Hadoop源码分析---Namenode和Datanode
一、Hadoop RPC框架
1. hadoop ipc框架代码位于org.apache.hadoop.ipc包内,有一个抽象类Server,实现监听服务的功能。其构造方法参数除了hostname, port之外,还有handlerCount,numReaders,queueSizePerHandler,分别对应handler线程数,reader线程数,每个handler所能处理队列的大小,handlerCount参数必须传入指定,如果没有指定numReaders参数,则numReaders = 1。如果传入的queueSizePerHandler参数没有指定,则默认值为100。而在handler之间共享的callQueue = handlerCount * queueSizePerHandler。同时还会在构造方法中创建两个对象new Listener()和new Responder()。
2. 在Listener类的构造方法中,会去绑定端口,创建ServerSocketChannel。创建Reader线程并将其放入数组中。并向channel上注册OP_ACCEPT事件。
3. 在Server对象创建完毕时,需要调用start方法,代码如下:
public synchronized void start() {
responder.start();
listener.start();
handlers = new Handler[handlerCount];
for (int i = 0; i < handlerCount; i++) {
handlers[i] = new Handler(i);
handlers[i].start();
}
}4. Listener类的run方法里面只做一件事,就是循环调用selector监听OP_ACCEPT事件,当有新的连接时,会去调用doAccept()方法,该方法先获得一个SocketChannel对象,然后向ConnectionManager类注册。该类会去创建一个Connection对象,然后将其加入到connections集合中。然后使用轮询算法获取一个Reader线程,将该connection放入其pendingConnections中等待处理。
5. Reader类的run()方法不断调用while循环,在循环里,先取出pendingConnections集合中的Connection对象,注册其OP_READ事件。然后调用select()方法,当存在可读消息时,会去调用Collection对象的readAndProcess()方法读取数据。
6. readAndProcess()方法调用while循环,如果第一次连接,则先去读取连接头,否则读取数据到一个data的ByteBuffer中。然后调用processOneRpc()方法,在该方法里面先解析出一个RpcRequestHeaderProto对象,从该对象里面可以解析出callId和retryCount。然后调用processRpcRequest()方法,该方法先根据传入的RpcRequestHeaderProto header对象解析出Class rpcRequestClass。然后调用该Class的反射方法,获取一个Writable rpcRequest实例,最后调用rpcRequest.readFields(dis)方法填充实例域值。方法最后根据这些解析的参数构造了一个Call对象,将其方法callQueue队列,该队列在handler线程间共享。
7. Handler线程的run()方法调用while循环,从callQueue队列里面取出一个Call实例,然后调用call方法,该方法是一个抽象方法,在RPC.Server类里面实现,该方法里面先通过rpcKind获取到一个RpcInvoker接口实现实例,有ProtoBuf和Writable两种。然后调用其实现类的call方法。
public Writable call(RPC.Server server, String protocol,
Writable writableRequest, long receiveTime) throws Exception {
RpcRequestWrapper request = (RpcRequestWrapper) writableRequest;
RequestHeaderProto rpcRequest = request.requestHeader;
String methodName = rpcRequest.getMethodName();
String protoName = rpcRequest.getDeclaringClassProtocolName();
long clientVersion = rpcRequest.getClientProtocolVersion();
}该方法先解析出methodName,protoName,以及clientVersion。根据protoName和clientVersion可以获取一个BlockingService service对象,然后调用service.callBlockingMethod(methodDescriptor, null, param)返回Writable result。
8. 在call方法调用返回结果后,Handler的run()方法先调用setupResponse()方法,将返回的result对象写进Call对象的rpcResponse属性中,写入完成后调用responder.doRespond(call)方法向客户端返回数据。
9. doRespond方法代码如下:
void doRespond(Call call) throws IOException {
synchronized (call.connection.responseQueue) {
call.connection.responseQueue.addLast(call);
if (call.connection.responseQueue.size() == 1) {
processResponse(call.connection.responseQueue, true);
}
}
}该方法先将Call插入connection的responseQueue队列,插入后如果该队列reponseQueue队列为1,则直接调用processResponse()方法。
10. processResponse()方法有两个地方调用,1个是在Handler的run()方法里面,一个是在Response线程的run()方法里面,该方法有个boolean inHandler参数区分。该方法先从responseQueue队列中取出一个Call,然后调用channelWrite方法,如果将数据全部写完,则返回true。否则,将该Call写入reponseQueue头部,然后判断如果该方法是在Handler类的run()方法里面调用,则调用select注册channel的OP_WRITE事件,等待下一次的WRITE事件发生,再调用processResponse()方法。
二、客户端写数据流程分析
1. 使用hadoop FileSystem类读取文件系统代码如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
try {
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(conf);
FileStatus[] fileStatuses = fs.listStatus(new Path("/tmp"));
for(FileStatus fileStatus : fileStatuses) {
System.out.println("status: " + fileStatus.getOwner());
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}Configuration类在初始化时会去加载resource目录下的hdfs-site.xml文件(如果存在),讲所有的key/value放入该对象中,而其中最重要的key就是fs.defaultFS。
最终调用了FileSystem.createFileSystem()方法,源码如下:
private static FileSystem createFileSystem(URI uri, Configuration conf)
throws IOException {
Tracer tracer = FsTracer.get(conf);
try(TraceScope scope = tracer.newScope("FileSystem#createFileSystem")) {
scope.addKVAnnotation("scheme", uri.getScheme());
Class clazz = getFileSystemClass(uri.getScheme(), conf);
FileSystem fs = (FileSystem)ReflectionUtils.newInstance(clazz, conf);
fs.initialize(uri, conf);
return fs;
}
}通过uril的scheme来创建FileSystem对象,如果schema是file://,则会创建LocalFileSystem对象,如果schema是hdfs,则会创建DistributedFileSystem对象, 然后调用其initialize()方法。关键代码如下:
public void initialize(URI uri, Configuration conf) throws IOException {
super.initialize(uri, conf);
this.dfs = new DFSClient(uri, conf, statistics);
this.uri = URI.create(uri.getScheme()+"://"+uri.getAuthority());
this.workingDir = getHomeDirectory();
}该方法先调用了父类的initialize()方法,然后创建了DFSClient对象。其关键构造代码方法如下:
public DFSClient(URI nameNodeUri, Configuration conf,
FileSystem.Statistics stats) throws IOException {
this(nameNodeUri, null, conf, stats);
}
public DFSClient(URI nameNodeUri, ClientProtocol rpcNamenode,
Configuration conf, FileSystem.Statistics stats) throws IOException {
this.ugi = UserGroupInformation.getCurrentUser();
this.namenodeUri = nameNodeUri;
ProxyAndInfo proxyInfo = null;
proxyInfo = NameNodeProxiesClient.createProxyWithClientProtocol(conf,
nameNodeUri, nnFallbackToSimpleAuth);
this.dtService = proxyInfo.getDelegationTokenService();
this.namenode = proxyInfo.getProxy();
} 方法调用NameNodeProxiesClient.createProxyWithClientProtocol()方法创建了ClientProtocol接口的代理类,关键代码如下:
public static ProxyAndInfo createProxyWithClientProtocol(
Configuration conf, URI nameNodeUri, AtomicBoolean fallbackToSimpleAuth)
throws IOException {
InetSocketAddress nnAddr = DFSUtilClient.getNNAddress(nameNodeUri);
Text dtService = SecurityUtil.buildTokenService(nnAddr);
ClientProtocol proxy = createNonHAProxyWithClientProtocol(nnAddr, conf,
UserGroupInformation.getCurrentUser(), true, fallbackToSimpleAuth);
return new ProxyAndInfo<>(proxy, dtService, nnAddr);
}
private static ClientProtocol createNNProxyWithClientProtocol(
InetSocketAddress address, Configuration conf, UserGroupInformation ugi,
boolean withRetries, AtomicBoolean fallbackToSimpleAuth)
throws IOException {
RPC.setProtocolEngine(conf, ClientNamenodeProtocolPB.class, ProtobufRpcEngine.class);
final long version = RPC.getProtocolVersion(ClientNamenodeProtocolPB.class);
ClientNamenodeProtocolPB proxy = RPC.getProtocolProxy(
ClientNamenodeProtocolPB.class, version, address, ugi, conf,
NetUtils.getDefaultSocketFactory(conf),
org.apache.hadoop.ipc.Client.getTimeout(conf), defaultPolicy,
fallbackToSimpleAuth).getProxy();
if (withRetries) { // create the proxy with retries
Map methodNameToPolicyMap
= new HashMap();
ClientProtocol translatorProxy =
new ClientNamenodeProtocolTranslatorPB(proxy);
return (ClientProtocol) RetryProxy.create(
ClientProtocol.class,
new DefaultFailoverProxyProvider(
ClientProtocol.class, translatorProxy),
methodNameToPolicyMap,
defaultPolicy);
} else {
return new ClientNamenodeProtocolTranslatorPB(proxy);
}
} 在createNNProxyWithClientProtocol()方法中,RPC.getProtocolProxy()方法返回了ClientNamenodeProtocolPB接口的代理实例proxy,该接口结构如下:public interface ClientNamenodeProtocolPB extends
ClientNamenodeProtocol.BlockingInterface {
}ClientNamenodeProtocol是一个抽象类,它是org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.protocol.proto.ClientNamenodeProtocolProtos类的内部类,该类由google的protocbuf工具编译生成的,其原始定义在hadoop-hdfs-project/hadoop-hdfs/src/main/proto/ClientNamenodeProtocol.proto文件中,其部分定义如下:
option java_package = "org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.protocol.proto";
option java_outer_classname = "ClientNamenodeProtocolProtos";
option java_generic_services = true;
option java_generate_equals_and_hash = true;
package hadoop.hdfs;
service ClientNamenodeProtocol {
rpc getBlockLocations(GetBlockLocationsRequestProto)
returns(GetBlockLocationsResponseProto);
rpc getServerDefaults(GetServerDefaultsRequestProto)
returns(GetServerDefaultsResponseProto);
rpc create(CreateRequestProto)returns(CreateResponseProto);
rpc append(AppendRequestProto) returns(AppendResponseProto);
}再来看RPC类的getProtocolProxy()方法:
public static ProtocolProxy getProtocolProxy(Class protocol,
long clientVersion,
InetSocketAddress addr,
UserGroupInformation ticket,
Configuration conf,
SocketFactory factory,
int rpcTimeout,
RetryPolicy connectionRetryPolicy,
AtomicBoolean fallbackToSimpleAuth)
throws IOException {
if (UserGroupInformation.isSecurityEnabled()) {
SaslRpcServer.init(conf);
}
return getProtocolEngine(protocol, conf).getProxy(protocol, clientVersion,
addr, ticket, conf, factory, rpcTimeout, connectionRetryPolicy,
fallbackToSimpleAuth);
} getProtocolEngine()方法返回PtotobufRpcEngine实例类,然后调用该类的getProxy()方法:
public ProtocolProxy getProxy(Class protocol, long clientVersion,
InetSocketAddress addr, UserGroupInformation ticket, Configuration conf,
SocketFactory factory, int rpcTimeout, RetryPolicy connectionRetryPolicy,
AtomicBoolean fallbackToSimpleAuth) throws IOException {
final Invoker invoker = new Invoker(protocol, addr, ticket, conf, factory,
rpcTimeout, connectionRetryPolicy, fallbackToSimpleAuth);
return new ProtocolProxy(protocol, (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
protocol.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{protocol}, invoker), false);
} 先构造了一个Invoker对象,该类关键代码如下:
private static class Invoker implements RpcInvocationHandler {
private Invoker(Class protocol, Client.ConnectionId connId,
Configuration conf, SocketFactory factory) {
this.remoteId = connId;
this.client = CLIENTS.getClient(conf, factory, RpcResponseWrapper.class);
this.protocolName = RPC.getProtocolName(protocol);
this.clientProtocolVersion = RPC
.getProtocolVersion(protocol);
}
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) {
RequestHeaderProto rpcRequestHeader = constructRpcRequestHeader(method);
Message theRequest = (Message) args[1];
final RpcResponseWrapper val;
try {
val = (RpcResponseWrapper) client.call(RPC.RpcKind.RPC_PROTOCOL_BUFFER,
new RpcRequestWrapper(rpcRequestHeader, theRequest), remoteId,
fallbackToSimpleAuth);
}
}
}所以最终得到的是ClientProtocol接口的实现类ClientNamenodeProtocolTranslatorPB,它实现方法如下:
public class ClientNamenodeProtocolTranslatorPB implements
ProtocolMetaInterface, ClientProtocol, Closeable, ProtocolTranslator {
final private ClientNamenodeProtocolPB rpcProxy;
public ClientNamenodeProtocolTranslatorPB(ClientNamenodeProtocolPB proxy) {
rpcProxy = proxy;
}
@Override
public LocatedBlocks getBlockLocations(String src, long offset, long length)
throws AccessControlException, FileNotFoundException,
UnresolvedLinkException, IOException {
GetBlockLocationsRequestProto req = GetBlockLocationsRequestProto
.newBuilder()
.setSrc(src)
.setOffset(offset)
.setLength(length)
.build();
try {
GetBlockLocationsResponseProto resp = rpcProxy.getBlockLocations(null,
req);
return resp.hasLocations() ?
PBHelper.convert(resp.getLocations()) : null;
} catch (ServiceException e) {
throw ProtobufHelper.getRemoteException(e);
}
}
}而ClientNamenodeProtocolPB并没有真正的子类,是由RPC.getProxy()方法生成的代理实现类,其Invoker类代理了所有方法,该类在初始化设计构造Client对象,ClientNamenodeProtocolPB类的所有方法调用变成了invoker类的client对象发送rpc请求来完成的。
2. 向hadoop写代码数据代码如下:
public class WriteDataToHDFS {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
DFSClient dfsClient = new DFSClient(URI.create("hdfs://localhost:8020"), conf);
DFSOutputStream outputStream = (DFSOutputStream) dfsClient.create("/tmp/test1.txt", false);
byte[] data = "sdfffffffffffafas;fd;as;flsadfsddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddda;f;asdf;as;fasf".getBytes();
outputStream.write(data);
outputStream.flush();
outputStream.close();
}
}
在调用dfscClient.create()方法时,会返回一个DFSOutpuStream对象,create()方法源码如下:
public DFSOutputStream create(String src,
FsPermission permission,
EnumSet flag,
boolean createParent,
short replication,
long blockSize,
Progressable progress,
int buffersize,
ChecksumOpt checksumOpt,
InetSocketAddress[] favoredNodes) throws IOException {
final DFSOutputStream result = DFSOutputStream.newStreamForCreate(this,
src, masked, flag, createParent, replication, blockSize, progress,
buffersize, dfsClientConf.createChecksum(checksumOpt),
favoredNodeStrs);
beginFileLease(result.getFileId(), result);
return result;
} DFSOutputStream.newStreamForCreate()方法源码如下:
static DFSOutputStream newStreamForCreate(DFSClient dfsClient, String src,
FsPermission masked, EnumSet flag, boolean createParent,
short replication, long blockSize, Progressable progress, int buffersize,
DataChecksum checksum, String[] favoredNodes) throws IOException {
HdfsFileStatus stat = null;
stat = dfsClient.namenode.create(src, masked, dfsClient.clientName,
new EnumSetWritable(flag), createParent, replication,
blockSize, SUPPORTED_CRYPTO_VERSIONS);
final DFSOutputStream out = new DFSOutputStream(dfsClient, src, stat,
flag, progress, checksum, favoredNodes);
out.start();
return out;
} 代码调用了Namenode.create()方法,返回了HdfsFileStatus对象,然后使用该对象构造了DFSOutputStream对象,该对象构造方法如下:
private DFSOutputStream(DFSClient dfsClient, String src, HdfsFileStatus stat,
EnumSet flag, Progressable progress,
DataChecksum checksum, String[] favoredNodes) throws IOException {
this(dfsClient, src, progress, stat, checksum);
this.shouldSyncBlock = flag.contains(CreateFlag.SYNC_BLOCK);
computePacketChunkSize(dfsClient.getConf().writePacketSize, bytesPerChecksum);
Span traceSpan = null;
if (Trace.isTracing()) {
traceSpan = Trace.startSpan(this.getClass().getSimpleName()).detach();
}
streamer = new DataStreamer(stat, traceSpan);
if (favoredNodes != null && favoredNodes.length != 0) {
streamer.setFavoredNodes(favoredNodes);
}
} 在这里创建了DataStreamer对象,该对象初始化方法如下:
class DataStreamer extends Daemon {
private volatile boolean streamerClosed = false;
private volatile ExtendedBlock block; // its length is number of bytes acked
private Token accessToken;
private DataOutputStream blockStream;
private DataInputStream blockReplyStream;
private ResponseProcessor response = null;
private volatile DatanodeInfo[] nodes = null; // list of targets for current block
private volatile StorageType[] storageTypes = null;
private volatile String[] storageIDs = null;
private DataStreamer(HdfsFileStatus stat, Span span) {
isAppend = false;
isLazyPersistFile = isLazyPersist(stat);
stage = BlockConstructionStage.PIPELINE_SETUP_CREATE;
traceSpan = span;
}
} 在DFSOutpuStream对象构造完毕并赋值给out变量,调用了out.start()方法,该方法代码如下:
private synchronized void start() {
streamer.start();
}DataStremer对象继承子Daemon类,而该类继承自Thread类,调用该方法,会启动新的线程,然后调用其run()方法,DataStreamer类的run()方法代码如下:
public void run() {
long lastPacket = Time.now();
TraceScope traceScope = null;
if (traceSpan != null) {
traceScope = Trace.continueSpan(traceSpan);
}
while (!streamerClosed && dfsClient.clientRunning) {
Packet one;
try {
// process datanode IO errors if any
boolean doSleep = false;
if (hasError && (errorIndex >= 0 || restartingNodeIndex >= 0)) {
doSleep = processDatanodeError();
}
synchronized (dataQueue) {
// wait for a packet to be sent.
long now = Time.now();
while ((!streamerClosed && !hasError && dfsClient.clientRunning
&& dataQueue.size() == 0 &&
(stage != BlockConstructionStage.DATA_STREAMING ||
stage == BlockConstructionStage.DATA_STREAMING &&
now - lastPacket < dfsClient.getConf().socketTimeout/2)) || doSleep ) {
long timeout = dfsClient.getConf().socketTimeout/2 - (now-lastPacket);
timeout = timeout <= 0 ? 1000 : timeout;
timeout = (stage == BlockConstructionStage.DATA_STREAMING)?
timeout : 1000;
try {
dataQueue.wait(timeout);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
DFSClient.LOG.warn("Caught exception ", e);
}
doSleep = false;
now = Time.now();
}
if (streamerClosed || hasError || !dfsClient.clientRunning) {
continue;
}
// get packet to be sent.
if (dataQueue.isEmpty()) {
one = createHeartbeatPacket();
} else {
one = dataQueue.getFirst(); // regular data packet
}
}
assert one != null;
// get new block from namenode.
if (stage == BlockConstructionStage.PIPELINE_SETUP_CREATE) {
if(DFSClient.LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
DFSClient.LOG.debug("Allocating new block");
}
setPipeline(nextBlockOutputStream());
initDataStreaming();
} else if (stage == BlockConstructionStage.PIPELINE_SETUP_APPEND) {
if(DFSClient.LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
DFSClient.LOG.debug("Append to block " + block);
}
setupPipelineForAppendOrRecovery();
initDataStreaming();
}
...... //后面代码省略
}
}初始创建对象时,stage变量赋值为BlockConstructionStage.PIPELINE_SETUP_CREATE,此时进入if代码块,先调用nextBlockOutputStream()方法,代码如下:
private LocatedBlock nextBlockOutputStream() throws IOException {
LocatedBlock lb = null;
DatanodeInfo[] nodes = null;
StorageType[] storageTypes = null;
int count = dfsClient.getConf().nBlockWriteRetry;
boolean success = false;
ExtendedBlock oldBlock = block;
long startTime = Time.now();
DatanodeInfo[] excluded =
excludedNodes.getAllPresent(excludedNodes.asMap().keySet())
.keySet()
.toArray(new DatanodeInfo[0]);
block = oldBlock;
lb = locateFollowingBlock(startTime,
excluded.length > 0 ? excluded : null);
block = lb.getBlock();
block.setNumBytes(0);
bytesSent = 0;
accessToken = lb.getBlockToken();
nodes = lb.getLocations();
storageTypes = lb.getStorageTypes();
//
// Connect to first DataNode in the list.
//
success = createBlockOutputStream(nodes, storageTypes, 0L, false);
}该方法调用了locateFollowingBlock()方法,该方法代码如下:
private LocatedBlock locateFollowingBlock(long start,
DatanodeInfo[] excludedNodes) throws IOException {
return dfsClient.namenode.addBlock(src, dfsClient.clientName,
block, excludedNodes, fileId, favoredNodes);
}而Namenode实现的addBlock()方法,会去调用FSNameSystem.getAdditionalBlock()方法,该方法会去调用BlockManager.chooseTarget4NewBlock()方法,该方法会去调用BlockPlacementPolicy.chooseTarget()方法,该类是一个抽象类,默认实现类是BlockPlacementPolicyDefault类,该类策略的注释如下:
/**
* The class is responsible for choosing the desired number of targets
* for placing block replicas.
* The replica placement strategy is that if the writer is on a datanode,
* the 1st replica is placed on the local machine,
* otherwise a random datanode. The 2nd replica is placed on a datanode
* that is on a different rack. The 3rd replica is placed on a datanode
* which is on a different node of the rack as the second replica.
*/该方法会根据设置的备份数找到的datanode节点,然后赋值给LocatedBlock类的locs变量,该变量是一个DatanodeInfo[]数组,
3. namenode初始化代码分析
3.1 namenode初始化时,关键代码如下:
clusterId = NNStorage.newClusterID();
public static String newClusterID() {
return "CID-" + UUID.randomUUID().toString();
}这里生成了唯一clusterId,然后使用代码初始化editlog和namespace,代码如下:
FSImage fsImage = new FSImage(conf, nameDirsToFormat, editDirsToFormat);
FSNamesystem fsn = new FSNamesystem(conf, fsImage);
fsImage.getEditLog().initJournalsForWrite();
if (!fsImage.confirmFormat(force, isInteractive)) {
return true; // aborted
}
fsImage.format(fsn, clusterId);调用FSImage的format()方法代码如下:
void format(FSNamesystem fsn, String clusterId) throws IOException {
long fileCount = fsn.getTotalFiles();
// Expect 1 file, which is the root inode
Preconditions.checkState(fileCount == 1,
"FSImage.format should be called with an uninitialized namesystem, has " +
fileCount + " files");
NamespaceInfo ns = NNStorage.newNamespaceInfo();
LOG.info("Allocated new BlockPoolId: " + ns.getBlockPoolID());
ns.clusterID = clusterId;
storage.format(ns);
editLog.formatNonFileJournals(ns);
saveFSImageInAllDirs(fsn, 0);
}代码调用了newNamespaceInfo方法生成namespaceId,namespaceId在联邦HDFS时比较有用。代码如下:
public static NamespaceInfo newNamespaceInfo()
throws UnknownHostException {
return new NamespaceInfo(newNamespaceID(), newClusterID(),
newBlockPoolID(), 0L);
}
public NamespaceInfo(int nsID, String clusterID, String bpID,
long cT, String buildVersion, String softwareVersion) {
super(HdfsConstants.NAMENODE_LAYOUT_VERSION, nsID, clusterID, cT,
NodeType.NAME_NODE);
blockPoolID = bpID;
this.buildVersion = buildVersion;
this.softwareVersion = softwareVersion;
}
private static int newNamespaceID() {
int newID = 0;
while(newID == 0)
newID = DFSUtil.getRandom().nextInt(0x7FFFFFFF); // use 31 bits only
return newID;
}
public static String newClusterID() {
return "CID-" + UUID.randomUUID().toString();
}
static String newBlockPoolID() throws UnknownHostException{
String ip = "unknownIP";
try {
ip = DNS.getDefaultIP("default");
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
LOG.warn("Could not find ip address of \"default\" inteface.");
throw e;
}
int rand = DFSUtil.getSecureRandom().nextInt(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
String bpid = "BP-" + rand + "-"+ ip + "-" + Time.now();
return bpid;
}NameSpaceInfo类的构造方法代码如下:
public NamespaceInfo(int nsID, String clusterID, String bpID,
long cT) {
this(nsID, clusterID, bpID, cT, Storage.getBuildVersion(),
VersionInfo.getVersion());
}
public NamespaceInfo(int nsID, String clusterID, String bpID,
long cT, String buildVersion, String softwareVersion) {
super(HdfsConstants.NAMENODE_LAYOUT_VERSION, nsID, clusterID, cT,
NodeType.NAME_NODE);
blockPoolID = bpID;
this.buildVersion = buildVersion;
this.softwareVersion = softwareVersion;
}生成namespaceInfo需要6个关键信息,nsId,clusterId, bpId均由随机数算法加上前缀拼接而成。 layoutVersion :是一个负整数,定义 HDFS 的持久化数据结构的版本。这个版本号与 Hadoop 分发包的发布版本号没有关系。当布局发生变化时,版本号递减,代码定义如下:
public static enum Feature implements LayoutFeature {
ROLLING_UPGRADE(-55, -53, "Support rolling upgrade", false),
EDITLOG_LENGTH(-56, "Add length field to every edit log op"),
XATTRS(-57, "Extended attributes"),
CREATE_OVERWRITE(-58, "Use single editlog record for " +
"creating file with overwrite"),
XATTRS_NAMESPACE_EXT(-59, "Increase number of xattr namespaces"),
BLOCK_STORAGE_POLICY(-60, "Block Storage policy");
}接下来的两个参数是build_version和version。
二、hadoopIPC相关接口分析
org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.protocol.ClientProtocol 充当了与Namenode交互的接口以及与Namenode rpc通信。
/**********************************************************************
* ClientProtocol is used by user code via
* {@link org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.DistributedFileSystem} class to communicate
* with the NameNode. User code can manipulate the directory namespace,
* as well as open/close file streams, etc.
*
**********************************************************************/
public interface ClientProtocol {
public LocatedBlocks getBlockLocations(String src,
long offset,
long length);
public FsServerDefaults getServerDefaults() throws IOException;
public LocatedBlock append(String src, String clientName)
throws AccessControlException, DSQuotaExceededException,
FileNotFoundException, SafeModeException, UnresolvedLinkException,
SnapshotAccessControlException, IOException;
}该接口的真正实现类是org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.NameNodeRpcServer类:
class NameNodeRpcServer implements NamenodeProtocols{
}
public interface NamenodeProtocols
extends ClientProtocol,
DatanodeProtocol,
NamenodeProtocol,
RefreshAuthorizationPolicyProtocol,
RefreshUserMappingsProtocol,
RefreshCallQueueProtocol,
GenericRefreshProtocol,
GetUserMappingsProtocol,
HAServiceProtocol,
TraceAdminProtocol {
}NamenodeRpcServer类是在Namenode类中被初始化的,运行在namenode进程中。Client要与该类交互,只能通过rpc调用的方式。
在hadoop-hdfs-project/hadoop-hdfs/src/main/proto/ClientNamenodeProtocol.proto中定义了Client与Namenode交互的消息格式。接口org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.protocolPB.ClientNamenodeProtocolPB继承了ClientNamenodeProtocol.BlockingInterface接口。该接口的实现类是org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.protocolPB.ClientNamenodeProtocolServerSideTranslatorPB类,它是在NamenodeRpcServer类中被初始化:
public class ClientNamenodeProtocolServerSideTranslatorPB implements
ClientNamenodeProtocolPB {
public ClientNamenodeProtocolServerSideTranslatorPB(ClientProtocol server)
throws IOException {
this.server = server;
}
}它的构造方法传入了NamenodeRpcServer实例。
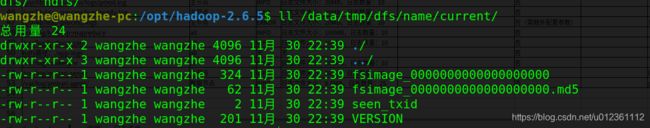
1. 使用hadoop namenode -format命令格式化系统时,会在hdfs namenode目录下(由dfs.namenode.name.dir属性指定)生成格式化文件:
使用命令/opt/hadoop-2.6.5/bin/hdfs oiv -i fsimage_0000000000000000000 -p XML -o test.xml, 可以查看image文件内容。
2. Namenode类启动时会去执行initiazlize()方法:
protected void initialize(Configuration conf) throws IOException {
if (NamenodeRole.NAMENODE == role) {
startHttpServer(conf);
}
loadNamesystem(conf);
}
protected void loadNamesystem(Configuration conf) throws IOException {
this.namesystem = FSNamesystem.loadFromDisk(conf);
}三、Datanode进程启动分析
1. DataNode类的main()方法会去调用secureMain()方法,该方法调用createDataNode方法,代码如下:
public static DataNode createDataNode(String args[], Configuration conf,
SecureResources resources) throws IOException {
DataNode dn = instantiateDataNode(args, conf, resources);
if (dn != null) {
dn.runDatanodeDaemon();
}
return dn;
}createDataNode方法里面又去调用了instantiateDataNode方法,关键代码如下:
public static DataNode instantiateDataNode(String args [], Configuration conf,
SecureResources resources) throws IOException {
if (conf == null)
conf = new HdfsConfiguration();
Collection dataLocations = getStorageLocations(conf);
UserGroupInformation.setConfiguration(conf);
SecurityUtil.login(conf, DFS_DATANODE_KEYTAB_FILE_KEY,
DFS_DATANODE_KERBEROS_PRINCIPAL_KEY);
return makeInstance(dataLocations, conf, resources);
} 方法调用了getStorageLocations方法,该方法去读取配置文件中的dfs.datanode.data.dir属性值,并将其转化为StorageLocation集合。然后调用了makeInstance方法,该方法去掉了DataNode类的构造方法DataNode(final Configuration conf, final List
void startDataNode(Configuration conf,
List dataDirs,
SecureResources resources
) throws IOException {
storage = new DataStorage();
// global DN settings
registerMXBean();
initDataXceiver(conf);
startInfoServer(conf);
pauseMonitor = new JvmPauseMonitor(conf);
pauseMonitor.start();
blockPoolManager = new BlockPoolManager(this);
blockPoolManager.refreshNamenodes(conf);
readaheadPool = ReadaheadPool.getInstance();
} 该方法先去初始化了一个DataStorage对象,DataStorage管理数据存储的生命周期,但是不负责具体的存储业务。该类是继承自Storage类,Storage是一个抽象类,被NameNode和DataNode等继承,而Storage类又是继承自StorageInfo类的,StorageInfo里面有4个关键属性:layoutVersion,namespaceID,clusterID,cTime。然后初始化了一个BlockPoolManager对象,调用起refreshNamenodes()方法,它通过解析配置文件hdfs-site.xml,可以取得namenode service地址。一般不启用联邦HDFS,所以只会有一个namespaceid。如果开启ha,会有两个namenode地址,否则只有一个 。它根据解析出来的namespaceId来创建相应的BPOfferService对象,一般只有一个BPOfferService。在BPOfferService对象的构造方法中,根据传入的namenode地址列表来构造相应的BPServiceActor对象,在对象创建完毕后,会分别去调用对象的start()方法。