Linux进程通信之匿名管道
(。・∀・)ノ゙嗨!你好这里是ky233的主页:这里是ky233的主页,欢迎光临~
https://blog.csdn.net/ky233?type=blog
点个关注不迷路⌯'▾'⌯
一、进程间通信介绍
1.进程通信的本质
首先我们要知道进程是具有独立性的!
那么所对应的,进程想要通信,难度其实是比较大的
进程通信的本质就是:先让不同的进程看到同一份资源(内存空间)!
看到的同一份资源不能隶属于任何一个进程,必须要共享
2.进程间通信目的
- 数据传输:一个进程需要将它的数据发送给另一个进程
- 资源共享:多个进程之间共享同样的资源。
- 通知事件:一个进程需要向另一个或一组进程发送消息,通知它(它们)发生了某种事件(如进程终止 时要通知父进程)。
- 进程控制:有些进程希望完全控制另一个进程的执行(如Debug进程),此时控制进程希望能够拦截另 一个进程的所有陷入和异常,并能够及时知道它的状态改变
最终目的是要多进程之间的协同
二、管道
1.什么是管道
- 管道是Unix中最古老的进程间通信的形式。
- 我们把从一个进程连接到另一个进程的一个数据流称为一个“管道”
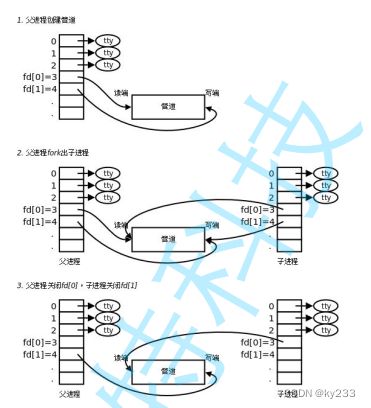
我们分别以读写的方式打开一个文件,然后创建子进程,相应的文件数据结构子进程会拷贝一份,然后双方关闭自己不需要的文件描述符,这个文件就叫做管道!管道通信是纯内存及的通信方式。
我们用这个|符号就可以使用管道
sleep 10000 | sleep 20000 &
我们创建两个正在运行中的后台进程,通过管道,使这两个进程变成了兄弟进程!ppid是一样的pid是连续的
三、匿名管道
1.pipe
#include
int pipe(int pipefd[2]);
这里面的参数是一个数组,pipefd[0]代表的是读端,pipefd[1]代表的是写端
int pipefd[2]={0};
int n=pipe(pipefd);使用方法如上,在使用此函数时,需要先创建好大小为 2 的 pipefd 数组,然后将其传入函数,成功创建匿名管道后,pipefd 数组中存储的就是匿名管道的读端和写端 fd
2.创建一个匿名管道
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//创建管道
int pipefd[2]={0};
int n=pipe(pipefd);
assert(n!=-1);
(void)n;
//创建子进程
pid_t id = fork();
assert(id!=-1);
//子进程读
if(id==0)
{
//关闭不需要的fd
close(pipefd[1]);
char buffer[1024];
while(1)
{
ssize_t s=read(pipefd[0],buffer,sizeof(buffer)-1);
if(s>0)
{
buffer[s]=0;
cout<<"子进程获得"<0);
(void)ret;
close(pipefd[1]);
return 0;
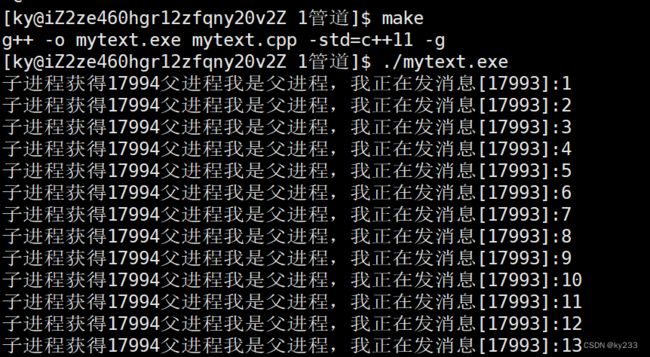
} 这就叫做管道,我们在父进程写入,由子进程来读,中间由pipe管道来进行传输
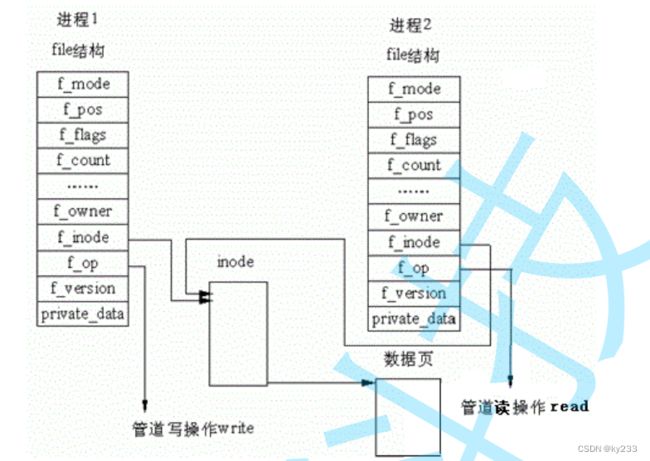
站在内核角度-管道本质
所以,看待管道,就如同看待文件一样!管道的使用和文件一致,迎合了“Linux一切皆文件思想”。
3.管道的读写规则
管道是一种半双工,单向通信的方式,所以在成功创建管道后,两个带通信的进程都用同一个pipefd数组,匿名管道只支持具有学研关系的进程通信,因为这样才能共享到同一个piepfd数组!
当双方获取到之后,就可以关闭不需要的fd,确保单向通信!
- 当没有数据可读时,read会调用阻塞,即进程暂停执行,一直等到有数据来到为止。
- 当管道被写满时,write会调用阻塞,直到有进程读走数据
- 如果所有管道写端对应的文件描述符被关闭,则read返回0,
- 如果所有管道读端对应的文件描述符被关闭,则write操作会产生信号SLGPIPE,进而可能导致weite进程退出
- 当要写入数据量不大于PIPE_BUF(管道大小),Linux将保证吸入的原子性
- 当要写入的数据量,大于PIPE_BUF时,Linux将不在保证写入的原子性
三、管道的特点
1.匿名管道管道是用来进行具有血缘关系的进程进行进程间通信的
pipe打开匿名管道,并不清楚管道的信息,pipefd数组等,所以需要有血缘关系的进程来继承这些!
2.管道具有通过让进程间协同,提供了访问控制!
当读端从管道中读取到数据时,如果没有数据就会阻塞,等待写端写入数据,如果读端正在读取,那么写端则会阻塞,等待读端!
3.管道提供的是面向字节流的通信服务
面向字节流又被成为流式服务,数据不会有明确的分割,不论写了多少的数据,只有写端停止,读端都会将管道内的数据全部读取。
4.管道是基于文件的,文件的生命周期是随进程的!管道的生命周期也是随进程的!
当父子进程都退出了,管道会自动释放
5.管道是单向通信的,就是半双工通信的一种特殊情况
什么是半双工呢?
就是管道的两端只能在同一时刻,每一端,只能从事不同的事情,如一端写,另一端就不能写入,可以是读取!
如果需要双方通信则需要建立起两个管道!
6.总结
- 只能用于具有共同祖先的进程(具有亲缘关系的进程)之间进行通信;通常,一个管道由一个进程创建,然后该进程调用fork,此后父、子进程之间就可应用该管道。
- 管道提供流式服务
- 一般而言,进程退出,管道释放,所以管道的生命周期随进程
- 一般而言,内核会对管道操作进行同步与互斥
- 管道是半双工的,数据只能向一个方向流动;需要双方通信时,需要建立起两个管道
四、进程池
1.概念
我们创建一个父进程,让父进程与多个子进程都有一个管道,子进程里面存放着预先处理任务的办法,我们的父进程给子进程派发任务,
完整源码
Taks:
#pragma once
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
typedef function func;
vector callbacks;
unordered_map desc;
void readMySQL()
{
cout << "sub process[" << getpid << "]执行访问数据库的任务\n"
<< endl;
}
void execuleUrl()
{
cout << "sub process[" << getpid << "]执行url解析\n\n"
<< endl;
}
void cal()
{
cout << "sub process[" << getpid << "]执行加密任务\n"
<< endl;
}
void save()
{
cout << "sub process[" << getpid << "]执行数据持久化任务\n"
<< endl;
}
void load()
{
desc.insert({callbacks.size(), "readMySQL:读取数据库"});
callbacks.push_back(readMySQL);
desc.insert({callbacks.size(), "execuleUrl: 进行url解析"});
callbacks.push_back(execuleUrl);
desc.insert({callbacks.size(), "cal: 进行加密计算"});
callbacks.push_back(cal);
desc.insert({callbacks.size(), "save: 进行数据的文件保存"});
callbacks.push_back(save);
}
void showHandler()
{
for (const auto &iter : desc)
{
cout << iter.first << "\t" << iter.second << endl;
}
}
int handlerSize()
{
return callbacks.size();
} ProessPool:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "Task.hpp"
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// 创建的进程个数
#define PROCESS_NUM 5
int waitCommand(int waitfd, bool &quit)
{
uint32_t command = 0;
ssize_t s = read(waitfd, &command, sizeof(command));
if (s == 0)
{
quit = true;
return -1;
}
assert(s == sizeof(uint32_t));
return command;
}
void sendAndWakeup(pid_t who, int fd, uint32_t command)
{
write(fd, &command, sizeof(command));
cout << "main process: call process " << who << " execute " << desc[command] << " through " << fd << endl;
}
int main()
{
load();
// 创建一个表,存放子进程的pid,和fd
vector> slots;
// 先创建多个进程
for (int i = 0; i < PROCESS_NUM; i++)
{
// 创建管道
int pipefd[2] = {0};
int n = pipe(pipefd);
assert(n == 0);
(void)n;
// 创建子进程
int id = fork();
assert(id != -1);
// 子进程读取
if (id == 0)
{
close(pipefd[1]);
while (1)
{
// 在这里进入阻塞状态等待写入
bool quit = false;
int command = waitCommand(pipefd[0], quit);
if (quit)
{
break;
}
// 执行对应的命令
if (command >= 0 && command < handlerSize())
{
callbacks[command]();
}
else
{
cout << "非法的command" << command << endl;
}
}
exit(1);
}
// 父进程写入
close(pipefd[0]);
slots.push_back(pair(id, pipefd[1]));
}
// 父进程分配任务
srand((unsigned long)time(nullptr) ^ getpid() ^ 23323123123L); // 让数据源更随机
while (true)
{
// 选择一个任务
int command = rand() % handlerSize();
// 选择一个进程
int choice = rand() % slots.size();
// 把任务给指定的进程
sendAndWakeup(slots[choice].first, slots[choice].second, command);
sleep(1);
}
// 关闭fd,结束所有进程
for (const auto &slot : slots)
{
close(slot.second);
}
// 回收子进程信息
for (const auto &slot : slots)
{
waitpid(slot.first, nullptr, 0);
}
}
Makefile:
ProcessPool:ProcessPool.cc
g++ -o $@ $^ -std=c++11 #-DDEBUG
.PHONY:clean
clean:
rm -f ProcessPool