java --- 异常
目录
一、异常体系介绍
二、异常的作用
三、异常处理方式
3.1 捕获异常
2.1 灵魂一问: 如果try中没有遇到问题,如何执行?
2.2 灵魂二问:如果try中可能会遇到多个问题,怎么执行?
2.3 灵魂三问:如果try中遇到的问题没有被捕获,怎么执行?
2.4 灵魂四问:如果try中遇到了问题,那么try下面的其他代码还会执行吗?
3. 抛出异常
四、 异常中常见方法
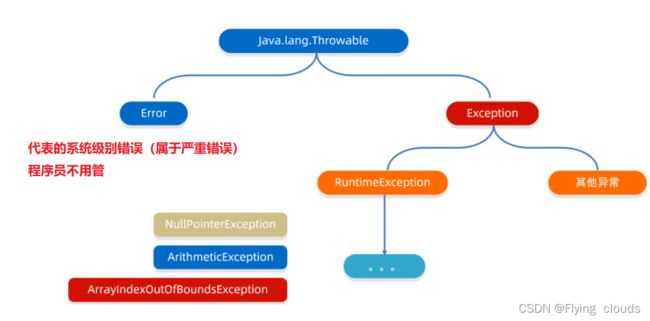
一、异常体系介绍
Exception:叫做异常,代表程序可能出现的问题。
我们通常会用Exception以及他的子类来封装程序出现的问题。
运行时异常:RuntimeException及其子类,编译阶段不会出现异常提醒。
运行时出现的异常。(如:数组索引越界异常)
编译时异常:没有继承RuntimeException的异常,直接继承与Exception。
编译阶段就会出现异常提醒。(如:日期解析异常)
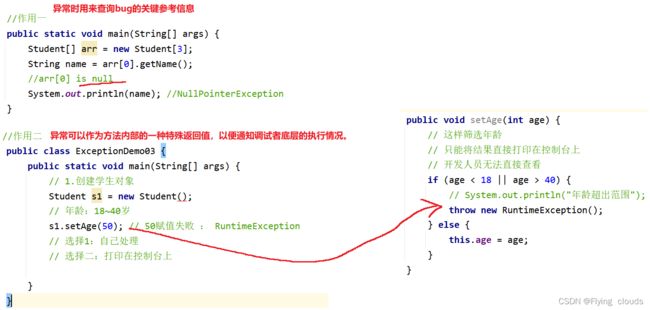
二、异常的作用
- 作用一:异常时用来查询bug的关键参考信息
- 作用二:异常可以作为方法内部的一种特殊返回值,以便通知调试者底层的执行情况。
三、异常处理方式
- JVM默认的处理方式:把异常信息以红色字体打印在控制台,并结束程序
- 捕获异常 try...catch:一般用在调用处,能让代码继续往下运行。
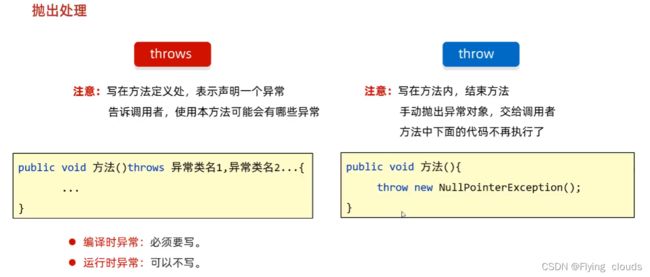
- 抛出异常 throw、throws:
- 在方法中,出现异常了。
- 方法就没有继续运行下去的意义了,采取抛出处理。
- 让该方法结束运行并告诉调用者出现了问题。
3.1 捕获异常
格式:
try{
可能出现的异常代码
}
catch(异常类名 变量名){
异常处理代码
}目的:当代码出现异常时,可以让程序继续往下执行。
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1,2,3,4,5,6};
//System.out.println(arr[10]);
try{
System.out.println(arr[10]);
}
catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){
System.out.println("数组越界");
}
System.out.println("hhhhhhhh");
}2.1 灵魂一问: 如果try中没有遇到问题,如何执行?
- 会把try里面的所有的代码执行完毕,不会执行catch里面的代码。
注意:只有当出现了异常,才会执行catch里面的代码
这就相当于没有触发异常一样。
2.2 灵魂二问:如果try中可能会遇到多个问题,怎么执行?
- 会写多个catch与之对应。
细节:如果我们要捕获多个异常,这些异常中如果存在父子关系的话,那么父类一定要写在下面。
了解性:在JDK7之后,我们可以在catch中同时捕获多个异常,中间用 | 进行隔开。
public class ExceptionDemo07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
try {
System.out.println(arr[10]); // ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
System.out.println(2 / 0); // ArithmeticException
String s = null;
System.out.println(s.equals("abc"));
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("索引越界");
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("除数不能为0");
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
System.out.println("空指针异常");
} catch (Exception e) {
//父类异常
System.out.println("exception");
}
System.out.println("看看我执行了吗");
// 索引越界
// 看看我执行了吗
}
}2.3 灵魂三问:如果try中遇到的问题没有被捕获,怎么执行?
- 相当于try...catch代码没有执行,最终还是会交给虚拟机进行处理。
public class ExceptionDemo08 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ,6};
try {
System.out.println(arr[10]); //ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
// new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
System.out.println("空指针异常");
}
System.out.println("看看我执行了吗");
}
}2.4 灵魂四问:如果try中遇到了问题,那么try下面的其他代码还会执行吗?
- 不会执行,直接跳转到对应的catch当中,执行catch里面的语句体。
- 但是如果没有对应的语句体,那么还是会交给虚拟机进行处理。
public class ExceptionDemo09 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ,6};
try {
System.out.println(arr[10]);
System.out.println("看看我执行了吗...try");
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("索引越界");
}
System.out.println("看看我执行了吗...其他代码");
//索引越界
//看看我执行了吗...其他代码
}
}3. 抛出异常
例子:求一个数组中的最大数
public class ExceptionDemo10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 需求:定义一个方法求数组最大值
// int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
// 以下两种数组代码无法运行
int[] arr = null;
int max = 0;
// int[] arr = {};
// 进行捕获
try {
max = getMax(arr);
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
System.out.println("空指针异常");
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("索引越界异常");
}
System.out.println(max);
}
// public static int getMax(int[] arr) throws
// NullPointerException,ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException{
// 都属于RuntimeException 运行时异常 可以不写
public static int getMax(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null) {
// 手动创建一个异常对象 并把这个异常交给方法的调用者处理
// 此时方法结束,下面代码不再执行
throw new NullPointerException();
}
if (arr.length == 0) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
System.out.println("看看我执行了吗");
int max = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] > max) {
max = arr[i];
}
}
return max;
}
}四、 异常中常见方法
Throwable的成员方法:
| 方法名称 | 说明 |
| public String getMessage ( ) | 返回此throwable的详细消息字符串 |
| public String toString ( ) | 返回此可抛出的简短描述 |
| public void printstackTrace ( ) | 把异常的错误信息输出在控制台 |
public class ExceptionDemo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
try {
System.out.println(arr[10]);
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
String message = e.getMessage();
System.out.println(message); // Index 10 out of bounds for length 6
String str = e.toString();
System.out.println(str); // java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException:10
e.printStackTrace(); // at Exception.ExceptionDemo11.main(ExceptionDemo11.java:8)
// 仅仅打印信息,不会停止程序运行
}
System.out.println("看看我执行了吗");
}
}