基于SpringSecurity OAuth2实现单点登录——入门示例和流程分析
1、《入门示例和流程分析》
2、《未认证的请求是如何重定向到登录地址的》
3、《应用A是如何重定向到授权服务器的授权地址呢?》
4、《授权服务器是如何实现授权的呢?》
5、《登录访问应用A后再访问应用B会发生什么呢?》
一、入门示例
1、模块规划
为了模拟单点登录,我们创建了了授权服务、资源服务、应用A、应用B四个模块,其中授权服务和资源服务在实际项目中可以考虑合并为一,这里为了学习,没有进行合并。
- qriver-auth-server 授权服务 端口号 8080
- qriver-user-server 资源服务 端口号 8081
- qriver-client-app 应用A 端口号 8082
- qriver-client-app2 应用B 端口号 8083
2、授权服务搭建
2.1、依赖
在授权服务中,核心的依赖有SpringSecurity、Oauth2等,如下所示:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-oauth2artifactId>
dependency>
dependencies>
2.2、TokenStore 配置
主要用来配置AccessToken的存储方式,这里选择了内存方式,即InMemoryTokenStore,实际工作中可以选择Redis、数据库等方式。
@Configuration
public class AccessTokenConfig {
/**
* 配置Token存储方式
* @return
*/
@Bean
TokenStore tokenStore(){
return new InMemoryTokenStore();
}
}
2.3、SpringSecurity 相关配置
这里主要是进行SpringSecurity 的配置,我们配置了加密方式、创建了两个基于内存的用户。
@Configuration
public class QriverSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
/**
* 密码加密器
* @return
*/
@Bean
PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder(){
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
@Override
public UserDetailsService userDetailsServiceBean() throws Exception {
InMemoryUserDetailsManager mg = new InMemoryUserDetailsManager();
mg.createUser(User.withUsername("user").password(passwordEncoder().encode("123456")).roles("USER").build());
mg.createUser(User.withUsername("admin").password(passwordEncoder().encode("123456")).roles("USER","ADMIN").build());
return mg;
}
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.userDetailsService(userDetailsServiceBean()).passwordEncoder(passwordEncoder());
}
/**
* 配置 过滤器
* @param http
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.csrf().disable().formLogin();
}
}
2.4、授权服务 相关配置
这里是配置授权服务需要的配置。首先,我们需要在配置类上添加@EnableAuthorizationServer注解,启动授权服务自动加载等配置内容。
然后,配置AuthorizationServerTokenServices相关内容,实际上就是注入DefaultTokenServices(AuthorizationServerTokenServices的实现类)对象,并设置一些对应的参数。
然后,配置授权码的存储方式,这里选择了基于内存的InMemoryAuthorizationCodeServices方式。
然后,把前面配置的AuthorizationServerTokenServices、AuthorizationCodeServices配置到授权服务中,即重写configure(AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfigurer endpoints)方法。
再,配置令牌端点的安全约束,即通过重写configure(AuthorizationServerSecurityConfigurer security)实现。
最后,配置客户端的相关信息,通过重写configure(ClientDetailsServiceConfigurer clients)方法实现,实际项目中该配置一般是持久化到数据库的。
注意:其实,授权服务器的配置不止这些,我们可以根据自己的需求进行配置,这里的配置主要是为了实现单点登录,且尽量简化的进行的配置。
完整的配置如下:
@Configuration
@EnableAuthorizationServer
public class AuthorizationServerConfig extends AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private TokenStore tokenStore;
@Autowired
private ClientDetailsService clientDetailsService;
@Autowired
private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
/**
* 配置 Token 的一些基本信息
* @return
*/
@Bean
AuthorizationServerTokenServices tokenServices(){
DefaultTokenServices services = new DefaultTokenServices();
services.setClientDetailsService(clientDetailsService);//配置客户端校验方式
services.setReuseRefreshToken(true);//设置Token是否支持刷新
services.setTokenStore(tokenStore);//设置Token的存储位置
services.setAccessTokenValiditySeconds(60 * 60 * 2);//设置Token有效期
services.setRefreshTokenValiditySeconds(60 * 60 * 24 * 7);//设置Token刷新有效期
return services;
}
/**
* 配置令牌端点的安全约束
* @param security
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void configure(AuthorizationServerSecurityConfigurer security) throws Exception {
security.checkTokenAccess("permitAll()")//Token 校验的端点,后续客户端验证Token使用
.allowFormAuthenticationForClients()
.passwordEncoder(passwordEncoder);
}
/**
* 配置客户端的详细信息,客户端信息可以存储数据库、内存等地方
* @param clients
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void configure(ClientDetailsServiceConfigurer clients) throws Exception {
//clientId,resourceIds,scopes,grantTypes,authorities
clients.inMemory().withClient("client1")//配置clientId,唯一标识,表示客户端,即第三方应用
.secret(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456"))//客户端访问密码
.autoApprove(true)
// .resourceIds("res-1")//客户端所能访问的资源id集合
//客户端支持的grant_type,可选值包括authorization_code,password,refresh_token,implicit,client_credentials, 若支持多个grant_type用逗号(,)分隔
.authorizedGrantTypes("authorization_code","refresh_token")
//客户端申请的权限范围,可选值包括read,write,trust;若有多个权限范围用逗号(,)分隔
.scopes("all")
//客户端的重定向URI
.redirectUris("http://localhost:8082/login")
.and()
.withClient("client2")
.secret(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456"))//客户端访问密码
.autoApprove(true)
// .resourceIds("res-2")//客户端所能访问的资源id集合
//客户端支持的grant_type,可选值包括authorization_code,password,refresh_token,implicit,client_credentials, 若支持多个grant_type用逗号(,)分隔
.authorizedGrantTypes("authorization_code","refresh_token")
//客户端申请的权限范围,可选值包括read,write,trust;若有多个权限范围用逗号(,)分隔
.scopes("all")
//客户端的重定向URI
.redirectUris("http://localhost:8083/login")
.and()
.withClient("resource1")
.secret(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456"));
}
/**
* 配置令牌的访问端点和令牌服务
* @param endpoints
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void configure(AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfigurer endpoints) throws Exception {
endpoints.authorizationCodeServices(authorizationCodeServices())
.tokenServices(tokenServices());
}
/**
* 配置授权码的存储
* @return
*/
@Bean
AuthorizationCodeServices authorizationCodeServices(){
return new InMemoryAuthorizationCodeServices();
}
}
2.5、其他
在授权服务器搭建过程中,还可以自定义统一登录界面、配置服务器的端口号等内容,我们这里准守尽量简单的原则,使用较简单的配置先实现单点登录的示例,其中也省略了启动配置类等内容,完整的代码请看文章最底部,进行下载。
3、资源服务
资源服务器,主要为第三方应用提供了获取用户信息的接口。首先,我们需要添加资源服务器所需的依赖,如下:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-oauth2artifactId>
dependency>
然后,我们再进行资源服务配置,首先该类需要继承ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter 类,然后添加@EnableResourceServer注解启动资源服务,最后再配置一个RemoteTokenServices ,主要是因为授权服务和资源服务分离,所以需要配置,代码如下:
@Configuration
@EnableResourceServer
public class ResourceServerConfig extends ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter {
/**
* 因为资源服务器和授权服务器是分开的,所以需要配置一个验证Token的远程地址
* @return
*/
@Bean
RemoteTokenServices tokenServices() {
RemoteTokenServices services = new RemoteTokenServices();
services.setCheckTokenEndpointUrl("http://localhost:8080/oauth/check_token");
services.setClientId("resource1");
services.setClientSecret("123456");
return services;
}
}
最后,再提供一个获取用户信息的地址,地址由用户自定义,后续在应用A、应用B中配置路径即可。
@RestController
public class UserController {
@GetMapping("/user")
public Principal getCurrentUser(Principal principal) {
return principal;
}
}
启动器类、配置文件相关代码未展示,可以下载完整代码查看。
4、应用A、应用B
应用A、应用B代码基本一样,我们以应用A为例进行。
首先,引入依赖,如下:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleafartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-oauth2artifactId>
dependency>
然后,修改配置文件(application.properties):
#端口
server.port=8082
#配置客户端client-id,用于授权服务器端的验证
security.oauth2.client.client-id=client1
#配置客户端client-secret
security.oauth2.client.client-secret=123456
#授权服务器获取授权的地址,用于获取code
security.oauth2.client.user-authorization-uri=http://localhost:8080/oauth/authorize
#获取token
security.oauth2.client.access-token-uri=http://localhost:8080/oauth/token
#通过资源服务器,获取用户信息
security.oauth2.resource.user-info-uri=http://localhost:8081/user
server.servlet.session.cookie.name=client1
然后,配置启动类,这里我们把单点登录的@EnableOAuth2Sso注解直接配置到了启动类上,同时提供了一个RestTemplate 实例注入到了Spring容器中,代码如下:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableOAuth2Sso
public class QriverClientAppApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(QriverClientAppApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
RestTemplate restTemplate(){
return new RestTemplate();
}
}
然后,添加了一个测试用的接口,如下:
@Controller
public class IndexController {
@GetMapping("/index")
public String index(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("msg","欢迎," +
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getName() + ",登录系统A!");
return "index";
}
}
最后,实现一个简单的前端页面,我们引入了thymeleaf依赖,为了简化配置,我们按照thymeleaf默认路径添加一个html页面,即在resources目录下创建templates目录,然后把index.html放到templates目录下,这样就可以使用thymeleaf的默认配置了。
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>系统A - 首页title>
head>
<body>
<h1>系统Ah1>
<p th:text="${msg}">p>
<a href="http://localhost:8083/index">跳转系统Ba>
body>
html>
5、测试
完成上述配置后,我们依次启动授权服务、资源服务、应用A、应用B(没有顺序要求),然后访问应用A的地址http://localhost:8082/index,然后就会跳转到登录界面,然后输入用户名密码,就可以看到了我们应用A中对应的页面,然后点击跳转链接,就可以跳转到应用B,而这时不需要在输入用户名密码。
二、流程分析
1>、第一次访问应用A(http://localhost:8082/index),因为未登录,经过Spring Security过滤器,会重定向到应用A的登录http://localhost:8082/login。
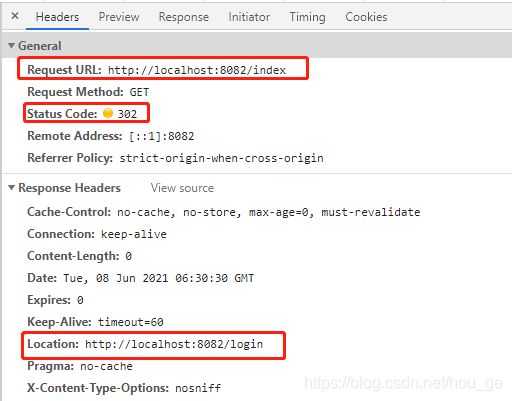
2>、因为我们启用了应用A的单点登录功能(即在启动类上增加了@EnableOAuth2Sso注解),当我们访问应用A的登录http://localhost:8082/login时,经过单点登录的过滤器,会重定向到授权服务的http://localhost:8080/oauth/authorize地址上。
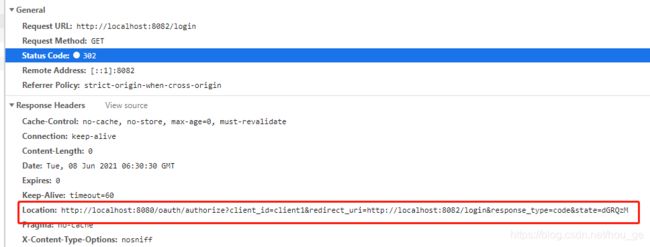
3>、因为访问授权服务的http://localhost:8080/oauth/authorize地址同样需要登录,所以这个时候,还是会被Spring Security过滤器拦截,并重定向到授权服务的登录地址http://localhost:8080/login上。需要注意的是,第一步中重定向到的是应用A的登录界面,这个时候重定向到了的是授权服务的登录界面。

4>、然后输入用户名密码,点击"登录"按钮。这个时候,会请求http://localhost:8080/login登录接口,需要注意该接口是POST请求,即登录验证接口。如果验证通过(用户名密码正确),则会重定向到http://localhost:8080/oauth/authorize?client_id=client1&redirect_uri=http://localhost:8082/login&response_type=code&state=dGRQzM地址上。

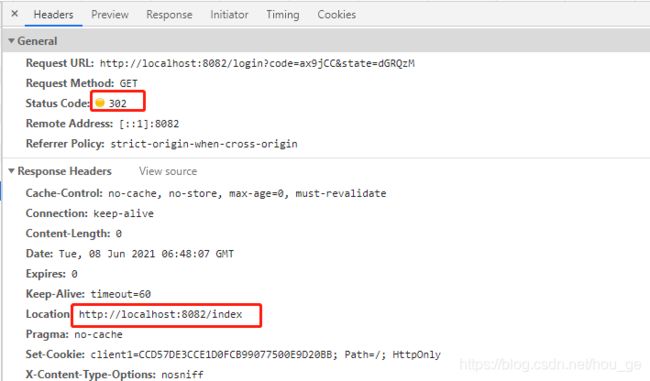
5>、访问http://localhost:8080/oauth/authorize?xxx地址时,又重定向到了应用A的登录地址http://localhost:8082/login?code=ax9jCC&state=dGRQzM,这个时候,和第一次访问应用A的登录相比,多了code参数。
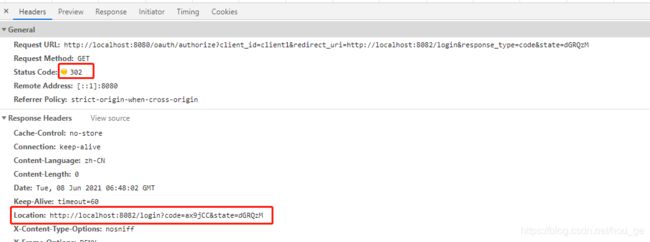
6>、访问应用A的登录地址http://localhost:8082/login?code=ax9jCC&state=dGRQzM,这个时候通过携带的code,换取到access_token,然后经过SpringSecurity处理,最终重定向到了应用A的访问地址http://localhost:8082/index。

写在最后
上述示例的完整源码,请移步查看下载:https://gitee.com/hsh2015/qriver-cloud-learning/tree/master/qriver-security-oauth。
这篇内容主要旨在记录单点登录示例的搭建和从前端视角了解浏览器和服务端的交互过程,后续我们将从源码级别分析这些重定向是如何实现的,最后是如何通过授权服务、资源服务器实现授权的。