基于深度残差网络(ResNet)的水果分类识别系统
提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档
文章目录
- 前言
- 一.背景含义项目说明
- 二、数据预处理
-
- 三.网络结构
-
- 1.采用残差网络 (ResNets)
- 四.损失函数
- 五.具体说明超参数的调节过程
- 六.拟合处理
- 七.训练过程中loss的变化
- 八.测试集上评估最后模型的效果
- 九. 经典算法/优点和缺点
-
-
- 1.研究方向:图像分类。图像分类领域最经典的3种算法莫过于Alex网络、VGG网络、ResNet网络。
-
- 2.优点所在:
- 3.*缺点所在*:
-
- 十.成品展示:
- 谢谢大家的参考
前言
本文主要介绍如何使用python搭建:一个基于深度残差网络(ResNet)的水果图像分类识别系统。
提示:以下是本篇文章正文内容,下面案例可供参考
一.背景含义项目说明
1.本文主要介绍如何使用python搭建:一个基于深度残差网络(ResNet)的水果图像分类识别系统。
项目只是用水果分类作为抛砖引玉,其中包含了使用ResNet进行图像分类的相关代码。(主要功能 如下):
- 数据预处理,生成用于输入TensorFlow模型的TFRecord的数据。
- 模型构建及训练,使用tensorflow.keras构建深度残差网络。
- 预测水果分类并进行模型评估。
二、数据预处理
1.数据介绍:
| 数据大小 | 81类水果数据集共计14124张图片 |
|---|---|
| 数据条目 | 训练集11331张图片–测试集2793张图片 |
| 数据格式 | jpg格式,ImageNet数据集格式 |
数据集格式为ImageNet数据集格式。该数据集包含81个种类的水果,数据集共81个类别:人参果、佛手瓜、哈密瓜、圣女果、山楂、山竹、无花果、木瓜、李子、杏、杨桃、杨梅、枇、枣、柚子、柠檬、柿子、树莓、桂圆、桑葚、梨、椰子、榴莲等

2.读取/获取数据:
使用pytorch工具类DataLoader读取该数据集,其中对数据按照224*224进行了随机裁剪、随机水平翻转、转化为张量、并按照均值mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406]标准差std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]进行了归一化处理。训练集与测试集按照8:2的比例进行划分。
3.部分代码展示:
- 导入包
import streamlit as st
import cv2
from PIL import Image,ImageDraw,ImageFont
import tempfile
import torch
from torchvision import transforms
import torch.nn.functional as F
import numpy as np
import config
- 采用PTL读取数据集
nput:PIL读取的image
return:经过模型预测的带有类别标签、置信度的PIL格式的图片
'''
device = torch.device('cuda:0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
#图片前处理
val_transforms = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize(256),
transforms.CenterCrop(224),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(
mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
])
uploaded_image=uploaded_image.convert('RGB')
transform_image = val_transforms(uploaded_image)
predict_image = transform_image.unsqueeze(0).to(device)
pred_logits = model(predict_image)
pred_softmax = F.softmax(pred_logits, dim=1)
n = 3
top_n = torch.topk(pred_softmax, n)
pred_ids = top_n[1].cpu().detach().numpy().squeeze()
confs = top_n[0].cpu().detach().numpy().squeeze()
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(uploaded_image)
try:
idx_to_labels = np.load(config.LABLE_DIR, allow_pickle=True).item()
except:
raise 'label目录或者label目录下idx_to_labels.npy 类别标签不存在!'
try:
font = ImageFont.truetype(str(config.FONT_DIR), 32)
except:
raise "font目录或者font目录下SimHei.ttf 字体文件不存在!"
for i in range(n):
class_name = idx_to_labels[pred_ids[i]]
confidence = confs[i] * 100
text = '{:<5} {:>.2f}%'.format(class_name, confidence)
draw.text((5, 30+50 * i), text, font=font, fill=(255, 0, 0, 1))
return uploaded_image
def _display_classfication_frames(model, st_frame, img):
"""
Display the detected objects on a video frame using the resnet model.
:param model (resnet101): An instance of the `resnet101` class containing the resnet101 model.
:param st_frame (Streamlit object): A Streamlit object to display the detected video.
:param image (numpy array): A numpy array representing the video frame.
:return: None
"""
img_rgb=Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGRA2RGBA))
# 模型对单张图片进行预测
res_plotted = predict_image(img_rgb,model)
st_frame.image(res_plotted,
caption='Detected Video',
channels="BGR",
use_column_width=True
)
``
- 加载模型
def load_model(model_path):
"""
加载模型
"""
# device = torch.device('cuda:0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
model = torch.load(model_path,map_location='cpu')
# model=model.to(device)
return model
def pre_process_image(image):
val_transforms = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize(256),
transforms.CenterCrop(224),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(
mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
])
- 预测处理s
"""
执行图片推理预测
"""
source_img = st.sidebar.file_uploader(
label="选择一张图片...",
type=("jpg", "jpeg", "png", 'bmp', 'webp')
)
col1, col2 = st.columns(2)
with col1:
if source_img:
uploaded_image = Image.open(source_img)
# adding the uploaded image to the page with caption
st.image(
image=source_img,
caption="原始图片",
use_column_width=True
)
if source_img:
if st.button("Execution"):
with st.spinner("执行中..."):
res_plotted = predict_image(uploaded_image,model)
with col2:
st.image(res_plotted,
caption="执行结果",
use_column_width=True)
代码如下(示例):
三.网络结构
1.采用残差网络 (ResNets)
3.1 采用的网络为ResNet18,该网络的部分结构图如下

3.2本次之所以采用ResNet18网络进行81类水果图像分类,是由于采用ResNet(残差网络)进行图像分类任务的优势主要体现在以下几个方面:
- 解决网络退化问题
- 提高精度
- 泛化能力强
- 易于调优
- 迁移学习能力强
3.3本次利用在ImageNet数据集上预训练好的resnet18预训练模型进行81类水果分类,采用预训练模型而不是从头开始训练能够大幅缩短训练时间,节约计算资源,并且借助resnet预训练模型的泛化能力可以在自己的81类水果数据集上取得非常好的效果。由于resnet预训练模型的输出层为1000,而本次分类任务水果种类数为81,因此需要将resnet18的输出层数目改为81,冻结其他网络层的所有参数。也就是说,仅仅改变了resnet18网络的输出层。
四.损失函数
本次进行的为图像分类任务,并且是多分类任务,选用CrossEntropyLoss(交叉熵损失函数)。
五.具体说明超参数的调节过程
| 超参数 | 学习率、优化器、训练轮数 |
|---|---|
| 练轮数 | epoch=50,当epoch<20时会欠拟合 |
详细信息:
5.1 学习率(优化器统一为Adam,Epoch=50) :
| 学习率(lr) | 验证集平均精度 |
|---|---|
| 0.0001 | 71.56% |
| 0.001 | 71.1% |
| 0.05 | 56.34% |
| 0.1 | 37.10% |
5.2 优化器(学习率lr=0.001,epcoh=50):
| 优化器 | 验证集平均精度 |
|---|---|
| Adam | 71.56% |
| Adam | 72.03% |
| SGD | 68.56% |
六.拟合处理
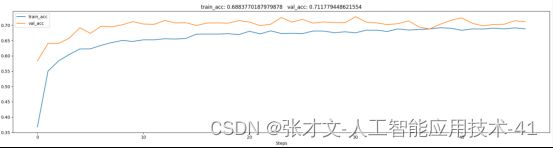
如下图所示,train loss曲线与val loss曲线在20个epoch之后一直平稳,不再下降也不再上升而是稳定在某一个值上下,说明训练充分,没有出现过拟合、欠拟合的情况。
七.训练过程中loss的变化
八.测试集上评估最后模型的效果
如下图所示,使用Resnet18网络在81类水果数据集的测试集上的精度在71%左右。
九. 经典算法/优点和缺点
1.研究方向:图像分类。图像分类领域最经典的3种算法莫过于Alex网络、VGG网络、ResNet网络。
2.优点所在:
- AlexNet:这是最早的深度卷积神经网络之一,具有开创性的意义。使用ReLU激活函数和Dropout正则化技术,显著提高了图像分类的准确率。
- VGG:VGG网络通过堆叠多个3x3的卷积核来替代更大尺寸的卷积核,减少了参数量。这种设计思想被证明是有效的,而且VGG网络的结构非常规整,易于理解和实现。
- ResNet:ResNet通过引入残差块有效地解决了深度神经网络的退化问题,使得网络可以设计得更深,从而提高了模型的表示能力和分类精度。
3.缺点所在:
- AlexNet:AlexNet的一些设计思想已经过时,例如它使用了较大的卷积核(11x11和5x5),而现在更常用的是3x3的卷积核。此外,Dropout在现在的实践中已经不常用。
- VGG:VGG网络的深度较大,参数量主要集中在最后三个全连接层中,这可能导致过拟合的问题。另外,VGG网络在全连接层之前的特征图尺寸较大,这可能会增加计算量和内存消耗。
- ResNet:然而,ResNet在实现上相对复杂一些,需要处理残差块的连接和维度的匹配等问题。




