if (jedisPool != null) {
return jedisPool.getResource();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 释放Jedis资源
*/
public static void close(final Jedis jedis) {
if (jedis != null) {
jedis.close();
}
}
}2.2.3 操作redis
本次就演示String数据类型的操作。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//1、建立连接
Jedis jedis = JedisPoolFactory.getJedis();
//2、操作redis
System.out.println("清空数据:"+jedis.flushDB());
System.out.println("判断某个键是否存在:"+jedis.exists("xhz"));
System.out.println("新增键:"+jedis.set("xhz","ctr"));
System.out.println("xhz键是否存在:"+jedis.exists("xhz"));
System.out.println("所有键:"+jedis.keys("*"));
System.out.println("给xhz键设置生存时间:"+jedis.expire("xhz",100L));
//sleep1秒
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println("查看xhz键剩余生存时间:"+jedis.ttl("xhz"));
System.out.println("查看xhz键的编码方式:"+jedis.objectEncoding("xhz"));
System.out.println("查看xhz键的类型:"+jedis.type("xhz"));
System.out.println("获取xhz键:"+jedis.get("xhz"));
System.out.println("删除xhz键:"+jedis.del("xhz"));
//关闭连接
JedisPoolFactory.close(jedis);
}
} 测试结果:
清空数据:OK
判断某个键是否存在:false
新增键:OK
xhz键是否存在:true
所有键:[xhz]
给xhz键设置生存时间:1
查看xhz键剩余生存时间:99
查看xhz键的编码方式:embstr
查看xhz键的类型:string
获取xhz键:ctr
删除xhz键:1 2.3 集群配置
redis通常是通过集群配置,来保证服务的高可用。常用的搭建的方式有2种:
哨兵模式:在主从复制的基础上,增加一个节点对redis服务进行监控,如果master宕机,就从slave节点选一个作为master,实现自动切换。
Cluster模式:将数据进行分片存储,避免全部节点数据一样,浪费空间。
ps:这里就简单介绍一下,后续会专门有一篇介绍redis集群的文章。
2.3.1 哨兵模式
哨兵模式简单来说就是一台主机、一台或多台备机、外加一台监控节点(哨兵节点),当主机宕机,监控节点就会将备用节点自动切换成主机,以便继续提供服务。
public class SentinePoolUtil {
private static Jedis jedis;
private static JedisSentinelPool jedisSentinelPool;
static{
try {
JedisPoolConfig config = new JedisPoolConfig();
//最大空闲连接数, 默认8个
config.setMaxIdle(8);
//最大连接数, 默认8个
config.setMaxTotal(8);
//最小空闲连接数, 默认0
config.setMinIdle(0);
//获取连接时的最大等待毫秒数(如果设置为阻塞时BlockWhenExhausted),如果超时就抛异常, 小于零:阻塞不确定的时间, 默认-1
config.setMaxWaitMillis(3000);
//在获取连接的时候检查有效性,表示取出的redis对象可用, 默认false
config.setTestOnBorrow(true);
//redis服务器列表
Set sentinels = new HashSet<>();
sentinels.add("host:port1");
sentinels.add("host:port2");
sentinels.add("host:port3");
//初始化连接池
jedisSentinelPool = new JedisSentinelPool("mymaster", sentinels, config, "password");
// 从池中获取一个Jedis对象
jedis = jedisSentinelPool.getResource();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} 2.3.2 Cluster集群配置
Cluster模式是一种高级集群模式,它通过数据分片和分布式存储实现了负载均衡和高可用。在Cluster模式下,redis将所有键值对数据分散在多个节点上。每个节点负责一部分数据(slot槽),简而言之,Cluster模式突破了单节点的内存限制,实现了更大规模的数据存储。
public class ClusterUtil {
private static JedisCluster jedisCluster;
static{
try {
Set nodes = new HashSet<>();
nodes.add(new HostAndPort("host", 2222));
nodes.add(new HostAndPort("host", 3333));
nodes.add(new HostAndPort("host", 4444));
nodes.add(new HostAndPort("host", 5555));
nodes.add(new HostAndPort("host", 6666));
nodes.add(new HostAndPort("host", 7777));
jedisCluster = new JedisCluster(nodes);
jedisCluster.set("key", "hello world");
jedisCluster.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} 2.4 byte[]方式操作
使用的时候不难发现,除了String方式,还支持byte[]方式操作。Spring提供了序列化byte[]的操作
-
导入依赖
org.springframework
spring-context
5.2.10.RELEASE
-
测试
public class ByteTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Jedis jedis = JedisPoolFactory.getJedis();
//2.1 准备对象-注意:要实现Serializable接口
User user = new User();
user.setAge(18);
user.setName("娃哈哈哈哈哈哈哈哈");
//2.2 通过Spring提供的工具类将user对象转为byte[]
byte[] value = SerializationUtils.serialize(user);
byte[] key = SerializationUtils.serialize("user");
//2.3 存储
jedis.setex(key,888888,value);
//2.5 获取
byte[] value1 = jedis.get(key);
//2.4 反序列化byte[]
User user1 = (User) SerializationUtils.deserialize(value1);
System.out.println(user1);//User(name=娃哈哈哈哈哈哈哈哈, age=18)
}
}2.5 Jedis管道操作
Redis更多的使用来做缓存。
应当在项目启动时,就从传统的MySQL、Oracle数据库中将作为缓存的数据查询出来并且同步到Redis服务中。
可能需要在项目启动时,将数10W甚至上百万的数据同步到Redis中,会在客户端和Redis服务交互时,网络传输数据所带来的性能损耗是很大的,采用管道来解决这个问题。
管道可以实现将大量的请求任务在客户端封装好,一次性的发送给Redis服务,从而减少网络请求带来的损耗
-
现测试不用管道存储10w条数据(测试4.06秒)
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Jedis jedis = JedisPoolFactory.getJedis();
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 不采用管道,向Redis存储10W条数据
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
jedis.setex("key" + i,500, UUID.randomUUID().toString());
}
System.out.println((System.currentTimeMillis()-start)+"ms");//4060ms
//返还连接对象
jedis.close();
}
}-
采用管道(测试0.64秒)
public class PipelineTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Jedis jedis = JedisPoolFactory.getJedis();
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 采用管道,向Redis存储10W条数据
Pipeline pipelined = jedis.pipelined();
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
pipelined.setex("key" + i,500, UUID.randomUUID().toString());
}
pipelined.sync();
System.out.println((System.currentTimeMillis()-start)+"ms");//649ms
//返还连接对象
jedis.close();
}
}2.6 优缺点
优点:
- Jedis 提供了简单直观的API,它的API与Redis命令一一对应,易于学习和使用。
- Jedis 客户端使用高性能的连接池,支持连接复用,可有效地减少频繁创建和关闭连接对性能的影响。同时支持 pipelining 等批量操作,能够有效地提升 Redis 的性能,减少网络开销。并且使用高效的序列化机制(如使用对象池和二进制序列化)来提供快速的数据访问和传输。
- Jedis 客户端提供了对 Redis Cluster(Redis 集群)的支持,可以轻松地与 Redis 集群进行交互、自动故障转移和负载均衡。
缺点:
- Jedis 客户端的使用方式相对简单,只提供了一些基本的接口方法,如果需要实现自己的功能,需要自己重写或者拓展 Jedis 客户端。
- Jedis 客户端实例不是线程安全的,需要借助连接池来管理和使用 Jedis。
- 使用阻塞的I/O,且其方法调用都是同步的,程序流需要等到 sockets 处理完 I/O 才能执行,不支持异步
三、Lettuce
3.1 简介
Lettuce是一个高级redis客户端,支持高级的redis特性,比如Sentinel、集群、流水线、自动重新连接和redis数据模型等。目前已成为SpringBoot 2.0版本默认的redis客户端。
相比于Jedis,lettuce不仅功能丰富,而且提供了很多新的功能特性,比如异步操作、响应式编程等,同时还解决了Jedis线程不安全的问题。
官方地址:GitHub - lettuce-io/lettuce-core: Advanced Java Redis client for thread-safe sync, async, and reactive usage. Supports Cluster, Sentinel, Pipelining, and codecs.
3.2 基本使用
3.2.1 导入依赖
io.lettuce
lettuce-core
5.3.3.RELEASE
3.2.2 建立连接
Lettuce连接设计的时候,就是线程安全的,所以一个连接可以被多个线程共享,同时lettuce连接默认是自动重连的,使用单连接基本可以满足业务需求,大多数情况下不需要配置线程池,多连接并不会给操作带来性能上的提升。
工具类:
public class LettuceSyncClient {
private static final String HOST = "127.0.0.1";
private static final int PORT = 6379;
private static RedisClient redisClient;
private static StatefulRedisConnection connection;
private static RedisCommands syncCommands;
//响应式编程
private static RedisReactiveCommands reactiveCommands;
//发布订阅
private static StatefulRedisPubSubConnection pubSubConn;
public static RedisCommands getConnection() {
if (syncCommands == null) {
getConn();
syncCommands = connection.sync();
}
return syncCommands;
}
/**
* 响应式编程
* @return
*/
public static RedisReactiveCommands getReactiveConn() {
if (reactiveCommands == null) {
getConn();
//响应式编程
reactiveCommands = connection.reactive();
}
return reactiveCommands;
}
/**
* 发布订阅
* @return
*/
public static StatefulRedisPubSubConnection getPubSubConn(){
if (pubSubConn == null) {
getConn();
//发布订阅
pubSubConn = redisClient.connectPubSub();
}
return pubSubConn;
}
public static void getConn(){
RedisURI redisUri = RedisURI.builder()
.withHost(HOST)
.withPort(PORT)
// .withPassword("password")
.withTimeout(Duration.of(10, ChronoUnit.SECONDS))
.build();
redisClient = RedisClient.create(redisUri);
connection = redisClient.connect();
}
public static void close() {
if (connection != null && syncCommands != null) {
connection.close();
redisClient.shutdown();
}
}
} 测试:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取RedisCommands
RedisCommands commands = LettuceClient.getConnection();
//测试连接
System.out.println(commands.ping());//PONG
//关闭连接
LettuceClient.close();
}
} 3.2.3 操作redis
其实和Jedis操作大差不差,这里就不纠结了:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//1、获取RedisCommands
RedisCommands commands = LettuceClient.getConnection();
//2、操作redis
System.out.println("清空数据:"+commands.flushdb());
System.out.println("判断某个键是否存在:"+commands.exists("xhz"));
System.out.println("新增键:"+commands.set("xhz","ctr"));
System.out.println("是否存在:"+commands.exists("xhz"));
System.out.println("所有键:"+commands.keys("*"));
System.out.println("给xhz键设置生存时间:"+commands.expire("xhz",100L));
//sleep1秒
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println("查看xhz键剩余生存时间:"+commands.ttl("xhz"));
System.out.println("查看xhz键的编码方式:"+commands.objectEncoding("xhz"));
System.out.println("查看xhz键的类型:"+commands.type("xhz"));
System.out.println("获取xhz键:"+commands.get("xhz"));
System.out.println("删除xhz键:"+commands.del("xhz"));
//3、关闭连接
LettuceClient.close();
}
} 3.2.4 响应式编程
Lettuce引入响应式编程框架时Project Reactor,通过使用Lettuce的响应式API,可以以流式方式处理redis:
public class ReactiveTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//建立连接
RedisReactiveCommands commands = LettuceSyncClient.getReactiveConnection();
//操作redis
Mono setc = commands.set("name", "xhz");
System.out.println(setc.block());
Mono getc = commands.get("name");
getc.subscribe(System.out::println);
Flux keys = commands.keys("*");
keys.subscribe(System.out::println);
//开启一个事务,先把count设置为1,再将count自增1
commands.multi().doOnSuccess(r -> {
commands.set("count", "1").doOnNext(value -> System.out.println("count1:" + value)).subscribe();
commands.incr("count").doOnNext(value -> System.out.println("count2:" + value)).subscribe();
}).flatMap(s -> commands.exec())
.doOnNext(transactionResult -> System.out.println("transactionResult:" + transactionResult.wasDiscarded())).subscribe();
Thread.sleep(1000 * 5);
//关闭连接
LettuceSyncClient.close();
}
} 运行结果:
OK
xhz
name
count1:OK
count2:2
transactionResult:false3.2.5 发布订阅
public class PubSubTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
StatefulRedisPubSubConnection pubSubConn = LettuceSyncClient.getPubSubConn();
// 监听器对象,用于接收订阅频道的消息
pubSubConn.addListener(new RedisPubSubListener() {
@Override
public void message(String channel, String message) {
System.out.println("Received new message - Channel: " + channel + ", Message: " + message);
}
@Override
public void message(String pattern, String channel, String message) {
System.out.println("pattern = " + pattern + ",channel = "+channel+",message = "+message);
}
@Override
public void subscribed(String channel, long count) {
System.out.println("channel = " + channel);
}
@Override
public void psubscribed(String pattern, long count) {
System.out.println("pattern = " + pattern);
}
@Override
public void unsubscribed(String channel, long count) {
System.out.println("channel = " + channel);
}
@Override
public void punsubscribed(String pattern, long count) {
System.out.println("pattern = " + pattern);
}
});
// 订阅聊天频道
pubSubConn.sync().subscribe("chat");
// 模拟用户发送消息
String user = "User1";
String message = "Hello, world!";
// 将消息发布到聊天频道
RedisCommands connection = LettuceSyncClient.getConnection();
Long messagesSent = connection.publish("chat", "[" + user + "]: " + message);
System.out.println("Messages sent: " + messagesSent);
//关闭连接
LettuceSyncClient.close();
}
} 测试结果:
channel = chat
Messages sent: 1
Received new message - Channel: chat, Message: [User1]: Hello, world!3.3 集群配置
3.3.1 主从模式
Lettuce支持自动发现主从模式下的节点信息,然后保存到本地,具体如下:
public class MsTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//这里只需要配置一个节点的连接信息,不一定需要是主节点的信息,从节点也可以;可以自动发现主从节点
RedisURI uri = RedisURI.builder()
.withHost("127.0.0.1")
.withPort(6379)
// .withPassword("123456")
.build();
RedisClient client = RedisClient.create(uri);
StatefulRedisMasterReplicaConnection connection = MasterReplica.connect(client, StringCodec.UTF8, uri);
//从节点读取数据
connection.setReadFrom(ReadFrom.REPLICA);
RedisCommands commands = connection.sync();
commands.set("name", "xhz");
System.out.println(commands.get("name"));
connection.close();
client.shutdown();
}
} 3.3.2 哨兵模式
public class SentinalTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//集群节点
List uris = new ArrayList();
uris.add(RedisURI.builder().withSentinel("host", 2222).withSentinelMasterId("mymaster").withPassword("123456").build());
uris.add(RedisURI.builder().withSentinel("host", 3333).withSentinelMasterId("mymaster").withPassword("123456").build());
uris.add(RedisURI.builder().withSentinel("host", 4444).withSentinelMasterId("mymaster").withPassword("123456").build());
RedisClient client = RedisClient.create();
StatefulRedisMasterReplicaConnection connection = MasterReplica.connect(client, StringCodec.UTF8, uris);
//从节点读取数据
connection.setReadFrom(ReadFrom.REPLICA);
RedisCommands commands = connection.sync();
commands.set("name", "xhz");
System.out.println(commands.get("name"));
connection.close();
client.shutdown();
}
} 3.3.3 Cluster模式
public class ClusterTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set uris = new HashSet<>();
uris.add(RedisURI.builder().withHost("host").withPort(1111).withPassword("123456").build());
uris.add(RedisURI.builder().withHost("host").withPort(2222).withPassword("123456").build());
uris.add(RedisURI.builder().withHost("host").withPort(3333).withPassword("123456").build());
uris.add(RedisURI.builder().withHost("host").withPort(4444).withPassword("123456").build());
uris.add(RedisURI.builder().withHost("host").withPort(5555).withPassword("123456").build());
uris.add(RedisURI.builder().withHost("host").withPort(6666).withPassword("123456").build());
RedisClusterClient client = RedisClusterClient.create(uris);
StatefulRedisClusterConnection connection = client.connect();
RedisAdvancedClusterCommands commands = connection.sync();
commands.set("name", "xhz");
System.out.println(commands.get("name"));
//选择从节点,只读
NodeSelection replicas = commands.replicas();
NodeSelectionCommands nodeSelectionCommands = replicas.commands();
Executions> keys = nodeSelectionCommands.keys("*");
keys.forEach(key -> System.out.println(key));
connection.close();
client.shutdown();
}
}
3.4 优缺点
优点:
- 异步和非阻塞:Lettuce 客户端使用异步和非阻塞的方式与 Redis 交互,可以处理并行的请求和高并发的场景,提供更高的吞吐量和响应速度。
- 响应式编程模型:Lettuce 客户端支持 Reactive 编程模型,可以通过使用 Reactive Streams、Flux 或 Mono 这样的响应式类型来处理异步操作和流式数据处理。
- 完整的特性支持:Lettuce 客户端支持 Redis 的所有高级特性,如事务、流水线操作、发布/订阅、Lua 脚本等,可以满足复杂的应用需求。
- 集群支持:Lettuce 客户端提供了对 Redis Cluster 的支持,可以轻松地与 Redis 集群进行交互,并进行自动的故障转移和节点发现。
- 可扩展性:Lettuce 客户端使用模块化的设计,可以通过插件机制进行功能扩展,可以根据需求选择所需的模块,减小依赖的大小。
缺点:
- 和其他 Redis 客户端相比,Lettuce 的使用可能稍微复杂,需要更多的学习和了解。
四、Redisson
Redis官方置顶推荐的Java客户端Redisson。
4.1 简介
Redisson是架设再redis基础上的一个Java驻内存数据网格(In-Memory Data Grid)。它不仅将原生的redis Hash、List、Set、String等数据结构封装为Java里大家熟悉的Map、List、Set、Object Bukcket等数结构,并在此基础上还提供了许多分布式服务,比如分布式锁、分布式对象、分布式集合、分布式调度任务等。
相比于Jedis、Lettuce等基于redis基础命令封装的客户端,Redisson提供的功能更加高端和抽象。
官方地址:GitHub - redisson/redisson: Redisson - Easy Redis Java client with features of In-Memory Data Grid. Sync/Async/RxJava/Reactive API. Over 50 Redis based Java objects and services: Set, Multimap, SortedSet, Map, List, Queue, Deque, Semaphore, Lock, AtomicLong, Map Reduce, Bloom filter, Spring Cache, Tomcat, Scheduler, JCache API, Hibernate, RPC, local cache ...
4.2 基本使用
4.2.1 导入依赖
org.redisson
redisson
3.21.3
4.2.2 建立连接
单机模式连接如下:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Config config = new Config();
config.useSingleServer()
.setAddress("redis://127.0.0.1:6379")
// .setPassword("123456")
.setDatabase(0);
//获取客户端
RedissonClient redisson = Redisson.create(config);
//哈希结构
RMap hash = redisson.getMap("hash");
hash.put("name","xhz");
String name = hash.get("name").toString();
System.out.println(name);//xhz
//关闭客户端
redisson.shutdown();
}
} 当然也可以用配置文件的方式:
redisson.yml:
singleServerConfig:
idleConnectionTimeout: 10000 # 空闲连接超时,单位:毫秒
connectTimeout: 10000 # 连接超时,单位:毫秒
timeout: 3000 # 命令等待超时,单位:毫秒
retryAttempts: 3 # 命令失败重试次数
retryInterval: 1500 # 命令重试发送间隔,单位:毫秒
password: null # Redis 服务器密码
subscriptionsPerConnection: 5 # 每个连接的最大订阅数量
clientName: null # Redis 客户端名称
address: "redis://127.0.0.1:6379" # Redis 服务器地址
subscriptionConnectionMinimumIdleSize: 1 # 订阅连接的最小空闲数量
subscriptionConnectionPoolSize: 50 # 订阅连接的最大连接数量
connectionMinimumIdleSize: 10 # 正常连接的最小空闲数量,至少保持10个空闲连接
connectionPoolSize: 50 # 正常连接的最大连接数量,最多可以创建50个连接
database: 0 # 连接的数据库编号,默认是0
dnsMonitoringInterval: 5000 # DNS监控间隔,单位:毫秒测试连接:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Config config = Config.fromYAML(Test.class.getClassLoader().getResource("redisson.yml"));
RedissonClient redisson = Redisson.create(config);
RMap hash = redisson.getMap("hash");
hash.put("name","xhz");
String name = hash.get("name").toString();
System.out.println(name);//xhz
redisson.shutdown();
}
} 4.2.3 操作redis
下面我们介绍一下5中基本类型的操作:
public class OperTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Config config = Config.fromYAML(Test.class.getClassLoader().getResource("redisson.yml"));
RedissonClient redisson = Redisson.create(config);
//1、字符串操作
RBucket运行结果:
xhz
User(name=xhz, age=18)
key = name: value = 张三
key = age: value = 18
[User(name=张三, age=18), User(name=李四, age=20)]
[User(name=赵六, age=20), User(name=王五, age=18)]
[User(name=王五, age=18), User(name=赵六, age=19)]4.2.4 布隆过滤器
布隆过滤器是由布隆在1970年提出的。它实际上是一个很长的二进制向量和一系列的随机映射函数(哈希函数)两部分组成的结构,用于快速检索一个元素是否可能存在于一个集合(bit数组中)。
实现方式有很多,比如Guava、Apache Commons、Jedis和Redisson等,我们今天就介绍一下Redisson的实现方式:
public class BloomTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Config config = Config.fromYAML(Test.class.getClassLoader().getResource("redisson.yml"));
RedissonClient redisson = Redisson.create(config);
RBloomFilter bloom = redisson.getBloomFilter("bloom");
//初始化预期插入的数据量为100和期望误差率为0.01
bloom.tryInit(100,0.01);
//插入数据
bloom.add("哈哈");
bloom.add("嘻嘻");
bloom.add("嘿嘿");
//判断数据是否存在
System.out.println(bloom.contains("哈哈"));//true
System.out.println(bloom.contains("呵呵"));//false
redisson.shutdown();
}
} 4.2.5 分布式锁
Redisson最大的亮点,也是使用最多的功能,就是分布式锁,使用起来还是挺简单的:
public class LockTest {
private static final String KEY = "xhz";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Config config = Config.fromYAML(Test.class.getClassLoader().getResource("redisson.yml"));
RedissonClient redisson = Redisson.create(config);
RLock lock = redisson.getLock(KEY);
if (!lock.tryLock()) {
//没获取到锁,提前结束
return;
}
try {
//处理业务逻辑
System.out.println("获取锁成功");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("发生异常");
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
//释放锁
if(lock.isLocked() && lock.isHeldByCurrentThread()){
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
}ps:另外,Redisson还支持公平锁、联锁、红锁、读写锁、信号量、闭锁等,后续会专门总结一篇分布式锁的文章。
4.3 集群配置
上面已经简单介绍过了,这次就简单说了。
4.3.1 主从模式
public class MsTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Config config = new Config();
config.useMasterSlaveServers()
//可以用"rediss://"来启用SSL连接
.setMasterAddress("redis://127.0.0.1:6379")
.addSlaveAddress("redis://127.0.0.1:6389", "redis://127.0.0.1:6332", "redis://127.0.0.1:6419")
.addSlaveAddress("redis://127.0.0.1:6399");
RedissonClient redisson = Redisson.create(config);
}
}yaml格式:
---
masterSlaveServersConfig:
idleConnectionTimeout: 10000
connectTimeout: 10000
timeout: 3000
retryAttempts: 3
retryInterval: 1500
failedAttempts: 3
password: null
subscriptionsPerConnection: 5
clientName: null
loadBalancer: ! {}
slaveSubscriptionConnectionMinimumIdleSize: 1
slaveSubscriptionConnectionPoolSize: 50
slaveConnectionMinimumIdleSize: 32
slaveConnectionPoolSize: 64
masterConnectionMinimumIdleSize: 32
masterConnectionPoolSize: 64
readMode: "SLAVE"
slaveAddresses:
- "redis://127.0.0.1:6381"
- "redis://127.0.0.1:6380"
masterAddress: "redis://127.0.0.1:6379"
database: 0
threads: 0
nettyThreads: 0
codec: ! {}
"transportMode":"NIO" 4.3.2 哨兵模式
public class SentinalTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Config config = new Config();
config.useSentinelServers()
.setMasterName("mymaster")
//可以用"rediss://"来启用SSL连接
.addSentinelAddress("127.0.0.1:26389", "127.0.0.1:26379")
.addSentinelAddress("127.0.0.1:26319");
RedissonClient redisson = Redisson.create(config);
}
}yaml格式:
---
sentinelServersConfig:
idleConnectionTimeout: 10000
connectTimeout: 10000
timeout: 3000
retryAttempts: 3
retryInterval: 1500
password: null
subscriptionsPerConnection: 5
clientName: null
loadBalancer: ! {}
slaveSubscriptionConnectionMinimumIdleSize: 1
slaveSubscriptionConnectionPoolSize: 50
slaveConnectionMinimumIdleSize: 32
slaveConnectionPoolSize: 64
masterConnectionMinimumIdleSize: 32
masterConnectionPoolSize: 64
readMode: "SLAVE"
sentinelAddresses:
- "redis://127.0.0.1:26379"
- "redis://127.0.0.1:26389"
masterName: "mymaster"
database: 0
threads: 0
nettyThreads: 0
codec: ! {}
"transportMode":"NIO" 4.3.3 Cluster模式
public class Cluster {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Config config = new Config();
config.useClusterServers()
.setScanInterval(2000) // 集群状态扫描间隔时间,单位是毫秒
//可以用"rediss://"来启用SSL连接
.addNodeAddress("redis://127.0.0.1:7000", "redis://127.0.0.1:7001")
.addNodeAddress("redis://127.0.0.1:7002");
RedissonClient redisson = Redisson.create(config);
}
}yaml格式:
---
clusterServersConfig:
idleConnectionTimeout: 10000
connectTimeout: 10000
timeout: 3000
retryAttempts: 3
retryInterval: 1500
password: null
subscriptionsPerConnection: 5
clientName: null
loadBalancer: ! {}
slaveSubscriptionConnectionMinimumIdleSize: 1
slaveSubscriptionConnectionPoolSize: 50
slaveConnectionMinimumIdleSize: 32
slaveConnectionPoolSize: 64
masterConnectionMinimumIdleSize: 32
masterConnectionPoolSize: 64
readMode: "SLAVE"
nodeAddresses:
- "redis://127.0.0.1:7004"
- "redis://127.0.0.1:7001"
- "redis://127.0.0.1:7000"
scanInterval: 1000
threads: 0
nettyThreads: 0
codec: ! {}
"transportMode":"NIO" 4.4 优缺点
优点:
- 实现了分布式特性和可扩展的 Java 数据结构,例如分布式锁,分布式集合,分布式对象,分布式远程调度等等高级功能,适合分布式开发
- 与 Lettuce 一样,基于 Netty 框架的事件驱动与 redis 通信,支持异步调用,性能高
- Redisson 的 API 是线程安全的,所以可以使用单个 Redisson 连接来完成各种操作。
- 支持读写分离,支持读负载均衡,在主从复制和 Redis Cluster 架构下都可以使用
- 内建 Tomcat Session Manager,为 Tomcat 6/7/8 提供了会话共享功能,可以与 Spring Session 集成,实现基于 Redis 的会话共享
- 相比于 Jedis、Lettuce 等基于 redis 命令封装的客户端,Redisson 提供的功能更加高端和抽象,Redisson 可以类比 Spring 框架,这些框架搭建了应用程序的基础框架和功能,可以显著提升开发效率,让开发者有更多的时间来关注业务逻辑
缺点:
- 和 Jedis、Lettuce 客户端相比,功能较为简单,对字符串的支持比较差,不支持排序、事务、管道、分区等 Redis 特性
- API 更加抽象,学习使用成本高
End:希望对大家有所帮助,如果有纰漏或者更好的想法,请您一定不要吝啬你的赐教。