数据结构之二叉搜索树(C++实现)
数据结构之二叉搜索树(C++)
我之前的博客已经介绍过了二叉树的基本概念和简单实现,具体参考数据结构-树(C语言实现篇)。
1. 二叉搜索树
1.1 二叉搜索树的概念
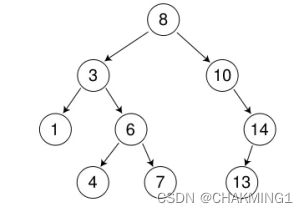
二叉搜索树又称二叉排序树,它可以是一颗空树或者满足以下性质的二叉树:
- 若它的左子树不为空,则左子树上所有节点的值小于根节点的值。
- 若它的右子树不为空,则右子树上所有节点的值小于根节点的值。
- 它的左右子树都是二叉搜索树。
1.2 二叉搜索树的操作
二叉搜索树的操作基本上是查找、插入、删除。
- 二叉搜索树的查找
- 从根开始比较,如果比当前结点要小,那么就往左子树查找,如果比当前结点要大,就往右子树查找。
- 最多查找高度次,如果走到空,说明该树不存在这个值。
- 二叉搜索树的插入
- 若树为空,则把当前要插入的结点作为根节点。
- 若树不为空,首先按照二叉搜索树的查找规则,找到要插入的结点的位置,进行插入。
- 二叉搜索树的删除
- 首先查找元素是否在二叉搜索树,如果不存在,就返回。如果存在,删除的结点可能分为以下四种情况:
- 要删除的结点无孩子结点。
- 要删除的结点只有左孩子。
- 要删除的结点只有右孩子。
- 要删除的结点有左右孩子。
- 针对以上四种情况,分别做的处理是:
- 直接删除该结点。
- 删除该结点并且使被删除结点的双亲结点指向被删除结点的左孩子结点。
- 删除该结点并且使被删除结点的双亲结点指向被删除结点的右孩子结点。
- 在它的右子树中寻找中序下第一个结点(关键值最小),用它的值填补到被删除节点中,再来处理该结点的删除问题。
- 首先查找元素是否在二叉搜索树,如果不存在,就返回。如果存在,删除的结点可能分为以下四种情况:
2. 二叉搜索树的实现
#ifndef BINARYSEARCHTREE_HPP
#define BINARYSEARCHTREE_HPP
#include 3. 二叉搜索树的应用
- K模型:K模型只有结构中只存储Key。具体场景如下:
- 给一个单词word,判断该单词是否拼写正确。用word去查找词库当中是否拥有这个单词,若无,表示拼写错误。
- KV模型:每一个关键字Key,都会有与之对应的Value值,即
- 我们知道一个单词会有对应的一个中文,那么这种结构就是根据一个英文单词去查找对应的Value值,也就是中文意思。
- 统计单词次数,将
// 改造二叉树为KV结构
namespace KeyValue {
template<class K, class V>
struct BSTreeNode {
BSTreeNode(const K &key, const V &value)
: _key(key), _value(value), _left(nullptr), _right(nullptr) {}
BSTreeNode<K, V> *_left; // 左节点
BSTreeNode<K, V> *_right; // 右节点
K _key; // 值
V _value;
};
// key,value型
template<class K, class V> // key
class BSTree {
using Node = BSTreeNode<K, V>;
public:
bool Insert(const K &key, const V &value) {
if (_root == nullptr) {
_root = new Node(key,value);
return true;
}
Node *cur = _root;
Node *parent = nullptr;
while (cur) {
parent = cur;
if (cur->_key < key)
cur = cur->_right;
else if (cur->_key > key)
cur = cur->_left;
else
return false; // 这个值在这个树已经存在
}
cur = new Node(key,value);
if (parent->_key < key)
parent->_right = cur;
else
parent->_left = cur;
return true;
}
Node *Find(const K &key) {
Node *cur = _root;
while (cur) {
if (cur->_key < key)
cur = cur->_right;
else if (cur->_key > key)
cur = cur->_left;
else
return cur;
}
return nullptr;
}
bool Erase(const K &key) {
return true;
}
void Inorder() {
_Inorder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
private:
// 中序遍历
void _Inorder(Node *root) {
if (root == nullptr)
return;
_Inorder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << " : " << root->_value << " ";
_Inorder(root->_right);
}
private:
Node *_root = nullptr;
};
}
4. 二叉搜索树的性能分析
插入和删除操作都必须先查找对应的位置,才能够进行插入和删除。所以查找是二叉搜索树的关键。
对于有n个结点的二叉搜索树,通常查找的次数为高度次,那么也就是说该结点的深度越深,比较的次数越多。
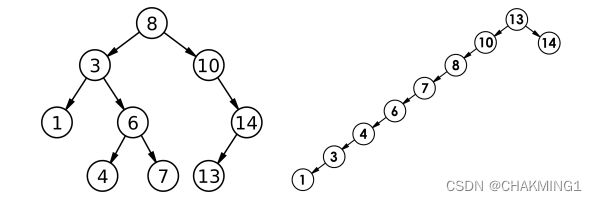
同样的数据,插入情况不同,可能得到不同的结果,不同的形状会导致查找效率不同。
最优情况下,二叉搜索树是完全二叉树,平均比较次数为log_2(n)。
最差情况下,二叉搜索树退化为单支数,比较次数为n。
那么,一旦退化成单支树,效率就会大大减少,所以我们可以用AVL树或者红黑树进行优化。
5. 二叉树的练习题
-
二叉树创建字符串
class Solution { public: string tree2str(TreeNode* root) { if(root == nullptr) return string(); string str; str += to_string(root->val); if(root->left || root->right) { str += '('; str += tree2str(root->left); str += ')'; } if(root->right) { str += '('; str += tree2str(root->right); str += ')'; } return str; } }; -
二叉树的分层遍历1
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) { queue<TreeNode*> q; vector<vector<int>> vv; if(root == nullptr) return vv; q.push(root); size_t levelSize = 1; // 用来控制每层的个数 while(!q.empty()) { // 控制一层一层出 vector<int> v; for(size_t i = 0;i < levelSize;++i) { TreeNode* front = q.front(); q.pop(); v.push_back(front->val); if(front->left) q.push(front->left); if(front->right) q.push(front->right); } vv.push_back(v); levelSize = q.size(); } return vv; } }; -
二叉树的分层遍历2
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode* root) { vector<vector<int>> v; if(root == nullptr) return v; stack<vector<int>> st; queue<TreeNode*> q; q.push(root); while(!q.empty()) { int size = q.size(); vector<int> tmp; for(int i = 0;i < size;++i) { TreeNode* cur = q.front(); q.pop(); tmp.push_back(cur->val); if(cur->left) q.push(cur->left); if(cur->right) q.push(cur->right); } st.push(tmp); } while(!st.empty()) { vector<int> tmp = st.top(); st.pop(); v.push_back(tmp); } return v; } }; -
二叉树的最近公共祖先
class Solution { public: bool FindPath(TreeNode* root,TreeNode* x,stack<TreeNode*>& path) { if(root == nullptr) return false; path.push(root); if(root == x) return true; if(FindPath(root->left,x,path)) return true; if(FindPath(root->right,x,path)) return true; path.pop(); return false; } TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) { stack<TreeNode*> pPath,qPath; FindPath(root,p,pPath); FindPath(root,q,qPath); while(pPath.size() != qPath.size()) { if(pPath.size() > qPath.size()) pPath.pop(); else qPath.pop(); } while(pPath.top() != qPath.top()) { pPath.pop(); qPath.pop(); } return pPath.top(); } }; -
二叉搜索树与双向链表
class Solution { public: void InOrderConvert(TreeNode* cur,TreeNode*& prev) { if(cur == nullptr) return; InOrderConvert(cur->left, prev); cur->left = prev; if(prev) prev->right = cur; prev = cur; InOrderConvert(cur->right, prev); } TreeNode* Convert(TreeNode* pRootOfTree) { TreeNode* prev = nullptr; InOrderConvert(pRootOfTree,prev); TreeNode *head = pRootOfTree; while(head && head->left) head = head->left; return head; } }; -
根据前序和中序构造二叉树
class Solution { public: TreeNode* _buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder, int& previ,int inbegin,int inend) { if(inbegin > inend) return nullptr; TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(preorder[previ++]); int ini = inbegin; while(ini <= inend) { if(inorder[ini] == root->val) break; else ++ini; } root->left = _buildTree(preorder,inorder,previ,inbegin,ini-1); root->right = _buildTree(preorder,inorder,previ,ini+1,inend); return root; } TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) { int i = 0; return _buildTree(preorder,inorder,i,0,inorder.size()-1); } }; -
根据中序和后序构造二叉树
class Solution { public: TreeNode* _buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder,int& posti,int inbegin,int inend) { if(inbegin > inend) return nullptr; TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(postorder[posti--]); // 找到根节点在中序的位置 int ini = inbegin; while(ini <= inend) { if(inorder[ini] == root->val) break; ini++; } // root->right = _buildTree(inorder,postorder,posti,ini+1,inend); root->left = _buildTree(inorder,postorder,posti,inbegin,ini-1); return root; } TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) { int i = postorder.size()-1; return _buildTree(inorder,postorder,i,0,inorder.size()-1); } }; -
前序遍历的非递归写法
class Solution { public: vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) { vector<int> v; stack<TreeNode*> st; TreeNode* cur = root; while(cur || !st.empty()) { // 先访问左路结点 while(cur) { v.push_back(cur->val); st.push(cur); cur = cur->left; } TreeNode* top = st.top(); st.pop(); cur = top->right; } return v; } }; -
中序遍历的非递归写法
class Solution { public: vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) { stack<TreeNode*> st; vector<int> v; TreeNode* cur = root; while(cur || !st.empty()) { while(cur) { st.push(cur); cur = cur->left; } TreeNode* top = st.top(); v.push_back(top->val); st.pop(); cur = top->right; } return v; } }; -
后序遍历的非递归写法
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> v;
stack<TreeNode*> st;
TreeNode* prev = nullptr;
TreeNode* cur = root;
while(cur || !st.empty())
{
while(cur)
{
st.push(cur);
cur = cur->left;
}
TreeNode* top = st.top();
if(top->right == nullptr || top->right == prev)
{
v.push_back(top->val);
prev = top;
st.pop();
}
else
{
cur = top->right;
}
}
return v;
}
};