MySQL数据库-基础运用及细节梳理(全概括版)
学习方法:
- 内容:连贯性极强、代码量骤增
- 随堂笔记:逐步淡化、直至消失
- 作业问题的解决:自我解决(百度)(15分钟)–>求助别人
数据库的概念
数据库是用来组织、存储和管理数据的系统。对数据进行增删改查的操作。
- 使用文件存放数据的劣势:
- 没有数据类型。所有文件数据都是字符串
- 缺少对大数据集的优化,大文件的操作效率很慢
- 增删改查的效率很慢
- 缺少并发。多个用户无法操作同一文件
- 缺少权限校验机制
- 缺少容灾机制。
数据库的分类
| 关系型数据库 | NoSql(Not Only Sql)数据库 | |
|---|---|---|
| 数据结构 | 结构化的数据,以表为单位进行存储 | 半结构化(xml、json)、非结构化(文档、图片、视频等) |
| 事务 | 强事务 | 弱事务 |
| 性能 | 高并发下性能较差 | 高并发下性能较好 |
-
实战开发中,两种数据库相辅相成
- 关系型:对事务要求比较高的数据,如金融类、个人信息等
- SQLServer、MySQL(免费、开源、被Oracle收购)、Oracle等
- 非关系型:对事务要求比较低、对性能要求比较高的数据,如聊天记录、商品详情等
- Redis、MonggoDB等
- 关系型:对事务要求比较高的数据,如金融类、个人信息等
数据库的工作模型
- 客户端+服务器的工作模型
- 一个软件可以同时为多个用户提供服务。
导入测试数据
- 新建数据库
- 导入SQL文件
数据库中的相关概念
- 库:数据库,内部存放着所有的表、视图、索引等内容
- 表:是数据库存储数据的基本单位,由行和列组成
- 列:又称为字段,是表的基本组成单位,相当于Java类中的属性
- 行:是表的基本组成单位,具体数据,每行信息是一个整体,由固定字段构成。相当于Java中由类实例化出来的一个又一个的对象
SQL
- SQL:结构化查询语言,提供了对数据库数据的增删改查操作对应的处理
SQL是一种规范,也是一种国际标准,所有的关系型数据库都支持SQL,不被MySQL独有
特点
- 不区分大小写
- 注释:
- 单行:-- (–空格)
- 多行:/* */
简单查询
查询所有字段
-- 查询所有列:select * from 表名(*:是通配符,表示所有列)
select * from employees
查询部分字段
select 列名1,列名2,... from 表名
- 也可以通过列出所有字段名的方式查询所有字段
- 优点:
- 效率更快
- 可读性较好
- 可维护性较高
- 缺点:
- 书写繁琐
- 优点:
-- 查询所有字段
SELECT * from employees
-- 查询员工id、员工工资
select employee_id,salary from employees
-- 列出所有字段名查询所有字段
select employee_id,salary,first_name,last_name,email,phone_number,job_id,commission_pct,manager_id,department_id,hiredate from employees
结果运算
+、-、*、/、%
select 列名 运算符 值 from 表名
-- 查询员工id和工资,及对工资进行加减乘除的运算
select employee_id,salary,salary+100,salary-100,salary*100,salary/100,salary%100 from employees
别名
- 对查询之后的结果起别名
select 列名 as 别名,列名 as 别名,列名,... from 表名
-
别名可以省略单引号
标准SQL中没有双引号,字符串通过单引号修饰
-
as关键字可省
-- 查看员工id和员工工资
select employee_id as 员工id,salary as 工资 from employees
-- as关键字可省
select employee_id 员工id,salary 工资 from employees
去重
select distinct 列名1,列名2,.. from 表名
- 当去重规则为多个字段时,只有当多个字段的值都相同时才会去重
-- 查询所有的职位id(根据job_id进行去重)
select distinct job_id from employees
-- 查询所有的职位和部门id(根据job_id和department_id去重)
select distinct job_id,department_id from employees
分支-case when
case
when 条件1 then 结果1
when 条件2 then 结果2
...
else 其他结果
end
-- 满足when中的条件,便执行对应then中的结果,如果when都不满足,则最终执行else,从上往下判断
-- 查询员工id、员工工资、工资等级(工资>=15000 高薪,工资>=10000 中薪,工资>=5000 一般,工资<5000 低薪)
select employee_id 员工id,salary 员工工资,
case
when salary>=15000 then '高薪'
when salary>=10000 then '中薪'
when salary>=5000 then '一般'
else '低薪'
end as 薪资等级
from employees
查看表详情
- 表详情:当前表的字段设计
describe 表名-- describe关键字可以简写为desc
-- 查看员工表详情
describe employees
desc employees
条件查询
- 能够支持的关系运算符:> < >= <= != =
单条件查询
select 列名... from 表名 where 筛选条件
- MySQL中对比字符串时默认不区分大小写,若想区分,则在对应字段前添加binary关键字即可
-- 查询工资大于10000的员工信息
select * from employees where salary>10000
-- 查询部门id<50的员工信息
select * from employees where department_id<50
-- 查询起始名为Steven的员工信息-不区分大小写
select * from employees where first_name='steven'
-- 区分大小写
select * from employees where binary first_name='Steven'
多条件查询
where 条件1 连接符 条件2
连接符:
and:表示并且,意为同时满足,相当于Java中的&&
or:表示或者,意为满足任意一个即可,相当于Java中的||
-- 查询员工工资>10000并且部门id<50的员工信息
select * from employees where salary>10000 and department_id<50
-- 查询员工id<120或者部门id=80的员工信息
select * from employees where employee_id<120 or department_id=80
区间查询
where 列名 [not] between 起始值 and 结束值
- 中括号中的内容意为可省
- 加上not表示不在此区间之内
-- 查询工资大于10000并且小于12000的员工信息
select * from employees where salary>=10000 and salary<=12000
-- 区间查询(在范围内):between 起始值 and 结束值
select * from employees where salary between 10000 and 12000
-- 区间查询(不在范围内):not between 起始值 and 结束值
select * from employees where salary not between 10000 and 12000
枚举查询
where 列名 [not] in(值1,值2,...)
-- 查询部门id是10、20、30的员工信息
select * from employees where department_id=10 or department_id=20 or department_id=30
-- 枚举查询(列举字段所有满足条件的值):列名 in(值1,值2,...)
select * from employees where department_id in(10,20,30)
-- 不在范围内:列名 not in(值1,...)
select * from employees where department_id not in(10,20,30)
空值查询
where 列名 is [not] null
-- 查询没有绩效的员工信息
-- 为空:列名 is null
select * from employees where commission_pct is null
-- 不为空:列名 is not null
select * from employees where commission_pct is not null
模糊查询
where 列名 [not] like '通配模式'
可用占位符:
%:表示n个字符
_:表示1个字符
-- 查询起始名以p开头的员工信息
select * from employees where first_name like 'p%'
-- 查询起始名中包含p的员工信息
select * from employees where first_name like '%p%'
-- 查询起始名第二个字母是a的员工信息
select * from employees where first_name like '_a%'
-- 查询起始名由5个字母组成的员工信息
select * from employees where first_name like '_____'
单行函数
- 一行数据得到一个结果
-
concat
- 将多个内容合并为一个内容,相当于字符串拼接
select concat(列名1,列名2,...) from 表名-- 以“起始名-结束名"的方式查询员工姓名 select concat(first_name,'-',last_name) from employees -
length
- 获取数据长度
select length(列名) from 表名- 也可用于where子句作为筛选条件
-- 获取员工起始名长度 select first_name,length(first_name) from employees -- 查询起始名长度>5的员工信息 select * from employees where length(first_name)>5 -
sysdate、now
- 获取当前系统时间
select sysdate()|now()- dual:虚拟表,作用为语法占位,特点是从该表查询只会得到一个结果
- from dual可省
-- 查看当前系统时间 select sysdate() from dual select now() -- from dual -
mod(值1,值2):获取值1%值2的结果。标准SQL中没有%
-- 获取10%3的结果 select mod(10,3) -- 查询所有员工工资%10000的结果 select employee_id,salary,mod(salary,10000) from employees -
date_format
- 将日期转换为固定格式的字符串
date_format(date,'format')-
format日期格式:
标识符 含义 %Y 年(4位) %y 年(2位) %m 月(格式为01-12) %c 月(格式为1-12) %d 天(格式为01-30|31) %e 天(格式为1-30|31) %H 小时(格式为00-23) %k 小时(格式为0-23) %i 分钟(格式为00-59) %s 秒(格式为00-59)
-- 查询各个员工入职的年份 select employee_id,hiredate,date_format(hiredate,'%Y') from employees -- 查询各个员工入职的年份和月份 select employee_id,hiredate,date_format(hiredate,'%Y-%m') from employees -
str_to_date
- 将日期格式的字符串转换为日期类型
str_to_date('日期格式的字符串','format')-- 将'2022-12-06 17:32:19'转换为对应的日期类型 select str_to_date('2022-12-06 17:32:19','%Y-%m-%d %H:%i:%s')
排序
select 列名...
from 表名
[where 条件]
order by 列名 排序规则
排序规则:asc(升序,默认值)|desc(降序)
单列排序
- 排序规则只有一列
-- 根据薪资进行从高到低的排序,查看结果
select * from employees order by salary desc
-- 查询工资大于10000的员工信息并对其按照薪资升序排列
select * from employees where salary>10000 order by salary
多列排序
order by 列名1 排序规则1,列名2 排序规则2,...
- 规则:先根据列1排,列1相同再根据列2排,以此类推
-- 根据员工工资进行降序排列,如果薪资相同,再根据员工id升序排序
select * from employees order by salary desc,employee_id asc
Day2
组函数
- 以组为操作单位,一组数据得到一个结果。
- 在没有手动分组的前提下,整张表默认为一组数据
- max(列名):获取最大值
- min(列名):获取最小值
- sum(列名):获取总和
- avg(列名):获取平均值
- count(列名):统计值的个数
- 所有组函数都会自动忽略null值
-- 查看员工的最高薪资
select max(salary) from employees
-- 查看员工的最低薪资、平均薪资、月薪资总和
select min(salary),avg(salary),sum(salary) from employees
-- 统计总共有多少名员工
select count(*) from employees
select count(employee_id) from employees
-- 统计员工表中部门的个数
-- 先对整张表的部门id进行去重,再count统计结果
select count(distinct department_id) from employees
分组
- 在某些情况下,我们需要根据需要对表中数据进行手动分组
- 规则:值相同的为同一组数据
select 列名 from 表名 group by 列名
执行顺序:from–>group by–>select
先确定从哪张表进行操作–>对表中数据进行分组–>基于分组结果进行查询操作
-- 查询各个部门的平均薪资
select department_id,avg(salary) from employees group by department_id
where+group by
-
先where,再group by
先筛选出符合要求的数据,再对符合要求的数据进行分组时,分组的工作量会被减少,效率更高
where 条件 group by 列名
-- 查询部门id为10,20,30的部门的平均薪资
select department_id,avg(salary)
from employees
where department_id in(10,20,30)
group by department_id
having子句
- 和where类似,也是用来做数据筛选,在分组之后执行
group by 列名 having 条件
-- 查询部门平均薪资>=7000的部门id
select department_id,avg(salary)
from employees
group by department_id -- 先分组
having avg(salary)>=7000 -- 后筛选
和where子句的区别
- where在分组前执行,having在分组后执行
- where子句存在分组时不能使用组函数,但是having可以
- 当既可以使用where,又能使用having时,优先使用where,效率更高
limit关键字
- 作用:限制查询结果显示的条目数,通常用于分页
select 列名.. from 表名
limit 显示的起始下标,显示的条数
- 使用:
- 该关键字是基于查询的最终结果进行限制显示,所以其与其他查询关键字使用时,必须最后执行,所以一定写在最后
- 下标为0时,可以省略不写
-- 查询工资最高的前十名员工信息
select employee_id,salary
from employees
order by salary desc -- 先根据工资进行降序排序
limit 0,10 -- 显示前十行
-- 查看前十条员工信息
select * from employees limit 10
-- 查询部门平均薪资最高的前3个部门id
-- 分析:
-- 部门平均薪资:根据部门id分组 group by
-- 最高:根据平均薪资进行降序排序 order by avg(salary)
-- 前三个:limit从最终查询结果中提取出前三条
select department_id,avg(salary)
from employees
group by department_id -- 根据部门id分组
order by avg(salary) desc -- 根据平均薪资进行降序排序
limit 3 -- 从最终查询结果中提取出前三条
查询关键字的顺序
- select 、 from 、where 、 order by 、 group by 、 having 、 limit
语法顺序:
select 、 from 、where、 group by、having 、order by 、limit
子查询
- 当一个SQL的执行需要借助另一个SQL的执行结果时,则需要进行SQL嵌套,该语法结构称之为子查询
select 列名... from 表名 where 列名 =|in (子SQL语句)
- 执行顺序:优先执行小括号内的子SQL,根据子SQL的执行结果再执行外层SQL
- 只要逻辑完整,对SQL的嵌套层数不做要求
- 执行:从内向外执行
where单值子查询
- 子SQL(被嵌套的SQL)返回的时一行一列的单个结果
-- 查询员工id为101号员工的领导信息
-- 先查询员工id为101号员工的直接领导的id
select manager_id from employees where employee_id=101
-- 拼装
select * from employees
where employee_id=(select manager_id from employees where employee_id=101
)
-- 查询员工id为100的员工所在的部门信息
-- 查询员工id为100的员工所在的部门id
select department_id from employees where employee_id=100
-- 拼装
select * from departments
where department_id =(select department_id from employees where employee_id=100)
where多值子查询
- 子SQL返回的是多个结果
-- 查询工资>10000的员工所在的部门信息
select * from departments
where department_id in(select department_id from employees where salary>10000)
from子查询(了解)
- 将子SQL的查询结果临时看作一张表进行后续操作
- 为了符合语法要求,需要给子查询的结果起别名充当临时表的表名
-- 查询工资最高的前十名员工的总薪资
-- 分析:1. 把工资最高的前十名员工的薪资查出来
-- 2. 对这十个工资进行求和
-- 查询SQL的基本语法:select 列名 from 表名
select sum(salary)
from (select salary from employees order by salary desc limit 10) as e
-- 子SQL:把工资最高的前十名员工的薪资查出来
select salary from employees order by salary desc limit 10
表连接
关系字段:两表中有关联关系的字段
- 什么是表连接?
- 当我们的查询结果需要从多张表中获取时,此时应该让表之间建立连接,同时获取数据
内连接
- 特点:同时对连接双方做约束,双方只有符合连接条件的数据才会进行显示
select 表名.列名, 表名.列名,...
from 表名1 inner join 表名2
on 连接条件 -- 两表间的关系字段
-- 查询员工的id、工资与部门名称
-- 第一步:确定数据来自于哪些表
-- 第二步:确定两表之间的关系字段
-- 书写表连接完成查询操作
select e.employee_id 员工id,e.salary 员工工资,d.department_name -- 基于连接结果进行查询操作
from employees e inner join departments d -- 起别名,方便后续书写
on e.department_id=d.department_id -- 关系字段:员工表的部门id=部门表的部门id
from–>join on:确定数据来源
select:查询操作
左外连接
- 特点:左表中的数据无论如何都会显示,右表中的数据只有符合连接条件才会显示
select 表名.列名, 表名.列名,...
from 左表 left outer join 右表
on 连接条件 -- 两表间的关系字段
-- 使用左外连接显示员工信息及其部门信息
select e.*,d.*
from employees e left outer join departments d -- 员工信息无论如何都会显示,部门信息符合连接条件才会显示
on e.department_id=d.department_id
右外连接
- 特点:右表中的数据无论如何都会显示,左表中的数据只有符合连接条件才会显示
select 表名.列名, 表名.列名,...
from 左表 right outer join 右表
on 连接条件 -- 两表间的关系字段
-- 使用右外连接显示部门信息及对应员工信息
select e.*,d.*
from employees e right outer join departments d
on e.department_id=d.department_id
连接关键字中的inner、outer可以省略
全外连接(了解)
- 特点:对双方都不做约束
- 作用:将两个查询结果进行合并
查询结果1 union 查询结果2
- 使用:
- 合并双方字段数目、内容必须一致
- union关键字可以去重
- union all 不会对结果去重
-- 查询员工表所有信息
select employee_id,first_name,salary from employees
union all -- 合并,不去重
-- 查询员工表所有信息
select employee_id,first_name,salary from employees
自连接
-
特点:是特殊的表连接,参与连接的是同一张表
-
使用:
-
表中的两个字段为关系字段,作为连接条件
-- 按照指定要求查询员工信息:员工id,员工姓名,直接领导的id,直接领导的姓名 select e1.employee_id 员工id,e1.first_name 员工姓名,e1.manager_id 领导id,e2.first_name 领导姓名 from employees e1 left join employees e2 -- e1:员工信息 e2:领导信息 on e1.manager_id=e2.employee_id -- 连接条件:员工的领导id=领导的员工id -
连接双方判断同一字段,作为连接条件
-- 查询工资相同的员工id及其工资 select e1.employee_id,e1.salary,e2.employee_id,e2.salary from employees e1 left join employees e2 -- 连接参与比较的两个员工 on e1.salary=e2.salary -- 两个员工的工资相同 where e1.employee_id>e2.employee_id
-
- 如果查询字段来自于多张表,内连接或左外连接
- 如果查询字段来自于一张表并且来自同一行数据,则简单查询|子查询
- 如果查询字段来自于一张表但是不来自于同一行数据。则自连接
多表连接
- 特点:同时从多张表中获取数据
select 表名.列名, 表名.列名,...
from 表1 left join 表2
on 连接条件 -- 表1和表2的关系字段
left join 表3
on 连接条件 -- 表1和表3的关系字段|表2和表3的关系字段
-- 查询员工id,员工姓名,所属部门id,部门名称,部门所在城市
select e.employee_id,e.first_name,d.department_id,d.department_name,l.city
from employees e left join departments d -- 先让员工表和部门表建立连接
on e.department_id=d.department_id -- 员工的部门id=部门的id
left join locations l -- 再让地址表参与连接
on d.location_id=l.location_id -- 部门表的地址id=地址表的id
实际开发中,不建议表连接超过3张表,否则会有性能问题
Day3
SQL的分类
- DQL:数据库查询语言,进行查询操作的SQL
- DCL:数据库控制语言,对数据库用户进行权限设定和更改的SQL
- DDL:数据库定义语言,进行库、表、视图、索引等创建和销毁的SQL
- DML:数据库操作语言,对数据进行增删改的SQL
- TCL:事务控制语言,控制事务操作的SQL
DCL:通常由数据库超级管理员操作
DDL-定义
数据库的创建和销毁
创建
create database [if not exists] 数据库名 [default charset 字符集]
- if not exists:表示如果不存在才会创建
- default charset 字符集:设置数据库字符集
create DATABASE 2302demo2 -- 如果数据库已经存在,会报错
create DATABASE if not exists 2302demo2 -- 如果数据库已经存在,不会报错
create DATABASE if not exists 2302demo2 default charset utf8mb4 -- 直接设置字符集
销毁
drop database [if exists] 数据库
- if exists:如果存在才会销毁
drop database 2302demo2 -- 如果不存在,报错
drop database if exists 2302demo2 -- 如果不存在,不做操作,不会报错
表的创建和销毁
创建
create table [if not exists] 表名(
字段名 数据类型 [约束],
字段名 数据类型 [约束],
...[最后一行内容末尾不能添加,]
)
-
命名
- 不区分大小写,不能使用关键字,每部分之间使用_连接
- 表名:通常以**t_**开头(如:t_student)
- 字段名:关键列通常以**表名缩写_**开头(如:学生id:stu_id)
-
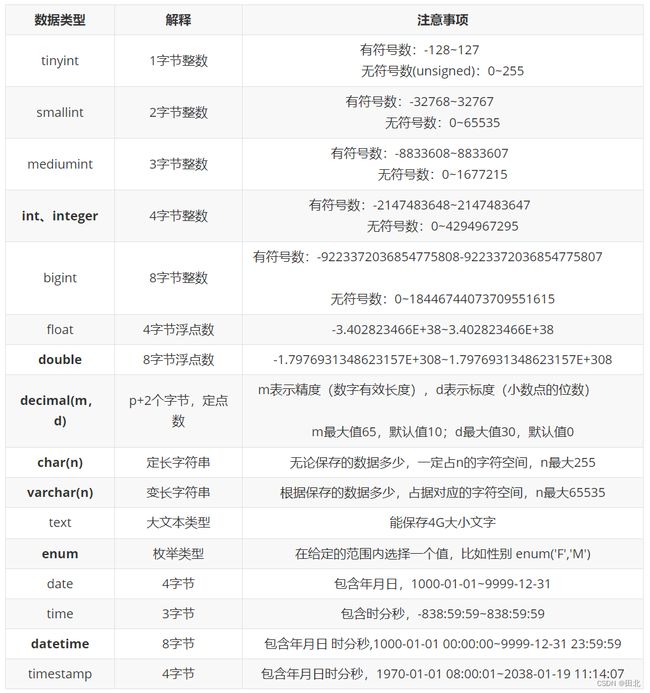
数据类型
- 需要掌握的数据类型:
- 整数:tinyint、int、integer
- 小数:decimal
- 字符串:varchar
- 枚举:enum
- 日期:datetime
- 实战建议:
- 只有数字一定大于等于0并且一定不会进行减运算时,才会用到无符号数,否则都是默认的有符号数
- float和double存在精度问题,后续MySQL将不再支持
- char和varchar底层实现完全一致,只是空间分配的模式不同,推荐使用varchar
- date和time不够实用,timestamp下限太高上限太低,推荐datetime
-- person表:id(唯一标识)、姓名、性别、年龄、身高、出生日期
create table t_person(
person_id int,
person_name varchar(30),
sex enum('男','女','奥特曼'),
age tinyint UNSIGNED,-- 无符号数 没有负数
height decimal(4,1),
birthday datetime
)
约束
| 约束名 | 解释 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| primary key | 主键 | 标志一列为主键列 |
| not null | 非空 | 标志一列的值不能为null |
| unique | 唯一 | 约束一列的值不能重复 |
| default | 默认 | 给一列设置默认值 |
| foreign key | 外键 | 标志一列为外键列 |
check:检查约束|自定义约束 MySQL不支持
普通约束
-
主键
- 作用:作为唯一标识辅助锁定某行数据
- 特点:非空+唯一
- 使用:一张表只能存在一个主键列
-
非空:
- 使用:字段值不能为null,必须进行值的设定
-
唯一:
- 特点:字段值不能重复,值可以为null,并且可以存在多个null
- 不约束null值,只约束已经存在的值
非空+唯一 != 主键
- 特点:字段值不能重复,值可以为null,并且可以存在多个null
-
默认:
- 特点:当设置了默认约束,则在该字段未显式赋值时,值默认为设置的默认值
列级约束
- 将约束声明在字段的声明语法中
create table t_student(
stu_id int primary key, -- 主键
stu_name varchar(30) not null unique,-- 非空 唯一
sex enum('男','女','奥特曼') default'奥特曼',
age tinyint unsigned,
score decimal(3,1),
birthday datetime
)
表级约束
- 将约束单独的声明到所有字段的下方,not null和default不能设置表级约束
约束类型(字段名)
create table t_student(
stu_id int,
stu_name varchar(30) not null,-- 非空
sex enum('男','女','奥特曼') default'奥特曼',
age tinyint unsigned,
score decimal(3,1),
birthday datetime,
-- 添加表级约束
primary key(stu_id),-- 给学生id添加主键约束
unique(stu_name) -- 给学生姓名添加唯一约束
)
外键约束
-
作用:用来表示两张表之间的关联关系,必须结合另一张表使用
不是所有的关系字段都必须存在外键约束
- 外键字段一定是关系字段
- 关系字段并不一定存在外键约束
-
特点:
-
必须连接另一张表的主键列或唯一列
-
外键列的值不可自定义,必须来自于关联字段已经存在的值
- 只对外键列中值不为null的做约束
-
外键列值可以为null
-
必须使用表级约束创建
foreign key(需要添加外键约束的字段名) references 其他表的表名(其他表中的连接字段)
-
-
使用:
- 建表顺序:先建没有外键的表,再建有外键的表
- 删表顺序:先删有外键的表,再删没有外键的表
- 命名:外键字段的名字与数据类型应与关联字段保持一致
-- 班级表:id、班级名称
create table t_class(
class_id int primary key auto_increment, -- 主键、自增
class_name varchar(10) not null unique -- 唯一+非空
)
-- 老师表:id、姓名、所属的班级id
create table t_teacher(
teacher_id int primary key auto_increment,-- 主键、自增
teachet_name varchar(30) not null,-- 非空
class_id int ,-- 所属班级id
-- 通过表级约束添加外键约束
FOREIGN key(class_id) REFERENCES t_class(class_id)
)
销毁
drop table [if exists] 表名
-- 先删老师表
drop table t_teacher
-- 删除班级表
drop table t_class
DML-增删改
增
insert into 表名(列名1,列名2,...) values(值1,值2,...) -- 给指定字段添加数据,值的顺序应与语法中的列名保持一致
insert into 表名 values(值1,值2,...) -- 给所有字段添加数据,值的顺序应与建表顺序保持一致
-- 给person表添加数据
insert into t_person(person_id,person_name,sex,age,height,birthday) values(1,'zhangsan','男',20,180.5,'2000-01-01')
-- 增:insert into 表名 values(值1,值2,..)
-- 注意:默认手动给表中所有字段添加数据,值的顺序必须与表中字段定义保持一致
insert into t_person values(2,'lisi','男',21,170.7,'2000-02-02')
-- 给person表中的部分字段添加值
insert into t_person(person_name,age) values('wangwu',23)
-- 同时添加多条数据:insert into 表名(列名1,列名2..) values(值1,值2,..),(值1,值2,..),(值1,值2,..),..
insert into t_person(person_name,age) values('zhaoliu',22),('sunqi',21)
-
可以为某个数据类型为整型的列设置自增约束,使其自动维护,每次新增数据值+1,通常主键列会设置自增
create table 表名( 字段名 数据类型 auto_increment --设置自增 )create table t_student( stu_id int auto_increment, -- 设置自增 ..., -- 添加表级约束 primary key(stu_id),-- 给学生id添加主键约束 ... )
删
delete from 表名 [where 条件]
- 不添加where条件则删除表中所有数据,添加where条件只会删除符合条件的数据
-- 删除姓名为zhangsan的学生信息
delete from t_student where stu_name='zhangsan'
-- 删除表中所有数据
delete from t_student
-
也可以使用表截断的方式删除表中所有数据
truncate table 表名- 与delete删除所有数据的区别:
- delete是在物理空间中将数据一条一条的删除,效率低,自增不会重新开始
- 表截断是在物理空间中直接将表的空间删除,效率高,自增会重新开始
- 与delete删除所有数据的区别:
改
update 表名 set 列名=新值,列名=新值,... [where 条件]
- 不添加where条件,会修改整张表的指定字段
- 添加where条件,只会修改符合要求的行数据
-- 修改李四的年龄为22
update t_student set age=22 where stu_name='lisi'
-- 将所有学生的年龄改为20
update t_student set age=20
DDL-补充
索引
- 是数据库为了提高查询效率所提供的一种存储机制
查看
show index from 表名
创建
create index 索引名 on 表名(字段名)
销毁
drop index 索引名 on 表名
-- 查看员工表的索引
show index from employees
-- 为first_name创建索引
create index emp_name on employees(first_name)
-- 根据first_name字段进行查询:查询起始名为neena的员工信息
-- explain:用来查看SQL语句的索引使用情况
explain select * from employees where first_name='Neena'
-- 销毁索引
drop index emp_name on employees
特点-面试点
- 使用:索引无须手动使用,当使用某个索引列作为筛选条件时,则自动使用其索引
- 作为:提高查询效率
- 索引并不是越多越好,会占用和浪费空间并且会影响增删改的效率,所以只需要给必要字段添加索引即可
- 主键和唯一列会自动创建索引
- 索引在特定情况下会失效,如空值查询、占位符在第一位的模糊查询等
TCL-事务
- 作用:是保证SQL执行完整性的机制,可以确保事务中的多条SQL操作要么同时成功,要么同时失败
开启事务
begin|start transation
结束事务
提交:commit -- 确认操作
回滚:rollback -- 撤销操作
-- 创建一张账户表id、username、password、余额
create table t_account(
acc_id int primary key auto_increment,
username varchar(20) not null,
password varchar(10),
balance decimal(5,1)
)
-- 添加信息
insert into t_account(username,password,balance) values('王璐瑶','123123',1000),('何宇航','123123',1000)
-- 模拟转账操作
-- 王璐瑶给何宇航转520
-- 流程:王璐瑶余额-520 480 何宇航余额+520 1520
-- 开启事务
begin
update t_account set balance=balance-520 where username='王璐瑶'
update t_account set balance=balance+520 where username='何宇航'
-- 结束事务
-- 1. 回滚事务:当SQL执行有异常时 撤销
rollback
-- 2. 提交事务:SQL执行无异常时 确认
commit
-- 结合后台代码的逻辑判断
开启事务
执行SQL:
update t_account set balance=balance-520 where username='王璐瑶'
update t_account set balance=balance+520 where username='何宇航'
if(sql执行无异常){
commit;
}else{
rollback;
}
特性-面试点
- ACID
- A:原子性。多条SQL要么同时成功,要么同时失败
- C:一致性。事务执行前后,数据状态是一致的
- I:隔离性。每个事务都是单独的个体,事务之间各自的执行结果互不影响
- D:持久性。事务一旦结束,对数据库的改变将是永久性的,无法再次撤回