ES的索引库操作
索引库操作
索引库就类似数据库表,mapping映射就类似表的结构。
我们要向es中存储数据,必须先创建“库”和“表”。
1.mapping映射属性
mapping是对索引库中文档的约束,常见的mapping属性包括:
-
type:字段数据类型,常见的简单类型有:
-
字符串:text(可分词的文本)、keyword(精确值,例如:品牌、国家、ip地址)
-
数值:long、integer、short、byte、double、float、
-
布尔:boolean
-
日期:date
-
对象:object
-
-
index:是否创建索引,默认为true
-
analyzer:使用哪种分词器
-
properties:该字段的子字段
例如下面的json文档:
{
"age": 21,
"weight": 52.1,
"isMarried": false,
"info": "黑马程序员Java讲师",
"email": "[email protected]",
"score": [99.1, 99.5, 98.9],
"name": {
"firstName": "云",
"lastName": "赵"
}
}对应的每个字段映射(mapping):
-
age:类型为 integer;参与搜索,因此需要index为true;无需分词器
-
weight:类型为float;参与搜索,因此需要index为true;无需分词器
-
isMarried:类型为boolean;参与搜索,因此需要index为true;无需分词器
-
info:类型为字符串,需要分词,因此是text;参与搜索,因此需要index为true;分词器可以用ik_smart
-
email:类型为字符串,但是不需要分词,因此是keyword;不参与搜索,因此需要index为false;无需分词器
-
score:虽然是数组,但是我们只看元素的类型,类型为float;参与搜索,因此需要index为true;无需分词器
-
name:类型为object,需要定义多个子属性
-
name.firstName;类型为字符串,但是不需要分词,因此是keyword;参与搜索,因此需要index为true;无需分词器
-
name.lastName;类型为字符串,但是不需要分词,因此是keyword;参与搜索,因此需要index为true;无需分词器
-
2.创建索引库和映射
-
请求方式:PUT
-
请求路径:/索引库名,可以自定义
-
请求参数:mapping映射
3.查询索引库
-
请求方式:GET
-
请求路径:/索引库名
-
请求参数:无
4.修改索引库
倒排索引结构虽然不复杂,但是一旦数据结构改变(比如改变了分词器),就需要重新创建倒排索引,这简直是灾难。因此索引库一旦创建,无法修改mapping。
虽然无法修改mapping中已有的字段,但是却允许添加新的字段到mapping中,因为不会对倒排索引产生影响。
添加新字段:
语法说明:
PUT /索引库名/_mapping
{
"properties": {
"新字段名":{
"type": "integer"
}
}
}
5.删除索引库
初始化RestClient
在elasticsearch提供的API中,与elasticsearch一切交互都封装在一个名为RestHighLevelClient的类中,必须先完成这个对象的初始化,建立与elasticsearch的连接。
分为三步:
1)引入es的RestHighLevelClient依赖:
org.elasticsearch.client
elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client
2)因为SpringBoot默认的ES版本是7.6.2,所以我们需要覆盖默认的ES版本:
1.8 7.12.1
3)初始化RestHighLevelClient:
初始化的代码如下:
RestHighLevelClient client = new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(
HttpHost.create("http://192.168.150.101:9200")
));这里为了单元测试方便,我们创建一个测试类HotelIndexTest,然后将初始化的代码编写在@BeforeEach方法中:
package cn.itcast.hotel;
import org.apache.http.HttpHost;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
public class HotelIndexTest {
private RestHighLevelClient client;
@BeforeEach
void setUp() {
this.client = new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(
HttpHost.create("http://192.168.150.101:9200")
));
}
@AfterEach
void tearDown() throws IOException {
this.client.close();
}
}创建索引库:
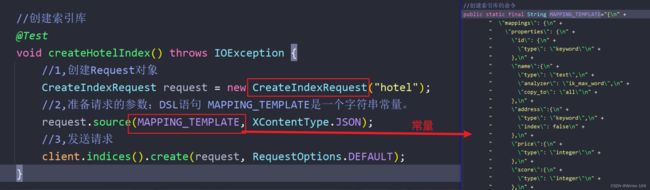
//创建索引库
@Test
void createHotelIndex() throws IOException {
//1,创建Request对象
CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest("hotel");
//2,准备请求的参数:DSL语句
request.source(MAPPING_TEMPLATE, XContentType.JSON);
//3,发送请求
client.indices().create(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}删除索引库:
//删除索引库
@Test
void deleteHotelIndex() throws IOException {
//1,创建Request对象
DeleteIndexRequest request = new DeleteIndexRequest("hotel");
//2,发送请求
client.indices().delete(request,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}查看索引库是否存在:
//查看索引库是否存在
@Test
void testExistsHotelIndex() throws IOException {
//1,创建request对象
GetIndexRequest request = new GetIndexRequest("hotel");
//2,发送请求
boolean exists = client.indices().exists(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//3,输出
System.err.println(exists? "索引库已经存在" : "索引库不存在!");
}