js 哈希表 02
文章目录
- 封装Hash函数
- 封装Hash表结构
- 方法实现
-
- 插入和修改
-
- 注意
- 获取
- 删除
- 其它方法
- 哈希表测试(有冲突)
- 哈希表扩容思想
- 扩容保证质数
-
- 判断质数1 -- 不好
- 判断质数2 -- 不全
- 质数补全代码
封装Hash函数
代码
// 设计哈希函数
// 1> 将字符串转成比较大的数字:hashCode
// 2> 将大的数字hashCode压缩到数组范围(大小)之内
function hashFunc(str,size){
// 1 定义hashCode变量
let hashCode = 0;
// 2 霍纳算法,来计算hashCode的值
// eg: cats -> Unicode编码
for(let i = 0;i<str.length; i++){
// 用得比较多的质数 -> 37
hashCode = 37 * hashCode + str.charCodeAt(i);
}
// 3 取余操作
let index = hashCode % size;
return index;
}
// 测试哈希函数
alert(hashFunc('abc',7)); // 4
alert(hashFunc('cba',7)); // 3
alert(hashFunc('nba',7)); // 5
alert(hashFunc('jkd',7)); // 3
其实就是理解上一篇文章,怎么将字符串转化成大的数字就行,转化成大数时又由于需要计算很多的乘法,所以就将其用霍纳法则代替,就出现了这里的for循环里面的操作,菜鸟感觉难一点的可能就是这里了!
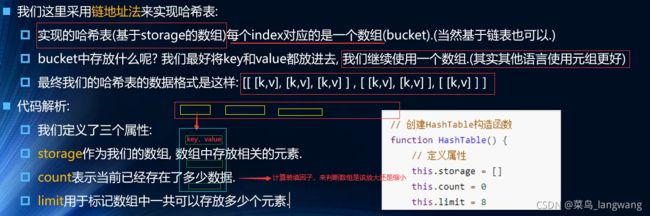
封装Hash表结构
// 链地址法 -- 数组实现
function Hashtable(){
// 属性
this.storage = [];
// 后面要使用count计算装填因子,>0.75就扩容,<0.25就缩小
this.count = 0;
// 当前总长度
this.limit = 7; // 这个值随意,因为要扩容或者缩小的,但是最好每次变化都是质数
//哈希函数
Hashtable.prototype.hashFunc = function (str,size){
let hashCode = 0;
for(let i = 0;i<str.length; i++){
hashCode = 37 * hashCode + str.charCodeAt(i);
}
let index = hashCode % size;
return index;
}
// 方法
}
这里视频是用数组嵌套数组实现哈希表的,但是感觉常见的别人封装的哈希表都是数组加链表,所以感兴趣的读者最好用链表写写,也希望积极在品论区留言!
菜鸟感觉算法题的话,用数组更多一点!说实话,感觉算法题基本上都是数组加算法,其它的数据结构很少出现在算法题中,因为太复杂容易超时!、
后面看视频,发现这个结构不是特别好,对于同名的人员的信息是存不了的,会替换原来的,既然会替换那感觉弹幕中说用 对象/Map 存k/v结构的确实比较好!
方法实现
插入和修改
注意
视频里面有一点不是很严谨,就是当bucket不存在时,应该是undefined,但是视频用的却是null,因为undefined == null 是true,但是菜鸟建议用 = = =,所以后面或者上面的截图,null理解为undefined就行!
代码
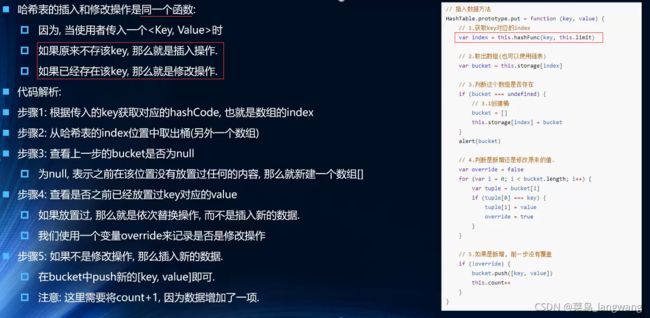
// 1 插入修改
Hashtable.prototype.put = function(key,value){
// 1 根据key获取对应的index
let index = this.hashFunc(key,this.limit);
// 2 根据index取出对应的bucket
let bucket = this.storage[index];
// 3 判断该bucket是否为undefined
if(bucket === undefined){
bucket = [];
this.storage[index] = bucket;
}
// 4 判断是否是修改数据,是修改,就修改了直接return,不会执行后面了;不是修改就直接执行后面的,加入
for(let i = 0;i < bucket.length;i++){
let tuple = bucket[i];
// 这个tuple是存放 k/v 的数组
if(tuple[0] == key){
tuple[1] = value;
return ;
}
}
// 添加操作
bucket.push([key,value]);
this.count += 1;
}
获取
哈希表不存在用下标来获取值,而是直接通过key转化的下标获取值,所以知道key求value就相当于知道下标求值!
如果是知道value求key的话,感觉哈希表并不适合!

代码
// 2 获取操作
Hashtable.prototype.get = function(key){
// 根据key获取index
let index = this.hashFunc(key,this.limit);
// 2 根据index获取对应的bucket
let bucket = this.storage[index];
// 3 判断bucket是否为undefined
if(bucket === undefined){
return null;
}
// 4 有bucket,进行线性查找
for(let i = 0;i<bucket.length;i++){
let tuple = bucket[i];
if(tuple[0] === key){
return tuple[1];
}
}
// 5 没找到
return null;
}
删除
// 3 删除操作
Hashtable.prototype.remove = function(key){
let index = this.hashFunc(key,this.limit);
let bucket = this.storage[index];
if(bucket === undefined){
return null;
}
for(let i=0;i<bucket.length;i++){
let tuple = bucket[i];
if(tuple[0] === key){
bucket.splice(i,1);
this.count -= 1;
return tuple[1];
}
}
return null;
}
菜鸟感觉,其实只要会写一个,其它的只要知道思路,类比一下就很好写,反正这种数组的方式书写哈希表挺简单的!
其它方法
哈希表测试(有冲突)
let Hash = new Hashtable();
Hash.put('abc',2);
Hash.put('cba',7);
Hash.put('nba',7);
Hash.put('jkd',7);
alert(Hash.get("abc"));
console.log(Hash);
Hash.put("abc",222);
alert(Hash.get("abc"));
console.log(Hash);
Hash.remove("nba");
alert(Hash.get("nba"));
console.log(Hash);
菜鸟这里建议,测一个就注释一下,因为 console.log 手动打开的异步性!这里菜鸟在之前的数据结构和算法的文章中提及过,这里就不多说了!
哈希表扩容思想
// 插入修改 --> 加入扩容
Hashtable.prototype.put = function(key,value){
// 1 根据key获取对应的index
let index = this.hashFunc(key,this.limit);
// 2 根据index取出对应的bucket
let bucket = this.storage[index];
// console.log(bucket);
// 3 判断该bucket是否为null
if(bucket === undefined){
bucket = [];
this.storage[index] = bucket;
}
// 4 判断是否是修改数据,是修改,就修改了直接return,不会执行后面了;不是修改就直接执行后面的,加入
for(let i = 0;i < bucket.length;i++){
let tuple = bucket[i];
// 这个tuple是存放 k/v 的数组
if(tuple[0] == key){
tuple[1] = value;
return ;
}
}
// 添加操作
bucket.push([key,value]);
this.count += 1;
// 判断是否需要扩容
if(this.count > this.limit * 0.75){
this.resize(this.limit * 2);
}
}
// 删除操作 --> 加入缩容
Hashtable.prototype.remove = function(key){
let index = this.hashFunc(key,this.limit);
let bucket = this.storage[index];
if(bucket === undefined){
return null;
}
for(let i=0;i<bucket.length;i++){
let tuple = bucket[i];
if(tuple[0] === key){
bucket.splice(i,1);
this.count -= 1;
// 判断是否缩小
if(this.limit > 7 && this.count < this.limit * 0.25){
// 向下取整,因为总是除以2,可能会有小数
this.resize(Math.floor(this.limit / 2));
}
return tuple[1];
}
}
return null;
}
// 哈希表扩容/缩小
Hashtable.prototype.resize = function(newLimit){
// 1 保存旧数组的内容
let oldStorage = this.storage;
// 2 重置所有属性
this.storage = [];
this.count = 0;
this.limit = newLimit;
// 3 遍历oldStorage中所有的bucket
for(let i = 0;i<oldStorage.length;i++){
// 1 取出bucket
let bucket = oldStorage[i];
// 2 判断bucket是否为undefined
if(bucket === undefined){
continue;
}
// 3 bucket中有数据,取出数据,重新插入
// 视频方法
for(let j = 0;j<bucket.length;j++){
let tuple = bucket[j];
this.put(tuple[0],tuple[1]);
}
}
}
这里菜鸟本来是想到了自己的一个办法,代码如下
// 哈希表扩容/缩小
Hashtable.prototype.resize = function(newLimit){
// 1 保存旧数组的内容
let oldStorage = this.storage;
// 2 重置所有属性
this.storage = [];
this.count = 0;
this.limit = newLimit;
// 3 遍历oldStorage中所有的bucket
for(let i = 0;i<oldStorage.length;i++){
// 1 取出bucket
let bucket = oldStorage[i];
console.log(i,bucket);
// 2 判断bucket是否为undefined
if(bucket === undefined){
continue;
}
// 3 bucket中有数据,取出数据,重新插入
// 我的方法
let a = bucket[0];
let ind = this.hashFunc(a[0],this.limit);
console.log(this.limit,ind);
this.storage[ind] = bucket;
}
}
菜鸟的方法有一个好处,就是不需要两层循环!
视频中循环就是为了把bucket里面的所有元素移到新的bucket所以又要一层循环,菜鸟当时就想,循环一层为什么不直接把一整个bucket给移过去?那样不就直接了当了吗?但是发现结果不一样,然后想了好久,菜鸟对比代码差别才发现,我那个考虑漏掉了count+1,顿时醍醐灌顶,结束了自己的困惑!
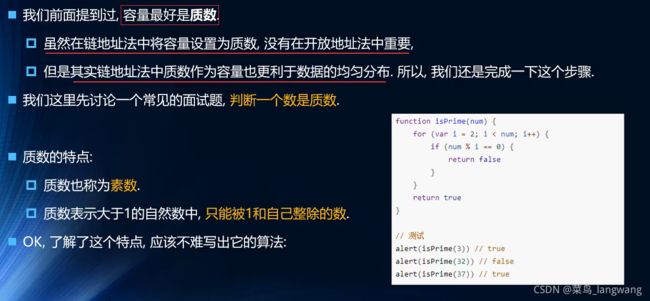
扩容保证质数
判断质数1 – 不好
// 封装函数:判断传入的数字是否是质数 --> 效率不高,不准确(eg:0,1)
// 特点:只能被1和自己整除,不能被2到num-1之间的数字整除
function isPrime(num){
for(let i = 2;i<num;i++){
if(num % i === 0){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
alert(isPrime(0));
alert(isPrime(1));
alert(isPrime(2));
alert(isPrime(3));
alert(isPrime(4));
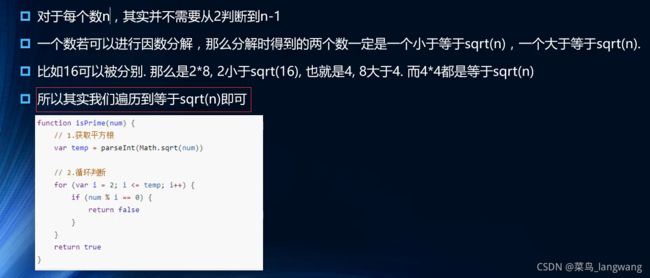
判断质数2 – 不全
// 封装函数:判断传入的数字是否是质数 --> 效率较高,不准确(eg:0,1)
function isP(num){
let temp = parseInt(Math.sqrt(num));
for(let i = 2;i<=temp;i++){
if(num % i ===0){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
视频规定了limit最小是7所以没有关系,如果没规定,一定要将0、1当成一种情况,单独return!
质数补全代码
判断质数和获得质数
// 判断某个数字是否是质数
Hashtable.prototype.isPrime = function(num){
let temp = parseInt(Math.sqrt(num));
for(let i = 2;i<=temp;i++){
if(num % i ===0){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// 获取质数
Hashtable.prototype.getPrime = function(num){
while(!this.isPrime(num)){
num++;
}
return num;
}
插入的修改
// 1 插入修改
Hashtable.prototype.put = function(key,value){
// 1 根据key获取对应的index
let index = this.hashFunc(key,this.limit);
// 2 根据index取出对应的bucket
let bucket = this.storage[index];
// console.log(bucket);
// 3 判断该bucket是否为null
if(bucket === undefined){
bucket = [];
this.storage[index] = bucket;
}
// 4 判断是否是修改数据,是修改,就修改了直接return,不会执行后面了;不是修改就直接执行后面的,加入
for(let i = 0;i < bucket.length;i++){
let tuple = bucket[i];
// 这个tuple是存放 k/v 的数组
if(tuple[0] == key){
tuple[1] = value;
return ;
}
}
// 添加操作
bucket.push([key,value]);
this.count += 1;
// 判断是否需要扩容
if(this.count > this.limit * 0.75){
let newSize = this.limit * 2;
let newPri = this.getPrime(newSize);
this.resize(newPri);
}
}
删除的修改
// 3 删除操作
Hashtable.prototype.remove = function(key){
let index = this.hashFunc(key,this.limit);
let bucket = this.storage[index];
if(bucket === undefined){
return null;
}
for(let i=0;i<bucket.length;i++){
let tuple = bucket[i];
if(tuple[0] === key){
bucket.splice(i,1);
this.count -= 1;
// 判断是否缩小
if(this.limit > 7 && this.count < this.limit * 0.25){
// 向下取整,因为总是除以2,可能会有小数
let newSize = Math.floor(this.limit / 2);
let newPri = this.getPrime(newSize);
this.resize(newPri);
}
return tuple[1];
}
}
return null;
}