05-SpringAOP的使用详解
大家好,我是徐庶老师,专注java,想要学习java的同学可以欢迎关注我。
结合视频观看效果更佳哦:2022最新Spring5入门到源码【完整资料+源码】_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
SpringAOP的使用详解
-
- 1、AOP切入点表达式
-
- 切点标识符
-
- 切点标识符—within表达式
- 切点标识符—execution()表达式
- 合并切点表达式
- 2、通知方法的执行顺序
- 3、获取方法的详细信息
-
- 获取返回值
- 获取异常信息
- 4、表达式的抽取
- 5、环绕通知的使用
- 6、基于XML配置的AOP配置
- 面试题
1、AOP切入点表达式
切点标识符
Spring AOP支持使用以下AspectJ切点标识符(PCD),用于切点表达式:
execution: 用于匹配方法执行连接点。 这是使用Spring AOP时使用的主要切点标识符。 可以匹配到方法级别 ,细粒度within: 只能匹配类这级,只能指定类, 类下面的某个具体的方法无法指定, 粗粒度this: 匹配实现了某个接口:this(com.xyz.service.AccountService)target: 限制匹配到连接点(使用Spring AOP时方法的执行),其中目标对象(正在代理的应用程序对象)是给定类型的实例。args: 限制与连接点的匹配(使用Spring AOP时方法的执行),其中变量是给定类型的实例。 AOP) where the arguments are instances of the given types.@target: 限制与连接点的匹配(使用Spring AOP时方法的执行),其中执行对象的类具有给定类型的注解。@args: 限制匹配连接点(使用Spring AOP时方法的执行),其中传递的实际参数的运行时类型具有给定类型的注解。@within: 限制与具有给定注解的类型中的连接点匹配(使用Spring AOP时在具有给定注解的类型中声明的方法的执行)。@annotation:限制匹配连接点(在Spring AOP中执行的方法具有给定的注解)。
这里重点介绍3个: execition、within、@annotation 更多详解有兴趣可通过视频学习:
2022最新Spring5入门到源码【完整资料+源码】_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
切点标识符—within表达式
通过类名进行匹配 粗粒度的切入点表达式
within(包名.类名)
则这个类中的所有的连接点都会被表达式识别,成为切入点。
在within表达式中可以使用*号匹配符,匹配指定包下所有的类,注意,只匹配当前包,不包括当前包的子孙包。
在within表达式中也可以用*号匹配符,匹配包
在within表达式中也可以用..*号匹配符,匹配指定包下及其子孙包下的所有的类
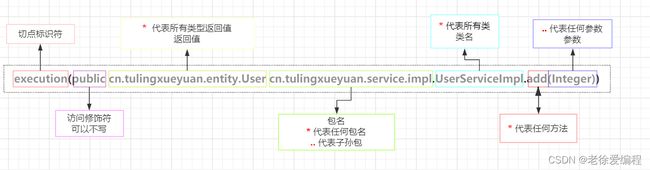
切点标识符—execution()表达式
细粒度的切入点表达式,可以以方法为单位定义切入点规则
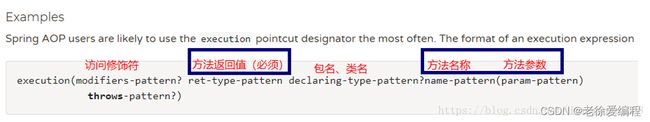
语法说明:
-
访问修饰符:(
public、protected…)可不写,不写则可以匹配任何一个访问修饰符 -
返回值:
- 如果是jdk自带类型可以不用写完整限定名;(如:
String,Integer等…) - 如果是自定义类型需要写上完整限定名;(如:
com.xushu.UserServiceImple等…) - 如果被切入的方法返回值不一样可以使用* 代表所有的方法值都能匹配
- 如果是jdk自带类型可以不用写完整限定名;(如:
-
包名:
- 示例:
cn.*==cn.tulingxuyuean==cn.任意名字,但是只能匹配一级比如 cn.tulingxueyuan.service就无法匹配 - 如果要匹配
cn.tulingxueyuan.service可以cn.tulingxueyuan.*但cn.tulingxueyuan.service.impl又无法匹配 - 可以用
..(代表子孙包) :cn.tulingxueyuan..*==cn.tulingxueyuan.service.impl可以匹配
- 示例:
-
类名:可以具体类名也 可以写
*,代表任何名字的类名。- 也可以模糊匹配
*ServiceImpl==>UserServiceImpl==>RoleServiceImpl
- 也可以模糊匹配
-
方法名:可以具体方法名也可以写
*,代表任何方法。- 也可以模糊匹配
*add==>useradd==>roleadd
- 也可以模糊匹配
-
参数:如果是jdk自带类型可以不用写完整限定名,如果是自定义类型需要写上完整限定名。
- 如果需要匹配任意参数 可以写:
..
- 如果需要匹配任意参数 可以写:
-
例子1:
该切入点规则表示,切出指定包下指定类下指定名称指定参数指定返回值的方法。
-
例子2:
该切入点规则表示,切出指定包下所有的类中的query方法,要求无参,但返回值类型不限。
-
例子3:
该切入点规则表示,切出指定包及其子孙包下所有的类中的query方法,要求无参,但返回值类型不限。
-
例子4:
该切入点规则表示,切出指定包及其子孙包下所有的类中的query方法,要求参数为int java.langString类型,但返回值类型不限。
-
例子5:
该切入点规则表示,切出指定包及其子孙包下所有的类中的query方法,参数数量及类型不限,返回值类型不限。
-
例子6:
该切入点规则表示,切出指定包及其子孙包下所有的类中的任意方法,参数数量及类型不限,返回值类型不限。这种写法等价于within表达式的功能。
-
例子7:
合并切点表达式
您可以使用 &&, || 和 !等符号进行合并操作。也可以通过名字来指向切点表达式。
-
//
&&:两个表达式同时=并且execution( public int cn.tulingxueyuan.inter.MyCalculator.*(..)) && execution(* *.*(int,int) ) -
//
||:任意满足一个表达式即可execution( public int cn.tulingxueyuan.inter.MyCalculator.*(..)) && execution(* *.*(int,int) ) -
//
!:只要不是这个位置都可以进行切入= 取反! execution( public int cn.tulingxueyuan.inter.MyCalculator.*(..))
2、通知方法的执行顺序
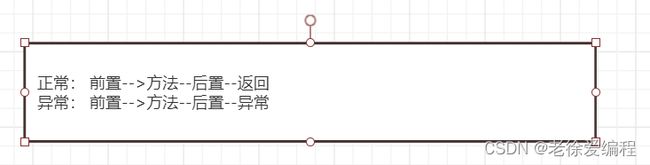
在之前的代码中大家一直对通知的执行顺序有疑问,其实执行的结果并没有错,大家需要注意:
1、正常执行:@Before--->@After--->@AfterReturning
2、异常执行:@Before--->@After--->@AfterThrowing
Spring在5.2.7之后改变了advice 的执行顺序。
之前:
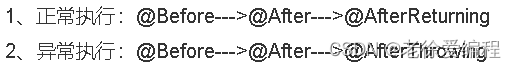
改后:
1、正常执行:@Before—>@AfterReturning—>@After
2、异常执行:@Before—>@AfterThrowing—>@After
如想追溯官方说明:在github官网版本更新说明中有说明:如图
更新说明:https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-framewor…
#25186链接:https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-framewor…
3、获取方法的详细信息
在上面的案例中,我们并没有获取Method的详细信息,例如方法名、参数列表等信息,想要获取的话其实非常简单,只需要添加JoinPoint参数即可。
LogUtil.java
package cn.tulingxueyuan.util;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Arrays;
@Component
@Aspect
public class LogUtil {
@Before("execution( public int cn.tulingxueyuan.inter.MyCalculator.*(int,int))")
public static void start(JoinPoint joinPoint){
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println(name+"方法开始执行,参数是:"+ Arrays.asList(args));
}
@AfterReturning("execution( public int cn.tulingxueyuan.inter.MyCalculator.*(int,int))")
public static void stop(JoinPoint joinPoint){
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println(name+"方法执行完成,结果是:");
}
@AfterThrowing("execution( public int cn.tulingxueyuan.inter.MyCalculator.*(int,int))")
public static void logException(JoinPoint joinPoint){
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println(name+"方法出现异常:");
}
@After("execution( public int cn.tulingxueyuan.inter.MyCalculator.*(int,int))")
public static void end(JoinPoint joinPoint){
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println(name+"方法执行结束了......");
}
}
获取返回值
刚刚只是获取了方法的信息,但是如果需要获取结果,还需要添加另外一个方法参数,并且告诉spring使用哪个参数来进行结果接收
LogUtil.java
@AfterReturning(value = "execution( public int cn.tulingxueyuan.inter.MyCalculator.*(int,int))",
returning = "result")
public static void stop(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object result){
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println(name+"方法执行完成,结果是:"+result);
}
获取异常信息
也可以通过相同的方式来获取异常的信息
LogUtil.java
@AfterThrowing(value = "execution( public int cn.tulingxueyuan.inter.MyCalculator.*(int,int))",throwing = "exception")
public static void logException(JoinPoint joinPoint,Exception exception){
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println(name+"方法出现异常:"+exception);
}
4、表达式的抽取
如果在实际使用过程中,多个方法的表达式是一致的话,那么可以考虑将切入点表达式抽取出来:
a、随便生命一个没有实现的返回void的空方法
b、给方法上标注@Potintcut注解
package cn.tulingxueyuan.util;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Arrays;
@Component
@Aspect
public class LogUtil {
@Pointcut("execution( public int cn.tulingxueyuan.inter.MyCalculator.*(int,int))")
public void myPoint(){}
@Before("myPoint()")
public static void start(JoinPoint joinPoint){
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println(name+"方法开始执行,参数是:"+ Arrays.asList(args));
}
@AfterReturning(value = "myPoint()",returning = "result")
public static void stop(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object result){
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println(name+"方法执行完成,结果是:"+result);
}
@AfterThrowing(value = "myPoint()",throwing = "exception")
public static void logException(JoinPoint joinPoint,Exception exception){
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println(name+"方法出现异常:"+exception.getMessage());
}
@After("myPoint()")
private int end(JoinPoint joinPoint){
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println(name+"方法执行结束了......");
return 0;
}
}
5、环绕通知的使用
LogUtil.java
package cn.tulingxueyuan.util;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Arrays;
@Component
@Aspect
public class LogUtil {
@Pointcut("execution( public int cn.tulingxueyuan.inter.MyCalculator.*(int,int))")
public void myPoint(){}
/**
* 环绕通知是spring中功能最强大的通知
* @param proceedingJoinPoint
* @return
*/
@Around("myPoint()")
public Object myAround(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint){
Object[] args = proceedingJoinPoint.getArgs();
String name = proceedingJoinPoint.getSignature().getName();
Object proceed = null;
try {
System.out.println("环绕前置通知:"+name+"方法开始,参数是"+Arrays.asList(args));
//利用反射调用目标方法,就是method.invoke()
proceed = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed(args);
System.out.println("环绕返回通知:"+name+"方法返回,返回值是"+proceed);
} catch (Throwable e) {
System.out.println("环绕异常通知"+name+"方法出现异常,异常信息是:"+e);
}finally {
System.out.println("环绕后置通知"+name+"方法结束");
}
return proceed;
}
}
环绕通知的执行顺序是优于普通通知的,具体的执行顺序如下:
环绕前置–>普通前置–>目标方法执行–>环绕正常结束/出现异常–>环绕后置–>普通后置–>普通返回或者异常。
但是需要注意的是,如果出现了异常,那么环绕通知会处理或者捕获异常,普通异常通知是接收不到的,因此最好的方式是在环绕异常通知中向外抛出异常。
6、基于XML配置的AOP配置
之前我们讲解了基于注解的AOP配置方式,下面我们开始讲一下基于xml的配置方式,虽然在现在的企业级开发中使用注解的方式比较多,但是你不能不会,因此需要简单的进行配置,注解配置快速简单,配置的方式共呢个完善。
1、将所有的注解都进行删除
2、添加配置文件
spring.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
">
<context:component-scan base-package="cn.tulingxueyuan">context:component-scan>
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy>aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
<bean id="logUtil" class="cn.tulingxueyuan.util.LogUtil2">bean>
<bean id="securityAspect" class="cn.tulingxueyuan.util.SecurityAspect">bean>
<bean id="myCalculator" class="cn.tulingxueyuan.inter.MyCalculator">bean>
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="globalPoint" expression="execution(public int cn.tulingxueyuan.inter.MyCalculator.*(int,int))"/>
<aop:aspect ref="logUtil">
<aop:pointcut id="mypoint" expression="execution(public int cn.tulingxueyuan.inter.MyCalculator.*(int,int))"/>
<aop:before method="start" pointcut-ref="mypoint">aop:before>
<aop:after method="end" pointcut-ref="mypoint">aop:after>
<aop:after-returning method="stop" pointcut-ref="mypoint" returning="result">aop:after-returning>
<aop:after-throwing method="logException" pointcut-ref="mypoint" throwing="exception">aop:after-throwing>
<aop:around method="myAround" pointcut-ref="mypoint">aop:around>
aop:aspect>
aop:config>
beans>
面试题
- Spring通知有哪些类型?
- 解释基于XML Schema方式的切面实现
- 解释基于注解的切面实现