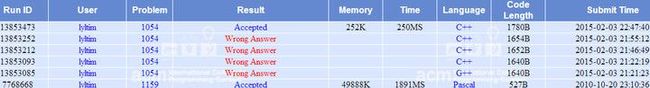
IOI2002 POJ1054 The Troublesome Frog 讨厌的青蛙 (离散化+剪枝)
Description
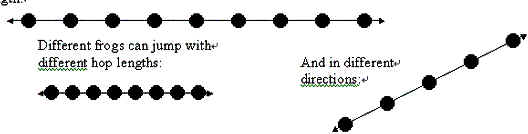
Your rice paddy has plants arranged on the intersection points of a grid as shown in Figure-1, and the troublesome frogs hop completely through your paddy, starting outside the paddy on one side and ending outside the paddy on the other side as shown in Figure-2:
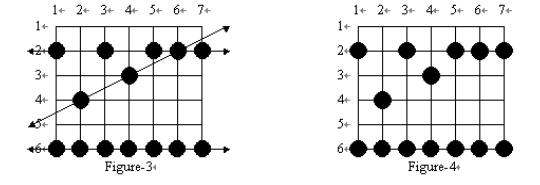
Many frogs can jump through the paddy, hopping from rice plant to rice plant. Every hop lands on a plant and flattens it, as in Figure-3. Note that some plants may be landed on by more than one frog during the night. Of course, you can not see the lines showing the paths of the frogs or any of their hops outside of your paddy ?for the situation in Figure-3, what you can see is shown in Figure-4:
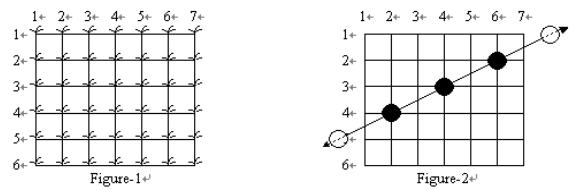
From Figure-4, you can reconstruct all the possible paths which the frogs may have followed across your paddy. You are only interested in frogs which have landed on at least 3 of your rice plants in their voyage through the paddy. Such a path is said to be a frog path. In this case, that means that the three paths shown in Figure-3 are frog paths (there are also other possible frog paths). The vertical path down column 1 might have been a frog path with hop length 4 except there are only 2 plants flattened so we are not interested; and the diagonal path including the plants on row 2 col. 3, row 3 col. 4, and row 6 col. 7 has three flat plants but there is no regular hop length which could have spaced the hops in this way while still landing on at least 3 plants, and hence it is not a frog path. Note also that along the line a frog path follows there may be additional flattened plants which do not need to be landed on by that path (see the plant at (2, 6) on the horizontal path across row 2 in Figure-4), and in fact some flattened plants may not be explained by any frog path at all.
Your task is to write a program to determine the maximum number of landings in any single frog path (where the maximum is taken over all possible frog paths). In Figure-4 the answer is 7, obtained from the frog path across row 6.
Input
Output
Sample Input
6 7 14 2 1 6 6 4 2 2 5 2 6 2 7 3 4 6 1 6 2 2 3 6 3 6 4 6 5 6 7
Sample Output
7
Source
解题思路
这个问题看起来很复杂,其实目的很简单:帮助农民找到为害最大的青蛙。也就是要找到
一条穿越稻田的青蛙路径,这个路径上被踩踏的水稻不少于其他任何青蛙路径上被踩踏的水
稻数。当然,整个稻田中也可能根本就不存在青蛙路径。问题的关键是:找到穿越稻田的全
部青蛙路径。任何一条穿越稻田的青蛙路径L,至少包括3棵被踩踏的水稻。假设其中前两
棵被踩踏的水稻分别是(X1,Y1)、(X2,Y2),那么:
令dx=X2-X1、dy=Y2-Y1;X0=X1-dx、Y0=Y1- dy;X3=X2 + dx、Y3=Y2+ dy
(X0,Y0)位于稻田之外,青蛙从该位置经一跳后进入稻田、踩踏位置(X1,Y1)上的水稻
(X3,Y3)位于稻田之内,该位置是L上第3棵被青蛙踩踏的水稻
Xi=X0 + idx、Yi=Y1 + idy(i3),如果(Xi,Yi)位于稻田之内,则(Xi,Yi)上的水稻必被
青蛙踩踏
根据上述规则,只要知道一条青蛙路径上的前两棵被踩踏的水稻,就可以找到该路径上其
他的水稻。为了找到全部的青蛙路径,只要从被踩踏的水稻中,任取两棵水稻(X1,Y1)、(X2,
Y2),判断(X1,Y1)、(X2,Y2)是否能够作为一条青蛙路径上最先被踩踏的两颗水稻。
解决方案
这个问题的描述中,最基本的元素是被踩踏的水稻。在程序中要选择一个合适的数据结构,
来表达这个基本元素。这个数据结构是否合适的标准是:在程序中要表达这个元素时,能否
用一个单词或者短语,即用一个变量来表示。
struct PLANT {//描述一棵被踩踏的水稻
int x; //水稻的行号
int y; //水稻的列号
}
这个问题的主要计算是:从被踩踏的水稻中选择两棵(X1,Y1)、(X2,Y2)。判断它们是否
能够作为一条青蛙路径上最先被踩踏的两颗水稻。(X1,Y1)、(X2,Y2)唯一确定了蛙跳的方
向和步长,从(X2,Y2)开始,沿着这个方向和步长在稻田内走。每走一步,判断所到达位置
上(X,Y)的水稻是否被踩踏,直到走出稻田为止。如果在某一步上,(X,Y)没有被踩踏,
则表明(X1,Y1)、(X2,Y2)是一条青蛙路径上最先被踩踏的两颗水稻的假设不成立。这个判
断的算法在问题求解过程中要反复使用,它的效率成为决定整个计算效率的关键。
用一个PLANT型的数组plants[5001]表示全部被踩踏的水稻
将plants中的元素按照行/列序号的升序(或者降序)排列
采用二分法查找plants中是否有值为(X,Y)的元素:将(X,Y)与plants中间的元素比较,
(1)相等,表明找到了元素;(2)比plants中间元素的小,继续在plants的前半部寻找;(3)
比plants中间元素的大,继续在plants的后半部寻找。
采用上述方法判断每走一步所到达位置上(X,Y)的水稻是否被踩踏,最多只要比较Log2N,
其中N是稻田中被踩踏水稻的总量。
参考程序
1 //By LYLtim 2 //2015.2.3 3 4 #include <iostream> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 using namespace std; 7 8 class Plant 9 { 10 public: 11 int x, y; 12 bool operator< (const Plant& p2) const { // binary_search 3rd argument const T& val 13 if (x == p2.x) 14 return y < p2.y; 15 return x < p2.x; 16 } 17 }; 18 19 int r, c, n; 20 Plant plants[5000]; 21 22 int searchPath(const Plant secPlant, const int dx, const int dy){ 23 Plant tmpPlant; 24 int steps = 2; 25 tmpPlant.x = secPlant.x + dx; 26 tmpPlant.y = secPlant.y + dy; 27 while( (tmpPlant.x <= r) && (tmpPlant.y >= 1 ) && (tmpPlant.y <= c) ) { 28 if (!binary_search(plants, plants + n, tmpPlant)) { 29 //每一步都必须踩倒水稻才算合理, 否则这就不是一条行走路径 30 steps = 0; 31 break; 32 } 33 steps++; 34 35 //print 36 // cout << tmpPlant.x << "," << tmpPlant.y << endl; 37 38 tmpPlant.x += dx; 39 tmpPlant.y += dy; 40 } 41 return steps; 42 } 43 44 int main() 45 { 46 int dx, dy, px, py, max = 2, steps; 47 cin >> r >> c; 48 cin >> n; 49 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 50 cin >> plants[i].x >> plants[i].y; 51 sort(plants, plants + n); 52 53 //print plants 54 // for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 55 // cout << plants[i].x << " " <<plants[i].y << endl; 56 57 for (int i = 0; i < n-2; i++) 58 for (int j = i+1; j < n-1; j++) { 59 dx = plants[j].x - plants[i].x; 60 dy = plants[j].y - plants[i].y; 61 px = plants[i].x - dx; 62 py = plants[i].y - dy; 63 if ( (px>=1) && (py>=1) && (py<=c)) 64 continue; 65 if (plants[i].x + (max-1)*dx > r) 66 break; 67 py = plants[i].y + (max-1)*dy; 68 if ( (py<1) || (py>c) ) 69 continue; 70 71 //print 72 // cout << "p1:" << plants[i].x << "," << plants[i].y << " p2:"<<plants[j].x << "," << plants[j].y << " dx,dy: " << dx << "," << dy << endl; 73 74 steps = searchPath(plants[j], dx, dy); 75 76 //print steps 77 // cout << "steps:" <<steps << endl << endl; 78 79 if (steps > max) 80 max = steps; 81 } 82 if (max == 2) 83 max = 0; 84 cout << max; 85 return 0; 86 }