网页盒子模型
一、盒子模型的概念及组成
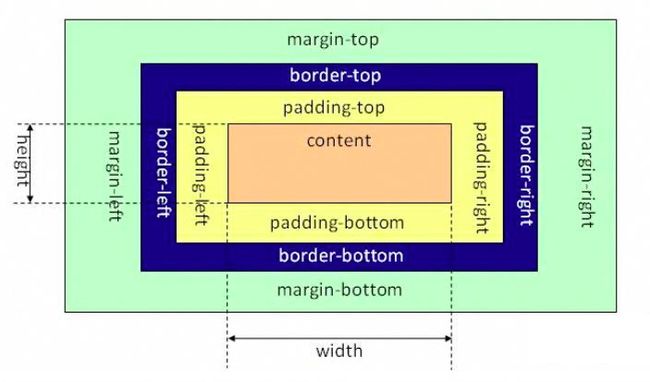
盒子模型:html页面把布局元素看做一个矩形的盒子,也就是一个盛装内容的容器。
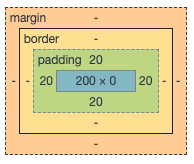
盒子模型包括外边距 margin、边框 border、内边距 padding、内容 content
margin:外边距,与其它盒子的距离
border:边框,盒子的边框
padding:内边距,边框与内容的距离
content:内容,一般设置了宽高
二、盒子的大小
盒子的大小就是盒子的宽高,这个宽高并不是指content的宽和高。默认是包括content、padding、border和margin。
盒子占用的宽=左外边距 + 左边框 + 左内边距 + 内容的宽 + 右内边距 + 右边框 + 右外边距
盒子占用的高=上外边距 + 上边框 + 上内边距 + 内容的高 + 下内边距 + 下边框 + 下外边距
1、标准盒子
在标准盒子中,css设置的width和height是content的宽高。
这里的width和height指的是css样式中的。
盒子实际占用的宽=margin-left + border-left + padding-left + width + padding-right + border-right + margin-right
盒子实际占用的高=margin-top + border-top + padding-top + height + padding-bottom + border-bottom + margin-bottom
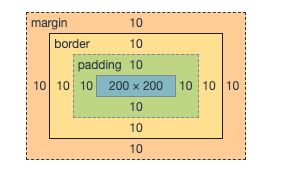
设置div属性 :background: pink; width: 200px; height: 200px; padding: 10px; margin: 10px; border: 10px solid red;
最终盒子实际占用的宽=10+10+10+200+10+10+10=260 px,盒子实际占用的高=10+10+10+200+10+10+10 =260 px
2、ie盒子模型

ie盒子比较特殊,就如上图,通过css设置width和height并不是只对content设置,而是对border+padding+content这三个属性设置。
这里的width和height指的是css样式中的。
盒子实际占用的宽=margin-left + width + margin-right
盒子实际占用的高=margin-top + height + margin-bottom
设置div属性 :background: pink; width: 200px; height: 200px; padding: 10px; margin: 10px; border: 10px solid red;
最终盒子实际占用的宽=10+200+10=220 px,盒子实际占用的高=10+200+10 =220 px
(因为用不了ie所以没有测试了! )
3、box-sizing
可以再css中通过设置box-sizing的值来设置盒子。
box-sizing的取值
- border-box
- content-box
- inherit
content-box(默认)
由 CSS2.1 规定的宽度高度行为。
宽度和高度分别应用到元素的内容框。
在宽度和高度之外绘制元素的内边距和边框。
就相当于标准盒子模型
border-box
为元素设定的宽度和高度决定了元素的边框盒。
就是说,为元素指定的任何内边距和边框都将在已设定的宽度和高度内进行绘制。
通过从已设定的宽度和高度分别减去边框和内边距才能得到内容的宽度和高度。
就相当于ie盒子模型,设置width和height包括border+padding+content
inherit
从父元素继承 box-sizing 属性的值
test:
设置一个div,样式如下。最终结果
div {
background: pink;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
padding: 10px;
margin: 10px;
border: 10px solid red;
}
添加 box-sizing: content-box
结果就与标准盒子一致。
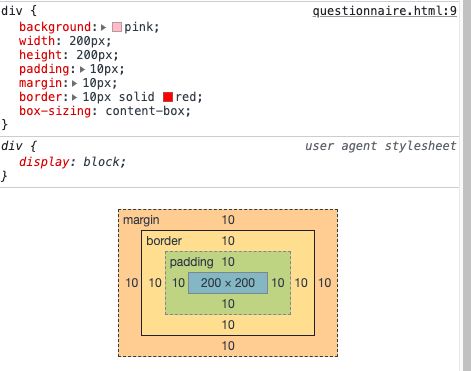
添加 box-sizing: bordert-box
结果content的宽变成了width - border-left - padding-left - border-right - padding-right
content的高变成了width - border-top - padding-top - border-bottom - padding-bottom
与ie盒子模型一致。
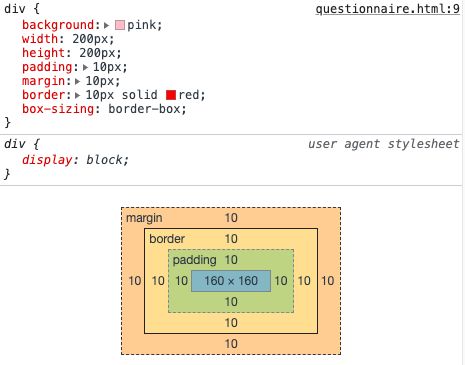
三、基本属性
1、border 边框
边框属性
一般使用复合属性较多。
/*设置上下左右边框的大小*/
border-width: 10px;
border-left-width: 10px;
border-top-width: 10px;
border-right-width: 10px;
border-bottom-width: 10px;
/*设置边框样式*/
border-style: solid;
border-left-style: solid;
border-top-style: dotted;
border-right-style: dashed;
border-bottom-style: double;
/*设置边框颜色*/
border-color: brown;
border-left-color: red;
border-top-color: blue;
border-right-color: green;
border-bottom-color: yellow;
/*边框的复合写法*/
border: 10px solid brown;
border-left: 10px solid red;
border-top: 10px dotted blue;
border-right: 10px dashed green;
border-bottom: 10px double yellow;
同时边框也存在圆角属性
border-top-left-radius: 8px;
border-top-right-radius: 8px;
border-bottom-left-radius: 8px;
border-bottom-right-radius: 8px;
/*四个角一起设置*/
border-radius: 8px;
/*左上右下2px,右上左下4px*/
border-radius: 2px 4px;
/*左上2px,右上左下4px,右下8px*/
border-radius: 2px 4px 8px;
/*左上2px,右上4px,右下8px,左下16px*/
border-radius: 2px 4px 8px 16px;
常见问题
在标准盒子模型里,css设置的width,height不包括border,所以设置border会使盒子变大。
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Documenttitle>
<style>
div{
background: pink;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
border: 10px solid red;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div>div>
body>
html>


最终结果整个盒子的大小为220px * 220px 所以在设置边框且想盒子大小不变,就需要在设置width和height时把边框的值减去。
给div添加css属性 box-sizing: border-box;结果边框没有撑大盒子。

2、padding 内边距
内边距属性
content与盒子边界的距离
padding-left: 10px;
padding-right: 10px;
padding-top: 10px;
padding-bottom: 10px;
/* 根据上右下左顺序设置内边距,缺省取对面内边距的值 */
/*四个内边距均为10px*/
padding: 10px;
/*上下内边距为10px,左右内边距为20px*/
padding: 10px 20px;
/*上内边距为10px,左右内边距为20px,下内边距为30px*/
padding: 10px 20px 30px;
/*上内边距为10px,右内边距为20px,下内边距为30px,左内边距为40px*/
padding: 10px 20px 30px 40px;
常见问题
padding撑大盒子
在标准盒子模型里,css设置的width,height不包括padding,所以设置padding会撑大盒子。
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Documenttitle>
<style>
div{
background: pink;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
padding: 10px;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div>div>
body>
html>

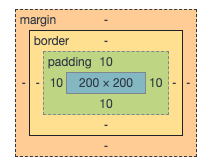
与设置边框类似,最终盒子大小变成了220 * 220,所以想要盒子不被撑大,需要减去内边距的大小。
同时我们也可以利用这一特性适当调整content在盒子中的相对位置。
同时我们继续测试一下给div添加box-sizing: border-box; 最终结果是,盒子的大小没有变化。

我们继续加大padding的值,到150px。最终content变成0*0。盒子还是被撑大了。

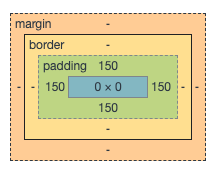
所以,当为border-box(类似ie盒子)时,width和height包括content、padding、border的宽高的设置,所以设置padding是会计算剩余的宽高,然后分配给content和border。所以不撑大盒子有一个临界值。在这里临界值为上下padding和200px,左右padding和200px。
border-box下,border也类似。
未指定width/height,padding不会撑大盒子
拿两个盒子,嵌套关系,外层盒子设置宽高,内层盒子测试,代码如下。
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Documenttitle>
<style>
.fa{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background: pink;
}
.son {
padding: 20px;
background: blue;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div class="fa">
<div class="son">div>
div>
body>
html>
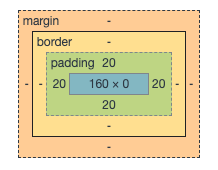
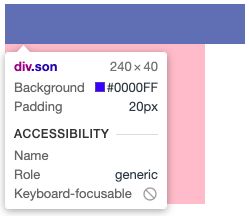
结果:子盒子未指定宽高,高度被撑开,为40px,div为块级元素,未指定宽度,自动占满一整行,所以子元素默认宽度为父元素的宽度,设置padding后content的宽度变小,加上左右padding后与父元素宽一致(20 + 160 + 20 = 200),不过前提在上下和左右内边距的和<=父元素的宽高(content的宽为0)。
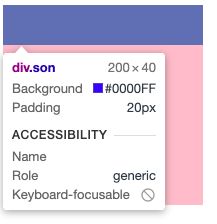
给子元素添加width: 100%;
结果:子元素的宽被撑开,大于父元素的宽。在左右内边距的和>父元素的宽高时content的宽也是200。
3、margin外边距
常用属性
与其它盒子的距离
margin-top: 10px;
margin-right: 10px;
margin-bottom: 10px;
margin-left: 10px;
/*与padding类似*/
/*上下左右外边距均为10px*/
margin: 10px;
/*上下外边距为10px,左右外边距为20px*/
margin: 10px 20px;
/*上外边距为10px,左右外边距为20px,下外边距为30px*/
margin: 10px 20px 30px;
/*上外边距为10px,右外边距为20px,下外边距为30px,左外边距为40px*/
margin: 10px 20px 30px 40px;
常见问题
1、相邻盒子的外边距合并
相邻的块元素,上方的块设置下外边距,下方的设置上外边距,外边距不会相加,而是变成加大的外边距
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Documenttitle>
<style>
.fa{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background: pink;
margin: 20px;
}
.son {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
margin: 10px;
background: blue;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div class="fa">div>
<div class="son">div>
body>
html>
结果:两个盒子的外边距没有成为想象那样 20 + 10 = 30px,而是只有20px,只有两者中较大的值。
解决:
只在一方设置外边距

2、嵌套盒子外边距塌陷
两个嵌套关系的盒子(父子关系),父元素和子元素都有上外边距,父元素会向子元素的塌陷,最终和子元素顶部平齐。
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Documenttitle>
<style>
.fa{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background: pink;
margin: 10px;
}
.son {
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
margin: 20px;
background: blue;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div class="fa">
<div class="son">div>
div>
body>
html>
最终父元素与子元素的顶部平齐,且相对于网页顶部来说外边距为20px。
解决:
- 为父元素增加上边框 border
- 为父元素设置上内边距 padding
- 为父元素添加overflow: hidden
一般使用第三种方法最好,前两种还要计算盒子大小防止盒子变大。
解决后的结果:

4、box-shadowy阴影
盒子阴影不占用空间
boxshadow: h-shadow v-shadow blur spread color inset/outset;
- h-shadow 必写,水平阴影的位置,允许负数
- v-shadow 必写,垂直阴影的位置,允许负数
- blur 可选,模糊距离
- spread 可选 阴影尺寸
- color 可选阴影颜色
- inset/outset 可选,内阴影/外阴影(默认,但不能写上去)
5、清除内外边距
不同的元素可能有不同的内外边距,而且在不同的浏览器中可能也有不同。所以一般我们都会清除所有元素的内外边距。
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
I only see daylight, daylight, daylight, daylight!
后续继续补充没有考虑到的知识点