在WIN从零开始在QMUE上添加一块自己的开发板(二)
文章目录
- 一、前言
-
- 往期回顾
- 二、CPU虚拟化
-
- (一)相关源码
- (二)举个例子
- (三)测试
- 三、内存虚拟化
-
- (一)相关源码
- (二)举个例子
- 测试
- 参考资料
一、前言
笔者这篇博客作为平时学习时的笔记记录,如有不对还望指正,本博客大量借鉴资料,笔者只是拾人牙慧的小屁孩。
QEMU是一种通用的开源计算机仿真器和虚拟器。而QUME内置支持了一些开发板,我们可以基于这些内置的板子来做操作系统等软件的配置,但是实际市面上很多板子QUME中是没有提供支持的,这需要我们根据QUME的源码自定义一些开发板,然后再重新编译。
往期回顾
在WIN从零开始在QMUE上添加一块自己的开发板(一)
二、CPU虚拟化
(一)相关源码
QEMU中RISC-V CPU的支持
QOM的TYPE定义
target/riscv/cpu.h:
#define TYPE_RISCV_CPU "riscv-cpu"
#define RISCV_CPU_TYPE_SUFFIX "-" TYPE_RISCV_CPU
#define RISCV_CPU_TYPE_NAME(name) (name RISCV_CPU_TYPE_SUFFIX)
#define CPU_RESOLVING_TYPE TYPE_RISCV_CPU
#define TYPE_RISCV_CPU_ANY RISCV_CPU_TYPE_NAME("any")
#define TYPE_RISCV_CPU_BASE32 RISCV_CPU_TYPE_NAME("rv32")
#define TYPE_RISCV_CPU_BASE64 RISCV_CPU_TYPE_NAME("rv64")
#define TYPE_RISCV_CPU_IBEX RISCV_CPU_TYPE_NAME("lowrisc-ibex")
#define TYPE_RISCV_CPU_SIFIVE_E31 RISCV_CPU_TYPE_NAME("sifive-e31")
#define TYPE_RISCV_CPU_SIFIVE_E34 RISCV_CPU_TYPE_NAME("sifive-e34")
#define TYPE_RISCV_CPU_SIFIVE_E51 RISCV_CPU_TYPE_NAME("sifive-e51")
#define TYPE_RISCV_CPU_SIFIVE_U34 RISCV_CPU_TYPE_NAME("sifive-u34")
#define TYPE_RISCV_CPU_SIFIVE_U54 RISCV_CPU_TYPE_NAME("sifive-u54")
TYPE用于hash表的key(GHashTable.key),而hash表的值也就是ObjectClass、Object。
Class
RISCVCPUClass继承于CPUClass,然后继承于DeviceClass。
CPUClass中有很多接口:
struct CPUClass {
DeviceClass parent_class;
ObjectClass *(*class_by_name)();
void (*parse_features)();
int reset_dump_flags;
bool (*has_work)();
bool (*virtio_is_big_endian)();
int (*memory_rw_debug)();
void (*dump_state)();
GuestPanicInformation* (*get_crash_info)();
void (*dump_statistics)();
int64_t (*get_arch_id)();
bool (*get_paging_enabled)();
void (*get_memory_mapping)();
void (*set_pc)();
hwaddr (*get_phys_page_debug)();
hwaddr (*get_phys_page_attrs_debug)();
int (*asidx_from_attrs)();
int (*gdb_read_register)();
int (*gdb_write_register)();
int (*write_elf64_note)();
int (*write_elf64_qemunote)();
int (*write_elf32_note)();
int (*write_elf32_qemunote)();
const VMStateDescription *vmsd;
const char *gdb_core_xml_file;
gchar * (*gdb_arch_name)();
const char * (*gdb_get_dynamic_xml)();
void (*disas_set_info)();
const char *deprecation_note;
int gdb_num_core_regs;
bool gdb_stop_before_watchpoint;
struct AccelCPUClass *accel_cpu;
struct TCGCPUOps *tcg_ops;
};
我们着重看一下struct TCGCPUOps:
struct TCGCPUOps {
void (*initialize)(void);
void (*synchronize_from_tb)(CPUState *cpu, const TranslationBlock *tb);
void (*cpu_exec_enter)(CPUState *cpu);
void (*cpu_exec_exit)(CPUState *cpu);
bool (*cpu_exec_interrupt)(CPUState *cpu, int interrupt_request);
void (*do_interrupt)(CPUState *cpu);
bool (*tlb_fill)(CPUState *cpu, vaddr address, int size,
MMUAccessType access_type, int mmu_idx,
bool probe, uintptr_t retaddr);
void (*debug_excp_handler)(CPUState *cpu);
#ifdef NEED_CPU_H
#ifdef CONFIG_SOFTMMU
void (*do_transaction_failed)(CPUState *cpu, hwaddr physaddr, vaddr addr,
unsigned size, MMUAccessType access_type,
int mmu_idx, MemTxAttrs attrs,
MemTxResult response, uintptr_t retaddr);
void (*do_unaligned_access)(CPUState *cpu, vaddr addr,
MMUAccessType access_type,
int mmu_idx, uintptr_t retaddr);
vaddr (*adjust_watchpoint_address)(CPUState *cpu, vaddr addr, int len);
bool (*debug_check_watchpoint)(CPUState *cpu, CPUWatchpoint *wp);
bool (*io_recompile_replay_branch)(CPUState *cpu,
const TranslationBlock *tb);
#endif /* CONFIG_SOFTMMU */
#endif /* NEED_CPU_H */
};
可以看见里面有很多CPU运行时的接口。
在不同架构中,我们进行相应的实现,对于RISCVCPU,已经有相应的实现了:
static struct TCGCPUOps riscv_tcg_ops = {
.initialize = riscv_translate_init,
.synchronize_from_tb = riscv_cpu_synchronize_from_tb,
.cpu_exec_interrupt = riscv_cpu_exec_interrupt,
.tlb_fill = riscv_cpu_tlb_fill,
#ifndef CONFIG_USER_ONLY
.do_interrupt = riscv_cpu_do_interrupt,
.do_transaction_failed = riscv_cpu_do_transaction_failed,
.do_unaligned_access = riscv_cpu_do_unaligned_access,
#endif /* !CONFIG_USER_ONLY */
};
Object
对于CPU中寄存器的定义都在Object中:
struct CPURISCVState {
target_ulong gpr[32];
uint64_t fpr[32]; /* assume both F and D extensions */
/* vector coprocessor state. */
uint64_t vreg[32 * RV_VLEN_MAX / 64] QEMU_ALIGNED(16);
//vector reg
target_ulong pc;
target_ulong misa;
uint32_t features;
/* Hypervisor CSRs */
/* Virtual CSRs */
/* HS Backup CSRs */
/* temporary htif regs */
/* physical memory protection */
/* machine specific rdtime callback */
/* True if in debugger mode. */
bool debugger;
float_status fp_status;
/* Fields from here on are preserved across CPU reset. */
QEMUTimer *timer; /* Internal timer */
};
实例化
struct RISCVCPU {
/*< private >*/
CPUState parent_obj;
/*< public >*/
CPUNegativeOffsetState neg;
CPURISCVState env;
char *dyn_csr_xml;
/* Configuration Settings */
struct {
……
} cfg;
};
RISCV CPU TypeInfo注册:
.instance_init = riscv_cpu_init,
.class_init = riscv_cpu_class_init,
特殊的CPU使用特殊的函数进行实例
.instance_init = rvxx_sifive_e_cpu_init,
.class_init = riscv_cpu_class_init,
在特殊的函数中,将会针对不同CPU的特性进行个性化实例:
static void rvxx_sifive_e_cpu_init(Object *obj)
{
CPURISCVState *env = &RISCV_CPU(obj)->env;
set_misa(env, RVXLEN | RVI | RVM | RVA | RVC | RVU);
set_priv_version(env, PRIV_VERSION_1_10_0);
set_resetvec(env, 0x1004);
qdev_prop_set_bit(DEVICE(obj), "mmu", false);
}
(二)举个例子
我们为之前创建的开发板增加CPU。
我们去target\riscv\cpu-qom.h,添加一个我们自己的CPU:
...
#define RISCV_CPU_TYPE_SUFFIX "-" TYPE_RISCV_CPU
#define RISCV_CPU_TYPE_NAME(name) (name RISCV_CPU_TYPE_SUFFIX)
#define TYPE_RISCV_CPU_ANY RISCV_CPU_TYPE_NAME("any")
#define TYPE_RISCV_CPU_MAX RISCV_CPU_TYPE_NAME("max")
#define TYPE_RISCV_CPU_BASE32 RISCV_CPU_TYPE_NAME("rv32")
#define TYPE_RISCV_CPU_BASE64 RISCV_CPU_TYPE_NAME("rv64")
#define TYPE_RISCV_CPU_BASE128 RISCV_CPU_TYPE_NAME("x-rv128")
#define TYPE_RISCV_CPU_IBEX RISCV_CPU_TYPE_NAME("lowrisc-ibex")
#define TYPE_RISCV_CPU_SHAKTI_C RISCV_CPU_TYPE_NAME("shakti-c")
#define TYPE_RISCV_CPU_SIFIVE_E31 RISCV_CPU_TYPE_NAME("sifive-e31")
#define TYPE_RISCV_CPU_SIFIVE_E34 RISCV_CPU_TYPE_NAME("sifive-e34")
#define TYPE_RISCV_CPU_SIFIVE_E51 RISCV_CPU_TYPE_NAME("sifive-e51")
#define TYPE_RISCV_CPU_SIFIVE_U34 RISCV_CPU_TYPE_NAME("sifive-u34")
#define TYPE_RISCV_CPU_SIFIVE_U54 RISCV_CPU_TYPE_NAME("sifive-u54")
#define TYPE_RISCV_CPU_THEAD_C906 RISCV_CPU_TYPE_NAME("thead-c906")
#define TYPE_RISCV_CPU_VEYRON_V1 RISCV_CPU_TYPE_NAME("veyron-v1")
#define TYPE_RISCV_CPU_HOST RISCV_CPU_TYPE_NAME("host")
/* 添加自己的CPU */
#define TYPE_RISCV_CPU_NUCLEI_N600 RISCV_CPU_TYPE_NAME("nuclei-n600")
并在./target/riscv/cpu.c中,添加其初始化函数:
#if defined(TARGET_RISCV32)
/* 自己的CPU */
static void rv32_nuclei_n_cpu_init(Object *obj)
{
CPURISCVState *env = &RISCV_CPU(obj)->env;
RISCVCPU *cpu = RISCV_CPU(obj);
riscv_cpu_set_misa(env, MXL_RV32, RVI | RVM | RVA | RVC | RVF | RVD | RVU);
env->priv_ver= PRIV_VERSION_1_10_0;
#ifndef CONFIG_USER_ONLY
set_satp_mode_max_supported(cpu, VM_1_10_MBARE);
#endif
/* inherited from parent obj via riscv_cpu_init() */
cpu->cfg.ext_zifencei = true;
cpu->cfg.ext_zicsr = true;
cpu->cfg.pmp = true;
}
#endif
并在riscv_cpu_type_infos中添加DEFINE
static const TypeInfo riscv_cpu_type_infos[] = {
{
.name = TYPE_RISCV_CPU,
.parent = TYPE_CPU,
.instance_size = sizeof(RISCVCPU),
.instance_align = __alignof(RISCVCPU),
.instance_init = riscv_cpu_init,
.instance_post_init = riscv_cpu_post_init,
.abstract = true,
.class_size = sizeof(RISCVCPUClass),
.class_init = riscv_cpu_class_init,
},
{
.name = TYPE_RISCV_DYNAMIC_CPU,
.parent = TYPE_RISCV_CPU,
.abstract = true,
},
DEFINE_DYNAMIC_CPU(TYPE_RISCV_CPU_ANY, riscv_any_cpu_init),
DEFINE_DYNAMIC_CPU(TYPE_RISCV_CPU_MAX, riscv_max_cpu_init),
#if defined(TARGET_RISCV32)
DEFINE_DYNAMIC_CPU(TYPE_RISCV_CPU_BASE32, rv32_base_cpu_init),
DEFINE_CPU(TYPE_RISCV_CPU_IBEX, rv32_ibex_cpu_init),
DEFINE_CPU(TYPE_RISCV_CPU_SIFIVE_E31, rv32_sifive_e_cpu_init),
DEFINE_CPU(TYPE_RISCV_CPU_SIFIVE_E34, rv32_imafcu_nommu_cpu_init),
DEFINE_CPU(TYPE_RISCV_CPU_SIFIVE_U34, rv32_sifive_u_cpu_init),
/* 自己的CPU */
DEFINE_CPU(TYPE_RISCV_CPU_NUCLEI_N600, rv32_nuclei_n_cpu_init),
#elif defined(TARGET_RISCV64)
DEFINE_DYNAMIC_CPU(TYPE_RISCV_CPU_BASE64, rv64_base_cpu_init),
DEFINE_CPU(TYPE_RISCV_CPU_SIFIVE_E51, rv64_sifive_e_cpu_init),
DEFINE_CPU(TYPE_RISCV_CPU_SIFIVE_U54, rv64_sifive_u_cpu_init),
DEFINE_CPU(TYPE_RISCV_CPU_SHAKTI_C, rv64_sifive_u_cpu_init),
DEFINE_CPU(TYPE_RISCV_CPU_THEAD_C906, rv64_thead_c906_cpu_init),
DEFINE_CPU(TYPE_RISCV_CPU_VEYRON_V1, rv64_veyron_v1_cpu_init),
DEFINE_DYNAMIC_CPU(TYPE_RISCV_CPU_BASE128, rv128_base_cpu_init),
#endif
};
接着我们回到我们的开发板文件,
这里讲个小技巧,也就是从include\hw\riscv\virt.h(官方虚拟开发板的例程)看相关的引用,从而确定相关头文件的所在位置和相关代码的实现。
在我们的nuclei_n.h中(请注意,为了方便理解,这里对往期变量及函数的名字进行了更改):
引入头文件
#include "hw/riscv/riscv_hart.h"
并在SOC中添加CPU
/* CPU 定义 */
#define NUCLEI_N_CPU TYPE_RISCV_CPU_NUCLEI_N600
typedef struct NucLeiNSoCState
{
/*< private >*/
SysBusDevice parent_obj;
/*< public >*/
RISCVHartArrayState cpus;
} NucLeiNSoCState;
以及一些TYPE:
#define NUCLEI_N_CPU TYPE_RISCV_CPU_NUCLEI_N600
之后我们在Machine的Class里面增加最小CPU个数和默认CPU的TYPE:
static void nuclei_machine_class_init(ObjectClass *oc, void *data)
{
qemu_log(">>nuclei_machine_class_init \n");
MachineClass *mc = MACHINE_CLASS(oc);
mc->desc = "Nuclei MCU 200T FPGA Evaluation Kit";
mc->init = nuclei_mcu_machine_init;
mc->max_cpus = 1;
mc->default_cpu_type = NUCLEI_N_CPU;
}
我们在SOC实例初始化函数中,对CPU初始化:
static void nuclei_n_soc_instance_init(Object *obj)
{
qemu_log(">>nuclei_n_soc_instance_init \n");
NucLeiNSoCState *s = NUCLEI_N_SOC(obj);
object_initialize_child(obj, "cpus", &s->cpus, TYPE_RISCV_HART_ARRAY); //初始化CPU
}
并在SOC实现中(nuclei_n_soc_realize)进行CPU的实现:
static void nuclei_n_soc_realize(DeviceState *dev, Error **errp)
{
qemu_log(">>nuclei_n_soc_realize \n");
MachineState *ms = MACHINE(qdev_get_machine());
NucLeiNSoCState *s = NUCLEI_N_SOC(dev);
object_property_set_str(OBJECT(&s->cpus), "cpu-type", ms->cpu_type, &error_abort);
object_property_set_int(OBJECT(&s->cpus), "num-harts", ms->smp.cpus, &error_abort);
sysbus_realize(SYS_BUS_DEVICE(&s->cpus), &error_abort); //CPU实例化
}
附上完整:
nuclei_n.h:
#include "hw/sysbus.h"
#include "hw/riscv/riscv_hart.h"
#define TYPE_NUCLEI_N_SOC "riscv.nuclei.n.soc"
#define NUCLEI_N_SOC(obj) \
OBJECT_CHECK(NucLeiNSoCState, (obj), TYPE_NUCLEI_N_SOC)
/* CPU 定义 */
#define NUCLEI_N_CPU TYPE_RISCV_CPU_NUCLEI_N600
typedef struct NucLeiNSoCState
{
/*< private >*/
SysBusDevice parent_obj;
/*< public >*/
RISCVHartArrayState cpus;
} NucLeiNSoCState;
/* Machine state定义 */
#define TYPE_NUCLEI_MCU_FPGA_MACHINE MACHINE_TYPE_NAME("mcu_200t")
#define MCU_FPGA_MACHINE(obj) \
OBJECT_CHECK(NucLeiNState, (obj), TYPE_NUCLEI_MCU_FPGA_MACHINE)
typedef struct NucLeiNState
{
/*< private >*/
SysBusDevice parent_obj;
/*< public >*/
NucLeiNSoCState soc;
} NucLeiNState;
nuclei_n.c:
#include "qemu/osdep.h"
#include "qemu/log.h"
#include "qemu/error-report.h"
#include "qapi/error.h"
#include "hw/riscv/nuclei_n.h"
#include "hw/boards.h"
static void nuclei_n_soc_instance_init(Object *obj)
{
qemu_log(">>nuclei_n_soc_instance_init \n");
NucLeiNSoCState *s = NUCLEI_N_SOC(obj);
object_initialize_child(obj, "cpus", &s->cpus, TYPE_RISCV_HART_ARRAY); //初始化CPU
}
static void nuclei_n_soc_realize(DeviceState *dev, Error **errp)
{
qemu_log(">>nuclei_n_soc_realize \n");
MachineState *ms = MACHINE(qdev_get_machine());
NucLeiNSoCState *s = NUCLEI_N_SOC(dev);
object_property_set_str(OBJECT(&s->cpus), "cpu-type", ms->cpu_type, &error_abort);
object_property_set_int(OBJECT(&s->cpus), "num-harts", ms->smp.cpus, &error_abort);
sysbus_realize(SYS_BUS_DEVICE(&s->cpus), &error_abort); //CPU实例化
}
static void nuclei_n_soc_class_init(ObjectClass *oc, void *data)
{
qemu_log(">>nuclei_n_soc_class_init \n");
DeviceClass *dc = DEVICE_CLASS(oc);
dc->realize = nuclei_n_soc_realize;
dc->user_creatable = false;
}
static const TypeInfo nuclei_n_soc_type_info = {
.name = TYPE_NUCLEI_N_SOC,
.parent = TYPE_DEVICE,
.instance_size = sizeof(NucLeiNSoCState),
.instance_init = nuclei_n_soc_instance_init,
.class_init = nuclei_n_soc_class_init,
};
static void nuclei_n_soc_register_types(void)
{
type_register_static(&nuclei_n_soc_type_info);
}
type_init(nuclei_n_soc_register_types)
static void nuclei_mcu_machine_init(MachineState *machine)
{
NucLeiNState *s = MCU_FPGA_MACHINE(machine);
qemu_log(">>nuclei_mcu_machine_init \n");
/* Initialize SOC */
object_initialize_child(OBJECT(machine), "soc", &s->soc, TYPE_NUCLEI_N_SOC);
qdev_realize(DEVICE(&s->soc), NULL, &error_abort);
}
static void nuclei_machine_instance_init(Object *obj)
{
qemu_log(">>nuclei_machine_instance_init \n");
}
static void nuclei_machine_class_init(ObjectClass *oc, void *data)
{
qemu_log(">>nuclei_machine_class_init \n");
MachineClass *mc = MACHINE_CLASS(oc);
mc->desc = "Nuclei MCU 200T FPGA Evaluation Kit";
mc->init = nuclei_mcu_machine_init;
mc->max_cpus = 1;
mc->default_cpu_type = NUCLEI_N_CPU;
}
static const TypeInfo nuclei_machine_typeinfo = {
.name = TYPE_NUCLEI_MCU_FPGA_MACHINE,
.parent = TYPE_MACHINE,
.class_init = nuclei_machine_class_init,
.instance_init = nuclei_machine_instance_init,
.instance_size = sizeof(NucLeiNState),
};
static void nuclei_machine_init_register_types(void)
{
type_register_static(&nuclei_machine_typeinfo);
}
type_init(nuclei_machine_init_register_types)
不用忘记在./target/riscv/cpu.c去定义CPU哦。
(三)测试
执行run.sh:
SHELL_FOLDER=$(cd "$(dirname "$0")";pwd)
$SHELL_FOLDER/output/qemu/qemu-system-riscv32.exe \
-M mcu_200t
三、内存虚拟化
(一)相关源码
有了之前的开发经验,我们这次直接看相关API:
| Types of regions | initialize |
|---|---|
| RAM | memory_region_init_ram() |
| MMIO | memory_region_init_io() |
| ROM | memory_region_init_rom() |
| ROM_evice | memory_region_init_rom_device() |
| IOMMU region | memory_region_init_iommu() |
| container | memory_region_init() |
| alias | memory_region_init_alias() |
| reservation region | memory_region_init_io() |
其次是添加硬件的地址和映射的地址长度的结构体:
(注意这里的长度不能为0,不然会报错)
typedef struct MemMapEntry {
hwaddr base; //基址
hwaddr size; //长度
} MemMapEntry;
然后是关于ROM的指令初始化:
/* reset vector */
uint32_t reset_vec[8] = {
0x00000297, /* 1: auipc t0, %pcrel_hi(dtb) */
0x02028593, /* addi a1, t0, %pcrel_lo(1b) */
0xf1402573, /* csrr a0, mhartid */
#if defined(TARGET_RISCV32)
0x0182a283, /* lw t0, 24(t0) */
#elif defined(TARGET_RISCV64)
0x0182b283, /* ld t0, 24(t0) */
#endif
0x00028067, /* jr t0 */
0x00000000,
start_addr, /* start: .dword DRAM_BASE */
0x00000000,
};
/* copy in the reset vector in little_endian byte order */
for (i = 0; i < sizeof(reset_vec) >> 2; i++)
{
reset_vec[i] = cpu_to_le32(reset_vec[i]);
}
rom_add_blob_fixed_as("mrom.reset", reset_vec, sizeof(reset_vec),memmap[NUCLEI_N_ROM].base, &address_space_memory);
/* boot rom */
if (machine->kernel_filename)
{
riscv_load_kernel(machine>kernel_filename, start_addr, NULL);
}
这种是手动执行指令初始化,当然,因为我们使用的RISCV架构,直接使用riscv_setup_rom_reset_vec进行指令初始化也是可以的。
这里我们再讲一下内存模拟的一个步骤:
- 执行初始化函数,例如ROM的就是
memory_region_init_rom; - 分配/挂载,
memory_region_add_subregion,当然还会用上系统根节点获取get_system_memory; - ROM设置(指令初始化)或者加载kernel
(二)举个例子
enum
{
NUCLEI_N_DEBUG,
NUCLEI_N_ROM,
NUCLEI_N_TIMER,
NUCLEI_N_ECLIC,
NUCLEI_N_GPIO,
NUCLEI_N_UART0,
NUCLEI_N_QSPI0,
NUCLEI_N_PWM0,
NUCLEI_N_UART1,
NUCLEI_N_QSPI1,
NUCLEI_N_PWM1,
NUCLEI_N_QSPI2,
NUCLEI_N_PWM2,
NUCLEI_N_XIP,
NUCLEI_N_DRAM,
NUCLEI_N_ILM,
NUCLEI_N_DLM
};
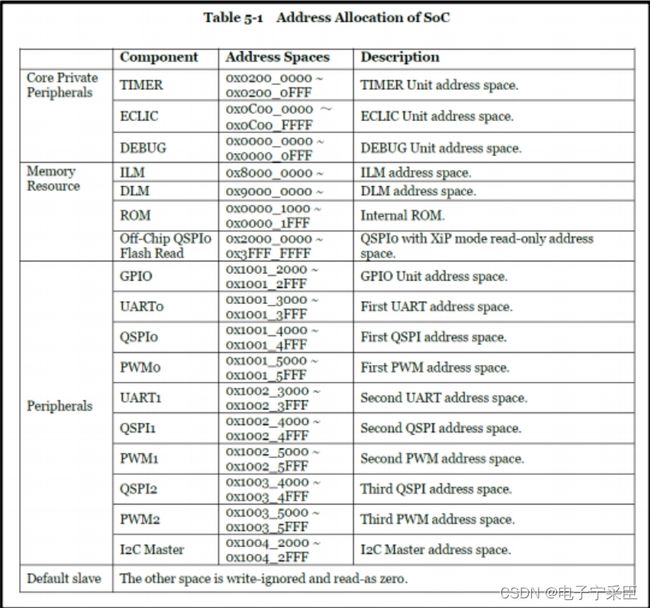
static MemMapEntry nuclei_n_memmap[] = {
[NUCLEI_N_DEBUG] = {0x0, 0x1000},
[NUCLEI_N_ROM] = {0x1000, 0x1000},
[NUCLEI_N_TIMER] = {0x2000000, 0x1000},
[NUCLEI_N_ECLIC] = {0xc000000, 0x10000},
[NUCLEI_N_GPIO] = {0x10012000, 0x1000},
[NUCLEI_N_UART0] = {0x10013000, 0x1000},
[NUCLEI_N_QSPI0] = {0x10014000, 0x1000},
[NUCLEI_N_PWM0] = {0x10015000, 0x1000},
[NUCLEI_N_UART1] = {0x10023000, 0x1000},
[NUCLEI_N_QSPI1] = {0x10024000, 0x1000},
[NUCLEI_N_PWM1] = {0x10025000, 0x1000},
[NUCLEI_N_QSPI2] = {0x10034000, 0x1000},
[NUCLEI_N_PWM2] = {0x10035000, 0x1000},
[NUCLEI_N_XIP] = {0x20000000, 0x10000000},
[NUCLEI_N_DRAM] = {0xa0000000, 0x0},
[NUCLEI_N_ILM] = {0x80000000, 0x20000},
[NUCLEI_N_DLM] = rub{0x90000000, 0x20000},
};
之后我们初始化ROM地址:
/* Internal ROM */
memory_region_init_rom(&s->internal_rom, OBJECT(obj), "riscv.nuclei.n.irom", memmap[NUCLEI_N_ROM].size, &error_fatal);
memory_region_add_subregion(sys_mem, memmap[NUCLEI_N_ROM].base, &s->internal_rom);
这里我们假设idlm和ROM都为Soc外设:
于是我们编写相关函数:
static void nuclei_n_soc_memory_create(Object *obj)
{
NucLeiNSoCState *s = NUCLEI_N_SOC(obj);
const MemMapEntry *memmap = nuclei_n_memmap;
MemoryRegion *sys_mem = get_system_memory();
/* Internal ROM */
memory_region_init_rom(&s->internal_rom, OBJECT(obj), "riscv.nuclei.n.irom", memmap[NUCLEI_N_ROM].size, &error_fatal);
memory_region_add_subregion(sys_mem, memmap[NUCLEI_N_ROM].base, &s->internal_rom);
/* Initialize ilm dlm */
memory_region_init_ram(&s->ilm, NULL, "riscv.nuclei.n.ilm", memmap[NUCLEI_N_ILM].size, &error_fatal);
memory_region_add_subregion(sys_mem, memmap[NUCLEI_N_ILM].base, &s->ilm);
memory_region_init_ram(&s->dlm, NULL, "riscv.nuclei.n.dlm", memmap[NUCLEI_N_DLM].size, &error_fatal);
memory_region_add_subregion(sys_mem, memmap[NUCLEI_N_DLM].base, &s->dlm);
/* SysTimer */
create_unimplemented_device("riscv.nuclei.n.timer", memmap[NUCLEI_N_TIMER].base, memmap[NUCLEI_N_TIMER].size);
/* Eclic */
create_unimplemented_device("riscv.nuclei.n.eclic", memmap[NUCLEI_N_ECLIC].base, memmap[NUCLEI_N_ECLIC].size);
/* GPIO */
create_unimplemented_device("riscv.nuclei.n.gpio", memmap[NUCLEI_N_GPIO].base, memmap[NUCLEI_N_GPIO].size);
}
因为还没有实现一些设备,所以我们创建unimplemented设备来占用内存:
/* SysTimer */
create_unimplemented_device("riscv.nuclei.n.timer", memmap[NUCLEI_N_TIMER].base, memmap[NUCLEI_N_TIMER].size);
/* Eclic */
create_unimplemented_device("riscv.nuclei.n.eclic", memmap[NUCLEI_N_ECLIC].base, memmap[NUCLEI_N_ECLIC].size);
/* GPIO */
create_unimplemented_device("riscv.nuclei.n.gpio", memmap[NUCLEI_N_GPIO].base, memmap[NUCLEI_N_GPIO].size);
这次我们把CPU的初始化和实例化也类似封装成一个函数:
static void nuclei_n_soc_cpu_create(Object *obj)
{
MachineState *ms = MACHINE(qdev_get_machine());
NucLeiNSoCState *s = NUCLEI_N_SOC(obj);
object_initialize_child(obj, "cpus", &s->cpus, TYPE_RISCV_HART_ARRAY); //初始化CPU
object_property_set_str(OBJECT(&s->cpus), "cpu-type", ms->cpu_type, &error_abort);
object_property_set_int(OBJECT(&s->cpus), "num-harts", ms->smp.cpus, &error_abort);
sysbus_realize(SYS_BUS_DEVICE(&s->cpus), &error_abort); //CPU实例化
}
然后我们在nuclei_n_soc_instance_init中调用:
static void nuclei_n_soc_instance_init(Object *obj)
{
/* SOC CPU */
nuclei_n_soc_cpu_create(obj);
/* SOC Memory */
nuclei_n_soc_memory_create(obj);
}
其次是设置ROM和加载kernel,我们在整个Machine实例中进行初始化:
static void nuclei_mcu_machine_init(MachineState *machine)
{
NucLeiNState *s = MCU_FPGA_MACHINE(machine);
const MemMapEntry *memmap = nuclei_n_memmap;
target_ulong start_addr;
int i;
/* Initialize SOC */
object_initialize_child(OBJECT(machine), "soc", &s->soc, TYPE_NUCLEI_N_SOC);
qdev_realize(DEVICE(&s->soc), NULL, &error_abort);
//选择启动方式
switch (s->msel)
{
case MSEL_ILM:
start_addr = memmap[NUCLEI_N_ILM].base;
break;
case MSEL_FLASH:
start_addr = memmap[NUCLEI_N_XIP].base;
break;
case MSEL_FLASHXIP:
start_addr = memmap[NUCLEI_N_XIP].base;
break;
case MSEL_DDR:
start_addr = memmap[NUCLEI_N_DRAM].base;
break;
default:
start_addr = memmap[NUCLEI_N_ILM].base;
break;
}
/* reset vector */
uint32_t reset_vec[8] = {
0x00000297, /* 1: auipc t0, %pcrel_hi(dtb) */
0x02028593, /* addi a1, t0, %pcrel_lo(1b) */
0xf1402573, /* csrr a0, mhartid */
#if defined(TARGET_RISCV32)
0x0182a283, /* lw t0, 24(t0) */
#elif defined(TARGET_RISCV64)
0x0182b283, /* ld t0, 24(t0) */
#endif
0x00028067, /* jr t0 */
0x00000000,
start_addr, /* start: .dword DRAM_BASE */
0x00000000,
};
/* copy in the reset vector in little_endian byte order */
for (i = 0; i < sizeof(reset_vec) >> 2; i++)
{
reset_vec[i] = cpu_to_le32(reset_vec[i]);
}
rom_add_blob_fixed_as("mrom.reset", reset_vec, sizeof(reset_vec),
memmap[NUCLEI_N_ROM].base, &address_space_memory); //CPU初始化地址
/* boot rom */
if (machine->kernel_filename)
{
riscv_load_kernel(machine, &s->soc.cpus, start_addr, true, NULL); //将裸机代码加载到地址start_addr
// riscv_load_kernel(machine->kernel_filename, start_addr, NULL);
}
}
测试
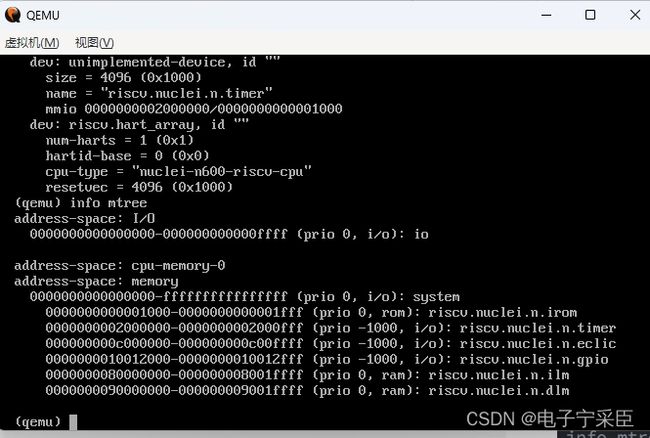
我们进行测试:
编译完成后运行程序并执行:
info mtree
结尾附上完整代码:
nuclei_n.h:
#include "hw/boards.h"
#include "hw/riscv/riscv_hart.h"
#include "hw/sysbus.h"
#define TYPE_NUCLEI_N_SOC "riscv.nuclei.n.soc"
#define NUCLEI_N_SOC(obj) \
OBJECT_CHECK(NucLeiNSoCState, (obj), TYPE_NUCLEI_N_SOC)
/* CPU 定义 */
#define NUCLEI_N_CPU TYPE_RISCV_CPU_NUCLEI_N600
typedef struct NucLeiNSoCState
{
/*< private >*/
DeviceState parent_obj;
/*< public >*/
RISCVHartArrayState cpus;
MemoryRegion internal_rom;
MemoryRegion ilm;
MemoryRegion dlm;
MemoryRegion xip_mem;
} NucLeiNSoCState;
/* Machine state定义 */
#define TYPE_NUCLEI_MCU_FPGA_MACHINE MACHINE_TYPE_NAME("mcu_200t")
#define MCU_FPGA_MACHINE(obj) \
OBJECT_CHECK(NucLeiNState, (obj), TYPE_NUCLEI_MCU_FPGA_MACHINE)
typedef struct NucLeiNState
{
/*< private >*/
MachineState parent;
/*< public >*/
NucLeiNSoCState soc;
uint32_t msel;
} NucLeiNState;
enum
{
MSEL_ILM = 1,
MSEL_FLASH = 2,
MSEL_FLASHXIP = 3,
MSEL_DDR = 4
};
enum
{
NUCLEI_N_DEBUG,
NUCLEI_N_ROM,
NUCLEI_N_TIMER,
NUCLEI_N_ECLIC,
NUCLEI_N_GPIO,
NUCLEI_N_UART0,
NUCLEI_N_QSPI0,
NUCLEI_N_PWM0,
NUCLEI_N_UART1,
NUCLEI_N_QSPI1,
NUCLEI_N_PWM1,
NUCLEI_N_QSPI2,
NUCLEI_N_PWM2,
NUCLEI_N_XIP,
NUCLEI_N_DRAM,
NUCLEI_N_ILM,
NUCLEI_N_DLM
};
nuclei_n.c:
#include "qemu/osdep.h"
#include "qemu/error-report.h"
#include "qapi/error.h"
#include "hw/riscv/nuclei_n.h"
#include "qapi/visitor.h"
#include "hw/boards.h"
#include "hw/loader.h"
#include "hw/sysbus.h"
#include "target/riscv/cpu.h"
#include "hw/misc/unimp.h"
#include "hw/riscv/riscv_hart.h"
#include "hw/riscv/boot.h"
static MemMapEntry nuclei_n_memmap[] = {
[NUCLEI_N_DEBUG] = {0x0, 0x1000},
[NUCLEI_N_ROM] = {0x1000, 0x1000},
[NUCLEI_N_TIMER] = {0x2000000, 0x1000},
[NUCLEI_N_ECLIC] = {0xc000000, 0x10000},
[NUCLEI_N_GPIO] = {0x10012000, 0x1000},
[NUCLEI_N_UART0] = {0x10013000, 0x1000},
[NUCLEI_N_QSPI0] = {0x10014000, 0x1000},
[NUCLEI_N_PWM0] = {0x10015000, 0x1000},
[NUCLEI_N_UART1] = {0x10023000, 0x1000},
[NUCLEI_N_QSPI1] = {0x10024000, 0x1000},
[NUCLEI_N_PWM1] = {0x10025000, 0x1000},
[NUCLEI_N_QSPI2] = {0x10034000, 0x1000},
[NUCLEI_N_PWM2] = {0x10035000, 0x1000},
[NUCLEI_N_XIP] = {0x20000000, 0x10000000},
[NUCLEI_N_DRAM] = {0xa0000000, 0x0},
[NUCLEI_N_ILM] = {0x80000000, 0x20000},
[NUCLEI_N_DLM] = {0x90000000, 0x20000},
};
static void nuclei_n_soc_cpu_create(Object *obj)
{
MachineState *ms = MACHINE(qdev_get_machine());
NucLeiNSoCState *s = NUCLEI_N_SOC(obj);
object_initialize_child(obj, "cpus", &s->cpus, TYPE_RISCV_HART_ARRAY); //初始化CPU
object_property_set_str(OBJECT(&s->cpus), "cpu-type", ms->cpu_type, &error_abort);
object_property_set_int(OBJECT(&s->cpus), "num-harts", ms->smp.cpus, &error_abort);
sysbus_realize(SYS_BUS_DEVICE(&s->cpus), &error_abort); //CPU实例化
}
static void nuclei_n_soc_memory_create(Object *obj)
{
NucLeiNSoCState *s = NUCLEI_N_SOC(obj);
const MemMapEntry *memmap = nuclei_n_memmap;
MemoryRegion *sys_mem = get_system_memory();
/* Internal ROM */
memory_region_init_rom(&s->internal_rom, OBJECT(obj), "riscv.nuclei.n.irom", memmap[NUCLEI_N_ROM].size, &error_fatal);
memory_region_add_subregion(sys_mem, memmap[NUCLEI_N_ROM].base, &s->internal_rom);
/* Initialize ilm dlm */
memory_region_init_ram(&s->ilm, NULL, "riscv.nuclei.n.ilm", memmap[NUCLEI_N_ILM].size, &error_fatal);
memory_region_add_subregion(sys_mem, memmap[NUCLEI_N_ILM].base, &s->ilm);
memory_region_init_ram(&s->dlm, NULL, "riscv.nuclei.n.dlm", memmap[NUCLEI_N_DLM].size, &error_fatal);
memory_region_add_subregion(sys_mem, memmap[NUCLEI_N_DLM].base, &s->dlm);
/* SysTimer */
create_unimplemented_device("riscv.nuclei.n.timer",
memmap[NUCLEI_N_TIMER].base, memmap[NUCLEI_N_TIMER].size);
/* Eclic */
create_unimplemented_device("riscv.nuclei.n.eclic",
memmap[NUCLEI_N_ECLIC].base, memmap[NUCLEI_N_ECLIC].size);
/* GPIO */
create_unimplemented_device("riscv.nuclei.n.gpio",
memmap[NUCLEI_N_GPIO].base, memmap[NUCLEI_N_GPIO].size);
}
static void nuclei_n_soc_instance_init(Object *obj)
{
/* SOC CPU */
nuclei_n_soc_cpu_create(obj);
/* SOC Memory */
nuclei_n_soc_memory_create(obj);
}
static void nuclei_n_soc_class_init(ObjectClass *oc, void *data)
{
DeviceClass *dc = DEVICE_CLASS(oc);
dc->user_creatable = false;
}
static const TypeInfo nuclei_n_soc_type_info = {
.name = TYPE_NUCLEI_N_SOC,
.parent = TYPE_DEVICE,
.instance_size = sizeof(NucLeiNSoCState),
.instance_init = nuclei_n_soc_instance_init,
.class_init = nuclei_n_soc_class_init,
};
static void nuclei_n_soc_register_types(void)
{
type_register_static(&nuclei_n_soc_type_info);
}
type_init(nuclei_n_soc_register_types)
static void nuclei_mcu_machine_init(MachineState *machine)
{
NucLeiNState *s = MCU_FPGA_MACHINE(machine);
const MemMapEntry *memmap = nuclei_n_memmap;
target_ulong start_addr;
int i;
/* Initialize SOC */
object_initialize_child(OBJECT(machine), "soc", &s->soc, TYPE_NUCLEI_N_SOC);
qdev_realize(DEVICE(&s->soc), NULL, &error_abort);
//选择启动方式
switch (s->msel)
{
case MSEL_ILM:
start_addr = memmap[NUCLEI_N_ILM].base;
break;
case MSEL_FLASH:
start_addr = memmap[NUCLEI_N_XIP].base;
break;
case MSEL_FLASHXIP:
start_addr = memmap[NUCLEI_N_XIP].base;
break;
case MSEL_DDR:
start_addr = memmap[NUCLEI_N_DRAM].base;
break;
default:
start_addr = memmap[NUCLEI_N_ILM].base;
break;
}
/* reset vector */
uint32_t reset_vec[8] = {
0x00000297, /* 1: auipc t0, %pcrel_hi(dtb) */
0x02028593, /* addi a1, t0, %pcrel_lo(1b) */
0xf1402573, /* csrr a0, mhartid */
#if defined(TARGET_RISCV32)
0x0182a283, /* lw t0, 24(t0) */
#elif defined(TARGET_RISCV64)
0x0182b283, /* ld t0, 24(t0) */
#endif
0x00028067, /* jr t0 */
0x00000000,
start_addr, /* start: .dword DRAM_BASE */
0x00000000,
};
/* copy in the reset vector in little_endian byte order */
for (i = 0; i < sizeof(reset_vec) >> 2; i++)
{
reset_vec[i] = cpu_to_le32(reset_vec[i]);
}
rom_add_blob_fixed_as("mrom.reset", reset_vec, sizeof(reset_vec),
memmap[NUCLEI_N_ROM].base, &address_space_memory); //CPU初始化地址
/* boot rom */
if (machine->kernel_filename)
{
riscv_load_kernel(machine, &s->soc.cpus, start_addr, true, NULL); //将裸机代码加载到地址start_addr
// riscv_load_kernel(machine->kernel_filename, start_addr, NULL);
}
}
static void nuclei_machine_class_init(ObjectClass *oc, void *data)
{
MachineClass *mc = MACHINE_CLASS(oc);
mc->desc = "Nuclei MCU 200T FPGA Evaluation Kit";
mc->init = nuclei_mcu_machine_init;
mc->max_cpus = 1;
mc->default_cpu_type = NUCLEI_N_CPU;
}
static const TypeInfo nuclei_machine_typeinfo = {
.name = TYPE_NUCLEI_MCU_FPGA_MACHINE,
.parent = TYPE_MACHINE,
.class_init = nuclei_machine_class_init,
.instance_size = sizeof(NucLeiNState),
};
static void nuclei_machine_init_register_types(void)
{
type_register_static(&nuclei_machine_typeinfo);
}
type_init(nuclei_machine_init_register_types)
参考资料
- [完结]从零开始的RISC-V模拟器开发·第一季·2021春季
- 新建quard-star开发板