深入理解 Flink(三)Flink 内核基础设施源码级原理详解
Hadoop 生态各大常见组件的 RPC 技术实现
Flink RPC 网络通信框架 Akka 详解
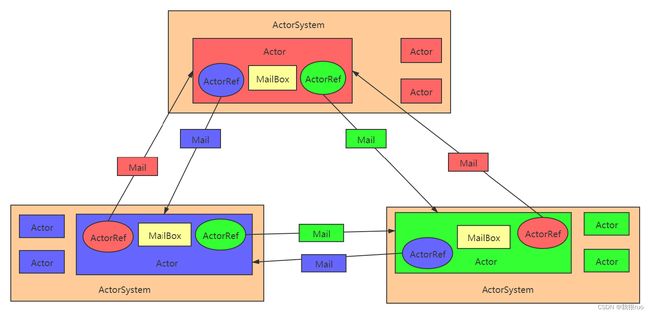
1、ActorSystem 是管理 Actor 生命周期的组件,Actor 是负责进行通信的组件。
2、每个 Actor 都有一个 MailBox,别的 Actor 发送给它的消息都首先储存在 MailBox 中,通过这种方式可以实现异步通信。
3、每个 Actor 是单线程的处理方式,不断的从 MailBox 拉取消息执行处理,所以对于 Actor 的消息处理,不适合调用阻塞方法。
4、Actor 可以改变他自身的状态,可以接收消息,也可以发送消息,还可以生成新的 Actor(谁生的谁养)。
5、每一个 ActorSystem 和 Actor 都在启动的时候会给定一个 name,如果要从 ActorSystem 中,获取一个 Actor,则通过以下的方式来进行 Actor 的获取:
akka.tcp://actorsystem_name@bigdata02:9527/user/actor_name
6、如果一个 Actor 要和另外一个 Actor 进行通信,则必须先获取对方 Actor 的 ActorRef 对象,然后通过该对象发送消息即可。
actorRef = actorSystem.actorOf("akka.tcp://actorsystem_name@bigdata02:9527/user/actor_name")
// 获取和对方 actor 进行通信的一个 actorRef 对象,类似于一个本地调用,但事实上,actorRef 和 对方actor 的通信细节被封装了。
actorRef = actorSystem.actorOf("schema://actorsystem_name@hostname:port/user/actor_name")
actorRef.getNow()
7、通过 tell 发送异步消息,不接收响应,通过 ask 发送异步消息,得到 Future 返回,通过异步回调返回处理结果。
深入理解 Flink RPC 网络通信框架
Flink RPC 采用了和 Akka 一样的一种抽象,底层是基于 Akka 来实现。Flink RPC 其实是封装了 Akka 但是上层抽象其实和 Akka 的工作机制是一样的。Flink 的 RPC 网络通信框架的底层依然使用 Akka Actor Model 模型设计实现,大致实现和 Spark RPC 差不多。
Flink 中的 RPC 实现主要在 flink-runtime 模块下的 org.apache.flink.runtime.rpc 包中,涉及到的最重要的 API 主要是以下这四个:

简单概况
1、RpcGateway 路由,RPC 的老祖宗。各种其他 RPC 服务组件,都是 RpcGateWay 的子类,类似于 Hadoop 中的通信协议 Protocol。
2、RpcEndpoint 业务逻辑载体,对应的 Actor 的封装。
3、RpcService 对应 ActorSystem 的封装,类似于 Spark 中的 RpcEnv。
4、RpcServer 为 RpcService(ActorSystem)和 RpcEndpoint(Actor)之间的粘合层
继承关系图
- TaskExecutor 集群中从节点中最重要的角色,负责资源管理。
- Dispatcher 主节点中的一个工作角色,负责 job 调度执行。
- JobMaster 应用程序中的主控程序,类似于 Spark 中的 Driver 的作用,或者 MapReduce 中的 MRAppMaster。
- ResourceManager 集群中的主节点 JobManager 中的负责资源管理的角色,和 TaskExecutor 一起构成资源管理的主从架构。
这四个组件的任何一个组件的实例对象创建成功之后,都会要调用 start() 去启动这个 RpcEndpoint,然后就会去执行他的 RpcEndpoint 的 onStart() 方法。一般来说,对应的 RpcEndpoint 组件都会重写,在这些 RpcEndpoint 组件启动的时候,一些重要的逻辑,都有可能被放在这个 onStart() 生命周期方法里。
关于 Flink Standalone 集群:
逻辑概念:JobManager + TaskManager
物理概念:ClusterEntryPoint(ResourceManager) + TaskManagerRunner(TaskExecutor)
主节点 ClusterEntryPoint 的内部其实有四种重要的组件:
- ResourceManager
- Dispatcher
- RestServer
- JobMaster
例如,在 TaskExecutor 的内部,持有 ResourceManager 的一个 Gateway 对象,当 TaskExecutor 需要给 ResourceManager 的时候,就通过 ResourceManagerGateWay 给 ResourceManager 发送消息。
Flink RpcEndpoint
JobManager 的 ResourceManager
ResourceManager 的职责就是帮助 主节点 JobManager 完成从节点 TaskManager 的管理和资源的管理和分配等工作。

TaskManager 的 TaskExecutor
Flink Standalone 集群是一个主从架构,主节点叫做 JobManager,从节点叫做 TaskManager。

这个 TaskExecutor 是存在于 TaskManager 的内部,真正完成资源提供和分配,接收任务和执行等相关工作。这个角色的意义更等同于 Spark 中的 Worker, YARN 集群中的 NodeManager。
Flink 核心工作组件整体架构抽象
Flink on YARN 的三种运行模式
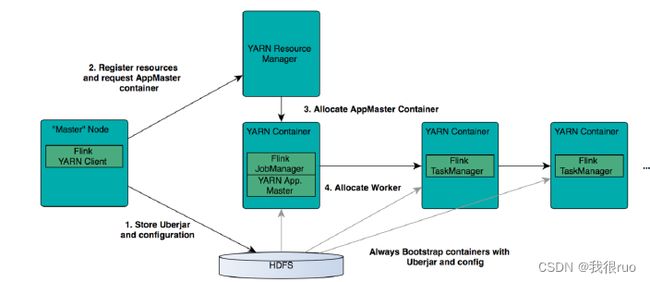
Flink 通过 YARN 的接口实现了自己的 ApplicationMaster。当在 YARN 中部署了Flink,YARN 就会用自己的 Container 来启动 Flink 的 JobManager(也就是 ApplicationMaster)和 TaskManager。
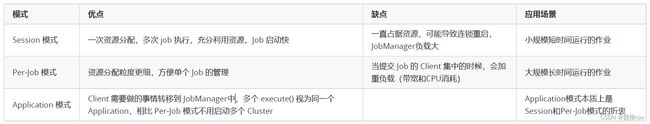
- Session 模式:在 YARN 中初始化一个 Flink 集群,开辟指定的资源,之后我们提交的 Flink Job 都在这个 Flink yarn-session 中,也就是说不管提交多少个 job,这些 job 都会共用开始时在 YARN 中申请的资源。这个 Flink 集群会常驻在 YARN 集群中,除非手动停止。
- Per-Job 模式:在 YARN 中,每次提交 job 都会创建一个新的 Flink 集群,任务之间相互独立,互不影响并且方便管理。任务执行完成之后创建的集群也会消失。 所以每个 Job 执行完毕,Flink 集群关闭,释放资源。
- Application 模式:Flink-1.11 引入,Client 需要做的事情(main 方法的执行)转移到 JobManager中,多个 env.execute() 视为同一个 Application,相比 Per-Job 模式不用启动多个 Cluster。
./bin/flink run --target yarn-session # Submission to an already running Flink on YARN cluster
./bin/flink run --target yarn-per-job # Submission spinning up a Flink on YARN cluster in Per-Job Mode
./bin/flink run-application --target yarn-application # Submission spinning up Flink YARN cluster in Application Mode
具体可以参考官网:
https://ci.apache.org/projects/flink/flink-docs-stable/deployment/cli.html
https://ci.apache.org/projects/flink/flink-docs-stable/deployment/cli.html#advanced-cli
https://ci.apache.org/projects/flink/flink-docs-stable/deployment/resource-providers/yarn.html
Flink On YARN 不同的模式,其实入口是不一样的,总的来说是:ClusterEntryPoint,ClusterEntryPoint 是 Flink 集群模式的入口基类,它的实现类结构如下:

注意:1.14 版本之后,Mesos 的支持已经被移除。(Mesos 背后的商业化公司 Mesosphere 于 2023 年破产倒闭)
YARN 模式 和 Standalone 模式最大的区别就是:
- Standalone 模式,已经提前把 ClusterEntrypoint 和 TaskManagerRunner 启动好了。集群的资源总量是固定的。
- Flink On YARN 模式中,在 YARN 集群中,申请到一个 Container 用来启动一个 SessionClusterEntrypoint,然后动态申请足够数量的 Container 来启动 TaskManagerRunner 来运行 Task。
Flink 高可用服务 HighAvailabilityServices

在 Flink 的内部,需要保证高可用服务的有:ResourceManager,Dispatcher,JobManager,WebMonitorEndpoint 四大组件。
ZooKeeperHaServices 内部最重要的两个方法:
public class ZooKeeperHaServices extends AbstractHaServices {
@Override
protected LeaderElectionService createLeaderElectionService(String leaderName) {
// 创建选举服务
return ZooKeeperUtils.createLeaderElectionService(client, configuration, leaderName);
}
@Override
protected LeaderRetrievalService createLeaderRetrievalService(String leaderName) {
// 创建监听服务
return ZooKeeperUtils.createLeaderRetrievalService(client, configuration, leaderName);
}
}
其次重要的三个方法:
public class ZooKeeperHaServices extends AbstractHaServices {
@Override
public CheckpointRecoveryFactory createCheckpointRecoveryFactory() {
// TODO_MA 注释:
return new ZooKeeperCheckpointRecoveryFactory(client, configuration, ioExecutor);
}
@Override
public JobGraphStore createJobGraphStore() throws Exception {
// TODO_MA 注释:JobGraphStore + ExecutionGraphStore
return ZooKeeperUtils.createJobGraphs(client, configuration);
}
@Override
public RunningJobsRegistry createRunningJobsRegistry() {
// TODO_MA 注释:
return new ZooKeeperRunningJobsRegistry(client, configuration);
}
}
Flink 选举服务 LeaderElectionService 和监听 LeaderRetrievalService 机制
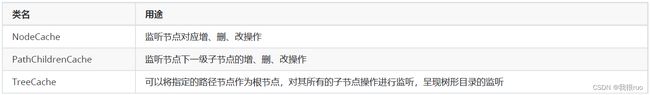
- LeaderElectionService : 用来做选举的服务,基于 ZK 实现,真正实现类的名字叫做: DefaultLeaderElectioinService。它的内部通过一个 选举驱动器 LeaderElectionDriver 来完成。LeaderElectionDriver 的内部其实通过 curator 框架提供的一个选举组件:LeaderLatch 来负责进行选举。
- Flink 的选举和监听机制,都是依托于 Curator 框架的 API 进行封装提供了的实现,具体涉及到的实现类包括:LeaderContender(用于竞选)和 LeaderElectionService(选举服务)和 LeaderRetrievalService(监听服务)。
- Curator 对应的监听 API
LeaderElectionService 接口定义
public interface LeaderElectionService {
// 启动选举,启动方法将竞争者作为参数
void start(LeaderContender contender) throws Exception;
// 停止
void stop() throws Exception;
// 确认
void confirmLeadership(UUID leaderSessionID, String leaderAddress);
// 判断是否拥有指定 session 下的 leadership
boolean hasLeadership(@Nonnull UUID leaderSessionId);
}
LeaderContender 是 LeaderElectionService 中的参与选举的竞选者。它有四种实现(1.14):

也即前文中提到的需要保证高可用服务:ResourceManager,Dispatcher,JobManager,WebMonitorEndpoint 四大组件。这四个组件中组合了 LeaderElectionService,同时 LeaderElectionService 也组合了 LeaderContender(你中有我,我中有你)。
LeaderElectionService 选举实现
LeaderElectionService 实现了 LeaderElectionEventHandler 接口的两个方法:onGrantLeadership、onRevokeLeadership。
LeaderElectionService 调用 leaderElectionService.start(this) 开始执行选举,最终通过 ZooKeeperLeaderElectionDriver 实现选举;
ZooKeeperLeaderElectionDriver 实现了 LeaderLatchListener 接口的 isLeader、notLeader 方法,监听到 zookeeper 的对应事件后触发。
isLeader、notLeader 方法的内部,其实是调用 LeaderElectionService 实现的 LeaderElectionEventHandler 接口的两个方法:onGrantLeadership、onRevokeLeadership;
而上述两个方法最终会调用 LeaderContender 的 grantLeadership、revokeLeadership 方法。
// LeaderLatch 基于分布式锁实现的一个选举类
// NodeCache 监听类
public ZooKeeperLeaderElectionDriver(....){
// 当 当前组件 选举成功,则回调 this 的 isLeader() 方法
// 当 当前组件 没有选举成功,则回到 this 的 notLeader() 方法
leaderLatch = new LeaderLatch(client, checkNotNull(latchPath));
leaderLatch.addListener(this);
leaderLatch.start();
// 当监听响应,则会回调 this 的 nodeChanged() 方法
cache = new NodeCache(client, leaderPath);
cache.getListenable().addListener(this);
cache.start();
}
LeaderRetrievalService 接口定义
public interface LeaderRetrievalService {
// 开启监听
void start(LeaderRetrievalListener listener) throws Exception;
// 结束监听
void stop() throws Exception;
}
public interface LeaderRetrievalListener {
// 监听回调
void notifyLeaderAddress(@Nullable String leaderAddress, @Nullable UUID leaderSessionID);
void handleError(Exception exception);
}
LeaderRetrievalService 实现了 LeaderRetrievalEventHandler 接口的 notifyLeaderAddress 方法。
LeaderRetrievalService 通过 start(LeaderRetrievalListener) 方法开启监听,最终通过 ZookeeperLeaderRetrievalDriver 实现监听响应。
当发生事件响应的时候,会执行 ZookeeperLeaderRetrievalDriver 的 handleStateChange 方法;最终会在 LeaderRetrievalService 的 notifyLeaderAddress 方法中调用 LeaderRetrievalListener 的同名方法 notifyLeaderAddress。
LeaderRetrievalListener 的实现类:

小结
上述过程应用到了:监听者模式(观察者模式) + 模板方法模式
Flink 文件/大对象服务 BlobService

在 Flink 框架中,Flink 提供了一个 BlobService 专门用来提供大文件、对象服务。通俗的说,就是一个文件服务器。存储方式在逻辑上,就是一个 Map,作用是为了集中分发;key 就是 BlobKey,value 就是一个文件。BlobService 接口的定义:
public interface BlobService extends Closeable {
PermanentBlobService getPermanentBlobService();
TransientBlobService getTransientBlobService();
int getPort();
}
BlobService 有两个实现类:
![]()
其中 BlobServer 最为重要,BlobServer 的实现如下:
public class BlobServer extends Thread implements BlobService, BlobWriter, PermanentBlobService, TransientBlobService {
// TODO_MA 注释: BlobServer 的内部,启动了一个 BIO 的服务端。用来给 BlobClient 提供服务
private final ServerSocket serverSocket;
// TODO_MA 注释: 提供存储服务
private final BlobStore blobStore;
// TODO_MA 注释: Active BlobServerConnection 链接集合
private final Set activeConnections = new HashSet<>();
// TODO_MA 注释: 最大链接数,默认 50,可以通过 blob.fetch.num-concurrent 参数进行修改或者配置
private final int maxConnections;
// TODO_MA 注释: 定时清理任务相关
private final ConcurrentHashMap, Long> blobExpiryTimes = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final long cleanupInterval;
private final Timer cleanupTimer;
// TODO_MA 注释: 构造方法,详细见代码注释
public BlobServer(Configuration config, BlobStore blobStore) throws IOException {
// 见代码注释,主要是初始化一些成员变量和一些参数,然后启动一个定时任务,启动一个BIO服务端
}
// TODO_MA 注释: BlobServer 本身是一个线程
public void run() {
while(!this.shutdownRequested.get()) {
// BlobServer 每接收到一个客户端的链接,就使用一个 线程来专门提供服务
BlobServerConnection conn = new BlobServerConnection(serverSocket.accept(), this);
// BlobServerConnection 是一个线程,线程启动
conn.start();
}
}
}
Flink 提供了 BlobServer 用来提供文件服务,当然也提供了一个 BlobClient 用来提交请求。这是一个典型的 C/S 架构。BlobClient 的内部,封装了一个 BIO 客户端。在 BlobServer 中,由一个 BlobServerConnection 专门给一个 BlobClient 提供服务。
BlobServerConnection 的结构:
class BlobServerConnection extends Thread {
private final Socket clientSocket;
private final BlobServer blobServer;
public void run() {
final InputStream inputStream = this.clientSocket.getInputStream();
final OutputStream outputStream = this.clientSocket.getOutputStream();
switch(operation) {
// 存 文件
case PUT_OPERATION:
put(inputStream, outputStream, new byte[BUFFER_SIZE]);
break;
// 取 文件
case GET_OPERATION:
get(inputStream, outputStream, new byte[BUFFER_SIZE]);
break;
default:
throw new IOException("Unknown operation " + operation);
}
}
// 存文件实现,具体工作机制,看源代码注释
private void put(InputStream inputStream, OutputStream outputStream, byte[] buf) throws IOException {}
// 取文件实心,具体工作机制,看源代码注释
private void get(InputStream inputStream, OutputStream outputStream, byte[] buf) throws IOException {}
}
BlobClient 的结构:
// 客户端
public final class BlobClient implements Closeable {
// Socket 客户端
private final Socket socket;
// 构造方法
public BlobClient(InetSocketAddress serverAddress, Configuration clientConfig) throws IOException {
Socket socket = new Socket();
socket.connect();
}
// 文件上传服务
public PermanentBlobKey uploadFile(JobID jobId, Path file) throws IOException {}
public static List uploadFiles(InetSocketAddress serverAddress, Configuration clientConfig, JobID
jobId,
List files) throws IOException {}
// 文件下载服务
static void downloadFromBlobServer(@Nullable JobID jobId, BlobKey blobKey, File localJarFile, InetSocketAddress
serverAddress, Configuration blobClientConfig, int numFetchRetries) throws IOException {}
}