threejs react fiber 最佳实践
Intro
在使用的相当一段时间的 threejs 和 react-three-fiber 后,在中文资料环境极其匮乏的情况下,做个极简·笔记式的分享。目标是能让大家在 最快 的速度上手,且 半·精通
Install
npm install three @react-three/fiber 官方文档
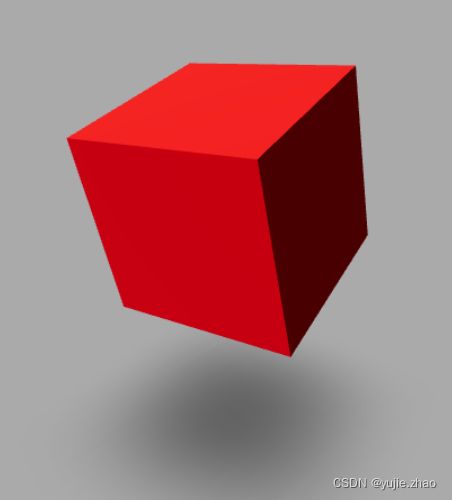
Demo1 - 全局概览
这是一个短小精悍的 demo1,对着下面代码看解析
- 物体
盒子:new BoxGeometry()球:new SphereGeometry(.5, 32, 16) - 物体上色
- 光1
intensity光的强度 - 光2
colorposition:照射方向 - 控制
OrbitControls交互操作,鼠标旋转:左键拖拽平移:右键拖拽放大:滚轮 - 阴影
- 背景
import React, { Suspense } from 'react'
import { BoxGeometry, MeshStandardMaterial } from 'three'
import { Canvas } from '@react-three/fiber'
import { ContactShadows, OrbitControls } from '@react-three/drei'
const ball = new BoxGeometry()
const mtl1 = new MeshStandardMaterial({ color: '#f00' })
export default function Demo () {
return (
<Canvas style={{ height: 800 }} camera={{ fov: 75, near: 0.1, far: 1000, position: [2, 1, 2] }}>
<Suspense fallback={null}>
<ambientLight intensity={0.1} />
<directionalLight color={'#fff'} intensity={1} position={[-3, 5, 5]} />
<mesh geometry={ball} material={mtl1} />
<OrbitControls makeDefault />
<ContactShadows rotation-x={Math.PI / 2} position={[0, -1.4, 0]} opacity={0.75} width={10} height={10} blur={2.6} far={2} />
<color attach='background' args={['#aaa']} />
</Suspense>
</Canvas>
)
}
如果你认真看完 demo1 每一处细节,你已经对 threejs 有了 50% 的认识了。。。后续就是对每个部分的展开和丰富
Demo2 - 文件加载
实际项目并不会像 demo1 中使用系统物体,通常是
外部文件,常见格式有 obj,gltf,glb,fbx 等。 demo2 从外部加载,并添加了一些常用工具
- 远程加载
useLoader(OBJLoader, src)不同的格式,只需要切换加载类,快捷版:useFBX(src)useGLTF(src, true) - 坐标系
new AxesHelper(100)方便查看三维世界 - 性能工具
- 环境设置
- 错误抑制
import React, { Suspense, useRef } from 'react'
import { AxesHelper } from 'three'
import { Canvas, useLoader } from '@react-three/fiber'
import { Environment, OrbitControls, Stats } from '@react-three/drei'
import ErrorBoundary from 'antd/es/alert/ErrorBoundary'
import { OBJLoader } from 'three/examples/jsm/loaders/OBJLoader'
function MyMesh () {
const src = '/obj/demo2.obj'
const object = useLoader(OBJLoader, src)
console.log(object)
return (
<primitive object={object} />
)
}
export default function Demo () {
const statRef = useRef(null)
return (
<div ref={statRef}>
<Stats showPanel={0} parent={statRef} style={{ top: 'auto', bottom: 0 }} />
<ErrorBoundary>
<Canvas style={{ height: 800 }} camera={{ fov: 75, near: 0.1, far: 1000, position: [2, 1, 2] }}>
<Suspense fallback={null}>
<directionalLight color={'#fff'} intensity={1} position={[-3, 5, 5]} />
<primitive object={new AxesHelper(100)} />
<MyMesh />
<OrbitControls makeDefault />
<color attach='background' args={['#aaa']} />
<Environment
background={false} preset={null} scene={undefined}
path={'/img/three/env/'}
files={['px.png', 'nx.png', 'py.png', 'ny.png', 'pz.png', 'nz.png']}
/>
</Suspense>
</Canvas>
</ErrorBoundary>
</div>
)
}
如果不出意外,你的模型已经出来了,但是有 一半 的可能你只是一个灰白物体,没上色。因为obj格式的 材质 部分是有要求的。首先 obj 可能没直接包含 mtl 文件,或者 mtl 文件没有相对路径于 obj 文件(同一目录)。其次 mtl 中的图片定义,也没有相对路径于 obj 文件。 情况复杂且多,需要大家根据 Network 自我 debug。
Demo3 自动对焦
这个需求很多,网上解释也很多,但我是没看懂,也没见人真解决。在翻看 threejs-editor 时,发现了 auto-focus 的源码(editor/js/EditorControls.js:34 focus),然后进行改装,这边给个参考。过程:先计算物体边界,转化成盒子模型,然后倍数,算出合适的位置 + 角度,然后设置回去。
import React, { Suspense, useEffect, useState } from 'react'
import { Box3, Sphere, Vector3 } from 'three'
import { Canvas, useLoader } from '@react-three/fiber'
import { OrbitControls, PerspectiveCamera } from '@react-three/drei'
import { OBJLoader } from 'three/examples/jsm/loaders/OBJLoader'
const OBJ_POS_000 = [0, 0, 0]
const CAM_POS_212 = [1, .5, 1]
function calcBound (object, x = 1.5) {
const box = new Box3().setFromObject(object)
const center = new Vector3()
let distance
let objPos2 = new Vector3()
if (box.isEmpty() === false) {
/** @var {Vector3} */
objPos2 = box.getCenter(center)
objPos2.negate()
distance = box.getBoundingSphere(new Sphere()).radius
} else {
center.setFromMatrixPosition(object.matrixWorld)
distance = 0.1
}
const delta = new Vector3()
delta.set(...CAM_POS_212)
delta.applyQuaternion(object.quaternion)
delta.multiplyScalar(distance * x)
const camPos2 = new Vector3()
camPos2.copy(objPos2).add(delta)
return [objPos2.toArray(), camPos2.toArray()]
}
function MyMesh () {
const [objPos, setObjPos] = useState(OBJ_POS_000)
const [camPos, setCamPos] = useState(CAM_POS_212)
const src = '/obj/demo2.obj'
const object = useLoader(OBJLoader, src)
useEffect(() => {
const [objPos2, camPos2] = calcBound(object, 2.5)
setObjPos(objPos2)
setCamPos(camPos2)
// eslint-disable-next-line
}, [object])
return (
<>
<primitive object={object} position={objPos} />
<PerspectiveCamera makeDefault fov={50} far={5000} near={.01} position={camPos} />
</>
)
}
export default function Demo () {
return (
<Canvas style={{ height: 800 }} camera={{ fov: 75, near: 0.1, far: 1000, position: [2, 1, 2] }}>
<Suspense fallback={null}>
<ambientLight intensity={0.1} />
<directionalLight color={'#fff'} intensity={1} position={[-3, 5, 5]} />
<MyMesh />
<OrbitControls makeDefault />
<color attach='background' args={['#aaa']} />
</Suspense>
</Canvas>
)
}
进阶部分
前面的 demo 都给了完整可运行代码,后面部分由于需要配套的基础代码太多,只能给
关键部分。大家自行整合,实在不行,留言询问 up。
编辑物体位置、旋转、缩放
这个 demo 来自网上,但是缺少保存的过程,这边给个保存参考
// 保存逻辑参考
const { gl, scene, camera } = useThree()
// 前提是要有 uuid
const obj = scene.getObjectByName(uuid)
const partObj = packRef.current.getObjByUuid(uuid)
const position = partObj.position.toArray()
const rotation = partObj.rotation.toVector3().toArray()
console.log(partObj, position, rotation)
// 然后自己定义数据结构,入库
import { Suspense, useState } from 'react'
import { Canvas, useThree } from '@react-three/fiber'
import { ContactShadows, OrbitControls, TransformControls, useCursor, useGLTF } from '@react-three/drei'
import { proxy, useSnapshot } from 'valtio'
// Reactive state model, using Valtio ...
const modes = ['translate', 'rotate', 'scale']
const state = proxy({ current: null, mode: 0 })
function Model ({ name, ...props }) {
// Ties this component to the state model
const snap = useSnapshot(state)
// Fetching the GLTF, nodes is a collection of all the meshes
// It's cached/memoized, it only gets loaded and parsed once
const { nodes } = useGLTF('https://utihp1.csb.app/compressed.glb')
// Feed hover state into useCursor, which sets document.body.style.cursor to pointer|auto
const [hovered, setHovered] = useState(false)
useCursor(hovered)
return (
<mesh
// Click sets the mesh as the new target
onClick={(e) => {
e.stopPropagation()
state.current = name
}}
// If a click happened but this mesh wasn't hit we null out the target,
// This works because missed pointers fire before the actual hits
onPointerMissed={(e) => {if (e.type === 'click') state.current = null}}
// Right click cycles through the transform modes
onContextMenu={(e) => {
if (snap.current === name) {
e.stopPropagation()
state.mode = (snap.mode + 1) % modes.length
}
}}
onPointerOver={(e) => {
e.stopPropagation()
setHovered(true)
}}
onPointerOut={() => setHovered(false)}
name={name}
geometry={nodes[name].geometry}
material={nodes[name].material}
material-color={snap.current === name ? '#ff6080' : 'white'}
{...props}
dispose={null}
/>
)
}
function Controls () {
// Get notified on changes to state
const snap = useSnapshot(state)
const scene = useThree((state) => state.scene)
return (
<>
{/* As of [email protected] transform-controls can refer to the target by children, or the object prop */}
{snap.current && <TransformControls object={scene.getObjectByName(snap.current)} mode={modes[snap.mode]} />}
{/* makeDefault makes the controls known to r3f, now transform-controls can auto-disable them when active */}
<OrbitControls makeDefault minPolarAngle={0} maxPolarAngle={Math.PI / 1.75} />
</>
)
}
export default function Home () {
return (
<Canvas camera={{ position: [0, -10, 80], fov: 50 }} dpr={[1, 2]}>
<pointLight position={[100, 100, 100]} intensity={0.8} />
<hemisphereLight color='#ffffff' groundColor='#b9b9b9' position={[-7, 25, 13]} intensity={0.85} />
<Suspense fallback={null}>
<group position={[0, 10, 0]}>
<Model name='Curly' position={[1, -11, -20]} rotation={[2, 0, -0]} />
<Model name='DNA' position={[20, 0, -17]} rotation={[1, 1, -2]} />
<Model name='Headphones' position={[20, 2, 4]} rotation={[1, 0, -1]} />
<Model name='Notebook' position={[-21, -15, -13]} rotation={[2, 0, 1]} />
<Model name='Rocket003' position={[18, 15, -25]} rotation={[1, 1, 0]} />
<Model name='Roundcube001' position={[-25, -4, 5]} rotation={[1, 0, 0]} scale={0.5} />
<Model name='Table' position={[1, -4, -28]} rotation={[1, 0, -1]} scale={0.5} />
<Model name='VR_Headset' position={[7, -15, 28]} rotation={[1, 0, -1]} scale={5} />
<Model name='Zeppelin' position={[-20, 10, 10]} rotation={[3, -1, 3]} scale={0.005} />
<ContactShadows rotation-x={Math.PI / 2} position={[0, -35, 0]} opacity={0.25} width={200} height={200} blur={1} far={50} />
</group>
</Suspense>
<Controls />
</Canvas>
)
}
截图拍照
当需要预览图时,生成出来的会更方便。 两种方式提供,第一种直接截屏当前状态,第二种新摄像头
const { gl, scene, camera } = useThree()
function doPhoto1() {
gl.render(scene, camera)
return gl.domElement.toDataURL()
}
function doPhotot2() {
const camera2 = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(75, 1, 0.01, 1000)
camera2.copy(camera)
camera2.position.set(.6, .6, .6)
gl.render(scene, camera2)
return gl.domElement.toDataURL('image/jpeg', .5)
}
如何改色
最复杂的留到最后,前面的部分基本都是应用层,只需要对 api 足够了解就能做出很多案例。这部分将需要
自定义 Class,改写官方实现。这里有两种方式,一种是改写加载类,一种是提取后自己组装
还记得 const object = useLoader(OBJLoader, src) 吗
OBJLoader 是官方的类 examples/jsm/loaders/OBJLoader.js
其中parse 方法 this.materials.create( sourceMaterial.name ) 就是关键
所以我们可以定义一个 MyOBJLoader 然后改写 parse
// 另一种方式,维护一个 mapping 表格,然后使用 mesh
export function useMcc (metaTable) {
useEffect(async () => {
for (const unitOne of metaTable) {
const { objName, mtlName, mtlId, mtlUdfEnable, mtlUdfUrl } = unitOne
// const name = Math.random().toString(36).slice(-6)
const name = `${objName}-${mtlName}`
if (mtlId) {
mccObjects[name] = await loadByMid(mtlId, mtlUdfEnable, mtlUdfUrl)
} else {
mccObjects[name] = new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial({ color: str2rgb(name) })
}
}
setMccObjects({ ...mccObjects })
}, [metaTable])
return { mccObjects }
}
export function useMetaTable (mccObjects, object) {
const [tb, set] = useState([])
useEffect(() => {
if (!mccObjects) return
// console.log('mccObjects', mccObjects)
const ret = []
for (let mesh of object.children) {
ret.push({
uuid: mesh.uuid,
geometry: mesh.geometry,
material: mesh.material.length
? mesh.material.map(v => get(mccObjects, mesh.name, v.name))
: get(mccObjects, mesh.name, mesh.material.name),
})
}
set(ret)
}, [mccObjects])
function get (arr, objName, mtlName) {
const name = `${objName}-${mtlName}`
return arr[name]
}
return tb
}
const { mccObjects } = useMcc(meta)
const metaTable = useMetaTable(mccObjects, object)
<group position={objPos}>
{metaTable.map(v => (
<mesh key={v.uuid} geometry={v.geometry} material={v.material} />
))}
</group>
总结
这些 demo 覆盖了很多场景,有疑问欢迎交流。所有代码随意使用,转发请带原文。