红黑树理论详解与Java实现
文章目录
- 基本定义
- 五大性质
- 红黑树和2-3-4树的关系
- 红黑树和2-3-4树各结点对应关系
- 添加结点到红黑树
-
- 注意事项
- 添加的所有情况
- 添加导致不平衡
-
- 叔父节点不是红色节点(祖父节点为红色)
-
- 添加不平衡LL/RR
- 添加不平衡LR/RL
- 叔父节点是红色节点(祖父节点为黑色)
- 删除
-
- 删除红色节点
- 删除黑色节点
-
- 删除黑色叶子节点——情况一
- 删除黑色叶子节点——情况二
- 删除黑色叶子节点——情况三
- 删除黑色叶子节点——情况四
- 红黑树与AVL(平衡二叉树)树比较
- 红黑树与B树B+树比较
- 完整的Java测试代码
-
- RedBlackTree
- BinaryTreeInfo
- BinaryTrees
- InorderPrinter
- LevelOrderPrinter
- Printer
- Strings
- 总结
基本定义
红黑树是一颗二叉搜索树,它在每个结点上增加了一个存储位来表示结点的颜色,可以是红色或者黑色。
通过对任何一条从根到叶子的简单路径上各个结点的颜色进行约束,红黑树确保没有一条路径会比其他路径长出2倍,因而是近似平衡的。
五大性质
1、结点必须是红色或者黑色。
2、根节点是黑色。
3、叶子结点(外部结点、空结点,不是传统上认为的那种叶子结点,如图中的那些NIL结点)都是黑色
4、红色结点的子结点都是黑色
于是有推论:
4.1、红色结点的父结点都是黑色
4.2、从根结点到叶子结点的所有路径上不能有两个连续的红色结点
5、从任一结点到叶子结点(外部结点、空结点,不是传统上认为的那种叶子结点,如图中的那些NIL结点)的所有路径都包含相同数目的黑色结点
如图所示:
红黑树和2-3-4树的关系

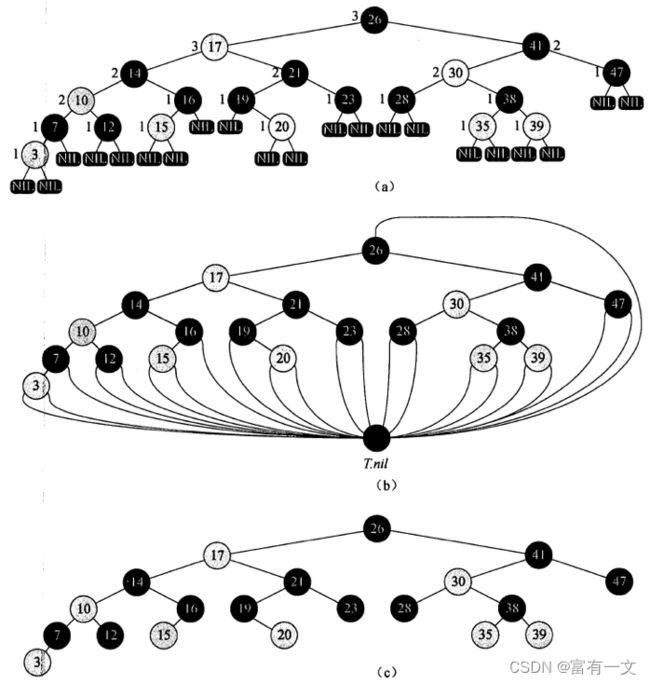
红黑树和4阶B树(2-3-4树)具有等价性
黑色节点与它的红色子节点融合在一起,形成一个B树节点
红黑树的黑色节点个数与4阶B树的节点总个数相等
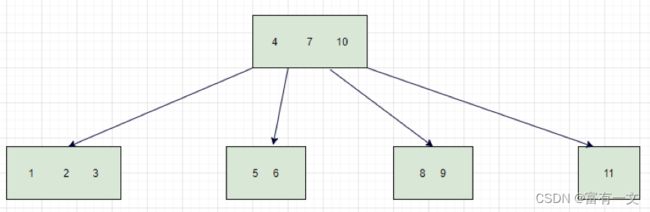
红黑树和2-3-4树各结点对应关系
添加结点到红黑树
注意事项
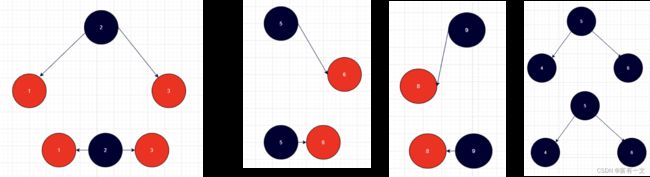
一般新添加的节点默认为红色,这样对红黑树的性质影响最小(性质1、2、3、5都满足,性质4不一定)
如果新添加的节点是根节点,染成黑色即可
添加的所有情况
添加结点到红黑树总共有12中情况;
有4种情况满足红黑树的性质,父节点为黑色节点,因此不需要做任何处理。如下图所示的4种紫红色节点添加情况
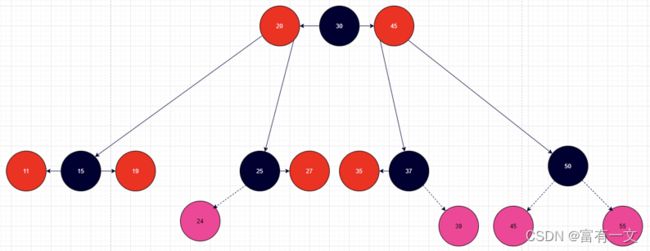
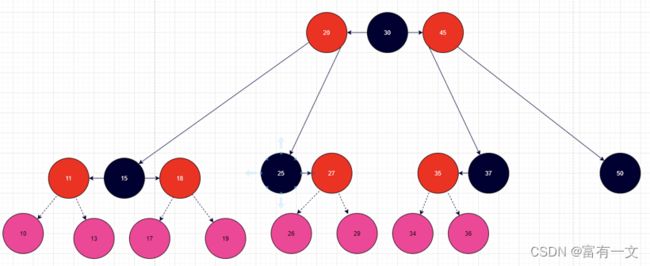
有8种情况不满足红黑树的性质,父节点为红色节点(但其实可以归纳为3种情况)。如下图所示的8种紫红色节点添加情况。
添加导致不平衡
添加结点导致红黑树出现不平衡的情况。
叔父节点不是红色节点(祖父节点为红色)
添加不平衡LL/RR
判断条件:叔父节点不是红色节点
父节点是祖父节点的左孩子,自己是父节点的左孩子(LL)
父节点是祖父节点的右孩子,自己是父节点的右孩子(RR)
如何恢复平衡:
1、父节点染成黑色,祖父节点染成红色
2、对祖父节点进行旋转操作(LL是右旋,RR是左旋)
添加不平衡LR/RL
判断条件:叔父节点不是红色节点
父节点是祖父节点的左孩子,自己是父节点的右孩子(LR)
父节点是祖父节点的右孩子,自己是父节点的左孩子(RL)
如何恢复平衡:
1、把自己染成黑色,祖父节点染成红色
2、进行两次旋转,第一次旋转是转换成LL/RR情况,第二次旋转恢复平衡
2.1、LR:先按照父节点左旋,变成LL,再按照祖父节点右旋
2.2、RL:先按照父节点右旋,变成RR,再按照祖父节点左旋

叔父节点是红色节点(祖父节点为黑色)
判断条件:叔父节点为红色
如何恢复平衡:
1、父节点、叔父节点都染成黑色
2、祖父节点染成红色,并把祖父节点当成新添加的节点,继续处理
2.1、如果祖父节点染成红色没有引起双红现象,则处理结束
2.2、如果祖父节点染成红色也导致双红现象,则继续按照是LL/RR,LR/RL,还是叔父节点为红色的三种情况处理,最差情况是处理直到根节点,把根节点染成了红色,这个时候只需要把根节点染成黑色即可。

删除
B树中,最后真正被删除的元素都在叶子节点中。详细见B树(B-tree、B-树)理论详解
删除红色节点
直接删除,无需任何调整
删除黑色节点
有3种情况
1、拥有两个红色子节点的黑色节点不可能直接被删除,因为会找它的红色子节点替代删除,因此这种情况无需考虑
2、拥有1个红色子节点的黑色节点 (删除黑色节点后,把替代的红色子节点染成黑色即可)
3、黑色叶子节点 (情况比较复杂)
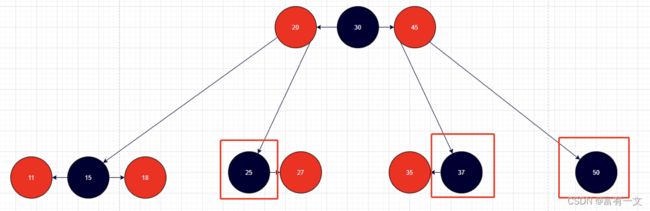
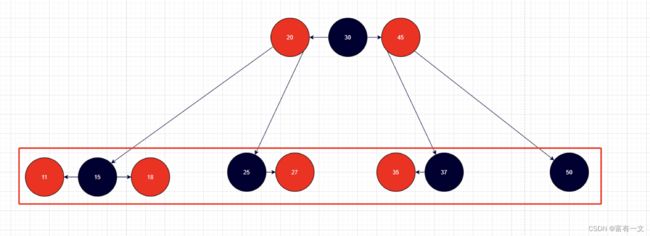
删除黑色叶子节点——情况一
如果兄弟节点是红色节点,
1、把兄弟节点染成黑色,父节点染成红色,对父节点进行旋转2、此时兄弟节点变成黑色,可以继续按照情况2,3,4进行处理
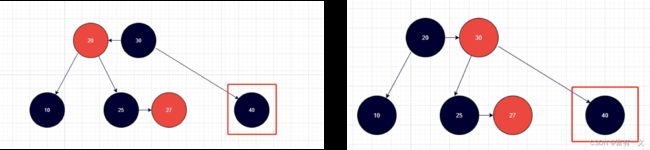
如图所示,40结点的兄弟结点是20,父结点是30。
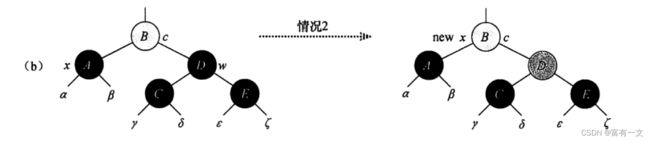
删除黑色叶子节点——情况二
黑色兄弟节点没有一个红色子节点,
1、如果父节点是红色,把兄弟节点染成红色,父节点染成黑色,完成平衡维护。
2、如果父节点是黑色,把兄弟节点染成红色,把父节点当成待删除的节点,向上递归或循环处理(依然有情况1,2,3,4)。
删除黑色叶子节点——情况三
兄弟节点是左节点,黑色兄弟节点的左孩子是黑色节点,为LR场景,需要先转变为LL,方便后面的平衡旋转。
1、把兄弟节点的右孩子设为黑色,兄弟节点设为红色,对兄弟节点进行左旋,确保兄弟节点有一个红色左孩子,此时变成情况4。

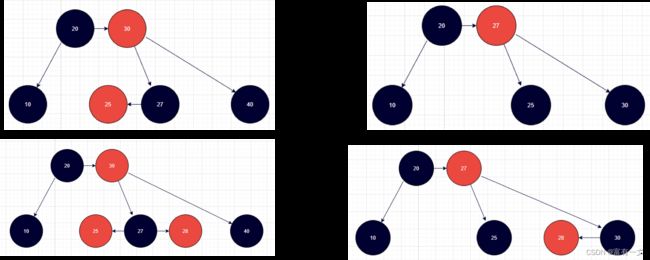
删除黑色叶子节点——情况四
兄弟节点是左节点,兄弟节点的左孩子是红色节点,LL场景,
1、把兄弟节点的颜色设置为父节点的颜色,父节点和兄弟节点的左孩子都设置为黑色,
对父节点进行右旋,恢复平衡。
红黑树与AVL(平衡二叉树)树比较
AVL树的平衡标准比较严格:每个左右子树的高度差不超过1。
红黑树的平衡标准比较宽松:没有一条路径会大于其他路径的两倍。
相对于AVL树来说,红黑树牺牲了部分平衡性以换取插入/删除操作时少量的旋转操作,总体性能要优于 AVL树。
红黑树的平均统计性能优于AVL树,实际应用中更多选择使用红黑树。
红黑树与B树B+树比较
红黑树的分叉少,适合在内存中使用,如果在硬盘中使用的话,当数据量大的时候,红黑树的层高比较高,会带来比较多的磁盘IO,影响查询性能,比如说100万的数据量,用红黑树的话,大概是20层的层高,会有20次磁盘IO。
B树和B+树的分叉比较多,B树分叉一般能到两三百,B+树分叉多的能到上千,所以B树和B+树适合磁盘存储,100万的数据量,一般3层树高即可搞定,只有3次磁盘IO,实际中数据库一般把根节点存放在内存中,所以其实只有两次IO。
完整的Java测试代码
RedBlackTree
package redblacktree;
public class RedBlackTree implements BinaryTreeInfo {
//红黑直接用布尔变量定义
private static final boolean RED = false;
private static final boolean BLACK = true;
//初始化一个唯一的叶结点
private final RBNode nil = new RBNode();
//根结点初始化为nil
private RBNode root = nil;
public RBNode getRoot() {
return root;
}
public void setRoot(RBNode root) {
this.root = root;
}
public RedBlackTree() {
this.root = nil;
}
public RedBlackTree(RBNode root) {
this.root = root;
}
//前序遍历二叉树
public void preorderTreeWalk(RBNode x) {
if(x != nil) {
System.out.print(x.key + " ");
preorderTreeWalk(x.left);
preorderTreeWalk(x.right);
}
}
//中序遍历二叉树
public void inorderTreeWalk(RBNode x) {
if(x != nil) {
inorderTreeWalk(x.left);
System.out.print(x.key + " ");
inorderTreeWalk(x.right);
}
}
//后序遍历二叉树
public void postorderTreeWalk(RBNode x) {
if(x != nil) {
postorderTreeWalk(x.left);
postorderTreeWalk(x.right);
System.out.print(x.key + " ");
}
}
//在二叉搜索树中查询某个值,递归版本
public RBNode treeSearch(RBNode x, Integer k) {
if(x == nil || k == x.key) {
return x;
}
if(k < x.key) {
return treeSearch(x.left, k);
} else {
return treeSearch(x.right, k);
}
}
//在二叉搜索树中查询某个值,循环版本
public RBNode iterativeTreeSearch(RBNode x, Integer k) {
while(x != nil && k != x.key) {
if(k < x.key) {
x = x.left;
} else {
x = x.right;
}
}
return x;
}
//在二叉搜索树中查找包含最小值的节点
public RBNode treeMinimum(RBNode x) {
while (x.left != nil) {
x = x.left;
}
return x;
}
//在二叉搜索树中查找包含最大值的节点
public RBNode treeMaximum(RBNode x) {
while (x.right != nil) {
x = x.right;
}
return x;
}
//查找节点x的后继节点
public RBNode treeSuccessor(RBNode x) {
if(x.right != nil) { //x的右子树不为空,找右子树的最小值
return treeMinimum(x.right);
}
RBNode y = x.parent;
while(y != nil && x == y.right) {
x = y;
y = y.parent;
}
return y;
}
//查找节点x的前驱节点
public RBNode treePredeceessor(RBNode x) {
if(x.left != nil) {
return treeMaximum(x.left);
}
RBNode y = x.parent;
while(y != nil && x == y.left) {
x = y;
y = y.parent;
}
return y;
}
/**
* 围绕x左旋
* xp xp
* / /
* x xr
* / \ ==> / \
* xl xr x rr
* / \ / \
* rl rr xl rl
*
* @param t,x
*/
void leftRotate(RedBlackTree t, RBNode x) {
RBNode y = x.right; //让y等于x的右子节点
x.right = y.left; //将y的左子树转成x的右子树
if(y.left != t.nil) { //假如y的左孩子不为空,将y的左孩子的父亲设置为x
y.left.parent = x;
}
y.parent = x.parent; //将y的父亲设置为x的父亲
if(x.parent == t.nil) {
t.root = y; //考虑x原来为根节点的情况
} else if (x.parent.left == x) {
x.parent.left = y;
} else {
x.parent.right = y;
}
y.left = x;
x.parent = y;
}
/**
* 围绕x右旋
* xp xp
* \ \
* x xl
* / \ => / \
* xl xr ll x
* / \ / \
* ll lr lr xr
*
* @param t,x
*/
void rightRotate(RedBlackTree t, RBNode x) {
RBNode y = x.left; //让y等于x的左子节点
x.left = y.right; //将y的右子树转成x的左子树
if(y.right != t.nil) { //假如y的右孩子不为空,将y的右孩子的父亲设置为x
y.right.parent = x;
}
y.parent = x.parent; //将y的父亲设置为x的父亲
if(x.parent == t.nil) {
t.root = y; //考虑x原来为根节点的情况
} else if (x.parent.left == x) {
x.parent.left = y;
} else {
x.parent.right = y;
}
y.right = x;
x.parent = y;
}
//红黑树的插入操作
public void RBInsert(RedBlackTree t, RBNode z) {
RBNode y = t.nil;
RBNode x = t.root;
while(x != t.nil) {
y = x;
if(z.key < x.key) {
x = x.left;
} else {
x = x.right;
}
}
z.parent = y;
if(y == t.nil) { //说明现在是棵空树
t.root = z;
} else if (z.key < y.key) {
y.left = z;
} else {
y.right = z;
}
z.left = t.nil;
z.right = t.nil;
z.color = RED;
rbInsertFixup(t, z);
}
//插入节点后维护红黑树性质的过程
public void rbInsertFixup(RedBlackTree t, RBNode z) {
while (z.parent.color == RED) {
if(z.parent == z.parent.parent.left) { //z的父节点是z的祖父节点的左孩子
RBNode y = z.parent.parent.right; //让y成为z的叔叔节点
if (y.color == RED) {
/*
* z的父亲和叔叔节点都是红色,
* 根据红黑树性质,z的祖父一定是黑色
* 所以这时候,可以把z的祖父设为红色,
* z的父亲和叔叔都设为黑色,但这可能
* 导致z的祖父产生双红节点的问题,这
* 时候把z设置成z的祖父,继续向上递归
*/
z.parent.color = BLACK;
y.color = BLACK;
z.parent.parent.color = RED;
z = z.parent.parent;
} else {
if (z == z.parent.right) {
/*
* z的父亲是左节点,z是右节点,
* 满足LR不平衡,需要对z的父亲进行左旋,
* 转变成LL不平衡
*/
z = z.parent;
leftRotate(t, z);
}
/*
* z的父亲是左节点,z也是左节点,
* 满足LL不平衡,把z的父亲设为黑色,
* z的祖父设为红色,对z进行右旋,
* 即可满足平衡
*/
z.parent.color = BLACK;
z.parent.parent.color = RED;
rightRotate(t, z.parent.parent);
}
} else {
RBNode y = z.parent.parent.left; //让y成为z的叔叔节点
if (y.color == RED) {
/*
* z的父亲和叔叔节点都是红色,
* 根据红黑树性质,z的祖父一定是黑色
* 所以这时候,可以把z的祖父设为红色,
* z的父亲和叔叔都设为黑色,但这可能
* 导致z的祖父产生双红节点的问题,这
* 时候把z设置成z的祖父,继续向上递归
*/
z.parent.color = BLACK;
y.color = BLACK;
z.parent.parent.color = RED;
z = z.parent.parent;
} else {
if (z == z.parent.left) {
/*
* z的父亲是右节点,z是左节点,
* 满足RL不平衡,需要对z的父亲进行右旋,
* 转变成RR不平衡
*/
z = z.parent;
rightRotate(t, z);
}
/*
* z的父亲是右节点,z也是右节点,
* 满足RR不平衡,把z的父亲设为黑色,
* z的祖父设为红色,对z进行左旋,
* 即可满足平衡
*/
z.parent.color = BLACK;
z.parent.parent.color = RED;
leftRotate(t, z.parent.parent);
}
}
}
t.root.color = BLACK;
}
public void rbTransplant(RedBlackTree t, RBNode u, RBNode v) {
if(u.parent == t.nil) {
t.root = v;
} else if(u == u.parent.left) {
u.parent.left = v;
} else {
u.parent.right = v;
}
v.parent = u.parent;
}
//删除节点操作
public void rbDelete(RedBlackTree t, RBNode z) {
RBNode x;
RBNode y = z;
boolean yOriginalColor = y.color;
if (z.left == t.nil) {
x = z.right;
//z的左孩子为空,用z的右孩子替换z,此时z的右孩子可以为空,也可以不为空
rbTransplant(t, z, z.right);
} else if (z.right == t.nil) {
x = z.left;
//z仅有一个孩子且其为左孩子,用z的左孩子替换z
rbTransplant(t, z , z.left);
} else {
//z有两个孩子,找z的后继节点
y = treeMinimum(z.right);
yOriginalColor = y.color;
x = y.right;
if(y.parent == z) {
x.parent = y;
} else {
//用以y的右孩子为根的树代替以y为根的树
rbTransplant(t, y, y.right);
y.right = z.right;
y.right.parent = y;
}
//用以y为根的树代替以z为根的树
rbTransplant(t, z, y);
y.left = z.left;
y.left.parent = y;
}
//如果删除的为黑节点,需要修复平衡
if (yOriginalColor == BLACK) {
// rbDeleteFixup(t, x);
fixAfterDelete(t, x);
}
}
//删除修复算法导论版代码,用红黑树解释
public void rbDeleteFixup(RedBlackTree t, RBNode x) {
while(x != t.root && x.color == BLACK) {
//x是左孩子
if(x == x.parent.left) {
//w为兄弟节点
RBNode w = x.parent.right;
//w为红色,要旋转成黑色,方便后续操作
if(w.color == RED) {
w.color = BLACK;
x.parent.color = RED;
leftRotate(t, x.parent);
//此时w为黑色
w = x.parent.right;
}
/*
* w是黑色,w的两个孩子都是黑色,
* 没办法通过旋转恢复平衡,只能把w拉下水,设为红色,
* x变成x的父节点,向上递归
*/
if(w.left.color == BLACK && w.right.color == BLACK) {
w.color = RED;
x = x.parent;
} else {
/*
* w是黑色,w的右孩子是黑色,
* w的左孩子是红色,为RL场景
* 此时把w的左孩子设为黑色,
* w设为红色,对w进行右旋,
* 确保w的右孩子为红色,此时为RR场景
*/
if(w.right.color == BLACK) {
w.left.color = BLACK;
w.color = RED;
rightRotate(t, w);
w = x.parent.right;
}
/*
* 此时一定是w为黑色,w的右孩子为红色,
* w设置为x父节点的颜色,
* x父节点设为黑色,
* w的右孩子设置为黑色,
* 这样w路径上多出来一个黑节点,
* 对x的父节点进行左旋,
* 相当于把原来w路径上多出来的黑节点补充到x的路径上,
* 这样就填补了原来删除的黑节点,恢复平衡
*/
w.color = x.parent.color;
x.parent.color = BLACK;
w.right.color = BLACK;
leftRotate(t, x.parent);
/*
* 这里已经恢复平衡,
* 所以直接把x设置为根节点结束循环
*/
x = t.root;
}
} else {
//x是右孩子,w是兄弟节点
RBNode w = x.parent.left;
//w为红色,要旋转成黑色,方便后续操作
if(w.color == RED) {
w.color = BLACK;
x.parent.color = RED;
rightRotate(t, x.parent);
//此时w为黑色
w = x.parent.right;
}
/*
* w是黑色,w的两个孩子都是黑色,
* 没办法通过旋转恢复平衡,只能把w拉下水,设为红色,
* x变成x的父节点,向上递归
*/
if(w.right.color == BLACK && w.left.color == BLACK) {
w.color = RED;
x = x.parent;
} else {
/*
* w是黑色,w的左孩子是黑色,
* w的右孩子是红色,为LR场景
* 此时把w的右孩子设为黑色,
* w设为红色,对w进行左旋,
* 确保w的左孩子一定为红色,此时为LL场景
*/
if(w.left.color == BLACK) {
w.right.color = BLACK;
w.color = RED;
leftRotate(t, w);
w = x.parent.left;
}
/*
* 此时一定是w为黑色,w的左孩子为红色,
* w设置为x父节点的颜色,
* x父节点设为黑色,
* w的左孩子设置为黑色,
* 这样w路径上多出来一个黑节点,
* 对x的父节点进行右旋,
* 相当于把原来w路径上多出来的黑节点补充到x的路径上,
* 这样就填补了原来删除的黑节点,恢复平衡
*/
w.color = x.parent.color;
x.parent.color = BLACK;
w.left.color = BLACK;
rightRotate(t, x.parent);
/*
* 这里已经恢复平衡,
* 所以直接把x设置为根节点结束循环
*/
x = t.root;
}
}
}
/*
* 循环结束,要么x是根节点,
* 要么x是红色节点,
* 直接把x设置成黑色,即可恢复平衡
*/
x.color = BLACK;
}
/**
* 根据2-3-4树解释的红黑树删除
* 删除后的调整处理
* 1.情况1:自己能搞定,对应的叶子节点是3节点或者4节点
* 2.情况2:自己搞不定,需要兄弟节点借,但是兄弟节点不能直接借,找父亲节点借,父亲下来,然后兄弟节点找一个人代替父亲当家
* 3.情况3:跟兄弟节点借,兄弟也没有
* @param t,x
*/
public void fixAfterDelete(RedBlackTree t, RBNode x){
while(x != t.root && x.color == BLACK){
//x是左孩子的情况
if(x == x.parent.left) {
//兄弟节点
RBNode w = x.parent.right;
//判断此时兄弟节点是否是真正的兄弟节点,只有黑色节点才是
if(w.color == RED){
w.color = BLACK;
x.parent.color = RED;
leftRotate(t, x.parent);
//找到真正的兄弟节点
w = x.parent.right;
}
//情况三,找兄弟借,兄弟没得借
if(w.left.color == BLACK && w.right.color == BLACK) {
//把兄弟拉下水,设为红色,向上递归
w.color = RED;
x = x.parent;
}
//情况二,找兄弟借,兄弟有的借
else{
//确保w的右孩子是红色
if(w.right.color == BLACK) {
w.left.color = BLACK;
w.color = RED;
rightRotate(t, w);
w = x.parent.right;
}
/*
* 此时一定是w为黑色,w的右孩子为红色,
* w设置为x父节点的颜色,
* x父节点设为黑色,
* w的右孩子设置为黑色,
* 这样w路径上多出来一个黑节点,
* 对x的父节点进行左旋,
* 相当于把原来w路径上多出来的黑节点补充到x的路径上,
* 这样就填补了原来删除的黑节点,恢复平衡
*/
w.color = x.parent.color;
x.parent.color = BLACK;
w.right.color = BLACK;
leftRotate(t, x.parent);
x = t.root;
}
}
//x是右孩子的情况
else{
//兄弟节点
RBNode w = x.parent.left;
//判断此时兄弟节点是否是真正的兄弟节点,只有黑色节点才是
if(w.color == RED) {
w.color = BLACK;
x.parent.color = RED;
rightRotate(t, x.parent);
//此时w为黑色,才是真正的兄弟节点
w = x.parent.right;
}
//情况三,找兄弟借,兄弟没得借
if(w.left.color == BLACK && w.right.color == BLACK) {
//把兄弟拉下水,设为红色,向上递归
w.color = RED;
x = x.parent;
}
//情况二,找兄弟借,兄弟有的借
else{
//确保w的左孩子是红色
if(w.left.color == BLACK) {
w.right.color = BLACK;
w.color = RED;
leftRotate(t, w);
w = x.parent.right;
}
/*
* 此时一定是w为黑色,w的左孩子为红色,
* w设置为x父节点的颜色,
* x父节点设为黑色,
* w的左孩子设置为黑色,
* 这样w路径上多出来一个黑节点,
* 对x的父节点进行右旋,
* 相当于把原来w路径上多出来的黑节点补充到x的路径上,
* 这样就填补了原来删除的黑节点,恢复平衡
*/
w.color = x.parent.color;
x.parent.color = BLACK;
w.left.color = BLACK;
rightRotate(t, x.parent);
x = t.root;
}
}
}
//情况一、替代节点是红色,则直接染红,补偿删除的黑色节点,这样红黑树依然保持平衡
x.color = BLACK;
}
//红黑树节点类定义
static class RBNode {
private Integer key; //节点值
private RBNode parent; //父节点
private RBNode left; //左孩子
private RBNode right; //右孩子
private boolean color = BLACK;
public RBNode() {
}
public RBNode(Integer key) {
this.key = key;
}
public RBNode(Integer key, RBNode parent) {
this.parent = parent;
this.color = BLACK;
this.key = key;
}
public RBNode(RBNode parent, RBNode left, RBNode right, Integer key, boolean color) {
this.parent = parent;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
this.key = key;
this.color = color;
}
public Integer getKey() {
return key;
}
public void setKey(Integer key) {
this.key = key;
}
public RBNode getParent() {
return parent;
}
public void setParent(RBNode parent) {
this.parent = parent;
}
public RBNode getLeft() {
return left;
}
public void setLeft(RBNode left) {
this.left = left;
}
public RBNode getRight() {
return right;
}
public void setRight(RBNode right) {
this.right = right;
}
}
@Override
public Object root() {
return root;
}
@Override
public Object left(Object RBNode) {
return ((RBNode)RBNode).left;
}
@Override
public Object right(Object RBNode) {
return ((RBNode)RBNode).right;
}
@Override
public Object string(Object RBNode) {
RBNode myRBNode = (RBNode)RBNode;
String color = myRBNode.color == RED ? "RED" : "BLACK";
return myRBNode.key + "(" + color + ")";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
RedBlackTree bst = new RedBlackTree();
bst.RBInsert(bst, new RBNode(12));
bst.RBInsert(bst, new RBNode(5));
bst.RBInsert(bst, new RBNode(2));
bst.RBInsert(bst, new RBNode(9));
bst.RBInsert(bst, new RBNode(18));
bst.RBInsert(bst, new RBNode(15));
bst.RBInsert(bst, new RBNode(19));
bst.RBInsert(bst, new RBNode(17));
bst.inorderTreeWalk(bst.root);
System.out.println();
BinaryTrees.print(bst);
bst.rbDelete(bst, bst.treeSearch(bst.root, 12));
System.out.println();
BinaryTrees.print(bst);
}
}
BinaryTreeInfo
package redblacktree;
public interface BinaryTreeInfo {
/**
* who is the root node
*/
Object root();
/**
* how to get the left child of the node
*/
Object left(Object node);
/**
* how to get the right child of the node
*/
Object right(Object node);
/**
* how to print the node
*/
Object string(Object node);
}
BinaryTrees
package redblacktree;
public final class BinaryTrees {
private BinaryTrees() {
}
public static void print(BinaryTreeInfo tree) {
print(tree, null);
}
public static void println(BinaryTreeInfo tree) {
println(tree, null);
}
public static void print(BinaryTreeInfo tree, PrintStyle style) {
if (tree == null || tree.root() == null) return;
printer(tree, style).print();
}
public static void println(BinaryTreeInfo tree, PrintStyle style) {
if (tree == null || tree.root() == null) return;
printer(tree, style).println();
}
public static String printString(BinaryTreeInfo tree) {
return printString(tree, null);
}
public static String printString(BinaryTreeInfo tree, PrintStyle style) {
if (tree == null || tree.root() == null) return null;
return printer(tree, style).printString();
}
private static Printer printer(BinaryTreeInfo tree, PrintStyle style) {
if (style == PrintStyle.INORDER) return new InorderPrinter(tree);
return new LevelOrderPrinter(tree);
}
public enum PrintStyle {
LEVEL_ORDER, INORDER
}
}
InorderPrinter
package redblacktree;
/**
┌──800
┌──760
│ └──600
┌──540
│ └──476
│ └──445
┌──410
│ └──394
381
│ ┌──190
│ │ └──146
│ ┌──40
│ │ └──35
└──12
└──9
*/
public class InorderPrinter extends Printer {
private static String rightAppend;
private static String leftAppend;
private static String blankAppend;
private static String lineAppend;
static {
int length = 2;
rightAppend = "┌" + Strings.repeat("─", length);
leftAppend = "└" + Strings.repeat("─", length);
blankAppend = Strings.blank(length + 1);
lineAppend = "│" + Strings.blank(length);
}
public InorderPrinter(BinaryTreeInfo tree) {
super(tree);
}
@Override
public String printString() {
StringBuilder string = new StringBuilder(
printString(tree.root(), "", "", ""));
string.deleteCharAt(string.length() - 1);
return string.toString();
}
/**
* 生成node节点的字符串
* @param nodePrefix node那一行的前缀字符串
* @param leftPrefix node整棵左子树的前缀字符串
* @param rightPrefix node整棵右子树的前缀字符串
* @return
*/
private String printString(
Object node,
String nodePrefix,
String leftPrefix,
String rightPrefix) {
Object left = tree.left(node);
Object right = tree.right(node);
String string = tree.string(node).toString();
int length = string.length();
if (length % 2 == 0) {
length--;
}
length >>= 1;
String nodeString = "";
if (right != null) {
rightPrefix += Strings.blank(length);
nodeString += printString(right,
rightPrefix + rightAppend,
rightPrefix + lineAppend,
rightPrefix + blankAppend);
}
nodeString += nodePrefix + string + "\n";
if (left != null) {
leftPrefix += Strings.blank(length);
nodeString += printString(left,
leftPrefix + leftAppend,
leftPrefix + blankAppend,
leftPrefix + lineAppend);
}
return nodeString;
}
}
LevelOrderPrinter
package redblacktree;
import java.util.*;
/**
┌───381────┐
│ │
┌─12─┐ ┌─410─┐
│ │ │ │
9 ┌─40─┐ 394 ┌─540─┐
│ │ │ │
35 ┌─190 ┌─476 ┌─760─┐
│ │ │ │
146 445 600 800
*/
public class LevelOrderPrinter extends Printer {
/**
* 节点之间允许的最小间距(最小只能填1)
*/
private static final int MIN_SPACE = 1;
private Node root;
private int minX;
private int maxWidth;
private List<List<Node>> nodes;
public LevelOrderPrinter(BinaryTreeInfo tree) {
super(tree);
root = new Node(tree.root(), tree);
maxWidth = root.width;
}
@Override
public String printString() {
// nodes用来存放所有的节点
nodes = new ArrayList<>();
fillNodes();
cleanNodes();
compressNodes();
addLineNodes();
int rowCount = nodes.size();
// 构建字符串
StringBuilder string = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < rowCount; i++) {
if (i != 0) {
string.append("\n");
}
List<Node> rowNodes = nodes.get(i);
StringBuilder rowSb = new StringBuilder();
for (Node node : rowNodes) {
int leftSpace = node.x - rowSb.length() - minX;
rowSb.append(Strings.blank(leftSpace));
rowSb.append(node.string);
}
string.append(rowSb);
}
return string.toString();
}
/**
* 添加一个元素节点
*/
private Node addNode(List<Node> nodes, Object btNode) {
Node node = null;
if (btNode != null) {
node = new Node(btNode, tree);
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, node.width);
nodes.add(node);
} else {
nodes.add(null);
}
return node;
}
/**
* 以满二叉树的形式填充节点
*/
private void fillNodes() {
// 第一行
List<Node> firstRowNodes = new ArrayList<>();
firstRowNodes.add(root);
nodes.add(firstRowNodes);
// 其他行
while (true) {
List<Node> preRowNodes = nodes.get(nodes.size() - 1);
List<Node> rowNodes = new ArrayList<>();
boolean notNull = false;
for (Node node : preRowNodes) {
if (node == null) {
rowNodes.add(null);
rowNodes.add(null);
} else {
Node left = addNode(rowNodes, tree.left(node.btNode));
if (left != null) {
node.left = left;
left.parent = node;
notNull = true;
}
Node right = addNode(rowNodes, tree.right(node.btNode));
if (right != null) {
node.right = right;
right.parent = node;
notNull = true;
}
}
}
// 全是null,就退出
if (!notNull) break;
nodes.add(rowNodes);
}
}
/**
* 删除全部null、更新节点的坐标
*/
private void cleanNodes() {
int rowCount = nodes.size();
if (rowCount < 2) return;
// 最后一行的节点数量
int lastRowNodeCount = nodes.get(rowCount - 1).size();
// 每个节点之间的间距
int nodeSpace = maxWidth + 2;
// 最后一行的长度
int lastRowLength = lastRowNodeCount * maxWidth
+ nodeSpace * (lastRowNodeCount - 1);
// 空集合
Collection<Object> nullSet = Collections.singleton(null);
for (int i = 0; i < rowCount; i++) {
List<Node> rowNodes = nodes.get(i);
int rowNodeCount = rowNodes.size();
// 节点左右两边的间距
int allSpace = lastRowLength - (rowNodeCount - 1) * nodeSpace;
int cornerSpace = allSpace / rowNodeCount - maxWidth;
cornerSpace >>= 1;
int rowLength = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < rowNodeCount; j++) {
if (j != 0) {
// 每个节点之间的间距
rowLength += nodeSpace;
}
rowLength += cornerSpace;
Node node = rowNodes.get(j);
if (node != null) {
// 居中(由于奇偶数的问题,可能有1个符号的误差)
int deltaX = (maxWidth - node.width) >> 1;
node.x = rowLength + deltaX;
node.y = i;
}
rowLength += maxWidth;
rowLength += cornerSpace;
}
// 删除所有的null
rowNodes.removeAll(nullSet);
}
}
/**
* 压缩空格
*/
private void compressNodes() {
int rowCount = nodes.size();
if (rowCount < 2) return;
for (int i = rowCount - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
List<Node> rowNodes = nodes.get(i);
for (Node node : rowNodes) {
Node left = node.left;
Node right = node.right;
if (left == null && right == null) continue;
if (left != null && right != null) {
// 让左右节点对称
node.balance(left, right);
// left和right之间可以挪动的最小间距
int leftEmpty = node.leftBoundEmptyLength();
int rightEmpty = node.rightBoundEmptyLength();
int empty = Math.min(leftEmpty, rightEmpty);
empty = Math.min(empty, (right.x - left.rightX()) >> 1);
// left、right的子节点之间可以挪动的最小间距
int space = left.minLevelSpaceToRight(right) - MIN_SPACE;
space = Math.min(space >> 1, empty);
// left、right往中间挪动
if (space > 0) {
left.translateX(space);
right.translateX(-space);
}
// 继续挪动
space = left.minLevelSpaceToRight(right) - MIN_SPACE;
if (space < 1) continue;
// 可以继续挪动的间距
leftEmpty = node.leftBoundEmptyLength();
rightEmpty = node.rightBoundEmptyLength();
if (leftEmpty < 1 && rightEmpty < 1) continue;
if (leftEmpty > rightEmpty) {
left.translateX(Math.min(leftEmpty, space));
} else {
right.translateX(-Math.min(rightEmpty, space));
}
} else if (left != null) {
left.translateX(node.leftBoundEmptyLength());
} else { // right != null
right.translateX(-node.rightBoundEmptyLength());
}
}
}
}
private void addXLineNode(List<Node> curRow, Node parent, int x) {
Node line = new Node("─");
line.x = x;
line.y = parent.y;
curRow.add(line);
}
private Node addLineNode(List<Node> curRow, List<Node> nextRow, Node parent, Node child) {
if (child == null) return null;
Node top = null;
int topX = child.topLineX();
if (child == parent.left) {
top = new Node("┌");
curRow.add(top);
for (int x = topX + 1; x < parent.x; x++) {
addXLineNode(curRow, parent, x);
}
} else {
for (int x = parent.rightX(); x < topX; x++) {
addXLineNode(curRow, parent, x);
}
top = new Node("┐");
curRow.add(top);
}
// 坐标
top.x = topX;
top.y = parent.y;
child.y = parent.y + 2;
minX = Math.min(minX, child.x);
// 竖线
Node bottom = new Node("│");
bottom.x = topX;
bottom.y = parent.y + 1;
nextRow.add(bottom);
return top;
}
private void addLineNodes() {
List<List<Node>> newNodes = new ArrayList<>();
int rowCount = nodes.size();
if (rowCount < 2) return;
minX = root.x;
for (int i = 0; i < rowCount; i++) {
List<Node> rowNodes = nodes.get(i);
if (i == rowCount - 1) {
newNodes.add(rowNodes);
continue;
}
List<Node> newRowNodes = new ArrayList<>();
newNodes.add(newRowNodes);
List<Node> lineNodes = new ArrayList<>();
newNodes.add(lineNodes);
for (Node node : rowNodes) {
addLineNode(newRowNodes, lineNodes, node, node.left);
newRowNodes.add(node);
addLineNode(newRowNodes, lineNodes, node, node.right);
}
}
nodes.clear();
nodes.addAll(newNodes);
}
private static class Node {
/**
* 顶部符号距离父节点的最小距离(最小能填0)
*/
private static final int TOP_LINE_SPACE = 1;
Object btNode;
Node left;
Node right;
Node parent;
/**
* 首字符的位置
*/
int x;
int y;
int treeHeight;
String string;
int width;
private void init(String string) {
string = (string == null) ? "null" : string;
string = string.isEmpty() ? " " : string;
width = string.length();
this.string = string;
}
public Node(String string) {
init(string);
}
public Node(Object btNode, BinaryTreeInfo opetaion) {
init(opetaion.string(btNode).toString());
this.btNode = btNode;
}
/**
* 顶部方向字符的X(极其重要)
*
* @return
*/
private int topLineX() {
// 宽度的一半
int delta = width;
if (delta % 2 == 0) {
delta--;
}
delta >>= 1;
if (parent != null && this == parent.left) {
return rightX() - 1 - delta;
} else {
return x + delta;
}
}
/**
* 右边界的位置(rightX 或者 右子节点topLineX的下一个位置)(极其重要)
*/
private int rightBound() {
if (right == null) return rightX();
return right.topLineX() + 1;
}
/**
* 左边界的位置(x 或者 左子节点topLineX)(极其重要)
*/
private int leftBound() {
if (left == null) return x;
return left.topLineX();
}
/**
* x ~ 左边界之间的长度(包括左边界字符)
*
* @return
*/
private int leftBoundLength() {
return x - leftBound();
}
/**
* rightX ~ 右边界之间的长度(包括右边界字符)
*
* @return
*/
private int rightBoundLength() {
return rightBound() - rightX();
}
/**
* 左边界可以清空的长度
*
* @return
*/
private int leftBoundEmptyLength() {
return leftBoundLength() - 1 - TOP_LINE_SPACE;
}
/**
* 右边界可以清空的长度
*
* @return
*/
private int rightBoundEmptyLength() {
return rightBoundLength() - 1 - TOP_LINE_SPACE;
}
/**
* 让left和right基于this对称
*/
private void balance(Node left, Node right) {
if (left == null || right == null) return;
// 【left的尾字符】与【this的首字符】之间的间距
int deltaLeft = x - left.rightX();
// 【this的尾字符】与【this的首字符】之间的间距
int deltaRight = right.x - rightX();
int delta = Math.max(deltaLeft, deltaRight);
int newRightX = rightX() + delta;
right.translateX(newRightX - right.x);
int newLeftX = x - delta - left.width;
left.translateX(newLeftX - left.x);
}
private int treeHeight(Node node) {
if (node == null) return 0;
if (node.treeHeight != 0) return node.treeHeight;
node.treeHeight = 1 + Math.max(
treeHeight(node.left), treeHeight(node.right));
return node.treeHeight;
}
/**
* 和右节点之间的最小层级距离
*/
private int minLevelSpaceToRight(Node right) {
int thisHeight = treeHeight(this);
int rightHeight = treeHeight(right);
int minSpace = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < thisHeight && i < rightHeight; i++) {
int space = right.levelInfo(i).leftX
- this.levelInfo(i).rightX;
minSpace = Math.min(minSpace, space);
}
return minSpace;
}
private LevelInfo levelInfo(int level) {
if (level < 0) return null;
int levelY = y + level;
if (level >= treeHeight(this)) return null;
List<Node> list = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(this);
// 层序遍历找出第level行的所有节点
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node node = queue.poll();
if (levelY == node.y) {
list.add(node);
} else if (node.y > levelY) break;
if (node.left != null) {
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
Node left = list.get(0);
Node right = list.get(list.size() - 1);
return new LevelInfo(left, right);
}
/**
* 尾字符的下一个位置
*/
public int rightX() {
return x + width;
}
public void translateX(int deltaX) {
if (deltaX == 0) return;
x += deltaX;
// 如果是LineNode
if (btNode == null) return;
if (left != null) {
left.translateX(deltaX);
}
if (right != null) {
right.translateX(deltaX);
}
}
}
private static class LevelInfo {
int leftX;
int rightX;
public LevelInfo(Node left, Node right) {
this.leftX = left.leftBound();
this.rightX = right.rightBound();
}
}
}
Printer
package redblacktree;
public abstract class Printer {
/**
* 二叉树的基本信息
*/
protected BinaryTreeInfo tree;
public Printer(BinaryTreeInfo tree) {
this.tree = tree;
}
/**
* 生成打印的字符串
*/
public abstract String printString();
/**
* 打印后换行
*/
public void println() {
print();
System.out.println();
}
/**
* 打印
*/
public void print() {
System.out.print(printString());
}
}
Strings
package redblacktree;
public class Strings {
public static String repeat(String string, int count) {
if (string == null) return null;
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
while (count-- > 0) {
builder.append(string);
}
return builder.toString();
}
public static String blank(int length) {
if (length < 0) return null;
if (length == 0) return "";
return String.format("%" + length + "s", "");
}
}
总结
这个实现过程比较复杂,更多的是在提现一个打印结果的实现,没有必要自己去手敲,可以全部拿下来,去运行,看具体核心实现红黑树对应的那些功能。对于红黑树更细节的去使用,我也还在探索中,之后会更加细节的去记录。
ps:计划每日更新一篇博客,今日2023-05-05,日更第十九天。
昨日更新:
B树(B-tree、B-树)理论详解