网络应用编程 实验3 矩阵并行计算练习实验
一、实验要求
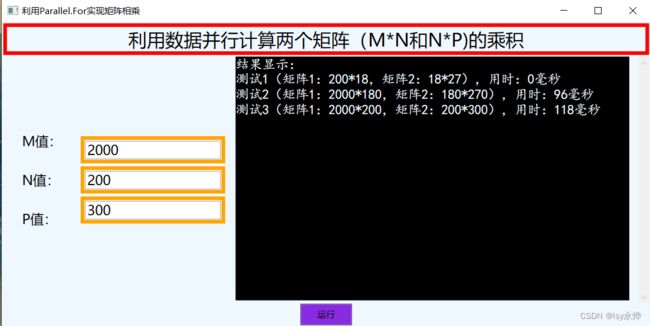
编写一个WPF应用程序,利用数据并行计算两个矩阵(M×N和N×P)的乘积,得到一个M×P的矩阵。
具体要求
(1)在代码中用多任务通过调用某方法实现矩阵并行运算,在调用的参数中分别传递M、N、P的大小。
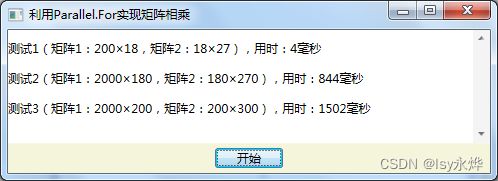
(2)程序中至少要测试3次有代表性的不同大小的矩阵运算,并显示其并行运行用时。
二、实验结果展示
三、实验代码展示
1.xml部分
2.cs部分
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
using System.Windows.Data;
using System.Windows.Documents;
using System.Windows.Input;
using System.Windows.Media;
using System.Windows.Media.Animation;
using System.Windows.Media.Imaging;
using System.Windows.Navigation;
using System.Windows.Shapes;
namespace 实验报告3
{
///
/// MainWindow.xaml 的交互逻辑
///
public partial class MainWindow : Window
{
//实验次数
int x = 0;
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private async void Button_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
//接收M,N,P
int aRow, aCol, bCol;
int.TryParse(t1.Text, out aRow);
int.TryParse(t2.Text, out aCol);
int.TryParse(t3.Text, out bCol);
//形成要用的两个矩阵ab ,里面存储的数是double类型的,当然在额外创建一个矩阵c接收结果
double[,] a, b, c;
a = initMatrix(aRow, aCol);
b = initMatrix(aCol, bCol);
c = new double[aRow, bCol];
//进行矩阵并行运算,并计算时间
long time1 = await Task.Run(() => timeSpan(a, b, c));
//将实验次数++
x++;
//将计算的值在右侧黑色文本框中显示出来
t4.Text += string.Format("\n测试{0}(矩阵1:{1}*{2},矩阵2:{3}*{4}),用时:{5}毫秒", x, aRow, aCol, aCol, bCol, time1);
}
//初始化矩阵
public double[,] initMatrix(int row, int column)
{
Random random= new Random();
double[,] matrix = new double[row,column];
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < column; j++)
{
matrix[i,j] = random.Next(100);
}
}
return matrix;
}
//并行矩阵乘法
public void ParallelMatrixMultiplication(double[,] a, double[,] b, double[,] c)
{
//获取两个矩阵的行列数,因为TryParse好像用不到全局变量里面,所以只能写的这么复杂了
int aRows = a.GetLength(0);
int aCols = a.GetLength(1);
int bCols = b.GetLength(1);
//计算并输出,但是 数太大 会产生 数组越界异常
// i是a行,j是b列,k是a列b行
Action action = i =>
{
for (int j = 0; j < bCols; j++)
{
double temp = 0;//用一个临时变量可提高并行效率
for (int k = 0; k < aCols; k++)
{
temp += a[i, k] * b[k, j];
}
c[i, j] = temp;
}
};
//action只是定义了一个方法,所以是不是自动运行的,真正运行的代码是下面这行 并行运行代码,这也解释了i的取值是多少的问题
Parallel.For(0, aRows , action);
}
//计算运算时间
public long timeSpan(double[,] a, double[,] b, double[,]c)
{
Stopwatch sw = Stopwatch.StartNew();
ParallelMatrixMultiplication(a, b, c);
sw.Stop();
return sw.ElapsedMilliseconds;
}
}
}
四、实验总结
1. 为什么要用panel控件(各种panel控件),明明用了跟没用一样。
答: 简单的说,panel控件是一个容器控件,你可以在上面放置别的控件,当做一个Form用。应用程序会尽可能将一个面板中的所有控件分页到同一屏幕上。通过将控件分组到 Panel 控件中, 应用程序还可使用单个命令隐藏或显示一组控件。
当移动 Panel 控件时,它包含的所有控件也将移动
2. 所以Form是什么意思?
简单来讲就是Windows窗体应用,创建wpf自动生成的xml界面,也可以独立添加新的。官方一点来说就是:
1.窗体也是对象,窗体类定义了生成窗体的模板,每当实例化一个窗体类,就产生一个窗体2.Form类是所有窗体类的基类。
3.在一个项目中,每个窗体都有自己的Form.cs代码,但所有窗体只有一个启动窗体,核心便是 Program.cs文件里的Main()函数作为程序的主入口点。
3. textbox和textblock的区别
前者可以编辑,后者不可以。4. task.Run 其实在读程序时,可以直接读成“运行.....”
5.与界面交互,例如:将结果在界面中显示出来
6. cts = new System.Threading.CancellationTokenSource();
放在task(任务,cts.token) 用于侦听取消通知7. 可以直接用int.TryParse(a,out b); 接收文本框中的值
8. Action本身是一种方法,后面必须加分号.
Action<>是没有返回值,而有没有参数取决于<>有没有值类型,如有int,就是含有一个int型的参数,这时候就可以像for循环里面 int i=0; 随便使用 i 这个参数了。9.本次实验有个小问题,就是结果数组写错了,写成了a列b列了,一直导致数组越界异常,耽误了两个多小时。。。。。
五、书上原码展示
1.xml部分
2.cs部分
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
using System.Windows.Data;
using System.Windows.Documents;
using System.Windows.Input;
using System.Windows.Media;
using System.Windows.Media.Imaging;
using System.Windows.Navigation;
using System.Windows.Shapes;
namespace Experiment3
{
///
/// MainWindow.xaml 的交互逻辑
///
public partial class MainWindow : Window
{
Stopwatch stopwatch = new Stopwatch();
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private async void btnStart_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
long[] t1 = await Task.Run(() => Multiply(200, 18, 27));
textBlock1.Text = string.Format("测试1(矩阵1:200×18,矩阵2:18×27),用时:{1}毫秒", t1[0], t1[1]);
long[] t2 = await Task.Run(() => Multiply(2000, 180, 270));
textBlock1.Text += string.Format("\n测试2(矩阵1:2000×180,矩阵2:180×270),用时:{1}毫秒", t2[0], t2[1]);
long[] t3 = await Task.Run(() => Multiply(3000, 200, 300));
textBlock1.Text += string.Format("\n测试3(矩阵1:2000×200,矩阵2:200×300),用时:{1}毫秒", t3[0], t3[1]);
}
private long[] Multiply(int rowCount, int colCount, int colCount2)//参数分别是M,N,P
{
long[] timeElapsed = new long[2];
//初始化两个矩阵
double[,] m1 = InitializeMatrix(rowCount, colCount);
double[,] m2 = InitializeMatrix(colCount, colCount2);
//乘之后得到的矩阵,这里相当于手动取得
double[,] result = new double[rowCount, colCount2];
// 并行,
//计时开始
stopwatch.Restart();
result = new double[rowCount, colCount2];//M*P
MultiplyMatricesParallel(m1, m2, result);
//计时结束
stopwatch.Stop();
//返回时间
timeElapsed[1] = stopwatch.ElapsedMilliseconds;
return timeElapsed;
}
#region 并行
///
/// 计算两个矩阵的乘积
///
/// 矩阵a
/// 矩阵b
/// 相乘的结果
public static void MultiplyMatricesParallel(double[,] a, double[,] b, double[,] result)
{
//如果是64位机,将int改为Int64可提高性能,但修改后将无法在32位机器上运行
int aRows = a.GetLength(0);//a的行
int aCols = a.GetLength(1);//a的列,b的行
int bCols = b.GetLength(1);//b的列
// 内循环不需要并行
Action action = i =>
{
for (int j = 0; j < bCols; j++)
{
double temp = 0; //用一个临时变量可提高并行效率
for (int k = 0; k < aCols; k++)
{
temp += a[i, k] * b[k, j];
}
result[i, j] = temp;
}
};
// 外循环并行执行
Parallel.For(0, aRows, action);//实际上就是矩阵a每行都单独去运算,最后结果汇总,上面action中的i就是a的行arows,比如第一行去跟b的j列运算,同时第二(i)行野区和b的j列运算
}
#endregion
public static double[,] InitializeMatrix(int rows, int cols)//初始化矩阵
{
double[,] matrix = new double[rows, cols];
Random r = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++)
{
matrix[i, j] = r.Next(100); //行列对应的数随机设置
}
}
return matrix;
}
}
}