激光雷达植被叶片入射角效应/地基高光谱激光雷达植被叶片入射角效应
文章目录
-
-
- 激光雷达入射角效应
- 地基高光谱激光雷达入射角效应
- 激光雷达入射角效应模型简要发展历史(还有其他模型,在此简要列举五种)
- 1. 朗伯余弦定律。
- 2. Poullain模型
- 3. Kai Tan等多项式模型
- 4. Kaasalainen等提出的改进的与波长相关的Poullain模型
- 5. Jie Bai等提出入射角效应满足同时与波长和入射角大小相关的改进的Poullain模型,并进一步提出了激光雷达回波强度和反射率的入射角效应校正公式。
-
激光雷达入射角效应
激光雷达入射角效应:激光雷达发射脉冲和目标物表面法线之间的夹角称为入射角,入射角效应指激光雷达发射脉冲在与目标物表面发生交互作用后返回的回波强度会随这个入射角变化而变化的现象。需要指出的是,激光雷达入射角效应与被测目标表面反射特性密切相关,除发射脉冲和系统噪声外,入射角效应与仪器本身构造无关。较为常见的入射角效应模型有朗伯余弦定律、多项式模型和Poullain模型及改进型等(还有其他方法,在此简要列举五种)。
地基高光谱激光雷达入射角效应
对于地基高光谱激光雷达来说,这种入射角效应更为复杂,丰富的波长信息使得入射角效应之间不尽相同,因此需要找出一种可以表达地基高光谱激光雷达植被入射角效应同时具有物理意义的模型。
激光雷达入射角效应模型简要发展历史(还有其他模型,在此简要列举五种)
1. 朗伯余弦定律。
I = f ∗ c o s α I = f*cos\alpha I=f∗cosα
2. Poullain模型
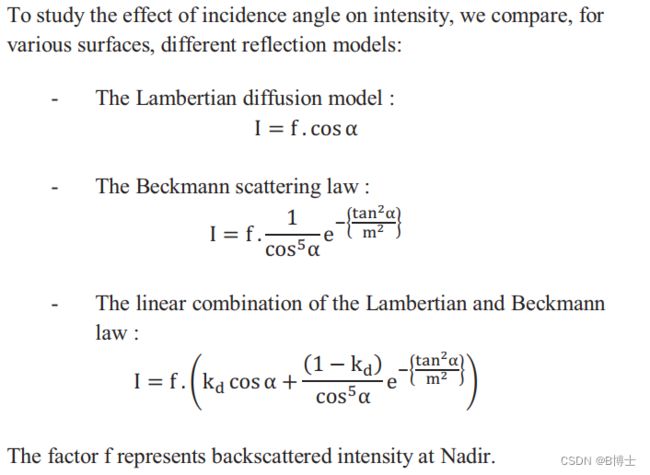
Poullain等于2012年提出Poullain模型,用一种朗伯余弦定律Lambertian cosine law和贝克曼散射定律Beckmann scattering law的组合(简称Poullain模型)去表征海岸带表面的后向散射强度分布。
参考文献
E. Poullain, F. Garestier, P. Bretel, and F. Levoy, “Modeling of ALS intensity behavior as a function of incidence angle for coastal zone surface study,” in Proc. IEEE Int. Geosci. Remote Sens. Symp., Jul. 2012, pp. 2849–2852.
3. Kai Tan等多项式模型
Tan, K., Cheng, X., 2015. Intensity data correction based on incidence angle and distance for terrestrial laser scanner. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 9 (1), 094094.
4. Kaasalainen等提出的改进的与波长相关的Poullain模型
Kaasalainen等2018年将Poullain模型用于8波长的多光谱激光雷达植被叶片入射角效应研究中,将粗糙度因子m视为一个广义粗糙度因子,计算出了不同波长下的Poullain模型中参数分布。
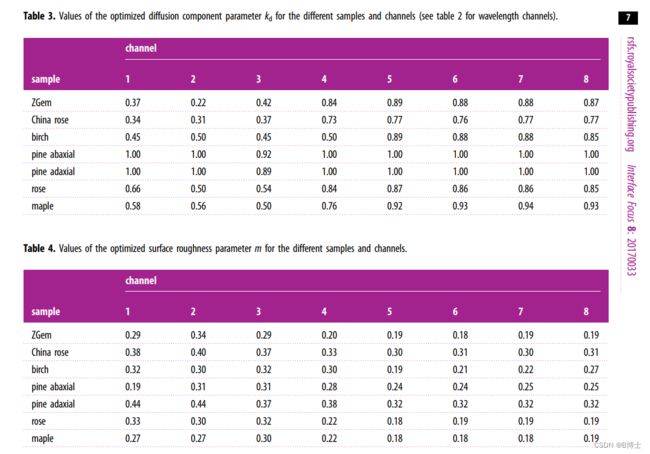
参考文献:
S. Kaasalainen, M. Åkerblom, O. Nevalainen, T. Hakala, and M. Kaasalainen, “Uncertainty in multispectral LiDAR signals caused by incidence angle effects,” Interface Focus, vol. 8, no. 2, Apr. 2018, Art. no. 20170033.
5. Jie Bai等提出入射角效应满足同时与波长和入射角大小相关的改进的Poullain模型,并进一步提出了激光雷达回波强度和反射率的入射角效应校正公式。
受Rees著《遥感物理》一书的启发,
Δ h < λ 8 c o s α \Delta h<\frac{\lambda}{8cos{\alpha}} Δh<8cosαλ
Jie Bai等2021年将改进的Poullain模型用于32波长的高光谱激光雷达植被叶片入射角效应研究中,他将漫反射因子 k d k_d kd和粗糙度因子 m m m视为广义漫反射和粗糙度因子,计算出了不同波长和入射角下的Poullain模型中参数分布。
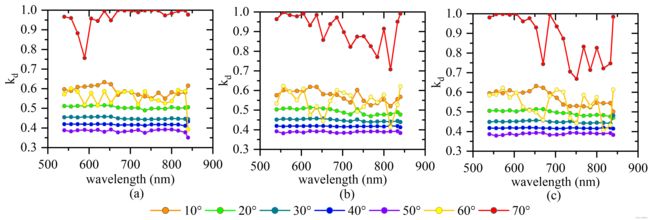

参考文献:
W. G. Rees, Physical Principles of Remote Sensing. Cambridge, U.K.: Cambridge Univ. Press, 2013, pp. 62–63.
Bai, J., Gao, S., Niu, Z., Zhang, C., Bi, K., Sun, G., Huang, Y., 2021. A Novel Algorithm for Leaf Incidence Angle Effect Correction of Hyperspectral LiDAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 60, 1–9.