spring security oauth其中的/oauth/token做了哪些
项目场景:
这里就详细聊一下,/oauth/token在请求的过程中到底执行了什么。这里可以参考http://blog.didispace.com/spring-security-oauth2-xjf-2/这位大佬写的文章.
技术详解:
过滤器的流程
ClientCredentialsTokenEndpointFilter | BasicAuthenticationFilter
—> DaoAuthenticationProvider
-> TokenEndpoint
-> TokenGranter我们现在来慢慢分析,首先从最开始的地址/oauth/token开始吧.
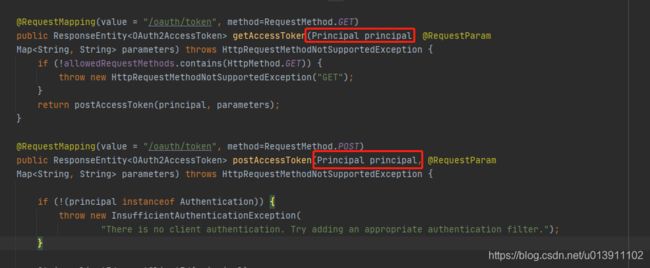
从请求的源地址就可以发现,多了一个Principal对象。哪么这个对象从哪里来?
具体的数据映射可以通过这边文章https://blog.csdn.net/a469517790/article/details/102839165来了解,我这边就说一下SecurityContextHolderAwareRequestWrapper.getUserPrincipal()的Principal什么时候放进去的.
首先我们来看看ClientCredentialsTokenEndpointFilter里面做了哪些东西
ClientCredentialsTokenEndpointFilter.javapublic class ClientCredentialsTokenEndpointFilter extends AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter {
@Override
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws AuthenticationException, IOException, ServletException {
if (allowOnlyPost && !"POST".equalsIgnoreCase(request.getMethod())) {
throw new HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException(request.getMethod(), new String[] { "POST" });
}
String clientId = request.getParameter("client_id");
String clientSecret = request.getParameter("client_secret");
// If the request is already authenticated we can assume that this
// filter is not needed
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
if (authentication != null && authentication.isAuthenticated()) {
return authentication;
}
if (clientId == null) {
throw new BadCredentialsException("No client credentials presented");
}
if (clientSecret == null) {
clientSecret = "";
}
clientId = clientId.trim();
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(clientId,
clientSecret);
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
}
}首先我们可以看到 ClientCredentialsTokenEndpointFilter是继承AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter的,我们之前就有说过的UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter也是继承了AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter。其实在spring security oauth还有两个类继承了AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter,分别是
OAuth2ClientAuthenticationProcessingFilter(主要用于资源服根据token去认证服获取凭证信息)
OAuth2LoginAuthenticationFilter(主要应用于第三方登录)上面的两个拦截器会在后面细讲,我们先说说ClientCredentialsTokenEndpointFilter里面做了哪些吧。
逻辑其实很简单,就是获取到clientId和clientSecret,然后构建成UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken,这里其实服用了DaoAuthenticationProvider里面的逻辑,其实很容易理解.因为这个和校验密码和账号没有什么区别.不过这里可以发现,在校验之前,有一层判断,如果已经认证了哪么就不需要重复认证。
// If the request is already authenticated we can assume that this
// filter is not needed
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
if (authentication != null && authentication.isAuthenticated()) {
return authentication;
}哪么之前是在哪里校验的呢?其实这里就可以看 BasicAuthenticationFilter了,我们先看看BasicAuthenticationFilter里面做了哪些操作吧
BasicAuthenticationFilter.javapublic class BasicAuthenticationFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter {
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
final boolean debug = this.logger.isDebugEnabled();
String header = request.getHeader("Authorization");
if (header == null || !header.startsWith("Basic ")) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
try {
String[] tokens = extractAndDecodeHeader(header, request);
assert tokens.length == 2;
String username = tokens[0];
if (debug) {
this.logger
.debug("Basic Authentication Authorization header found for user '"
+ username + "'");
}
if (authenticationIsRequired(username)) {
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
username, tokens[1]);
authRequest.setDetails(
this.authenticationDetailsSource.buildDetails(request));
Authentication authResult = this.authenticationManager
.authenticate(authRequest);
if (debug) {
this.logger.debug("Authentication success: " + authResult);
}
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authResult);
this.rememberMeServices.loginSuccess(request, response, authResult);
onSuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, authResult);
}
}
}
}这里只截取了部分的代码,其实这里就可以发现如果请求的头携带了Authorization字段,且是basic编码的话,哪么就会解密,然后获取到请求头的用户名和密码也对应着clientId和clientSecret。哪么这边就会做认证逻辑,具体的逻辑和ClientCredentialsTokenEndpointFilter大同小异。
好了,说到这里应该就可以知道/oauth/token里面的Principal的数据怎么来了.再回过头来说说/oauth/token里面的逻辑吧。
先上代码
@RequestMapping(value = "/oauth/token", method=RequestMethod.POST)
public ResponseEntity postAccessToken(Principal principal, @RequestParam
Map parameters) throws HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException {
if (!(principal instanceof Authentication)) {
throw new InsufficientAuthenticationException(
"There is no client authentication. Try adding an appropriate authentication filter.");
}
String clientId = getClientId(principal);
ClientDetails authenticatedClient = getClientDetailsService().loadClientByClientId(clientId);
TokenRequest tokenRequest = getOAuth2RequestFactory().createTokenRequest(parameters, authenticatedClient);
if (clientId != null && !clientId.equals("")) {
// Only validate the client details if a client authenticated during this
// request.
if (!clientId.equals(tokenRequest.getClientId())) {
// double check to make sure that the client ID in the token request is the same as that in the
// authenticated client
throw new InvalidClientException("Given client ID does not match authenticated client");
}
}
if (authenticatedClient != null) {
oAuth2RequestValidator.validateScope(tokenRequest, authenticatedClient);
}
if (!StringUtils.hasText(tokenRequest.getGrantType())) {
throw new InvalidRequestException("Missing grant type");
}
if (tokenRequest.getGrantType().equals("implicit")) {
throw new InvalidGrantException("Implicit grant type not supported from token endpoint");
}
if (isAuthCodeRequest(parameters)) {
// The scope was requested or determined during the authorization step
if (!tokenRequest.getScope().isEmpty()) {
logger.debug("Clearing scope of incoming token request");
tokenRequest.setScope(Collections. emptySet());
}
}
if (isRefreshTokenRequest(parameters)) {
// A refresh token has its own default scopes, so we should ignore any added by the factory here.
tokenRequest.setScope(OAuth2Utils.parseParameterList(parameters.get(OAuth2Utils.SCOPE)));
}
OAuth2AccessToken token = getTokenGranter().grant(tokenRequest.getGrantType(), tokenRequest);
if (token == null) {
throw new UnsupportedGrantTypeException("Unsupported grant type: " + tokenRequest.getGrantType());
}
return getResponse(token);
} 具体的逻辑可以分为以下几个步骤
1.校验clientId是否匹配
2.校验当前clientId是否支持grant_type
3.scpoe参数是否正确
4.找到对应TokenGranter生成token
逻辑其实并不复杂,这里就要说一下TokenGranter,因为后续自定义授权的话就需要实现对应的TokenGranter,这个是后话啦.
TokenGranter的最初入口是CompositeTokenGranter,CompositeTokenGranter内部也是应用了合成模式,把所有的TokenGranter聚集到一起。我们先看看CompositeTokenGranter里面的源码吧
CompositeTokenGranter.javapublic class CompositeTokenGranter implements TokenGranter {
private final List tokenGranters;
public CompositeTokenGranter(List tokenGranters) {
this.tokenGranters = new ArrayList(tokenGranters);
}
public OAuth2AccessToken grant(String grantType, TokenRequest tokenRequest) {
for (TokenGranter granter : tokenGranters) {
OAuth2AccessToken grant = granter.grant(grantType, tokenRequest);
if (grant!=null) {
return grant;
}
}
return null;
}
public void addTokenGranter(TokenGranter tokenGranter) {
if (tokenGranter == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Token granter is null");
}
tokenGranters.add(tokenGranter);
}
} 逻辑非常简单,就是常用的合成模式。 我们现在去看看TokenGranter的具体实现类。
AbstractTokenGranter :一个抽象类,实现了一些公共的方法。所有的实现类都继承了AbstractTokenGranter
AuthorizationCodeTokenGranter:授权码授权模式
ClientCredentialsTokenGranter:客服端授权模式
ImplicitTokenGranter:静默授权
RefreshTokenGranter:刷新token
ResourceOwnerPasswordTokenGranter:用户名密码授权
后续如果想要自定义授权方式的话,只需要继承AbstractTokenGranter,然后把自己实现的TokenGranter加入到CompositeTokenGranter即可。具体的TokenGranter的源码以及分析我就不贴了,感兴趣的可以自己的去看看。这里就想起说说授权码模式吧。
授权码模式的步骤如下:
第一步:请求oauth/authorize获取code
第二步:认证通过之后,重定向到redirect_uri,code的值在地址上
第三步:获取到code,请求/oauth/token,grant_type=authorization_code
第四步:认证通过之后,获取到token信息
然后我们在根据步骤,来一步一步的阅读源码吧
AuthorizationEndpoint.java@RequestMapping(value = "/oauth/authorize", method = RequestMethod.POST, params = OAuth2Utils.USER_OAUTH_APPROVAL)
public View approveOrDeny(@RequestParam Map approvalParameters, Map model,
SessionStatus sessionStatus, Principal principal) {
if (!(principal instanceof Authentication)) {
sessionStatus.setComplete();
throw new InsufficientAuthenticationException(
"User must be authenticated with Spring Security before authorizing an access token.");
}
AuthorizationRequest authorizationRequest = (AuthorizationRequest) model.get("authorizationRequest");
if (authorizationRequest == null) {
sessionStatus.setComplete();
throw new InvalidRequestException("Cannot approve uninitialized authorization request.");
}
try {
Set responseTypes = authorizationRequest.getResponseTypes();
authorizationRequest.setApprovalParameters(approvalParameters);
authorizationRequest = userApprovalHandler.updateAfterApproval(authorizationRequest,
(Authentication) principal);
boolean approved = userApprovalHandler.isApproved(authorizationRequest, (Authentication) principal);
authorizationRequest.setApproved(approved);
if (authorizationRequest.getRedirectUri() == null) {
sessionStatus.setComplete();
throw new InvalidRequestException("Cannot approve request when no redirect URI is provided.");
}
if (!authorizationRequest.isApproved()) {
return new RedirectView(getUnsuccessfulRedirect(authorizationRequest,
new UserDeniedAuthorizationException("User denied access"), responseTypes.contains("token")),
false, true, false);
}
if (responseTypes.contains("token")) {
return getImplicitGrantResponse(authorizationRequest).getView();
}
return getAuthorizationCodeResponse(authorizationRequest, (Authentication) principal);
}
finally {
sessionStatus.setComplete();
}
} 代码的逻辑其实不复杂,就是校验一下参数。因为使用授权码登录的话,登录成功之后会有一个选项,选择 approved。最后校验完成之后,会进行重定向。代码如下
这里说一下generateCode这个方法吧。首先授权码模式成功的code的来源是AuthorizationCodeServices。AuthorizationCodeServices的实现类是RandomValueAuthorizationCodeServices。
RandomValueAuthorizationCodeServices是一个抽象类,里面实现了生成code的逻辑。
InMemoryAuthorizationCodeServices和JdbcAuthorizationCodeServices都继承了 RandomValueAuthorizationCodeServices用以存储code的位置,如果是JdbcAuthorizationCodeServices的话,哪么需要创建表oauth_code,当然你也可以自定义,比如把code放到redis里面。
代码就不贴了,有兴趣的可以自己去看看。个人觉得JdbcAuthorizationCodeServices里面的代码还是可以去借鉴一下的,毕竟在不适用ORM框架的前提能够如此优雅的使用jdbc还是非常少的。
言归正传,我们这里已经重定向之后并且已经获取了code,哪么后续我们就需要根据这个code去获取token信息了。哪么之后就进入了第三步/oauth/token,然后我们直接进入到AuthorizationCodeTokenGranter。
AuthorizationCodeTokenGranter.javapublic class AuthorizationCodeTokenGranter extends AbstractTokenGranter {
@Override
protected OAuth2Authentication getOAuth2Authentication(ClientDetails client, TokenRequest tokenRequest) {
Map parameters = tokenRequest.getRequestParameters();
String authorizationCode = parameters.get("code");
String redirectUri = parameters.get(OAuth2Utils.REDIRECT_URI);
if (authorizationCode == null) {
throw new InvalidRequestException("An authorization code must be supplied.");
}
OAuth2Authentication storedAuth = authorizationCodeServices.consumeAuthorizationCode(authorizationCode);
if (storedAuth == null) {
throw new InvalidGrantException("Invalid authorization code: " + authorizationCode);
}
OAuth2Request pendingOAuth2Request = storedAuth.getOAuth2Request();
// https://jira.springsource.org/browse/SECOAUTH-333
// This might be null, if the authorization was done without the redirect_uri parameter
String redirectUriApprovalParameter = pendingOAuth2Request.getRequestParameters().get(
OAuth2Utils.REDIRECT_URI);
if ((redirectUri != null || redirectUriApprovalParameter != null)
&& !pendingOAuth2Request.getRedirectUri().equals(redirectUri)) {
throw new RedirectMismatchException("Redirect URI mismatch.");
}
String pendingClientId = pendingOAuth2Request.getClientId();
String clientId = tokenRequest.getClientId();
if (clientId != null && !clientId.equals(pendingClientId)) {
// just a sanity check.
throw new InvalidClientException("Client ID mismatch");
}
// Secret is not required in the authorization request, so it won't be available
// in the pendingAuthorizationRequest. We do want to check that a secret is provided
// in the token request, but that happens elsewhere.
Map combinedParameters = new HashMap(pendingOAuth2Request
.getRequestParameters());
// Combine the parameters adding the new ones last so they override if there are any clashes
combinedParameters.putAll(parameters);
// Make a new stored request with the combined parameters
OAuth2Request finalStoredOAuth2Request = pendingOAuth2Request.createOAuth2Request(combinedParameters);
Authentication userAuth = storedAuth.getUserAuthentication();
return new OAuth2Authentication(finalStoredOAuth2Request, userAuth);
}
} 这里面其实就是校验code的逻辑,如果校验成功了之后就生成OAuth2Authentication,逻辑其实不复杂。
总结:
好了,具体就分享到这里了。