python实现调和反距离空间插值法AIDW
1 简介
AIDW 主要是针对 IDW 的缺点进行了改进,考虑了样本点与预测点的位置,即方向和距离,具体见下图:
2 改进
IDW 公式:
从IDW算法可看出,插值点的估算值仅与插值样本距插值点的远近相关,并未考虑样本点的方位性(即样本点被表示为各向同性)。
IDW 插值的基本假设是样点在插值区呈均匀分布。但众多情况下,样点在各向分布并非均匀,甚至会出现样点集中于某一方向的现象,违背了基本假设,其插值合理性就难被保证。针对 IDW 这一插值局限,作者提出了调和反距离权重(AIDW)插值算法。
AIDW 增加了可反映插值点与样本点方位关系的调和权重系数 K,其基本假设是:距插值点近的样本点,对其后方的样本点有遮蔽效应,当两样本点与插值点的连线夹角 α < 360 ° / n \alpha<360°/n α<360°/n(n 为插值搜索邻域内的样点个数)时,遮蔽效应存在,当 α ≥ 360 ° / n \alpha≥360°/n α≥360°/n 时,遮蔽效应消失。在 AIDW 插值过程中,受遮蔽影响的样本点,其插值权重将被削弱,削弱的程度取决于该样点 K 值的大小。
按上述假设:
- 图1(a) 所示的 5 个样点在方向上均匀地分布在插值点(中心点)周围,任意两样点与插值点的连线夹角均大于或等于 72°(即α α ≥ 360 ° / 5 \alpha≥360°/5 α≥360°/5),即认为该5个样点间相互不存在遮蔽效应;
- 在图1©中,任意两样点与插值点的连线夹角均小于72°,即认为距插值点的近样点,对其后的样点均具有遮蔽效应;在大多情况下,样点在插值点周围的分布应类似图1(b),既不像图1(a)均匀分布,也不像图1©集中分布。
- 图1(b)中 Z 1 Z_1 Z1、 Z 3 Z_3 Z3 对任一样点均无遮蔽, Z 2 Z_2 Z2 对 Z 4 Z_4 Z4、 Z 5 Z_5 Z5 有遮蔽, Z 4 Z_4 Z4 对 Z 5 Z_5 Z5 也有遮蔽。
将 IDW 传统的算法思想与本文的基本假设结合,提出了 AIDW 算法:
sin p θ \sin ^p\theta sinpθ的理解:
- 从下图(a)可以看出, Z i Z_i Zi 逐渐移向 Z 0 Z_0 Z0 的过程种, θ \theta θ 逐渐增大,当三者形成等腰三角形时, θ = 90 ° \theta=90° θ=90°,此时最大,即 sin p θ = 1 \sin^p\theta=1 sinpθ=1, Z j Z_j Zj 不会对 Z i Z_i Zi 产生遮蔽影响。
- 从下图(b)可以看出, Z i Z_i Zi 保持与 Z 0 Z_0 Z0相同的距离向 Z j Z_j Zj 移动,当两者位于同一条线时, Z i Z_i Zi的影响完全被遮蔽,即 θ = 0 ° , sin p θ = 0 \theta=0°,\sin^p\theta=0 θ=0°,sinpθ=0。
计算样例:
按AIDW算法,在图3(b)中因 Z 1 Z_1 Z1对 Z 6 Z_6 Z6、 Z 3 Z_3 Z3对 Z 7 Z_7 Z7和 Z 8 Z_8 Z8、 Z 4 Z_4 Z4对 Z 7 Z_7 Z7有遮蔽影响,这些受遮蔽样点的插值权重被削减, Z 10 、 Z 11 、 Z 12 Z_{10}、Z_{11}、Z_{12} Z10、Z11、Z12分别被 Z 4 Z_{4} Z4、 Z 3 Z_3 Z3、 Z 7 Z_7 Z7 完全遮蔽,它们的插值权重降至为0。依照式(2)和式(3),最终插值点估算值的计算式为:
- Z Z Z 为插值点(中心点)估算值
- Z 1 − Z 9 Z_1-Z_9 Z1−Z9为样点观测值
- d 1 − d 9 d_1-d_9 d1−d9为样点与插值点的欧氏距离
- p 是幂指数
- θ \theta θ 角如图3(b)所示
3 程序设计流程
AIDW 的插值程序可分为插值前准备和插值计算两个过程:
- 插值前准备主要是用于搜索合适的插值样点,并为下一步的插值计算提供 d i d_i di 和 f i j f_{ij} fij 值;
- 插值计算过程主要是求算反映样点遮蔽程度的 sin p θ i j \sin^p\theta_{ij} sinpθij 值,并结合 d i 、 z i d_i、z_i di、zi 值求算插值点的Z值。
- 插值搜索邻域的大小以格点数(k×k)表示
- m 是搜索邻域内的样点数
- n 是插值所需的样点数
- d、f 分别为样点与插值点的欧氏距离和两样点间的欧氏距离
- i、j、u、v 均为插值样点的序号
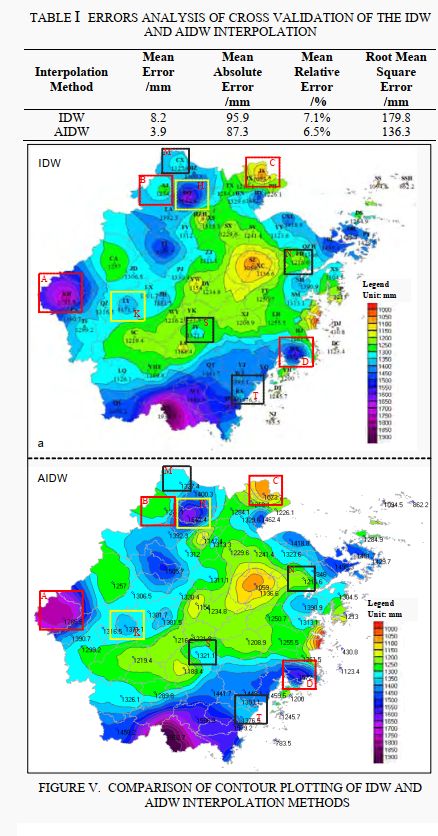
4 插值结果
- 对比 M 点(黑色框),IDW 出现孤立圆现象(站点集中于一侧),AIDW 消除了孤立圆现象
- 对比 C 点(红色框),IDW 出现同心圆现象,AIDW 消除了同心圆现象
- 对比 K 点(黄色框),两者均出现孤立圆,通过分析,K 点周围的站点分布均匀。
从上图可以看出 AIDW 有效改进了 IDW 的缺点,同时又能保留 IDW 的插值思想,但 AIDW 需要计算 θ \theta θ ,因此在插值时间上要比 IDW 慢。
5 python 实现
from sklearn.neighbors import NearestNeighbors
"""类函数"""
class AIDW:
def __init__(self, x, y, m,p=2):
self.m = m # 搜索邻域内的样点数
self.nbrs = NearestNeighbors(n_neighbors=m, algorithm='ball_tree').fit(x)
self.thresh = 360/m
self.p = p
self.y = y
self.x = x
def fit(self, x_new):
indices = self.nbrs.kneighbors(x_new, return_distance=False)
x_sample = self.x[indices[0]]
y_sample = self.y[indices[0]]
x_ = x_sample-x_new
zi = []
ki = 1
for i in range(1, self.m-1):
for j in range(i):
cos_ = np.sum(x_[i]*x_[j])/((np.sum(x_[i]**2)**(1/2))*(np.sum(x_[j]**2)**(1/2)))
radian = np.arccos(cos_)
angle = radian*180/np.pi
if angle>=self.thresh:continue
else:
ki*=np.sin(radian)**self.p
di = np.sum(x_[i]**2)**(1/2)
zi.append(ki/(di**self.p))
z = np.sum(np.array(zi)*y_sample[1:-1])/np.sum(zi)
return z
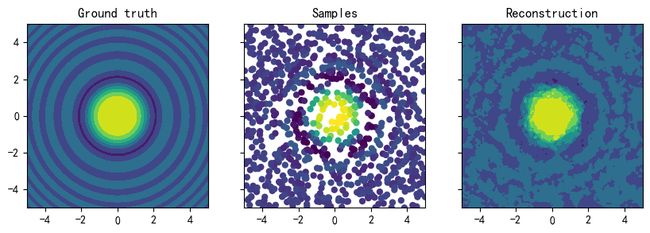
"""demo"""
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# create sample points with structured scores
X1 = 10 * np.random.rand(1000, 2) -5
def func(x, y):
return np.sin(x**2 + y**2) / (x**2 + y**2 )
z1 = func(X1[:,0], X1[:,1])
# 'train'
aidw = AIDW(X1, z1, m=15)
# 'test'
spacing = np.linspace(-5., 5., 100)
X2 = np.meshgrid(spacing, spacing)
grid_shape = X2[0].shape
X2 = np.reshape(X2, (2, -1)).T
z2 = []
for x2 in X2:
z2.append(aidw.fit(x2.reshape(1,-1)))
z2 = np.array(z2)
# plot
fig, (ax1, ax2, ax3) = plt.subplots(1, 3, sharex=True, sharey=True, figsize=(10,3))
ax1.contourf(spacing, spacing, func(*np.meshgrid(spacing, spacing)))
ax1.set_title('Ground truth')
ax2.scatter(X1[:,0], X1[:,1], c=z1, linewidths=0)
ax2.set_title('Samples')
ax3.contourf(spacing, spacing, z2.reshape(grid_shape))
ax3.set_title('Reconstruction')
plt.show()
参考:
顾及方向遮蔽性的反距离权重插值法.李正泉.
An Adjusted Inverse Distance Weighted Spatial Interpolation Method.