C++中的new和delete
相关文章
C++智能指针
文章目录
- 相关文章
- 前言
- 一、new 运算符
-
- 1. operator new 函数的范围
- 2. 在类中重载new运算符
- 3. 分配失败
- 二、delete 运算符
-
- 1. 内存泄露统计示例
- 2. 在类中重载delete运算符
- 总结
前言
在C++中,new和delete是用于动态内存管理的运算符,它们允许程序在运行时动态地分配和释放内存,而不需要在编译时知道确切的内存需求。动态内存分配是指在程序运行时根据需要分配内存空间,而静态内存分配是指在编译时分配内存空间。new和delete是C++中实现动态内存分配和释放的关键工具。
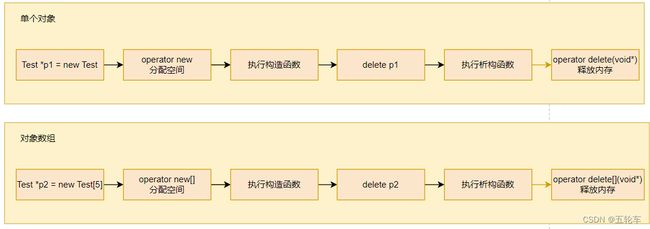
new运算符用于在堆上动态分配内存。它可以用于分配单个对象或数组。当使用new来分配单个对象时,它会返回一个指向所分配内存空间的指针,并自动调用对象的构造函数来初始化对象。当使用new来分配数组时,它会分配足够的内存来存储整个数组,并返回指向数组第一个元素的指针。这样,程序可以根据需要动态地创建数组,而不需要在编译时知道数组的大小。
delete运算符用于释放由new分配的内存。对于单个对象,使用delete;对于数组,使用delete[]。当不再需要动态分配的内存时,应该使用delete来释放内存,以防止内存泄漏。delete会调用对象的析构函数来清理对象,并释放所分配的内存。这样,程序可以在不需要内存时及时释放它,以避免内存资源的浪费。
new和delete提供了灵活的内存管理机制,使程序能够根据需要动态地分配和释放内存。然而,它们需要谨慎使用,因为错误的使用可能导致内存泄漏、悬空指针等问题。例如,在使用new分配内存后,如果忘记使用delete释放内存,就会导致内存泄漏;而在使用delete释放内存后,如果继续使用指向已释放内存的指针,就会导致悬空指针问题。因此,在使用new和delete时,需要确保正确地匹配内存的分配和释放,并避免出现悬空指针的情况。
C++ 支持使用 new 和 delete 运算符动态分配和解除分配对象。 这些运算符为来自称为“自由存储”(也称为“堆”)的池中的对象分配内存。 new 运算符调用特殊函数 operator new,delete 运算符调用特殊函数 operator delete。
一、new 运算符
operator new的第一个参数必须为 size_t 类型,且返回类型始终为 void*,编译器将如下语句转换为对函数 operator new 的调用:
char *p = new char[64];
重复调用 operator new 会返回不同的地址(指针)。
如果要申请的的存储空间为零字节,operator new 将返回指向不同对象的指针:
#include 如果分配请求的内存不足,operator new 会引发 std::bad_alloc 异常。 或者,如果使用了 placement 形式 new(std::nothrow),或者链接在非引发的 operator new 支持中,它将返回 nullptr。
1. operator new 函数的范围
| 运算符 | 范围 |
|---|---|
| ::operator new | 全局 |
| class-name::operator new | 类 |
在使用 new 运算符分配内置类型的对象、不包含用户定义的 operator new 函数的类类型的对象和任何类型的数组时,将调用全局 operator new 函数。 在使用 new 运算符分配类类型的对象时(其中定义了 operator new),将调用该类的 operator new。
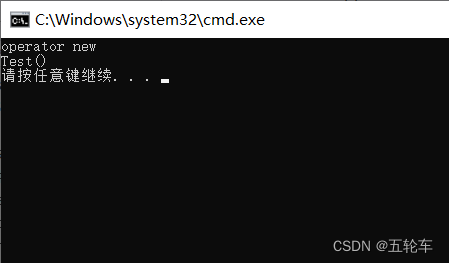
2. 在类中重载new运算符
示例:
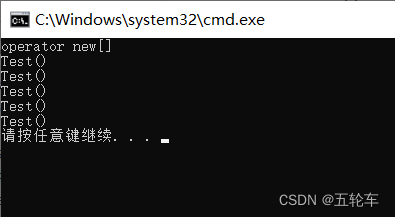
#include 在类声明中支持数组的 new 运算符。 例如:
#include 3. 分配失败
C++ 标准库中的 new 函数支持自 C++98 以来在 C++ 标准中指定的行为。 如果分配请求的内存不足,operator new 会引发 std::bad_alloc 异常。标准 C++ 要求分配器引发 std::bad_alloc 或派生自 std::bad_alloc 的类。 可以处理此类异常,如以下示例所示:
#include 执行结果:
二、delete 运算符
可使用 delete 运算符释放使用 new 运算符动态分配的内存。 delete 运算符调用 operator delete 函数,该函数将内存释放回可用池。 使用 delete 运算符也会导致调用类析构函数(如果存在)。
1. 内存泄露统计示例
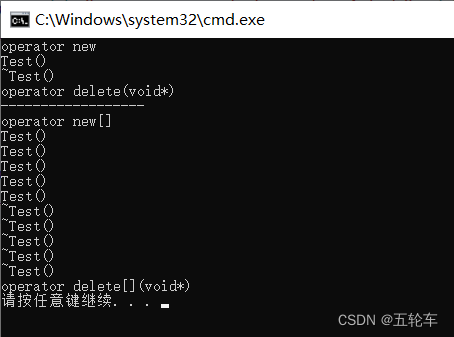
能过自定义 operator new 和 operator delete 函数,来记录申请内存和释放的次数,判断是否存在内存泄露,示例如下:
#include 2. 在类中重载delete运算符
示例如下:
#include 总结
new和delete是C++中用于动态内存管理的运算符,它们提供了灵活的内存分配和释放机制,但需要谨慎使用以避免内存泄漏和悬空指针等问题。随着智能指针的引入,程序员可以更安全地进行动态内存管理,减少了对new和delete的直接使用,提高了程序的可靠性和可维护性。
✍结尾 ❤️ 感谢您的支持和鼓励,关注不迷路✍