数据压缩实验——MPEG音频编码实验
目录
实验原理
MPEG-1 Audio LayerII编码器原理
基本思想
两条线
时-频分析的矛盾
心理声学模型
MPEG-1音频编码器框架图
MPEG-1声音的主要性能
多相滤波器组
心理声学模型
比特分配器
装帧
实验要求
程序分析
调试及实验结果
输出音频的采样率和目标码率
输出某个数据帧所分配的比特数,比例因子,比特分配结果
结果分析
实验原理
MPEG-1 Audio LayerII编码器原理
基本思想
分析信号,去掉不能被感知的部分
两条线
从流程图来看,MPEG音频编码分为清晰的上下两条线。上面一条线是一个标准的子带编码系统的流程,下面一条线的本质是为了帮助计算线性量化器的量化比特数,实现线性量化器这一块的优化,其中,下面一条线最为关键的部分是心理声学模型,它对去除冗余信息起到了极大的作用,其复杂度取决于所需要的压缩因子。
时-频分析的矛盾
第一条线中, 信号需要具有高的时间分辨率, 确保在短暂冲击信号情况下,编码的声音信号具有 足够高的质量。
第二条线中,又要使信号通过 FFT 运算具有高的频率分辨率, 因为掩蔽阈值是从功率谱密度推出来的。
但是FFT变换是无法同时保证时域和频域的精细度,增加时域的分辨力,频域的分辨力就会下降,反之亦然。
心理声学模型
- 生理(Physiological)感知极限(传感极限)
- 心理(Psychological)感知极限(信号处理极限)
➢ 听觉系统中存在一个听觉阈值电平,低于这个电平的声音 信号就听不到
◼ 听觉阈值的大小随声音频率的改变而改变。
◼ 一个人是否听到声音取决于声音的频率,以及声音的幅 度是否高于这种频率下的听觉阈值
➢ 听觉掩蔽特性。即听觉阈值电平是自适应的,会随听到的 不同频率声音而发生变化
听觉阈值
频域掩蔽
临界频带
临界频带是指当某个纯音被以它为中心频率、且具有一定带 宽的连续噪声所掩蔽时,如果该纯音刚好被听到时的功率等 于这一频带内的噪声功率,这个带宽为临界频带宽度。
通常认为从 20Hz 到 16kHz 有 25 个临界频带,单位为 bark , 1 Bark = 一个临界频带的宽度
人耳听觉系统
人类听觉系统大致等效于一个信号通过一组并联的不同中心 频率的带通滤波器
➢ 中心频率与信号频率相同的滤波器具有最大响应;中心频率偏离信号 频率较多的滤波器不会产生响应。
➢ 在 0Hz 到 20KHz 频率范围内由 25 个重叠的带通滤波器组成的滤波器组 。
➢ 听音者在噪声中听某一纯音信号时,只启用中心频率与信号频率相同 的那个听觉滤波器,纯音信号通过该滤波器,而噪声信号只有通带范 围内的部分信号能通过,通带以外的频率成分则被抑制,只有通过该 滤波器的噪声才对掩蔽起作用。
➢ 聆听复音时启动多个听觉滤波器。听觉能够计算各滤波器输出端的信噪比。当信噪比达到或者超过听阈因子时,即可听到该频率成分。
掩蔽效果的加和
Lutfi 对多个掩蔽音同时存在时的综合掩蔽效果进行了研究: 每个掩蔽音的掩蔽效果先独立变换然后再线性相加。
MPEG-1音频编码器框架图
MPEG-1声音的主要性能
· 输入为 PCM 信号,采样率为 32 , 44.1 或 48kHz ,输出为 32kbps 到 384kbps 。
· 三个独立的压缩层次
Layer1 :编码器最简单, 384kbps ( 4 : 1, 用于小型数字盒带 DCC , Compact Cassette )
Layer2 :编码器复杂程度中等, 256kbps ~ 192kbps ( 6: 1 ~ 8 : 1 , 用于 DAB 、 CD-I 和 VCD )
Layer3 :编码器最为复杂, 64kbps ,用于 ISDN ,网络 音频。
多相滤波器组
将 PCM 样本变换到 32 个子带的频域信号
多相滤波器缺点 :
◼ 等带宽的滤波器组与人类听觉系统的临界频带 不对应
在低频区域,单个子带会覆盖多个临界频带。在这 种情况下,量化比特数不能兼每个临界频带
◼ 滤波器组与其逆过程 不是 无失真的
但滤波器组引入的误差差很小,且听不到
◼ 子带间频率有混叠
滤波后的相邻子带有频率混叠现象,一个子带中的 信号可以影响相邻子带的输出
心理声学模型
MPEG-I 标准定义了两个模型
◼ 心理声学模型 1:
计算复杂度低
但对假设用户听不到的部分压缩太严重
◼ 心理声学模型 2 :
提供了适合 Layer III 编码的更多特征
◼ 实际实现的模型复杂度取决所需要的压缩 因子
心理声学模型1
1、将样本变换到频域(Layer I:每帧384个样本点,512个样本点足够覆盖;Layer II 和Layer III:每帧1152个样本点,每帧两次计算,模型1选择两个信号掩蔽比(SMR)中较小的一个)
比特分配器
根据心理声学模 型的计算结果,为每个子带信号分配比特数
在调整到固定的码率之前
➢ 先确定可用于样值编码的有效比特数
➢ 这个数值取决于比例因子、比例因子选择信息、比特分配信息 以及辅助数据所需比特数
比特分配的过程
对每个子带计算掩蔽 - 噪声比 MNR ,是信噪比 SNR– 信掩比 SMR ,即: MNR = SNR–SMR
NMR=SMR-SNR
➢ 使整个一帧和每个子带的总噪声 - 掩蔽比最 小。这是一个循环过程,每一次循环使获益 最大的子带的量化级别增加一级,当然所用 比特数不能超过一帧所能提供的最大数目
➢ 第 1 层一帧用 4 比特给每个子带的比特分配信 息编码;而第 2 层只在低频段用 4 比特,高频 段则用 2 比特
子带样值的量化和编码
输入以 12 个样本为一组,每组样本经过时间 - 频率变换 之后进行一次比特分配并记录一个比例因子 (scale factor)
比特分配信息告诉解码器每个样本由几位表示,比例 因子用 6 比特表示,解码器使用这个 6 比特的比例因子 乘逆量化器的每个输出样本值,以恢复被量化的子带 值。比例因子的作用是充分利用量化器的量化范围, 通过比特分配和比例因子相配合,可以表示态范围 超过 120dB 的样本 。
装帧
产生 MPEG-I 兼容的 比特流
实验要求
◼ 输出音频的采样率和目标码率
◼ 选择三个不同特性的音频文件
噪声(持续噪声、突发噪声); 音乐 ; 混合
◼ 某个数据帧,输出
该帧所分配的比特数
该帧的比例因子
该帧的比特分配结果
程序分析
main函数
int main (int argc, char **argv)
{
...
/***初始化及分配内存***/
static unsigned int bit_alloc[2][SBLIMIT], scfsi[2][SBLIMIT];//存放每个声道32个子带的比特分配数
static unsigned int scalar[2][3][SBLIMIT], j_scale[3][SBLIMIT]; //存放2声道3个组每组12个样值的32个子带的比例因子
...
int sb, ch, adb; //adb用于存放数据帧分配的比特数
...
programName = argv[0];
if (argc == 1) /* no command-line args */
short_usage ();
else
parse_args (argc, argv, &frame, &model, &num_samples, original_file_name,
encoded_file_name); //分析输入参数
print_config (&frame, &model, original_file_name, encoded_file_name); //输出配置信息
/* this will load the alloc tables and do some other stuff */
hdr_to_frps (&frame);
nch = frame.nch;
error_protection = header.error_protection;
//get_audio()读取3*32*12=1152个音频样值,while循环获取每一帧信息
while (get_audio (musicin, buffer, num_samples, nch, &header) > 0) {
if (glopts.verbosity > 1)
if (++frameNum % 10 == 0)
fprintf (stderr, "[%4u]\r", frameNum);
fflush (stderr);
win_buf[0] = &buffer[0][0];
win_buf[1] = &buffer[1][0];
adb = available_bits (&header, &glopts); //得到分配的比特数
lg_frame = adb / 8;
if (header.dab_extension) {
/* in 24 kHz we always have 4 bytes */
if (header.sampling_frequency == 1)
header.dab_extension = 4;
/* You must have one frame in memory if you are in DAB mode */
/* in conformity of the norme ETS 300 401 http://www.etsi.org */
/* see bitstream.c */
if (frameNum == 1)
minimum = lg_frame + MINIMUM;
adb -= header.dab_extension * 8 + header.dab_length * 8 + 16;
}
{
int gr, bl, ch;
/* New polyphase filter
Combines windowing and filtering. Ricardo Feb'03 */
for( gr = 0; gr < 3; gr++ )
for ( bl = 0; bl < 12; bl++ )
for ( ch = 0; ch < nch; ch++ )
WindowFilterSubband( &buffer[ch][gr * 12 * 32 + 32 * bl], ch,
&(*sb_sample)[ch][gr][bl][0] ); //多项滤波器组
}
#ifdef REFERENCECODE
{
...
}
#endif
#ifdef NEWENCODE
...
#else
scale_factor_calc (*sb_sample, scalar, nch, frame.sblimit); //计算比例因子
pick_scale (scalar, &frame, max_sc);
if (frame.actual_mode == MPG_MD_JOINT_STEREO) {
/* this way we calculate more mono than we need */
/* but it is cheap */
combine_LR (*sb_sample, *j_sample, frame.sblimit);
scale_factor_calc (j_sample, &j_scale, 1, frame.sblimit);
}
#endif
if ((glopts.quickmode == TRUE) && (++psycount % glopts.quickcount != 0)) {
/* We're using quick mode, so we're only calculating the model every
'quickcount' frames. Otherwise, just copy the old ones across */
for (ch = 0; ch < nch; ch++) {
for (sb = 0; sb < SBLIMIT; sb++)
smr[ch][sb] = smrdef[ch][sb];
}
} else {
/* calculate the psymodel 根据心理声学模型计算SMR*/
switch (model) {
case -1:
psycho_n1 (smr, nch); //计算SMR
break;
case 0: /* Psy Model A */
psycho_0 (smr, nch, scalar, (FLOAT) s_freq[header.version][header.sampling_frequency] * 1000);
break;
...
default:
fprintf (stderr, "Invalid psy model specification: %i\n", model);
exit (0);
}
if (glopts.quickmode == TRUE)
/* copy the smr values and reuse them later */
for (ch = 0; ch < nch; ch++) {
for (sb = 0; sb < SBLIMIT; sb++)
smrdef[ch][sb] = smr[ch][sb];
}
if (glopts.verbosity > 4)
smr_dump(smr, nch);
}
#ifdef NEWENCODE
...
#else
transmission_pattern (scalar, scfsi, &frame);
main_bit_allocation (smr, scfsi, bit_alloc, &adb, &frame, &glopts);//进行比特分配
if (error_protection)
CRC_calc (&frame, bit_alloc, scfsi, &crc);
encode_info (&frame, &bs);
if (error_protection)
encode_CRC (crc, &bs);
encode_bit_alloc (bit_alloc, &frame, &bs); //对比特分配信息进行编码
encode_scale (bit_alloc, scfsi, scalar, &frame, &bs); //对比例因子进行编码
subband_quantization (scalar, *sb_sample, j_scale, *j_sample, bit_alloc,
*subband, &frame); //量化子带
sample_encoding (*subband, bit_alloc, &frame, &bs); //进行编码
#endif
...
exit (0);
}调试及实验结果
输出音频的采样率和目标码率
print_config()
void print_config(frame_info* frame, int* psy, char* inPath,
char* outPath) //可输出音频的采样率和目标码率
{
frame_header* header = frame->header;
if (glopts.verbosity == 0)
return;
fprintf(stderr, "--------------------------------------------\n");
fprintf(stderr, "Input File : '%s' %.1f kHz\n",
(strcmp(inPath, "-") ? inPath : "stdin"),
s_freq[header->version][header->sampling_frequency]);//输入文件路径和音频采样率
fprintf(stderr, "Output File: '%s'\n",
(strcmp(outPath, "-") ? outPath : "stdout"));//输出文件路径
fprintf(stderr, "%d kbps ", bitrate[header->version][header->bitrate_index]);//目标码率
fprintf(stderr, "%s ", version_names[header->version]);
...
}
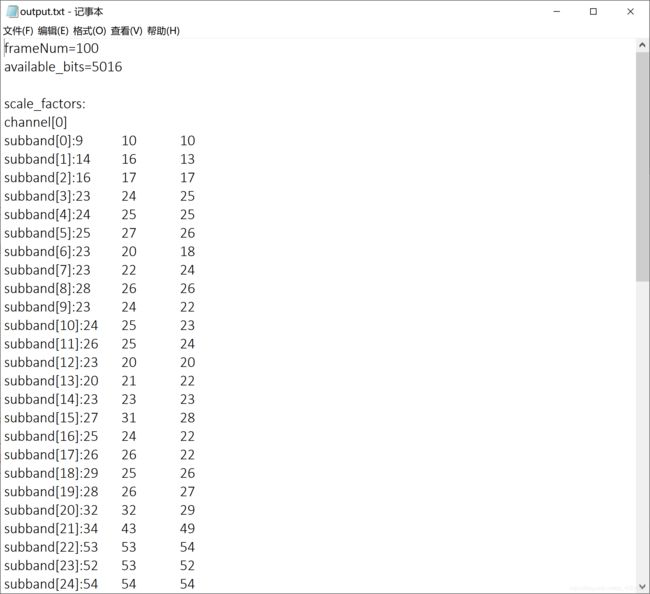
输出某个数据帧所分配的比特数,比例因子,比特分配结果
在main函数中添加代码
FILE* output = NULL;
output = fopen("output.txt", "wb");
......
if (frameNum == 100) {
fprintf(output, "frameNum=%d\n", frameNum);
fprintf(output, "available_bits=%d\n", adb);///输出该帧的可用比特数
fprintf(output, "\nscale_factors:\n");//输出该帧的比例因子
for (int k = 0; k < nch; k++) {
fprintf(output, "channel[%d]\n", k);
for (int i = 0; i < frame.sblimit; i++) {
fprintf(output, "subband[%d]:", i);
for (int t = 0; t < 3; t++) {
fprintf(output, "%d\t", scalar[k][t][i]);
}
fprintf(output, "\n");
}
}
}
transmission_pattern (scalar, scfsi, &frame);
main_bit_allocation (smr, scfsi, bit_alloc, &adb, &frame, &glopts);
if (frameNum == 100) {
int k, i;
fprintf(output, "\nbit_allocation:\n");///输出该帧的比特分配结果
for (k = 0; k < nch; k++) {
fprintf(output, "channel[%d]\n", k);
for (i = 0; i < frame.sblimit; i++) {
fprintf(output, "subband[%d]:%d\n", i, bit_alloc[k][i]);
}
}
}得到output.txt