算法:BFS宽度优先遍历
文章目录
- BFS与Queue相结合
-
- N叉树的层序遍历
- 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历
- 二叉树的最大宽度
- BFS和FLoodFill相结合
-
- 图像渲染
- 岛屿数量
- 岛屿的最大面积
- BFS解决最短路问题
-
- 最小基因变化
- 单词接龙
- 为高尔夫比赛砍树
- 拓扑排序
-
- 课程表
- 课程表II
- 火星词典
本篇总结的是BFS算法,BFS算法相比起DFS算法来说还是比较简单的
BFS与Queue相结合
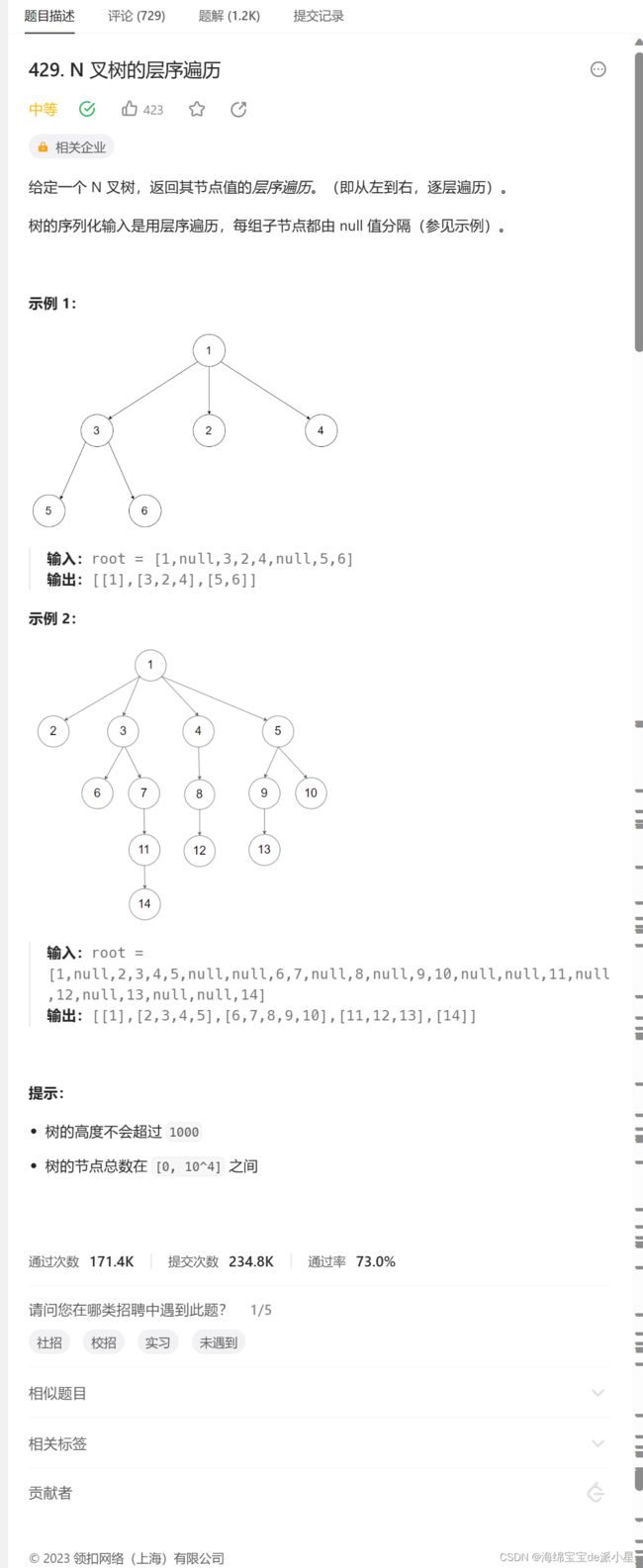
N叉树的层序遍历
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
vector children;
Node() {}
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
Node(int _val, vector _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution
{
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(Node* root)
{
vector<vector<int>> ret;
if(root == nullptr)
return ret;
queue<Node*> qe;
qe.push(root);
while(!qe.empty())
{
int size = qe.size();
vector<int> tmp;
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
// 取队列头节点
Node* front = qe.front();
qe.pop();
// 把值入到数组中
tmp.push_back(front->val);
// 如果有孩子,就把孩子入到队列中
for(int j = 0; j < (front->children).size(); j++)
qe.push((front->children)[j]);
}
ret.push_back(tmp);
}
return ret;
}
};
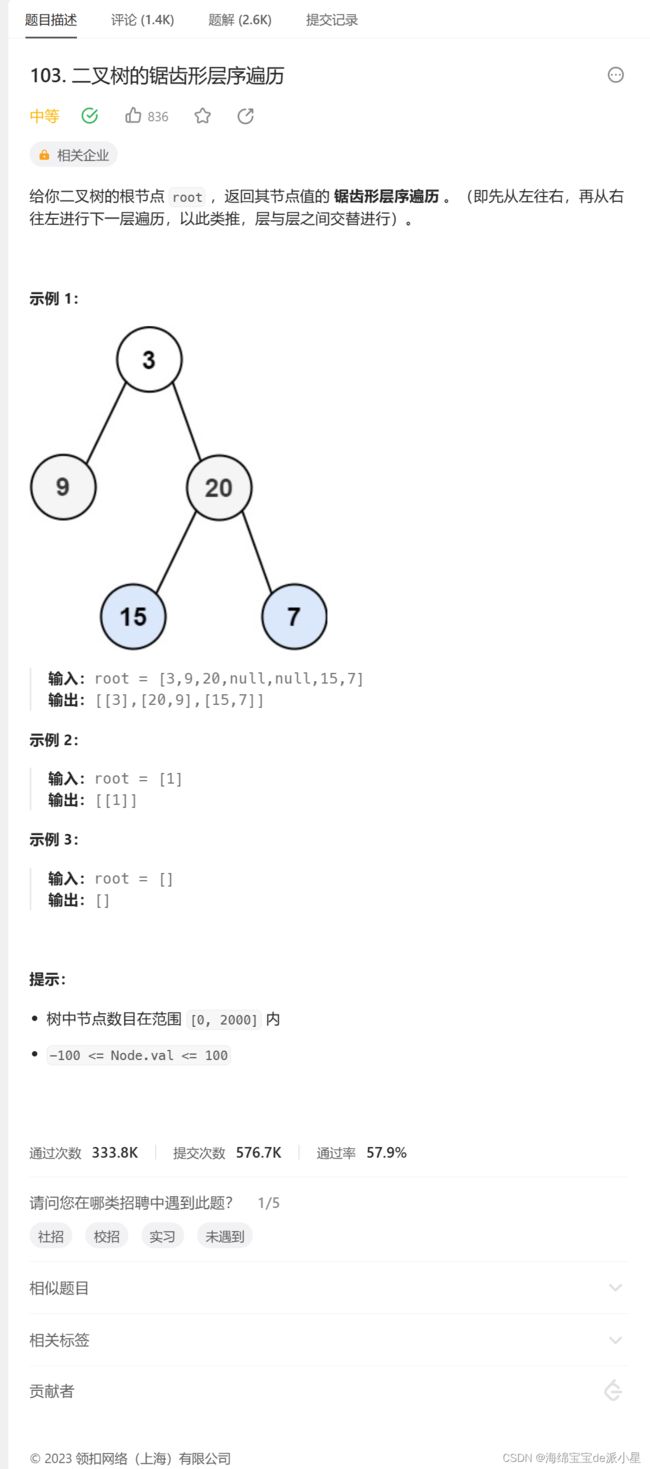
二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution
{
public:
vector<vector<int>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode* root)
{
vector<vector<int>> res;
if(root == nullptr)
return res;
bool status = true;
queue<TreeNode*> qe;
qe.push(root);
while(!qe.empty())
{
int size = qe.size();
deque<int> v;
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
TreeNode* front = qe.front();
qe.pop();
if(status)
v.push_back(front->val);
else
v.push_front(front->val);
if(front->left)
qe.push(front->left);
if(front->right)
qe.push(front->right);
}
res.push_back(vector<int>(v.begin(), v.end()));
status = !status;
}
return res;
}
};
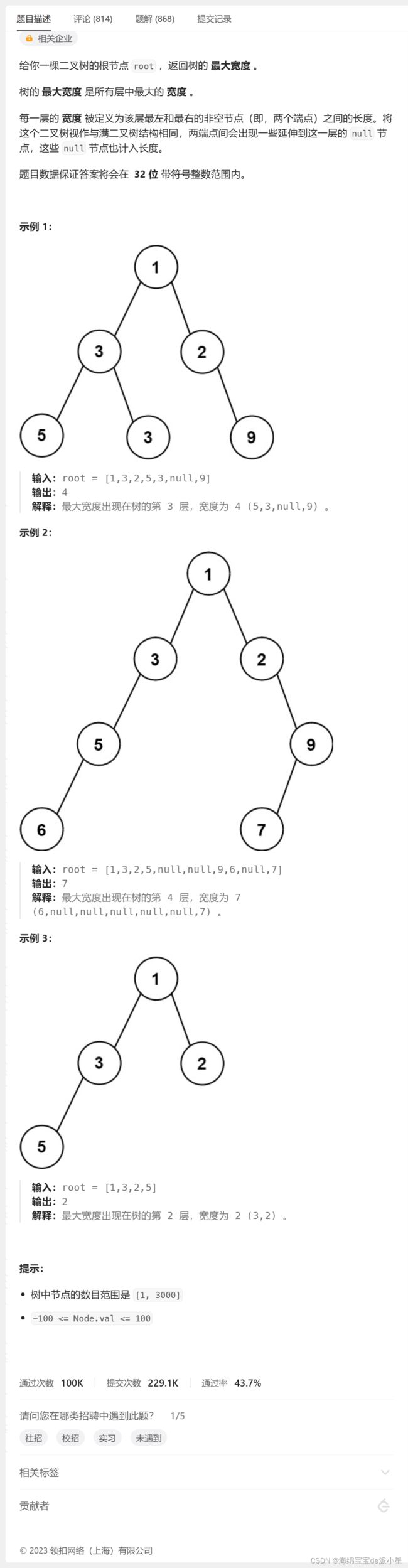
二叉树的最大宽度
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution
{
public:
int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode* root)
{
// 用数组来模拟队列,有助于最后计算,这里没用
queue<pair<TreeNode*, unsigned int>> v;
v.push(make_pair(root, 1));
unsigned int lenth = 0;
while(!v.empty())
{
// 计算一下这中间长度的差
lenth = max(lenth, v.back().second - v.front().second + 1);
int size = v.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
// 取头
auto front = v.front();
v.pop();
// 如果有左或者有右节点,就进去
if(front.first->left)
v.push(make_pair(front.first->left, (front.second) * 2));
if(front.first->right)
v.push(make_pair(front.first->right, (front.second) * 2 + 1));
}
}
return lenth;
}
};
BFS和FLoodFill相结合
图像渲染
class Solution
{
int dx[4] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
int dy[4] = {0, 0, 1, -1};
public:
vector<vector<int>> floodFill(vector<vector<int>>& image, int sr, int sc, int color)
{
int oldcolor = image[sr][sc];
int newcolor = color;
if(oldcolor == newcolor)
return image;
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.push({sr, sc});
while(!q.empty())
{
auto [a, b] = q.front();
q.pop();
image[a][b] = newcolor;
for(int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
int x = dx[k] + a, y = dy[k] + b;
if(x >= 0 && x < image.size() && y >=0 && y < image[0].size() && image[x][y] == oldcolor)
q.push({x, y});
}
}
return image;
}
};
岛屿数量
class Solution
{
int res = 0;
int dx[4] = { 1, -1, 0, 0 };
int dy[4] = { 0, 0, 1, -1 };
public:
int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid)
{
vector<vector<bool>> check;
check.resize(grid.size(), vector<bool>(grid[0].size(), false));
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
for (int i = 0; i < grid.size(); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].size(); j++)
{
if (grid[i][j] == '1' && check[i][j] == false)
{
check[i][j] = true;
q.push({ i, j });
while (!q.empty())
{
auto [a, b] = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
int x = dx[k] + a, y = dy[k] + b;
if (x >= 0 && x < grid.size() && y >= 0 && y < grid[0].size() && grid[x][y] == '1' && check[x][y] == false)
{
check[x][y] = true;
q.push({ x, y });
}
}
}
res++;
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
岛屿的最大面积
class Solution
{
public:
int maxAreaOfIsland(vector<vector<int>>& grid)
{
int res = 0, maxsize = 0, dx[4] = {1, -1, 0, 0}, dy[4] = {0, 0, 1, -1};
vector<vector<bool>> check(grid.size(), vector<bool>(grid[0].size(), false));
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
for(int i = 0; i < grid.size(); i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < grid[0].size(); j++)
{
if(check[i][j] == false && grid[i][j] == 1)
{
check[i][j] = true;
q.push({i, j});
res++;
while(!q.empty())
{
auto [a, b] = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
int x = dx[k] + a, y = dy[k] + b;
if(x >= 0 && x < grid.size() && y >= 0 && y < grid[0].size() && grid[x][y] == 1 && check[x][y] == false)
{
check[x][y] = true;
q.push({x, y});
res++;
}
}
}
maxsize = max(res, maxsize);
res = 0;
}
}
}
return maxsize;
}
};
BFS解决最短路问题
最小基因变化
class Solution
{
public:
int minMutation(string startGene, string endGene, vector<string>& bank)
{
// 首先把符合要求的字符串丢到哈希表中
unordered_map<string, int> hash;
for (auto& str : bank)
hash[str]++;
// vis数组用来存储已经加过的状态
unordered_map<string, int> visited;
char arr[4] = { 'A', 'C', 'G', 'T' };
int step = 0;
queue<string> q;
q.push(startGene);
visited[startGene]++;
while (!q.empty())
{
step++;
int qsize = q.size();
for (int k = 0; k < qsize; k++)
{
string front = q.front();
q.pop();
// 对于字符串中的每一个元素都要进行枚举
for (int i = 0; i < front.size(); i++)
{
string tmp = front;
// front中的每一个元素都要被枚举四次
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++)
{
tmp[i] = arr[j];
// 如果front在visited中存在,说明这个元素已经被找过了
if (visited.count(tmp) == 0)
{
// 如果这个元素还在bank中,那么就是有效状态,那么就可以进入队列中
if (hash.count(tmp))
{
q.push(tmp);
visited[tmp]++;
if (tmp == endGene)
return step;
}
}
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
};
单词接龙
class Solution
{
public:
int ladderLength(string beginWord, string endWord, vector<string>& wordList)
{
// 用哈希表存储符合要求的顶点和已经访问过的顶点
unordered_map<string, int> hash;
unordered_map<string, int> visited;
// 把wordlist中元素存储到哈希中
for(auto& str : wordList)
hash[str]++;
// 把wordlist中的元素含有的字母进行标记
set<int> st;
for(auto str : wordList)
{
for(auto e : str)
{
st.insert(e);
}
}
int stsize = st.size();
// 定义一些变量
int ret = 1;
queue<string> q;
q.push(beginWord);
visited[beginWord]++;
while(!q.empty())
{
int qsize = q.size();
ret++;
for(int i = 0; i < qsize; i++)
{
// 进入循环中一次,就意味着走了一步
string front = q.front();
q.pop();
// 单词的每一个字母都可以进行变换
for(int j = 0; j < front.size(); j++)
{
string tmp = front;
// 每一个字母都有26种变换方式
for(int k = 0; k < 26; k++)
{
// 如果这个元素在set中出现过就可以使用
if(st.count('a' + k))
tmp[j] = 'a' + k;
else
continue;
// 对于变换后的结果tmp,如果这个结果在list中才能继续
if(hash.count(tmp) && visited.count(tmp) == 0)
{
// 如果tmp没有被访问过才能继续
visited[tmp]++;
q.push(tmp);
if(tmp == endWord)
return ret;
}
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
};
为高尔夫比赛砍树
struct Cmp
{
bool operator()(const pair<int, pair<int, int>>& p1, const pair<int, pair<int, int>>& p2)
{
return p1.first > p2.first;
}
};
class Solution
{
int dx[4] = { 1, -1, 0, 0 };
int dy[4] = { 0, 0, 1, -1 };
public:
int cutOffTree(vector<vector<int>>& forest)
{
int m = forest.size(), n = forest[0].size();
// 首先要把矩阵的信息存储起来
priority_queue<pair<int, pair<int, int>>, vector<pair<int, pair<int, int>>>, Cmp> heap;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
if (forest[i][j] != 1 && forest[i][j] != 0)
heap.push(make_pair(forest[i][j], make_pair(i, j)));
// 此时堆中就是按高度排列,并且每一个高度会对应其下标
int step = 0;
int x = 0, y = 0;
while (!heap.empty())
{
auto top = heap.top();
heap.pop();
int ans = bfs(x, y, top.second.first, top.second.second, forest);
if (ans == -1)
return -1;
step += ans;
x = top.second.first;
y = top.second.second;
}
return step;
}
// bfs函数,用来寻找从[curx, cury]到[nextx, nexty]的最短路径
int bfs(int curx, int cury, int nextx, int nexty, vector<vector<int>>& forest)
{
if (curx == nextx && cury == nexty)
return 0;
int m = forest.size(), n = forest[0].size();
vector<vector<bool>> visited(m, vector<bool>(n, false));
int step = 0;
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.push({ curx, cury });
visited[curx][cury] = true;
while (!q.empty())
{
int qsize = q.size();
step++;
for (int i = 0; i < qsize; i++)
{
auto [a, b] = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
int x = a + dx[k], y = b + dy[k];
if (x == nextx && y == nexty)
return step;
// 如果这个下标合法,并且没有被选过,并且不是障碍,就进队列
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && visited[x][y] == false && forest[x][y] != 0)
{
visited[x][y] = true;
q.push({ x, y });
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
};
拓扑排序
课程表
class Solution
{
public:
bool canFinish(int numCourses, vector<vector<int>>& prerequisites)
{
// 1. 建图
// 一个用来存储图的边信息,一个用来存储图的入度信息
unordered_map<int, vector<int>> graph;
vector<int> in(numCourses);
// 2. 把图的信息存储到图中
for(auto& e : prerequisites)
{
int pre = e[1], next = e[0];
graph[pre].push_back(next);
in[next]++;
}
// 3. 多源bfs遍历
queue<int> q;
for(int e = 0; e < numCourses; e++)
if(in[e] == 0)
q.push(e);
while(!q.empty())
{
int front = q.front();
q.pop();
for(auto e : graph[front])
{
in[e]--;
if(in[e] == 0)
q.push(e);
}
}
// 4. 判断有没有环
for(auto e : in)
if(e)
return false;
return true;
}
};
课程表II
class Solution
{
public:
vector<int> findOrder(int numCourses, vector<vector<int>>& prerequisites)
{
vector<int> res;
// 1. 建表
unordered_map<int, vector<int>> graph;
vector<int> in(numCourses);
// 2. 把信息入表
for(auto e : prerequisites)
{
int prev = e[1], next = e[0];
graph[prev].push_back(next);
in[next]++;
}
// 3. 多源bfs
queue<int> q;
// 把入度为0的点入到队列中
for(int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++)
if(in[i] == 0)
q.push(i);
while(!q.empty())
{
int front = q.front();
q.pop();
res.push_back(front);
for(auto& e : graph[front])
{
in[e]--;
if(in[e] == 0)
{
q.push(e);
}
}
}
// 4. 判环
for(int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++)
if(in[i])
return {};
return res;
}
};
火星词典
class Solution
{
// 1. 建图
unordered_map<char, unordered_set<char>> edge;
unordered_map<char, int> in;
bool check;
public:
string alienOrder(vector<string>& words)
{
for(auto& str : words)
for(auto& ch : str)
in[ch] = 0;
string res;
// 2. 存储信息
int n = words.size();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for(int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
add(words[i], words[j]);
if(check)
return "";
// 3. 拓扑排序
queue<char> q;
for(auto& [a, b] : in)
if(b == 0)
q.push(a);
while(!q.empty())
{
char front = q.front();
q.pop();
res += front;
for(auto& ch : edge[front])
{
in[ch]--;
if(in[ch] == 0)
q.push(ch);
}
}
// 4. 检查
for(auto& [a, b] : in)
if(b)
return "";
return res;
}
void add(string& s1, string& s2)
{
int n = min(s1.size(), s2.size());
int i = 0;
for(; i < n; i++)
{
if(s1[i] != s2[i])
{
char a = s1[i], b = s2[i];
if(edge.count(a) == 0 || edge[a].count(b) == 0)
{
edge[a].insert(b);
in[b]++;
}
break;
}
}
if(i == s2.size() && i < s1.size())
check = true;
}
};