09|链(下):想学“育花”还是“插花”?用RouterChain确定客户意图
09|链(下):想学“育花”还是“插花”?用RouterChain确定客户意图
任务设定
首先,还是先看一下今天要完成一个什么样的任务。
这里假设咱们的鲜花运营智能客服 ChatBot 通常会接到两大类问题。
- 鲜花养护(保持花的健康、如何浇水、施肥等)
- 鲜花装饰(如何搭配花、如何装饰场地等)
你的需求是,如果接到的是第一类问题,你要给 ChatBot A 指示;如果接到第二类的问题,你要给 ChatBot B 指示。
我们可以根据这两个场景来构建两个不同的目标链。遇到不同类型的问题,LangChain 会通过 RouterChain 来自动引导大语言模型选择不同的模板。
当然我们的运营过程会遇到更多种类的问题,你只需要通过同样的方法扩充逻辑即可。
整体框架
RouterChain,也叫路由链,能动态选择用于给定输入的下一个链。我们会根据用户的问题内容,首先使用路由器链确定问题更适合哪个处理模板,然后将问题发送到该处理模板进行回答。如果问题不适合任何已定义的处理模板,它会被发送到默认链。
在这里,我们会用 LLMRouterChain 和 MultiPromptChain(也是一种路由链)组合实现路由功能,该 MultiPromptChain 会调用 LLMRouterChain 选择与给定问题最相关的提示,然后使用该提示回答问题。
具体步骤如下:
- 构建处理模板:为鲜花护理和鲜花装饰分别定义两个字符串模板。
- 提示信息:使用一个列表来组织和存储这两个处理模板的关键信息,如模板的键、描述和实际内容。
- 初始化语言模型:导入并实例化语言模型。
- 构建目标链:根据提示信息中的每个模板构建了对应的 LLMChain,并存储在一个字典中。
- 构建 LLM 路由链:这是决策的核心部分。首先,它根据提示信息构建了一个路由模板,然后使用这个模板创建了一个 LLMRouterChain。
- 构建默认链:如果输入不适合任何已定义的处理模板,这个默认链会被触发。
- 构建多提示链:使用 MultiPromptChain 将 LLM 路由链、目标链和默认链组合在一起,形成一个完整的决策系统。
具体实现
下面,就是用路由链自动选择处理模板的具体代码实现。
构建提示信息的模板
首先,我们针对两种场景,构建两个提示信息的模板。
# 构建两个场景的模板
flower_care_template = """你是一个经验丰富的园丁,擅长解答关于养花育花的问题。
下面是需要你来回答的问题:
{input}"""
flower_deco_template = """你是一位网红插花大师,擅长解答关于鲜花装饰的问题。
下面是需要你来回答的问题:
{input}"""
# 构建提示信息
prompt_infos = [
{
"key": "flower_care",
"description": "适合回答关于鲜花护理的问题",
"template": flower_care_template,
},
{
"key": "flower_decoration",
"description": "适合回答关于鲜花装饰的问题",
"template": flower_deco_template,
}]
初始化语言模型
接下来,我们初始化语言模型。
# 初始化语言模型
from langchain.llms import OpenAI
import os
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = '你的OpenAI Key'
llm = OpenAI()
构建目标链
下面,我们循环 prompt_infos 这个列表,构建出两个目标链,分别负责处理不同的问题。
# 构建目标链
from langchain.chains.llm import LLMChain
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
chain_map = {}
for info in prompt_infos:
prompt = PromptTemplate(template=info['template'],
input_variables=["input"])
print("目标提示:\n",prompt)
chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=prompt,verbose=True)
chain_map[info["key"]] = chain
这里,目标链提示是这样的:
目标提示:
input_variables=['input']
output_parser=None partial_variables={}
template='你是一个经验丰富的园丁,擅长解答关于养花育花的问题。\n 下面是需要你来回答的问题:\n
{input}' template_format='f-string'
validate_template=True
目标提示:
input_variables=['input']
output_parser=None partial_variables={}
template='你是一位网红插花大师,擅长解答关于鲜花装饰的问题。\n 下面是需要你来回答的问题:\n
{input}' template_format='f-string'
validate_template=True
对于每个场景,我们创建一个 LLMChain(语言模型链)。每个链会根据其场景模板生成对应的提示,然后将这个提示送入语言模型获取答案。
构建路由链
下面,我们构建路由链,负责查看用户输入的问题,确定问题的类型。
# 构建路由链
from langchain.chains.router.llm_router import LLMRouterChain, RouterOutputParser
from langchain.chains.router.multi_prompt_prompt import MULTI_PROMPT_ROUTER_TEMPLATE as RounterTemplate
destinations = [f"{p['key']}: {p['description']}" for p in prompt_infos]
router_template = RounterTemplate.format(destinations="\n".join(destinations))
print("路由模板:\n",router_template)
router_prompt = PromptTemplate(
template=router_template,
input_variables=["input"],
output_parser=RouterOutputParser(),)
print("路由提示:\n",router_prompt)
router_chain = LLMRouterChain.from_llm(llm,
router_prompt,
verbose=True)
输出:
路由模板:
Given a raw text input to a language model select the model prompt best suited for the input. You will be given the names of the available prompts and a description of what the prompt is best suited for. You may also revise the original input if you think that revising it will ultimately lead to a better response from the language model.
<< FORMATTING >>
Return a markdown code snippet with a JSON object formatted to look like:
```json
{{
"destination": string \ name of the prompt to use or "DEFAULT"
"next_inputs": string \ a potentially modified version of the original input
}}
```
REMEMBER: "destination" MUST be one of the candidate prompt names specified below OR it can be "DEFAULT" if the input is not well suited for any of the candidate prompts.
REMEMBER: "next_inputs" can just be the original input if you don't think any modifications are needed.
<< CANDIDATE PROMPTS >>
flower_care: 适合回答关于鲜花护理的问题
flower_decoration: 适合回答关于鲜花装饰的问题
<< INPUT >>
{input}
<< OUTPUT >>
路由提示:
input_variables=['input'] output_parser=RouterOutputParser(default_destination='DEFAULT', next_inputs_type=<class 'str'>, next_inputs_inner_key='input')
partial_variables={}
template='Given a raw text input to a language model select the model prompt best suited for the input. You will be given the names of the available prompts and a description of what the prompt is best suited for. You may also revise the original input if you think that revising it will ultimately lead to a better response from the language model.\n\n
<< FORMATTING >>\n
Return a markdown code snippet with a JSON object formatted to look like:\n```json\n{{\n "destination": string \\ name of the prompt to use or "DEFAULT"\n "next_inputs": string \\ a potentially modified version of the original input\n}}\n```\n\n
REMEMBER: "destination" MUST be one of the candidate prompt names specified below OR it can be "DEFAULT" if the input is not well suited for any of the candidate prompts.\n
REMEMBER: "next_inputs" can just be the original input if you don\'t think any modifications are needed.\n\n<< CANDIDATE PROMPTS >>\n
flower_care: 适合回答关于鲜花护理的问题\n
flower_decoration: 适合回答关于鲜花装饰的问题\n\n
<< INPUT >>\n{input}\n\n<< OUTPUT >>\n'
template_format='f-string'
validate_template=True
这里我说一下路由器链是如何构造提示信息,来引导大模型查看用户输入的问题并确定问题的类型的。
先看路由模板部分,这段模板字符串是一个指导性的说明,目的是引导语言模型正确处理用户的输入,并将其定向到适当的模型提示。
1. 路由模板的解释
路由模板是路由功能得以实现的核心。我们来详细分解一下这个模板的每个部分。
引言
Given a raw text input to a language model select the model prompt best suited for the input.
这是一个简单的引导语句,告诉模型你将给它一个输入,它需要根据这个输入选择最适合的模型提示。
You will be given the names of the available prompts and a description of what the prompt is best suited for.
这里进一步提醒模型,它将获得各种模型提示的名称和描述。
You may also revise the original input if you think that revising it will ultimately lead to a better response from the language model.
这是一个可选的步骤,告诉模型它可以更改原始输入以获得更好的响应。
格式说明 (<< FORMATTING >>)
指导模型如何格式化其输出,使其以特定的方式返回结果。
Return a markdown code snippet with a JSON object formatted to look like:
表示模型的输出应该是一个 Markdown 代码片段,其中包含一个特定格式的 JSON 对象。
下面的代码块显示了期望的 JSON 结构,其中 destination 是模型选择的提示名称(或“DEFAULT”),而 next_inputs 是可能被修订的原始输入。
额外的说明和要求
REMEMBER: “destination” MUST be one of the candidate prompt names specified below OR it can be “DEFAULT”…
这是一个重要的指导,提醒模型 “destination” 字段的值必须是下面列出的提示之一或是 “DEFAULT”。
REMEMBER: “next_inputs” can just be the original input if you don’t think any modifications are needed.
这再次强调,除非模型认为有必要,否则原始输入不需要修改。
候选提示 (<< CANDIDATE PROMPTS >>)
列出了两个示例模型提示及其描述:
- “flower_care: 适合回答关于鲜花护理的问题”,适合处理与花卉护理相关的问题。
- “flower_decoration: 适合回答关于鲜花装饰的问题”,适合处理与花卉装饰相关的问题。
输入 / 输出部分
<< INPUT >>\n{input}\n\n<< OUTPUT >>\n:
这部分为模型提供了一个格式化的框架,其中它将接收一个名为 {input} 的输入,并在此后的部分输出结果。
总的来说,这个模板的目的是让模型知道如何处理用户的输入,并根据提供的提示列表选择一个最佳的模型提示来回应。
2. 路由提示的解释
路由提示 (router_prompt)则根据路由模板,生成了具体传递给 LLM 的路由提示信息。
- 其中 input_variables 指定模板接收的输入变量名,这里只有 “input”。
- output_parser 是一个用于解析模型输出的对象,它有一个默认的目的地和一个指向下一输入的键。
- template 是实际的路由模板,用于给模型提供指示。这就是刚才详细解释的模板内容。
- template_format 指定模板的格式,这里是 “f-string”。
- validate_template 是一个布尔值,如果为 True,则会在使用模板前验证其有效性。
简而言之,这个构造允许你将用户的原始输入送入路由器,然后路由器会决定将该输入发送到哪个具体的模型提示,或者是否需要对输入进行修订以获得最佳的响应。
构建默认链
除了处理目标链和路由链之外,我们还需要准备一个默认链。如果路由链没有找到适合的链,那么,就以默认链进行处理。
# 构建默认链
from langchain.chains import ConversationChain
default_chain = ConversationChain(llm=llm,
output_key="text",
verbose=True)
构建多提示链
最后,我们使用 MultiPromptChain 类把前几个链整合在一起,实现路由功能。这个 MultiPromptChain 类是一个多路选择链,它使用一个 LLM 路由器链在多个提示之间进行选择。
MultiPromptChain 中有三个关键元素。
- router_chain(类型 RouterChain):这是用于决定目标链和其输入的链。当给定某个输入时,这个 router_chain 决定哪一个 destination_chain 应该被选中,以及传给它的具体输入是什么。
- destination_chains(类型 Mapping[str, LLMChain]):这是一个映射,将名称映射到可以将输入路由到的候选链。例如,你可能有多种处理文本输入的方法(或“链”),每种方法针对特定类型的问题。destination_chains 可以是这样一个字典:{‘weather’: weather_chain, ‘news’: news_chain}。在这里,weather_chain 可能专门处理与天气相关的问题,而 news_chain 处理与新闻相关的问题。
- default_chain(类型 LLMChain):当 router_chain 无法将输入映射到 destination_chains 中的任何一个链时,LLMChain 将使用此默认链。这是一个备选方案,确保即使路由器不能决定正确的链,也总有一个链可以处理输入。
它的工作流程如下:
- 输入首先传递给 router_chain。
- router_chain 根据某些标准或逻辑决定应该使用哪一个 destination_chain。
- 输入随后被路由到选定的 destination_chain,该链进行处理并返回结果。
- 如果 router_chain 不能决定正确的 destination_chain,则输入会被传递给 default_chain。
这样,MultiPromptChain 就为我们提供了一个在多个处理链之间动态路由输入的机制,以得到最相关或最优的输出。
实现代码如下:
# 构建多提示链
from langchain.chains.router import MultiPromptChain
chain = MultiPromptChain(
router_chain=router_chain,
destination_chains=chain_map,
default_chain=default_chain,
verbose=True)
运行路由链
好了,至此我们的链路已经准备好了。现在开始提出各种问题,测试一下我们的链。
测试 A:
print(chain.run(“如何为玫瑰浇水?”))
输出:
测试 B:
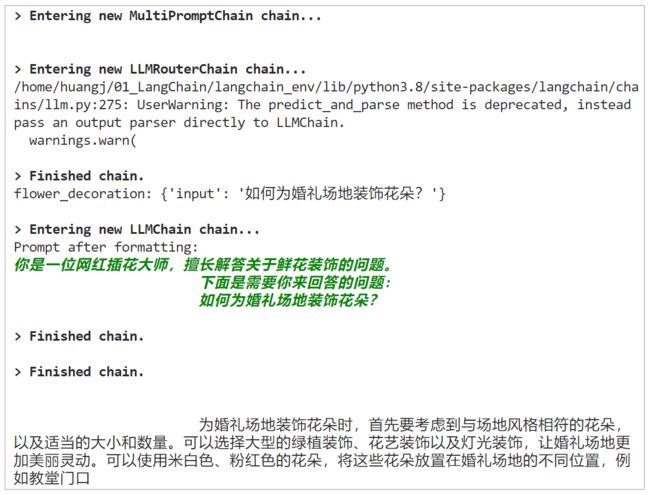
print(chain.run(“如何为婚礼场地装饰花朵?”))
输出:
测试 C:
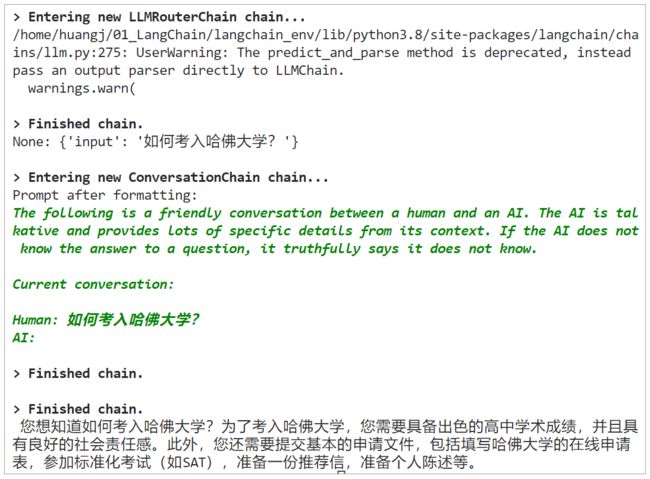
print(chain.run(“如何考入哈佛大学?”))
输出:
这三个测试,分别被路由到了三个不同的目标链,其中两个是我们预设的“专家类型”目标链,而第三个问题:如何考入哈佛大学?被模型一眼看穿,并不属于任何鲜花运营业务场景,路由链把它抛入了一个 “default chain” —— ConversationChain 去解决。