程序A标准输出重定向B的标准输入(c++)
背景:两个程序A,B,B有自己的操作.现将A的标准输出和B的标准输入重定向,B的标准输入和A的标准输出重定向到一起。使得A收到输入等同B收到输入,逻辑处理后A可以直接使用结果。
B必须是一个可执行文件。起初研究了一下popen,但这个函数只能实现单向流动,要么w,要么r。后来又研究了一下pipe管道,但管道基本是半双工的,要实现A B互通,只能是两个pipe来实现,管道的一端关闭写,一端关闭读。
相关技术(简单解释):
协同进程:进程自己提供输入,子进程处理操作,进程最终获取结果
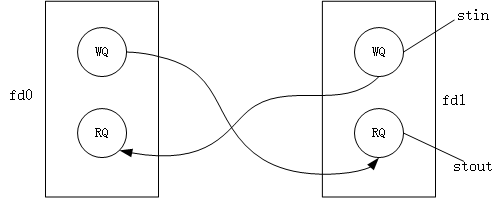
streams管道:和一般的pipe不同的是,它是一个全双工管道,其内部结构如图
fork: 执行此函数会启动两个进程,会返回两次,父进程返回子进程ID,子进程返回 0
dup:创建一个文件描述符的副本
B程序一端,实现将收到的输入字符串进行反转,写到输出
#include "sgapue.h"
#include
#include "my_err.h"
char *strrev(char *str)
{
char *p1, *p2;
if (! str || ! *str)
return str;
for (p1 = str, p2 = str + strlen(str) - 1; p2 > p1; ++p1, --p2)
{
*p1 ^= *p2;
*p2 ^= *p1;
*p1 ^= *p2;
}
return str;
}
int main(void) {
int n;
char line[MAXLINE];
while ((n = read(STDIN_FILENO, line, MAXLINE)) > 0){
line[n] = 0;
strrev(line);
n = strlen(line);
if (write(STDOUT_FILENO, line, n) != n){
err_sys("write err!!!");
}
}
exit(0);
}
两个自定义的头文件如下,my_err.h 和 sgapue.h其实就是参考的Unix高级编程:
#include
#include
static void err_doit(int, int, const char *, va_list);
/*
* Nonfatal error related to a system call.
* Print a message and return.
*/
void
err_ret(const char *fmt, ...)
{
va_list ap;
va_start(ap, fmt);
err_doit(1, errno, fmt, ap);
va_end(ap);
}
/*
* Fatal error related to a system call.
* Print a message and terminate.
*/
void
err_sys(const char *fmt, ...)
{
va_list ap;
va_start(ap, fmt);
err_doit(1, errno, fmt, ap);
va_end(ap);
exit(1);
}
/*
* Fatal error unrelated to a system call.
* Error code passed as explict parameter.
* Print a message and terminate.
*/
void
err_exit(int error, const char *fmt, ...)
{
va_list ap;
va_start(ap, fmt);
err_doit(1, error, fmt, ap);
va_end(ap);
exit(1);
}
/*
* Fatal error related to a system call.
* Print a message, dump core, and terminate.
*/
void
err_dump(const char *fmt, ...)
{
va_list ap;
va_start(ap, fmt);
err_doit(1, errno, fmt, ap);
va_end(ap);
abort(); /* dump core and terminate */
exit(1); /* shouldn't get here */
}
/*
* Nonfatal error unrelated to a system call.
* Print a message and return.
*/
void
err_msg(const char *fmt, ...)
{
va_list ap;
va_start(ap, fmt);
err_doit(0, 0, fmt, ap);
va_end(ap);
}
/*
* Fatal error unrelated to a system call.
* Print a message and terminate.
*/
void
err_quit(const char *fmt, ...)
{
va_list ap;
va_start(ap, fmt);
err_doit(0, 0, fmt, ap);
va_end(ap);
exit(1);
}
/*
* Print a message and return to caller.
* Caller specifies "errnoflag".
*/
static void
err_doit(int errnoflag, int error, const char *fmt, va_list ap)
{
char buf[MAXLINE];
vsnprintf(buf, MAXLINE, fmt, ap);
if (errnoflag)
snprintf(buf+strlen(buf), MAXLINE-strlen(buf), ": %s",
strerror(error));
strcat(buf, "\n");
fflush(stdout); /* in case stdout and stderr are the same */
fputs(buf, stderr);
fflush(NULL); /* flushes all stdio output streams */
} #ifndef _APUE_H
#define _APUE_H
#define _XOPEN_SOURCE 600 /* Single UNIX Specification, Version 3 */
#include /* some systems still require this */
#include
#include /* for winsize */
#ifndef TIOCGWINSZ
#include
#endif
#include /* for convenience */
#include /* for convenience */
#include /* for offsetof */
#include /* for convenience */
#include /* for convenience */
#include /* for SIG_ERR */
#define MAXLINE 4096 /* max line length */
/*
* Default file access permissions for new files.
*/
#define FILE_MODE (S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR | S_IRGRP | S_IROTH)
/*
* Default permissions for new directories.
*/
#define DIR_MODE (FILE_MODE | S_IXUSR | S_IXGRP | S_IXOTH)
typedef void Sigfunc(int); /* for signal handlers */
#if defined(SIG_IGN) && !defined(SIG_ERR)
#define SIG_ERR ((Sigfunc *)-1)
#endif
#define min(a, b) ((a) < (b) ? (a) : (b))
#define max(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b))
/*
* Prototypes for our own functions.
*/
char *path_alloc(int *); /* Figure 2.15 */
long open_max(void); /* Figure 2.16 */
void clr_fl(int, int); /* Figure 3.11 */
void set_fl(int, int); /* Figure 3.11 */
void pr_exit(int); /* Figure 8.5 */
void pr_mask(const char *); /* Figure 10.14 */
Sigfunc *signal_intr(int, Sigfunc *); /* Figure 10.19 */
int tty_cbreak(int); /* Figure 18.20 */
int tty_raw(int); /* Figure 18.20 */
int tty_reset(int); /* Figure 18.20 */
void tty_atexit(void); /* Figure 18.20 */
#ifdef ECHO /* only if has been included */
struct termios *tty_termios(void); /* Figure 18.20 */
#endif
void sleep_us(unsigned int); /* Exercise 14.6 */
ssize_t readn(int, void *, size_t); /* Figure 14.29 */
ssize_t writen(int, const void *, size_t); /* Figure 14.29 */
void daemonize(const char *); /* Figure 13.1 */
int s_pipe(int *); /* Figures 17.6 and 17.13 */
int recv_fd(int, ssize_t (*func)(int,
const void *, size_t));/* Figures 17.21 and 17.23 */
int send_fd(int, int); /* Figures 17.20 and 17.22 */
int send_err(int, int,
const char *); /* Figure 17.19 */
int serv_listen(const char *); /* Figures 17.10 and 17.15 */
int serv_accept(int, uid_t *); /* Figures 17.11 and 17.16 */
int cli_conn(const char *); /* Figures 17.12 and 17.17 */
int buf_args(char *, int (*func)(int,
char **)); /* Figure 17.32 */
int ptym_open(char *, int); /* Figures 19.8, 19.9, and 19.10 */
int ptys_open(char *); /* Figures 19.8, 19.9, and 19.10 */
#ifdef TIOCGWINSZ
pid_t pty_fork(int *, char *, int, const struct termios *,
const struct winsize *); /* Figure 19.11 */
#endif
int lock_reg(int, int, int, off_t, int, off_t); /* Figure 14.5 */
#define read_lock(fd, offset, whence, len) \
lock_reg((fd), F_SETLK, F_RDLCK, (offset), (whence), (len))
#define readw_lock(fd, offset, whence, len) \
lock_reg((fd), F_SETLKW, F_RDLCK, (offset), (whence), (len))
#define write_lock(fd, offset, whence, len) \
lock_reg((fd), F_SETLK, F_WRLCK, (offset), (whence), (len))
#define writew_lock(fd, offset, whence, len) \
lock_reg((fd), F_SETLKW, F_WRLCK, (offset), (whence), (len))
#define un_lock(fd, offset, whence, len) \
lock_reg((fd), F_SETLK, F_UNLCK, (offset), (whence), (len))
pid_t lock_test(int, int, off_t, int, off_t); /* Figure 14.6 */
#define is_read_lockable(fd, offset, whence, len) \
(lock_test((fd), F_RDLCK, (offset), (whence), (len)) == 0)
#define is_write_lockable(fd, offset, whence, len) \
(lock_test((fd), F_WRLCK, (offset), (whence), (len)) == 0)
void err_dump(const char *, ...); /* Appendix B */
void err_msg(const char *, ...);
void err_quit(const char *, ...);
void err_exit(int, const char *, ...);
void err_ret(const char *, ...);
void err_sys(const char *, ...);
void log_msg(const char *, ...); /* Appendix B */
void log_open(const char *, int, int);
void log_quit(const char *, ...);
void log_ret(const char *, ...);
void log_sys(const char *, ...);
void TELL_WAIT(void); /* parent/child from Section 8.9 */
void TELL_PARENT(pid_t);
void TELL_CHILD(pid_t);
void WAIT_PARENT(void);
void WAIT_CHILD(void);
#endif A端的程序:先创建两个streams管道 fd0, fd1.调用fork,根据其两次返回进行逻辑分支,子进程就进行dup绑定标准输入输出,执行execel启动B;父进程直接将stdin输入写到stdout.
#include "sgapue.h"
#include "my_err.h"
#include
#include
using namespace std;
static void sig_pipe(int);
int main(void) {
int n;
int fd[2];
pid_t pid;
char line[MAXLINE];
if (signal(SIGPIPE, sig_pipe) == SIG_ERR)
err_sys("signal error");
if (s_pipe(fd) < 0)
err_sys("pip_err");
if ((pid = fork()) < 0) {
err_sys("fork err");
} else if (pid > 0) {//parent
close(fd[1]);
while (fgets(line, MAXLINE, stdin) != NULL) {
n = strlen(line);
if (write(fd[0], line, n) != n)
err_sys("write err to pipe");
if ((n = read(fd[0], line, MAXLINE)) < 0)
err_sys("read err from pipe");
if (n == 0) {
err_msg("child close pipe");
break;
}
line[n] = 0;
if (fputs(line, stdout) == EOF)
err_sys("fputs err");
}
} else {//child
close(fd[0]);
if (fd[1] != STDIN_FILENO && dup2(fd[1], STDIN_FILENO) != STDIN_FILENO)
err_sys("dup2 err to stdin");
if (fd[1] != STDOUT_FILENO && dup2(fd[1], STDOUT_FILENO) != STDOUT_FILENO)
err_sys("dup2 err to stdout");
if (execl("./cortest", "cortest", (char *) 0) < 0)
err_sys("execl err");
}
exit(0);
}
static void sig_pipe(int signo) {
cout << "SIGPIPE caught" << endl;
exit(1);
}
int s_pipe(int fd[2]) {
return (socketpair(AF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM, 0, fd));
} 参考文献
https://linux.die.net/man/2/dup2
https://www.jianshu.com/p/4a5f71b9bf1d
《unix环境高级编程》figure.17