汽车价格预测回归分析模型
内容简介:
本文使用python的sklearn库对汽车历史价格信息进行回归分析,包括数据预处理、特征相关性分析等步骤,最后利用lasso回归建立价格预测模型。
数据集简介
数据中有分类变量也有连续变量,主要包括3类指标:
1. 汽车的各种特性.
2. 保险风险评级:(-3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3).
3. 每辆保险车辆年平均相对损失支付.
类别属性
- make: 汽车的商标(奥迪,宝马。。。)
- fuel-type: 汽油还是天然气
- aspiration: 涡轮
- num-of-doors: 两门还是四门
- body-style: 硬顶车、轿车、掀背车、敞篷车
- drive-wheels: 驱动轮
- engine-location: 发动机位置
- engine-type: 发动机类型
- num-of-cylinders: 几个气缸
- fuel-system: 燃油系统
连续指标
- bore: continuous from 2.54 to 3.94.
- stroke: continuous from 2.07 to 4.17.
- compression-ratio: continuous from 7 to 23.
- horsepower: continuous from 48 to 288.
- peak-rpm: continuous from 4150 to 6600.
- city-mpg: continuous from 13 to 49.
- highway-mpg: continuous from 16 to 54.
- price: continuous from 5118 to 45400.
一、数据读取与分析
# loading packages
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from pandas import datetime
# data visualization and missing values
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns # advanced vizs
import missingno as msno # missing values 对缺失值进行可视化展示
%matplotlib inline
# stats
from statsmodels.distributions.empirical_distribution import ECDF
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, r2_score
# machine learning
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.linear_model import Lasso, LassoCV
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, cross_val_score
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
seed = 123
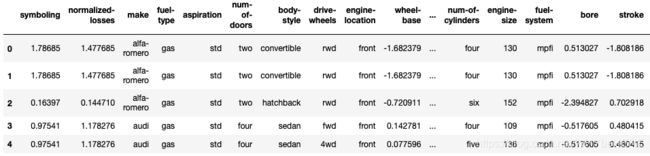
# importing data ( ? = missing values)
data = pd.read_csv("Auto-Data.csv", na_values = '?')
# 查看数据信息
data.columns #查看每列列名
data.dtypes #查看字符类型
data.shape #查看数据有几行几列
data.head(5) #查看前面5行内容
-
数据集一共有, 26个特征,205行数据
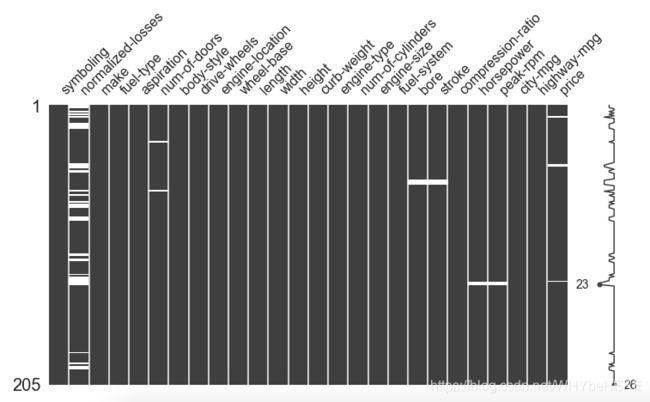
二、缺失值处理 (missingno缺失值可视化)
sns.set(style = "ticks") #指定风格
msno.matrix(data) #画图
- 空白的地方表示存在缺失值,这里一共有7个特征数据包含缺失值,其中normalized-losses 缺失比较严重。
sns.set(style = "ticks")
plt.figure(figsize = (12, 5))
c = '#366DE8'
# ECDF
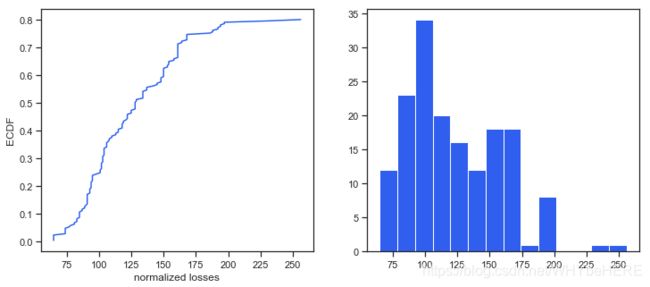
plt.subplot(121)
cdf = ECDF(data['normalized-losses']) #查看连续分布,累计结果
plt.plot(cdf.x, cdf.y, label = "statmodels", color = c);
plt.xlabel('normalized losses'); plt.ylabel('ECDF');
# overall distribution
plt.subplot(122)
plt.hist(data['normalized-losses'].dropna(),
bins = int(np.sqrt(len(data['normalized-losses']))),
color = c);
- 通过查看缺失值具体情况,可以发现 80% 的 normalized losses 是低于200 并且绝大多数低于125。
- 这种情况下,如果直接用中位数或者平均数来填充缺失值可能不够精确。因此,可以考虑这个特征与那些因素有关系。
接下来,根据不同的风险等级来划分组,在使用每组的平均数来填充normalized losses的缺失值。
#查看每组的情况
data.groupby('symboling')['normalized-losses'].describe()
#删除和填充缺失值
data = data.dropna(subset = ['price', 'bore', 'stroke', 'peak-rpm', 'horsepower', 'num-of-doors']) #对于缺失值少的几列,直接删掉缺失值
data['normalized-losses'] = data.groupby('symboling')['normalized-losses'].transform(lambda x: x.fillna(x.mean())) #填充缺失值
#查看结果
print('In total:', data.shape)
data.head()
- 缺失值处理之后,数据变成了193*26的数据集。
三、特征相关性
4.1 相关性计算和展示
cormatrix = data.corr()
# cormatrix #查看结果
#不同的展现格式
cormatrix *= np.tri(*cormatrix.values.shape, k=-1).T #返回函数的上三角矩阵,把对角线上的置0,让他们不是最高的。
cormatrix = cormatrix.stack() #某一指标与其他指标的关系
# 找出前十个最相关的特征
cormatrix = cormatrix.reindex(cormatrix.abs().sort_values(ascending=False).index).reset_index()
cormatrix.columns = ["FirstVariable", "SecondVariable", "Correlation"]
cormatrix.head(10)
- 第一行中,
city_mpg和highway-mpg两个特征的相关性高达0.97,需要删除掉其中一个。 - 对于数据中长宽高,他们应该存在某种配对关系,可以让这几个特征组合成一个新特征。
data['volume'] = data.length * data.width * data.height
data.drop(['width', 'length', 'height',
'curb-weight', 'city-mpg'],
axis = 1, # 1 for columns
inplace = True)
4.2 热度图展示
# Compute the correlation matrix
corr_all = data.corr()
# Generate a mask for the upper triangle
mask = np.zeros_like(corr_all, dtype = np.bool)
mask[np.triu_indices_from(mask)] = True
# Set up the matplotlib figure
f, ax = plt.subplots(figsize = (11, 9))
# Draw the heatmap with the mask and correct aspect ratio
sns.heatmap(corr_all, mask = mask,
square = True, linewidths = .5, ax = ax, cmap = "BuPu")
plt.show()
- 看起来 price 跟这几个的相关程度比较大 wheel-base,enginine-size, bore,horsepower.
-也可以用seaborn展示具体的指标情况sns.pairplot(data, hue = 'fuel-type', palette = 'plasma')
4.3 进一步回归分析
从上面热力图中,得出价格price和另外几个变量之间相关性很大。因此,接下来使用IMplot 进一步查看两个因素之间的关系。 lmplot对所选数据集进行了一元线性回归,拟合出了一条最佳的直线。
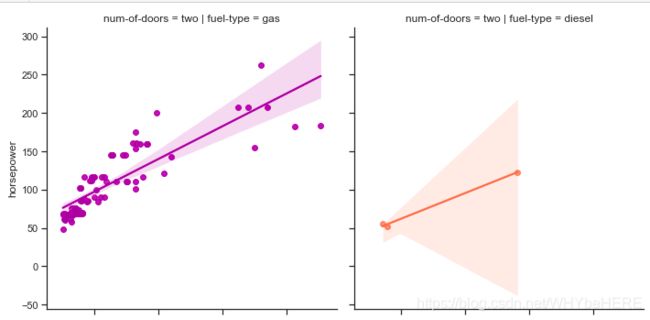
print('fuel_type:', data['fuel-type'].unique(), '\ndoors:', data['num-of-doors'].unique())
- fuel_type 和doors 是两个分类变量,可根据两个变量分组进行分析。
sns.lmplot('price', 'horsepower', data,
hue = 'fuel-type', col = 'fuel-type', row = 'num-of-doors',
palette = 'plasma',
fit_reg = True);
- 根据燃料的类型和门的数量的不同,划分成4组,即4个图。我们看到,无论是那种组合下,一辆汽车马力与价格都是正相关。。
四、数据预处理
4.1 标准化
对连续值进行标准化。
# target and features
target = data.price
regressors = [x for x in data.columns if x not in ['price']]
features = data.loc[:, regressors]
num = ['symboling', 'normalized-losses', 'volume', 'horsepower', 'wheel-base',
'bore', 'stroke','compression-ratio', 'peak-rpm']
# scale the data
standard_scaler = StandardScaler()
features[num] = standard_scaler.fit_transform(features[num])
# glimpse
features.head()
4.2 独热编码
对分类属性就行one-hot编码。
# categorical vars
classes = ['make', 'fuel-type', 'aspiration', 'num-of-doors',
'body-style', 'drive-wheels', 'engine-location',
'engine-type', 'num-of-cylinders', 'fuel-system']
# create new dataset with only continios vars
dummies = pd.get_dummies(features[classes])
features = features.join(dummies).drop(classes,
axis = 1)
# new dataset
print('In total:', features.shape)
features.head()
五、模型建立:Lasso回归
5.1 划分数据集
# 按照30%划分数据集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(features, target,
test_size = 0.3,
random_state = seed)
print("Train", X_train.shape, "and test", X_test.shape)
![]()
-将数据集分成135的训练集和58的测试集。
5.2 Lasso回归
基于线性回归的基础上,多加了一个绝对值想来惩罚过大的系数。
# logarithmic scale: log base 2
# high values to zero-out more variables
alphas = 2. ** np.arange(2, 12) #指定alphas的范围
scores = np.empty_like(alphas)
for i, a in enumerate(alphas):
lasso = Lasso(random_state = seed)
lasso.set_params(alpha = a)
lasso.fit(X_train, y_train)
scores[i] = lasso.score(X_test, y_test)
# 交叉验证cross validation
lassocv = LassoCV(cv = 10, random_state = seed)
lassocv.fit(features, target)
lassocv_score = lassocv.score(features, target)
lassocv_alpha = lassocv.alpha_
plt.figure(figsize = (10, 4))
plt.plot(alphas, scores, '-ko')
plt.axhline(lassocv_score, color = c)
plt.xlabel(r'$\alpha$')
plt.ylabel('CV Score')
plt.xscale('log', basex = 2)
sns.despine(offset = 15)
print('CV results:', lassocv_score, lassocv_alpha)
5.3 特征重要性分析
# lassocv coefficients
coefs = pd.Series(lassocv.coef_, index = features.columns)
# prints out the number of picked/eliminated features
print("Lasso picked " + str(sum(coefs != 0)) + " features and eliminated the other " + \
str(sum(coefs == 0)) + " features.")
# 展示前5个和后5个
coefs = pd.concat([coefs.sort_values().head(5), coefs.sort_values().tail(5)])
plt.figure(figsize = (10, 4))
coefs.plot(kind = "barh", color = c)
plt.title("Coefficients in the Lasso Model")
plt.show()
# 将 上面计算出来的Alphas 代入
model_l1 = LassoCV(alphas = alphas, cv = 10, random_state = seed).fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred_l1 = model_l1.predict(X_test)
model_l1.score(X_test, y_test)
![]()
5.4 结果评估
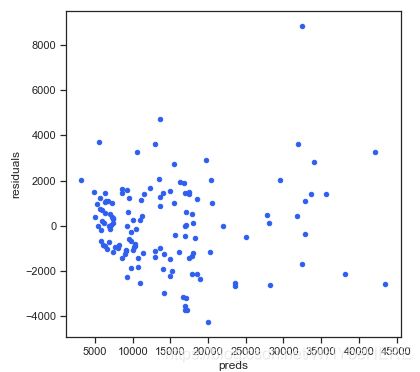
5.4.1 residual plot 残差图
画图表示实际值和预测值之间的差异。
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (6.0, 6.0)
preds = pd.DataFrame({"preds": model_l1.predict(X_train), "true": y_train})
preds["residuals"] = preds["true"] - preds["preds"]
preds.plot(x = "preds", y = "residuals", kind = "scatter", color = c)
5.4.2 MSE和R2
#计算指标:MSE和R2
def MSE(y_true,y_pred):
mse = mean_squared_error(y_true, y_pred)
print('MSE: %2.3f' % mse)
return mse
def R2(y_true,y_pred):
r2 = r2_score(y_true, y_pred)
print('R2: %2.3f' % r2)
return r2
MSE(y_test, y_pred_l1); R2(y_test, y_pred_l1);
5.4.3 查看具体实际值和预测值
#结果预测
# predictions
d = {'true' : list(y_test),
'predicted' : pd.Series(y_pred_l1)
}
pd.DataFrame(d).head()
资料链接:https://edu.csdn.net/learn/7380/149737
missingno:https://github.com/ResidentMario/missingno