刷题记录Day16-二叉树(二叉树的最大最小深度、完全二叉树的节点个数)
刷题记录Day16-二叉树(二叉树的最大最小深度、完全二叉树的节点个数)
文章目录
- 刷题记录Day16-二叉树(二叉树的最大最小深度、完全二叉树的节点个数)
- 前言
- 一、二叉树的最大深度
-
- 1. 104二叉树的最大深度
- 2. 559n叉树的最大深度
- 二、二叉树最小深度
-
- 1. 111最小深度
- 三、 完全二叉树的节点个数
-
- 1. 222完全二叉树的节点个数
- 总结
前言
题目来源:leetcode
刷题顺序:代码随想录
刷题工具:VSCode+leetcode插件
补充:延毕时间充裕,会结合LeetCode 101: A LeetCode Grinding Guide (C++ Version)相似题目一起做。
一、二叉树的最大深度
1. 104二叉树的最大深度
这道题在前一篇文章中用层序遍历做过一次 这次使用后序递归遍历做
题目:
给定一个二叉树 root ,返回其最大深度。
二叉树的 最大深度 是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
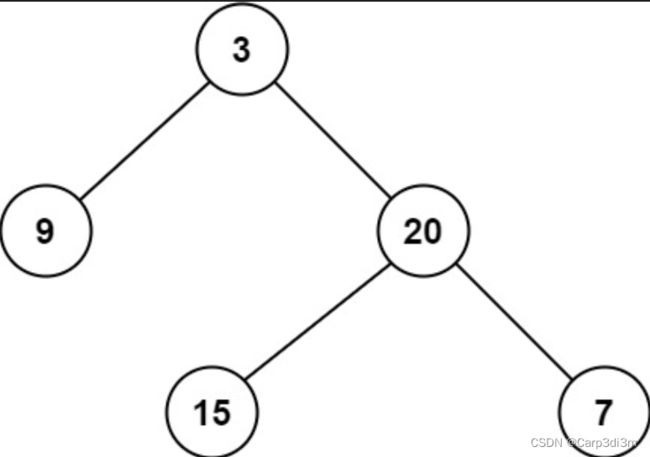
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:3
代码:
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
//采取后序遍历递归的方法
if (root == NULL) return 0;
int leftHeight = maxDepth(root->left); //左
int rightHeight = maxDepth(root->right); //右
int height = 1 + max(leftHeight, rightHeight); //中
return height;
}
};
2. 559n叉树的最大深度
题目:
给定一个 N 叉树,找到其最大深度。
最大深度是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点总数。
N 叉树输入按层序遍历序列化表示,每组子节点由空值分隔(请参见示例)。
输入:root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6]
输出:3
代码:
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(Node* root) {
if (root == NULL) return 0;
int height = 0;
for (auto node : root->children){
height = max(height,maxDepth(node));
}
return 1+height;
}
};
二、二叉树最小深度
1. 111最小深度
这道题也在昨天练习中用层序遍历做过了 今天用后序递归迭代再做一次
题目:
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
说明:叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:2
代码:
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return 0;
int leftHeight = minDepth(root->left);
int rightHeight = minDepth(root->right);
if (root->left == NULL && root->right != NULL){
return 1+rightHeight;
}
if (root->right == NULL && root->left != NULL){
return 1+leftHeight;
}
int height = 1 + min(leftHeight,rightHeight);
return height;
}
};
三、 完全二叉树的节点个数
1. 222完全二叉树的节点个数
题目:
给你一棵 完全二叉树 的根节点 root ,求出该树的节点个数。
完全二叉树 的定义如下:在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第 h 层,则该层包含 1~ 2h 个节点。
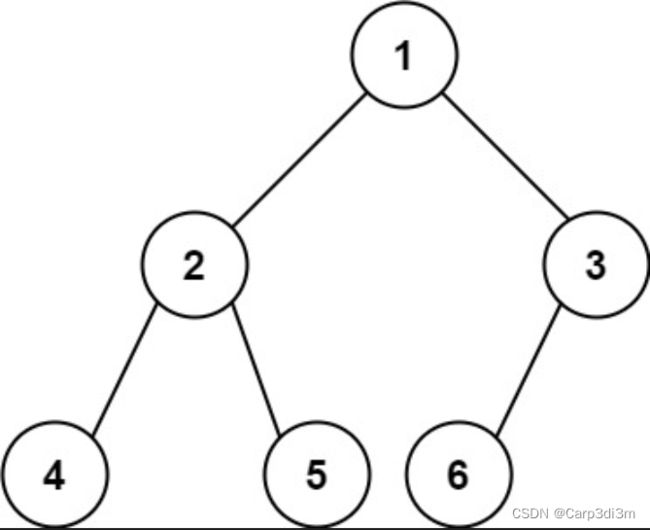
输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
输出:6
代码:
方法一,后序遍历递归
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return 0;
int lcount = countNodes(root->left);
int rcount = countNodes(root->right);
int count = 1 + lcount + rcount;
return count;
}
};
方法二,层序遍历
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
int res = 0;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
if (root != NULL) que.push(root);
while (!que.empty()){
int size = que.size();
while (size--){
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
++res;
if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
}
return res;
}
};
方法三,基于完全二叉树的性质
如果左深度等于右深度,说明子树是一个满二叉树,那就可以直接返回2^深度-1。
如果不相等,则遍历下一层的左右子树。
相当于增加了迭代终止条件。
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL) return 0;
TreeNode* leftNode = root->left;
TreeNode* rightNode = root->right;
int leftHeight =0, rightHeight = 0;
while (leftNode){
leftNode = leftNode->left;
++leftHeight;
}
while (rightNode){
rightNode = rightNode->right;
++rightHeight;
}
if (leftHeight == rightHeight){
return (2 << leftHeight)-1;
}
return countNodes(root->left)+countNodes(root->right)+1;
}
};
总结
感觉二叉树最重要的地方在于掌握递归和迭代,尤其是递归很多地方比较难理解。