代码训练营Day.16 | 104. 二叉树的最大深度、111. 二叉树的最小深度、222. 完全二叉树的节点个数
104. 二叉树的最大深度
1. LeetCode链接
力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
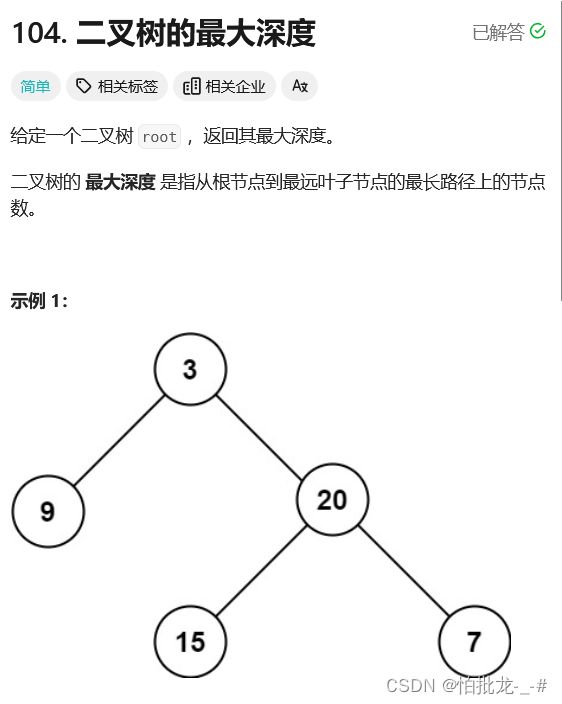
2. 题目描述
3. 想法
1. 迭代法
层序遍历时,顺便记录层数,返回最大层数。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
queue qu;
if (root == NULL) return 0;
qu.push(root);
int depth = 0;
while (!qu.empty()) {
int f_size = qu.size();
for (int i = 0; i < f_size; i++) {
TreeNode* cur = qu.front();
qu.pop();
if (cur->left != NULL) qu.push(cur->left);
if (cur->right != NULL) qu.push(cur->right);
}
depth++;
}
return depth;
}
}; 2. 递归法
有两种算最大深度的方法,一种是自顶向下depth叠加,另一种是自底向上depth叠加。但核心逻辑就是,当前树的最大深度,是其左右子树中深度最大的一个depth + 1。
自顶向下depth叠加(前序遍历把深度值传下去,返回最大深度值)(可以理解为求最大高度):
1. 参数和输出。参数:树节点和当前节点所在层的深度depth。输出:int
2. 终止条件。如果树节点为NULL,原原本本返回depth。
3. 单层递归逻辑。当前树节点不是NULL,说明在更下一层深度,depth++。返回当前节点最大子树深度。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int maxD(TreeNode* root, int depth) {
if (root == NULL) return depth;
depth++;
int left = maxD(root->left, depth);
int right = maxD(root->right, depth);
return max(left, right);
}
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return 0;
int depth = 0;
return maxD(root, depth);
}
};自底向上叠加(当前树节点最大深度,是子树最大深度+1):
1. 参数和输出。参数:某树节点。输出:int
2. 终止条件。如果当前树节点为NULL,return 0;
3. 单层递归逻辑。分别计算左子树和右子树的最大深度,并返回最大值 + 1.
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int maxD(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return 0;
int left = maxD(root->left);
int right = maxD(root->right);
return 1 + max(left, right);
}
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
return maxD(root);
}
};4. 扩展
力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
N叉树的最大深度。
这里改写自底向上递归方法。
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(Node* root) {
if (root == NULL) return 0;
if (root->children.size() == 0) return 1;
vector depth;
for (Node* x : root->children) {
depth.push_back(maxDepth(x));
}
return 1 + *max_element(depth.begin(), depth.end());
}
}; 相比于先把所有分支最大深度记录下来再找最大值的方法,不如直接一边遍历一遍找。
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(Node* root) {
if (root == NULL) return 0;
int depth = 0;
for (Node* x : root->children) {
depth = max(depth, maxDepth(x));
}
return 1 + depth;
}
};迭代法
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(Node* root) {
if (root == NULL) return 0;
int depth = 0;
queue qu;
qu.push(root);
while (!qu.empty()) {
int f_size = qu.size();
for (int i = 0; i < f_size; i++) {
Node* cur = qu.front();
qu.pop();
for (Node* x : cur->children) qu.push(x);
}
depth++;
}
return depth;
}
}; 111. 二叉树的最小深度
1. LeetCode链接
力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
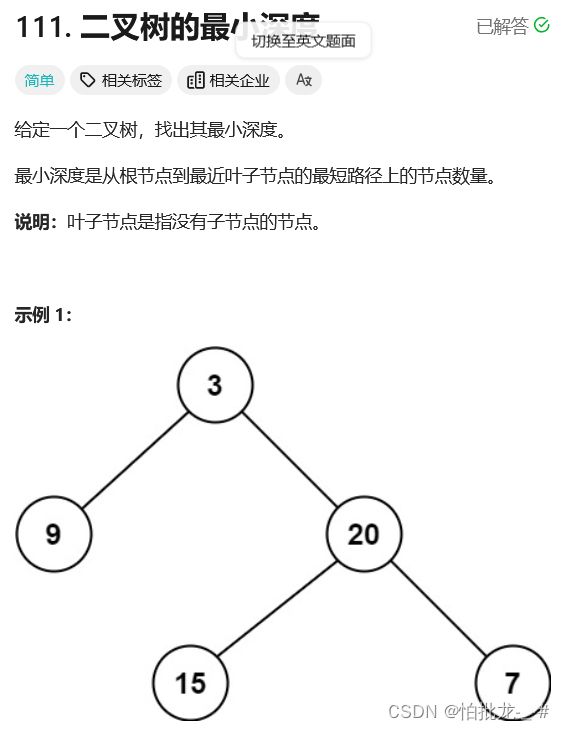
2. 题目描述
3. 解法
1. 迭代法
简单来说,层序遍历中,遇到空节点时,更新依次最小深度记录。(这就要求最小深度初值一定比树大,根据题中树节点数的范围最大100000,则depth初值可以设置为100000).
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
queue qu;
if (root == NULL) return 0;
qu.push(root);
int depth = 0;
int min = 100000;
while (!qu.empty()) {
int f_size = qu.size();
for (int i = 0; i < f_size; i++) {
TreeNode* cur = qu.front();
qu.pop();
if (cur->left != NULL) qu.push(cur->left);
if (cur->right != NULL) qu.push(cur->right);
if (cur->left == NULL && cur->right == NULL) {
if (depth + 1 < min) min = depth + 1;
}
}
depth++;
}
return min;
}
}; 其实,层序遍历第一个找到的叶节点必是最小深度时。所以,逻辑精简后:
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return 0;
int depth = 0;
queue que;
que.push(root);
while(!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
depth++; // 记录最小深度
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
if (!node->left && !node->right) { // 当左右孩子都为空的时候,说明是最低点的一层了,退出
return depth;
}
}
}
return depth;
}
};
2. 递归法
坑就坑在,深度结算在叶子节点才算有效。需要过滤,只有一个NULL节点的,就不考虑其NULL分支了。
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return 0;
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL) return 1;
int depth = 0;
if (root->left != NULL && root->right != NULL) depth = min(minDepth(root->right), minDepth(root->left));
else if (root->left == NULL) depth = minDepth(root->right);
else depth = minDepth(root->left);
return 1 + depth;
}
};自顶向下,求最小高度:
class Solution {
public:
int minD(TreeNode* root, int depth) {
if (root == NULL) return depth;
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL) return depth + 1;
if (root->left != NULL && root->right != NULL) return min(minD(root->left, depth + 1), minD(root->right, depth + 1)) ;
if (root->left == NULL) return minD(root->right, depth + 1);
return minD(root->left, depth + 1);
}
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
return minD(root, 0);
}
};另一种,result为全局变量时。这个基本思想就是前序遍历的递归法,在碰到叶子节点时再更新result。新设的函数,完全就是为了递归前序遍历。
class Solution {
public:
int result = INT_MAX;
void minD(TreeNode* root, int depth) {
if (root == NULL) {
result = 0;
return;
}
depth++;
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL) {
result = min(depth, result);
}
if (root->left) minD(root->left, depth);
if (root->right) minD(root->right, depth);
return;
}
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
minD(root, 0);
return result;
}
};222. 完全二叉树的节点个数
1. LeetCode链接
力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
2. 题目描述
3. 解法
1. 普通解法
把它当成普通二叉树,深度优先、广度优先、递归、迭代,随便用。略。
2. 完全二叉树的特性
完全二叉树有两种情况:1. 满完全二叉树。节点个数为(2 ^ depth) - 1。2. 不满。
递归法:
1. 参数和输出。参数:树节点。输出:int
2. 终止条件。如果为NULL,return 0;
3. 单层递归逻辑。判断是否为满完全二叉树,是则直接返回节点数。可以比较一直向左深入的深度和一直向右深入的深度是否相等来判断。如果不是满的,递归判断左右子树。
注意:<< 和 ^
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return 0;
int leftd = 0;
int rightd = 0;
TreeNode* left = root->left;
TreeNode* right = root->right;
while (left != NULL) {
left = left->left;
leftd++;
}
while (right != NULL) {
right = right->right;
rightd++;
}
if (leftd == rightd) return (2 << leftd) - 1;
return 1 + countNodes(root->left) + countNodes(root->right);
}
};