直方图与均衡化
直方图
统计图像中相同像素点的数量。
使用cv2.calcHist(images, channels, mask, histSize, ranges)函数
images:原图像图像格式为uint8或float32,当传入函数时应用[]括起来,例如[img]。
channels:同样用中括号括起来,告诉我们统幅图像的直方图,如果图像是灰度图就是[0],如果是彩色图可以是[0],[1],[2],分别对应BGR。
mask:掩膜图像,统幅图像使用None,若使用一部分需要自行制作。
histSize:BIN的数目,也要中括号。
ranges:像素值范围一般为[0,256]
灰度图
img = cv2.imread('deppb.jpg', 0)
show.cv_show('img', img)
hist = cv2.calcHist([img], [0], None, [256], [0, 256])
h1 = hist.shape
plt.hist(img.ravel(), 256)
plt.show()
彩色图
img2 = cv2.imread('deppb.jpg')
show.cv_show('img2', img2)
color = ('b', 'g', 'r')
for i, col in enumerate(color):
histr = cv2.calcHist([img2], [i], None, [256], [0, 256])
plt.plot(histr, color=col)
plt.xlim([0, 256])
plt.show()
mask操作
mask,在指定区域置为255,其余区域置为0,与原图相与,最后得到指定区域的像素点个数统计,绘制直方图。
# 创建mask
show.cv_show('img2', img2) # 原图
mask = np.zeros(img2.shape[:2], np.uint8)
print(mask.shape)
mask[200: 600, 100: 427] = 255
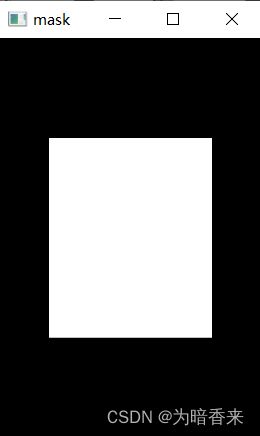
show.cv_show('mask', mask) # mask图
masked_img2 = cv2.bitwise_and(img2, img2, mask=mask)
show.cv_show('masked_img2', masked_img2) # 原图与mask
hist_full = cv2.calcHist([img2], [0], None, [256], [0, 256])
hist_mask = cv2.calcHist([img2], [0], mask, [256], [0, 256])
plt.plot(hist_full), plt.plot(hist_mask) # [0]通道直方图对比
plt.show()
mask图
mask与原图相与

[0]通道直方图对比

蓝色为整体直方图,橙色为特定区域直方图。
均衡化
将一副图像的直方图分布通过累积分布函数变成近似均匀分布,从而增强图像的对比度。

根据像素点个数得到概率值,再算出累积概率类似于分布函数,再由累积概率映射出新的像素值,最后取整。
img3 = cv2.imread('deppb.jpg', 0)
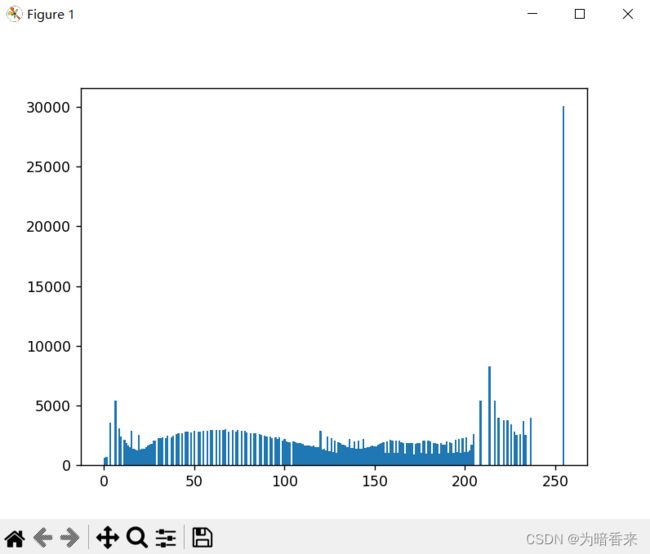
plt.hist(img3.ravel(), 256) # 原图直方图
plt.show()
equ = cv2.equalizeHist(img3)
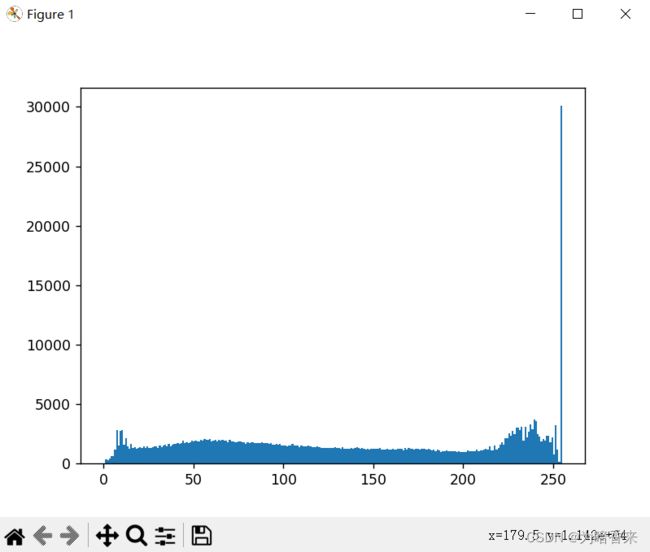
plt.hist(equ.ravel(), 256) # 均衡化后直方图
plt.show()
res = np.hstack((img3, equ))
show.cv_show('res', res) # 图像对比
自适应均衡化
其实是分区域进行均衡化,减少信息丢失。
clahe = cv2.createCLAHE(clipLimit=2.0, tileGridSize=(8, 8)) # 方法
res_clahe = clahe.apply(img3)
plt.hist(res_clahe.ravel(), 256) # 自适应均衡化后直方图
plt.show()
res = np.hstack((img3, equ, res_clahe)) # 与原图和整体均衡化对比
show.cv_show('res', res)