Java List按照某字段去重
Java List按照某字段去重
- 嘚吧嘚
- distinct
-
- 示例一
- 示例二
- 根据某个字段去重
- Collectors.collectingAndThen()
嘚吧嘚
Java8流的新类java.util.stream.Collectors实现了java.util.stream.Collector接口,同时又提供了大量的方法对流(stream)的元素执行各种统计操作。
distinct
示例一
List<Map<String, Object>> mapList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
HashMap<String, Object> e = new HashMap<>();
e.put("name", "Mike");
e.put("age", 19);
mapList.add(e);
HashMap<String, Object> f = new HashMap<>();
f.put("name", "John");
f.put("age", 19);
mapList.add(f);
}
System.out.println(mapList);
System.out.println("===================去重===================");
List<Map<String, Object>> collect = mapList.stream().distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
collect.forEach(System.out::println);
执行结果如下
 但是这种方式必须要
但是这种方式必须要每个键值对都一样,才会被判定成重复的,否则不会被判为重复,如下。
示例二
List<Map<String, Object>> mapList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
HashMap<String, Object> e = new HashMap<>();
e.put("name", "Mike");
e.put("age", 19 + i);
mapList.add(e);
HashMap<String, Object> f = new HashMap<>();
f.put("name", "John");
f.put("age", 19 + i);
mapList.add(f);
}
System.out.println(mapList);
System.out.println("===================去重===================");
List<Map<String, Object>> collect = mapList.stream().distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
collect.forEach(System.out::println);
执行结果如下
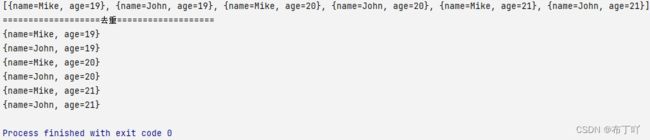 虽然name的值一样,但是age的值不一样,所以没有被被判定为重复。
虽然name的值一样,但是age的值不一样,所以没有被被判定为重复。
所以如果要按照某字段去重,请采用如下方式。
根据某个字段去重
List<Map<String, Object>> mapList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
HashMap<String, Object> e = new HashMap<>();
e.put("name", "Mike");
e.put("age", 19 + i);
mapList.add(e);
HashMap<String, Object> f = new HashMap<>();
f.put("name", "John");
f.put("age", 19 + i);
mapList.add(f);
}
System.out.println(mapList);
System.out.println("===================去重===================");
List<Map<String, Object>> collect = mapList.stream().collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.toCollection(() -> new TreeSet<>(Comparator.comparing(p -> String.valueOf(p.get("name"))))), ArrayList::new));
collect.forEach(System.out::println);
执行结果如下
 代码中用到了“Collectors.collectingAndThen”,这个函数是干什么的呢?咱们继续。
代码中用到了“Collectors.collectingAndThen”,这个函数是干什么的呢?咱们继续。
Collectors.collectingAndThen()
从函数名字就可以看出,这个函数分为两个部分,一个是collecting,另一个是then。
Collectors.collectingAndThen()函数很像map and reduce,它可接受两个参数,第一个参数用于reduce(collecting)操作,而第二参数用于map(then)操作。
也就是,先把流中的所有元素传递给第一个参数,然后把生成的集合传递给第二个参数来处理。
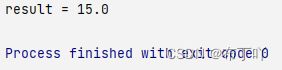
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4);
Double result = list.stream().collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.averagingLong(item -> item * 2), res -> res * 3));
System.out.println("result = " + result);
执行结果如下
- 把[1,2,3,4]这个集合传递给item -> item * 2这个lambda表达式,计算得出结果为[2,4,6,8]
- 然后再把[2,4,6,8]传递给Collectors.averagingLong表达式,计算得出5.0
- 然后传递给res -> res * 3这个lambda表达式,计算得到结果为15.0
欢迎大家进行指正或者补充!